
作者介绍
一、前言
DBA 的基本职责可分为两部分,一是保证数据库服务稳定性,二是保持良好的性能。
一个表的数据量达到一定程度后,稳定性和性能就会出现瓶颈,"化整为零"对DBA 来说无疑是一个很好的选择,此时如何分表就成为摆在业务线开发同学和 DBA 面前的一道不可回避的课题。
相对于传统的开发同学自己根据业务及自己在应用代码中实现分表的方案,本文介绍一下 PostgreSQL 中如何实现对业务相对透明的分区方案。
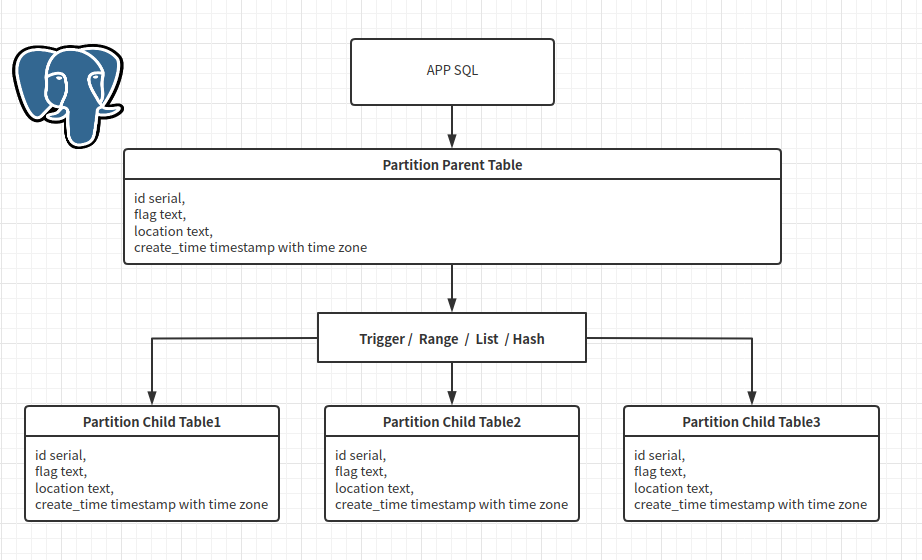
二、什么是表分区
所谓表分区就是将一个完整的大表,按照一定的分区策略,将数据打散到不同的子表中,并通过子表继承父表的方式,物理上将数据文件拆分成多个较小的文件。
但对业务来说,却是基本透明的(当然为了提升性能,需要注意 where 或 join 中带分区键),仍然可以像未分区的 1 个表来进行各种 CURD ,而不需要关心子表那些具体实现细节。
三、为什么需要表分区?
对表进行合理的分区可获得更高的可用性,提升 SQL 运行效率(性能)及降低维护成本(可管理性)。
1. 更高的可用性
俗话说的好,不要将鸡蛋都放到一个篮子里,同样的对于数据库而言也是如此,想象一下,一个数百 GB 的表,当某一个数据页面损坏引起整个表不可用时,是多么的悲催。
2. 提升SQL运行效率
对于只查询表中部分数据的场景,好的分区策略,可大幅减少定位数据所需扫描的物理文件数量,从而显著的提升 CURD 的效率。
3. 降低数据维护成本
对于需要定期进行数据归档的表,使用 PostgreSQL 提供的 DETACH 方式,直接解除与父表的继承关系,而无需在原表上进行备份后删除,既能极大的提高工作效率,也能减少对表不必要的操作,从而可降低表的膨胀,同时也以减少 WAL 的量,从而节省不必要资源消耗。
四、PostgreSQL的表分区实现方式
PostgreSQL 中分区分为 2 大类,即继承式及声明式。
1. 继承式分区
postgres=# create table test_trigger_part(id serial, flag text, location text, create_time timestamp with time zone); --创建父表CREATE TABLEpostgres=# do *匿名块快速创建子表*/$$declare base text; sqlstring text; i int;beginbase = 'create table test_trigger_part_%s(check(create_time >= ''%s'' and create_time < ''%s'')) inherits (test_trigger_part)';for i in 0..9 loopsqlstring = format(base, to_char('2021-05-01'::date + (i || ' day')::interval, 'YYYYMMDD'), '2021-05-01'::date + (i || ' day')::interval, '2021-05-01'::date + (i + 1 || ' day')::interval);--raise notice '%', sqlstring;execute sqlstring;end loop;end$$language plpgsql;DOpostgres=# \d+ test_trigger_partTable "public.test_trigger_part"Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default | Storage | Stats target | Description-------------+--------------------------+-----------+----------+-----------------------------------------------+----------+--------------+-------------id | integer | | not null | nextval('test_trigger_part_id_seq'::regclass) | plain | |flag | text | | | | extended | |location | text | | | | extended | |create_time | timestamp with time zone | | | | plain | |Child tables: test_trigger_part_20210501,test_trigger_part_20210502,test_trigger_part_20210503,test_trigger_part_20210504,test_trigger_part_20210505,test_trigger_part_20210506,test_trigger_part_20210507,test_trigger_part_20210508,test_trigger_part_20210509,test_trigger_part_20210510Access method: heappostgres=# CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION ins_or_upd_on_test_trigger_part () *创建触发器函数*/RETURNS TRIGGERAS $$DECLAREsqlstring text;BEGINsqlstring = 'INSERT INTO test_trigger_part_%s values($1.*)';sqlstring := format(sqlstring, to_char(NEW.create_time, 'YYYYMMDD'));--RAISE NOTICE '%', sqlstring;EXECUTE sqlstring USING NEW;RETURN NULL;END$$LANGUAGE plpgsql;CREATE FUNCTIONpostgres=# create trigger tg_on_in_or_upd before insert ON test_trigger_part for each row execute function ins_or_upd_on_test_trigger_part (); *创建触发器*/CREATE TRIGGERpostgres=#postgres=# insert into test_trigger_part(flag, location, create_time)select 'flag' || mod(i, 10), md5(i::text), '2021-05-01 00:00:00+08'::timestamptz + (mod(i, 10) || ' day')::interval + (mod(i, 3600) || ' sec')::intervalfrom generate_series(1, 10000) i; /*插入测试数据*/INSERT 0 0postgres=# select count(*) from test_trigger_part;count-------10000(1 row)
继承的方式实现表分区较为复杂,声明式分区大大简化了表继承的过程,对用户来说更简单且高效。
PostgreSQL 在 10 版本开始支持 list , range 内置分区,并在 PostgreSQL 11 版本支持 hash 分区, 同时相对 PostgreSQL 10 版本性能有所提升,并在PostgreSQL 12 性能进一步大幅提升。
所以还在使用 PostgreSQL 9.x 的用户,升级至 PostgreSQL 11+ ,是十分有必要且明智的选择。
创建 list 分区表 test_list,包含 id,flag,location,create_time 四个列,并按 location 创建分区子表。
postgres=# create table test_list(id serial, flag text, location text, create_time timestamptz) partition by list(flag); --创建list分区父表CREATE TABLEpostgres=#postgres=# do --利用匿名块快速创建多个list分区子表$$declare base text; sqlstring text; i int;beginbase = 'create table test_list_%s partition of test_list for values in (''%s'')';for i in 0..9 loopsqlstring = format(base, 'flag' || i, 'flag' || i);--raise notice '%', sqlstring;execute sqlstring;end loop;end$$language plpgsql;DOpostgres=#postgres=# \d+ test_listPartitioned table "public.test_list"Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default | Storage | Stats target | Description-------------+--------------------------+-----------+----------+---------------------------------------+----------+--------------+-------------id | integer | | not null | nextval('test_list_id_seq'::regclass) | plain | |flag | text | | | | extended | |location | text | | | | extended | |create_time | timestamp with time zone | | | | plain | |Partition key: LIST (flag)Partitions: test_list_flag0 FOR VALUES IN ('flag0'),test_list_flag1 FOR VALUES IN ('flag1'),test_list_flag2 FOR VALUES IN ('flag2'),test_list_flag3 FOR VALUES IN ('flag3'),test_list_flag4 FOR VALUES IN ('flag4'),test_list_flag5 FOR VALUES IN ('flag5'),test_list_flag6 FOR VALUES IN ('flag6'),test_list_flag7 FOR VALUES IN ('flag7'),test_list_flag8 FOR VALUES IN ('flag8'),test_list_flag9 FOR VALUES IN ('flag9')postgres=# insert into test_list(flag, location, create_time)select 'flag' || mod(i, 10), md5(i::text), '2021-05-01 00:00:00+08'::timestamptz + (mod(i, 10) || ' day')::interval + (mod(i, 3600) || ' sec')::intervalfrom generate_series(1, 10000) i; --插入测试数据INSERT 0 10000
2. 2 range分区
postgres=# create table test_range(id serial, flag text, location text, create_time timestamptz) partition by range(create_time); --创建range分区父表CREATE TABLEpostgres=# do --利用匿名块快速创建多个range分区子表$$declare base text; sqlstring text; i int;beginbase = 'create table test_range_%s partition of test_range for values from (''%s'') to (''%s'')';for i in 0..9 loopsqlstring = format(base, to_char('2021-05-01'::timestamptz + (i || ' day')::interval, 'YYYYMMDD'), '2021-05-01'::timestamptz + (i || ' day')::interval, '2021-05-01'::timestamptz + (i + 1 || ' day')::interval);--raise notice '%', sqlstring;execute sqlstring;end loop;end$$language plpgsql;DOpostgres=#postgres=# \d+ test_range --查看分区表结构Partitioned table "public.test_range"Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default | Storage | Stats target | Description-------------+--------------------------+-----------+----------+----------------------------------------+----------+--------------+-------------id | integer | | not null | nextval('test_range_id_seq'::regclass) | plain | |flag | text | | | | extended | |location | text | | | | extended | |create_time | timestamp with time zone | | | | plain | |Partition key: RANGE (create_time)Partitions: test_range_20210501 FOR VALUES FROM ('2021-05-01 00:00:00+08') TO ('2021-05-02 00:00:00+08'),test_range_20210502 FOR VALUES FROM ('2021-05-02 00:00:00+08') TO ('2021-05-03 00:00:00+08'),test_range_20210503 FOR VALUES FROM ('2021-05-03 00:00:00+08') TO ('2021-05-04 00:00:00+08'),test_range_20210504 FOR VALUES FROM ('2021-05-04 00:00:00+08') TO ('2021-05-05 00:00:00+08'),test_range_20210505 FOR VALUES FROM ('2021-05-05 00:00:00+08') TO ('2021-05-06 00:00:00+08'),test_range_20210506 FOR VALUES FROM ('2021-05-06 00:00:00+08') TO ('2021-05-07 00:00:00+08'),test_range_20210507 FOR VALUES FROM ('2021-05-07 00:00:00+08') TO ('2021-05-08 00:00:00+08'),test_range_20210508 FOR VALUES FROM ('2021-05-08 00:00:00+08') TO ('2021-05-09 00:00:00+08'),test_range_20210509 FOR VALUES FROM ('2021-05-09 00:00:00+08') TO ('2021-05-10 00:00:00+08'),test_range_20210510 FOR VALUES FROM ('2021-05-10 00:00:00+08') TO ('2021-05-11 00:00:00+08')postgres=# insert into test_range(flag, location, create_time)select 'flag' || mod(i, 10), md5(i::text), '2021-05-01 00:00:00+08'::timestamptz + (mod(i, 10) || ' day')::interval + (mod(i, 3600) || ' sec')::intervalfrom generate_series(1, 10000) i; --插入测试数据INSERT 0 10000
postgres=# create table test_hash(id serial, flag text, location text, create_time timestamptz) partition by hash(location); --创建hash分区父表CREATE TABLEpostgres=#postgres=# do --利用匿名块快速创建多个hash分区子表$$declare base text; sqlstring text; i int;beginbase = 'create table test_hash_%s partition of test_hash for values with(modulus 10, remainder %s)';for i in 0..9 loopsqlstring = format(base, i, i);--raise notice '%', sqlstring;execute sqlstring;end loop;end$$language plpgsql;DOpostgres=# \d+ test_hash --查看分区表结构Partitioned table "public.test_hash"Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default | Storage | Stats target | Description-------------+--------------------------+-----------+----------+---------------------------------------+----------+--------------+-------------id | integer | | not null | nextval('test_hash_id_seq'::regclass) | plain | |flag | text | | | | extended | |location | text | | | | extended | |create_time | timestamp with time zone | | | | plain | |Partition key: HASH (location)Partitions: test_hash_0 FOR VALUES WITH (modulus 10, remainder 0),test_hash_1 FOR VALUES WITH (modulus 10, remainder 1),test_hash_2 FOR VALUES WITH (modulus 10, remainder 2),test_hash_3 FOR VALUES WITH (modulus 10, remainder 3),test_hash_4 FOR VALUES WITH (modulus 10, remainder 4),test_hash_5 FOR VALUES WITH (modulus 10, remainder 5),test_hash_6 FOR VALUES WITH (modulus 10, remainder 6),test_hash_7 FOR VALUES WITH (modulus 10, remainder 7),test_hash_8 FOR VALUES WITH (modulus 10, remainder 8),test_hash_9 FOR VALUES WITH (modulus 10, remainder 9)postgres=# insert into test_hash(flag, location, create_time)select 'flag' || mod(i, 10), md5(i::text),'2021-05-01 00:00:00+08'::timestamptz + (mod(i, 10) || ' day')::interval + (mod(i, 3600) || ' sec')::intervalfrom generate_series(1, 10000) i; --插入测试数据INSERT 0 10000
五、分区表的维护
ALTER TABLE [ IF EXISTS ] [ ONLY ] name [ * ] INHERIT parent_table;ALTER TABLE [ IF EXISTS ] [ ONLY ] name [ * ] NO INHERIT parent_table;
声明式分区表的维护,主要为 ATTACH 与 DETACH 。语法如下:
ALTER TABLE [ IF EXISTS ] name ATTACH PARTITION partition_name { FOR VALUES partition_bound_spec | DEFAULT };ALTER TABLE [ IF EXISTS ] name DETACH PARTITION partition_name;

六、PostgreSQL各大版本间分区表的差异
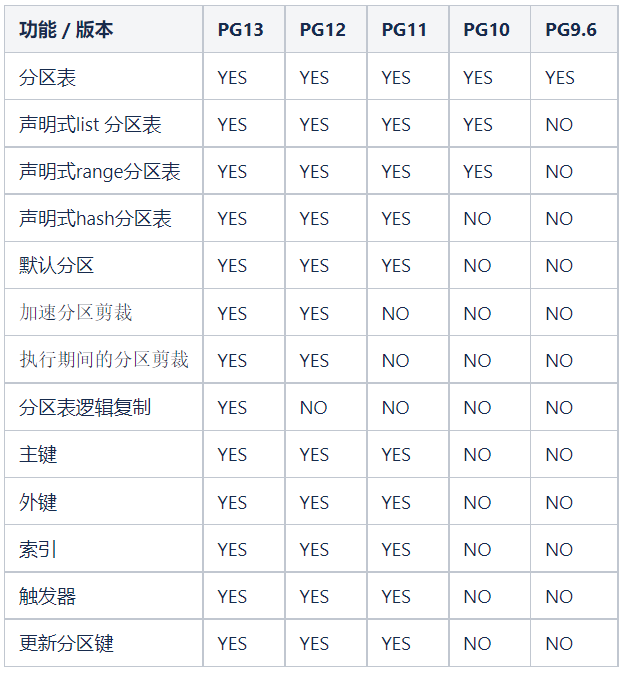
PostgreSQL 在 2005 年的 8.1 版本就支持了分区表,并在 PG10 支持声明式分区表,PG11 分区功能完善,以及 PG12 的快速分区剪裁,性能大幅提升, PG13 分区表支持逻辑复制。
七、问题 &思考
1. 什么时候需要分区?
a. 表多大需要区分?
100GB? 200GB? 1TB? 表的大小其实并不能决定是否需要分区,决定是否需要分区表的应该是 SQL 执行效率你是否能够接受。
b. 表的膨胀是否接受?对于经常需要进行数据归档的表,经常需要备份和清除, 一方面耗时,另一方面还会导致表膨胀,甚至影响 SQL 执行效率,分区后通过 attach detach partition 方式,能快速完成与线上表解除绑定,并且能很好的控制膨胀率,何乐而不为呢?
c. SQL 执行效率是否接受?随着时间的推移,业务量的增涨,表必将越来越大,SQL 执行效率也会随之降低。当效率降低到业务无法接受之时,分区表无疑是一个对应用影响小,且行之有效的方案。
2. 如何选择分区策略?list,range 或 hash ?
分区键的选择通常位于 SQL 中的 WHERE 和 JOIN 条件中,当查询在 WHERE 和 JOIN 子句中指定列时,它会告诉数据库“这是我想要的数据”,分区策略依赖于将这些列作为目标以分离数据,并使查询访问尽可能少的分区。
比如:带有日期类型的表,并且该列始终在 where 子句中使用,我们可以选择 range 分区;带有位置信息的客户表,例如居住省份,地区等,我们可以选择 list 分区;当 list 分区,range 分区都不太适用时,可以使用 hash 分区策略。
3. 如何取到 hash 分区表的 hash 值?
对需要性能极致化的要求来说,直接操作分区子表无疑是最佳的方式,list 或 range 分区表很容易就可以获取到子表表名,hash 分区却不太容易。
PostgreSQL 社区版本目前没有提供这种函数直接取 hash 值,但所有有用的信息都可以在源代码中找到,可以通过自定义函数,编译成共享库的方式来定制实现。
下面提供了 Qunar 在 PostgresQL 12 中定制函数取 hash 值的例子。
代码中提供了五个函数, 函数 hash_partition_value 参数为分区表的 OID , 分区数,以及分区的值,支持多字段,其它函数参数为分区的值和分区数, 不依赖与分区表 OID 。
postgres=# \df+ hash_partition_*List of functionsSchema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type | Volatility | Parallel | Owner | Security | Access privileges | Language | Source code | Description--------+----------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------+------+------------+----------+----------+----------+-------------------+----------+----------------------+-------------public | hash_partition_int2 | bigint | val smallint, modulus integer | func | volatile | unsafe | postgres | invoker | | c | hash_partition_int2 |public | hash_partition_int4 | bigint | val integer, modulus integer | func | volatile | unsafe | postgres | invoker | | c | hash_partition_int4 |public | hash_partition_int8 | bigint | val bigint, modulus integer | func | volatile | unsafe | postgres | invoker | | c | hash_partition_int8 |public | hash_partition_text | bigint | val text, modulus integer | func | volatile | unsafe | postgres | invoker | | c | hash_partition_text |public | hash_partition_value | bigint | oid, modulus integer, VARIADIC "any" | func | volatile | unsafe | postgres | invoker | | c | hash_partition_value |(6 rows)postgres=#
vim/home/postgres/
compute_hash_partition_value.c
#include "postgres.h"#include "access/relation.h"#include "access/tableam.h"#include "catalog/partition.h"#include "catalog/pg_collation_d.h"#include "parser/parse_coerce.h"#include "utils/builtins.h"#include "utils/partcache.h"#include "utils/lsyscache.h"#include "utils/syscache.h"#include "utils/hashutils.h"#include "utils/pg_locale.h"PG_MODULE_MAGIC;PG_FUNCTION_INFO_V1(hash_partition_value);Datumhash_partition_value(PG_FUNCTION_ARGS){typedef struct ColumnsHashData{Oid relid;int nkeys;Oid variadic_type;int16 variadic_typlen;bool variadic_typbyval;char variadic_typalign;Oid partcollid[PARTITION_MAX_KEYS];FmgrInfo partsupfunc[FLEXIBLE_ARRAY_MEMBER];} ColumnsHashData;Oid parentId;int modulus;int remainder;int temphash;Datum seed = UInt64GetDatum(HASH_PARTITION_SEED);ColumnsHashData *my_extra;uint64 rowHash = 0;/* Return null if the parent OID, modulus, or remainder is NULL. */if (PG_ARGISNULL(0) || PG_ARGISNULL(1) || PG_ARGISNULL(2))PG_RETURN_NULL();parentId = PG_GETARG_OID(0);modulus = PG_GETARG_INT32(1);/* Sanity check modulus and remainder. */if (modulus <= 0)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_INVALID_PARAMETER_VALUE),errmsg("modulus for hash partition must be a positive integer")));/** Cache hash function information.*/my_extra = (ColumnsHashData *) fcinfo->flinfo->fn_extra;if (my_extra == NULL || my_extra->relid != parentId){Relation parent;PartitionKey key;int j;/* Open parent relation and fetch partition keyinfo */parent = try_relation_open(parentId, AccessShareLock);if (parent == NULL)PG_RETURN_NULL();key = RelationGetPartitionKey(parent);/* Reject parent table that is not hash-partitioned. */if (parent->rd_rel->relkind != RELKIND_PARTITIONED_TABLE ||key->strategy != PARTITION_STRATEGY_HASH)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_INVALID_PARAMETER_VALUE),errmsg("\"%s\" is not a hash partitioned table",get_rel_name(parentId))));if (!get_fn_expr_variadic(fcinfo->flinfo)){int nargs = PG_NARGS() - 2;/* complain if wrong number of column values */if (key->partnatts != nargs)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_INVALID_PARAMETER_VALUE),errmsg("number of partitioning columns (%d) does not match number of partition keys provided (%d)",key->partnatts, nargs)));/* allocate space for our cache */fcinfo->flinfo->fn_extra =MemoryContextAllocZero(fcinfo->flinfo->fn_mcxt,offsetof(ColumnsHashData, partsupfunc) +sizeof(FmgrInfo) * nargs);my_extra = (ColumnsHashData *) fcinfo->flinfo->fn_extra;my_extra->relid = parentId;my_extra->nkeys = key->partnatts;memcpy(my_extra->partcollid, key->partcollation,key->partnatts * sizeof(Oid));/* check argument types and save fmgr_infos */for (j = 0; j < key->partnatts; ++j){Oid argtype = get_fn_expr_argtype(fcinfo->flinfo, j + 2);if (argtype != key->parttypid[j] && !IsBinaryCoercible(argtype, key->parttypid[j]))ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_INVALID_PARAMETER_VALUE),errmsg("column %d of the partition key has type \"%s\", but supplied value is of type \"%s\"",j + 1, format_type_be(key->parttypid[j]), format_type_be(argtype))));fmgr_info_copy(&my_extra->partsupfunc[j],&key->partsupfunc[j],fcinfo->flinfo->fn_mcxt);}}else{ArrayType *variadic_array = PG_GETARG_ARRAYTYPE_P(2);/* allocate space for our cache -- just one FmgrInfo in this case */fcinfo->flinfo->fn_extra =MemoryContextAllocZero(fcinfo->flinfo->fn_mcxt,offsetof(ColumnsHashData, partsupfunc) +sizeof(FmgrInfo));my_extra = (ColumnsHashData *) fcinfo->flinfo->fn_extra;my_extra->relid = parentId;my_extra->nkeys = key->partnatts;my_extra->variadic_type = ARR_ELEMTYPE(variadic_array);get_typlenbyvalalign(my_extra->variadic_type,&my_extra->variadic_typlen,&my_extra->variadic_typbyval,&my_extra->variadic_typalign);my_extra->partcollid[0] = key->partcollation[0];/* check argument types */for (j = 0; j < key->partnatts; ++j)if (key->parttypid[j] != my_extra->variadic_type)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_INVALID_PARAMETER_VALUE),errmsg("column %d of the partition key has type \"%s\", but supplied value is of type \"%s\"",j + 1, format_type_be(key->parttypid[j]), format_type_be(my_extra->variadic_type))));fmgr_info_copy(&my_extra->partsupfunc[0],&key->partsupfunc[0],fcinfo->flinfo->fn_mcxt);}/* Hold lock until commit */relation_close(parent, NoLock);}if (!OidIsValid(my_extra->variadic_type)){int nkeys = my_extra->nkeys;int i;/** For a non-variadic call, neither the number of arguments nor their* types can change across calls, so avoid the expense of rechecking* here.*/for (i = 0; i < nkeys; i++){Datum hash;/* keys start from fourth argument of function. */int argno = i + 2;if (PG_ARGISNULL(argno))continue;hash = FunctionCall2Coll(&my_extra->partsupfunc[i],my_extra->partcollid[i],PG_GETARG_DATUM(argno),seed);/* Form a single 64-bit hash value */rowHash = hash_combine64(rowHash, DatumGetUInt64(hash));}}else{ArrayType *variadic_array = PG_GETARG_ARRAYTYPE_P(2);int i;int nelems;Datum *datum;bool *isnull;deconstruct_array(variadic_array,my_extra->variadic_type,my_extra->variadic_typlen,my_extra->variadic_typbyval,my_extra->variadic_typalign,&datum, &isnull, &nelems);/* complain if wrong number of column values */if (nelems != my_extra->nkeys)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_INVALID_PARAMETER_VALUE),errmsg("number of partitioning columns (%d) does not match number of partition keys provided (%d)",my_extra->nkeys, nelems)));for (i = 0; i < nelems; i++){Datum hash;if (isnull[i])continue;hash = FunctionCall2Coll(&my_extra->partsupfunc[0],my_extra->partcollid[0],datum[i],seed);/* Form a single 64-bit hash value */rowHash = hash_combine64(rowHash, DatumGetUInt64(hash));}}PG_RETURN_UINT64(rowHash % modulus);}PG_FUNCTION_INFO_V1(hash_partition_text);Datumhash_partition_text(PG_FUNCTION_ARGS){text *key = PG_GETARG_TEXT_PP(0);int modulus = PG_GETARG_DATUM(1);Oid collid = PG_GET_COLLATION();if (!key)PG_RETURN_NULL();if (modulus < 0 )ereport(ERROR, (errcode(ERRCODE_INVALID_PARAMETER_VALUE),errmsg("function ""%s"" fail(""%s"")!", "hash_partition_text","modulus < 0")));if (!collid)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_INDETERMINATE_COLLATION),errmsg("could not determine which collation to use for string hashing"),errhint("Use the COLLATE clause to set the collation explicitly.")));Datum hash;uint64 rowHash = 0;pg_locale_t mylocale = 0;if (!lc_collate_is_c(collid) && collid != DEFAULT_COLLATION_OID)mylocale = pg_newlocale_from_collation(collid);if (!mylocale || mylocale->deterministic){hash = hash_any_extended((unsigned char *) VARDATA_ANY(key),VARSIZE_ANY_EXHDR(key),HASH_PARTITION_SEED);}else{#ifdef USE_ICUif (mylocale->provider == COLLPROVIDER_ICU){int32_t ulen = -1;UChar *uchar = NULL;Size bsize;uint8_t *buf;ulen = icu_to_uchar(&uchar, VARDATA_ANY(key), VARSIZE_ANY_EXHDR(key));bsize = ucol_getSortKey(mylocale->info.icu.ucol,uchar, ulen, NULL, 0);buf = palloc(bsize);ucol_getSortKey(mylocale->info.icu.ucol,uchar, ulen, buf, bsize);hash = hash_any_extended(buf, bsize, HASH_PARTITION_SEED);pfree(buf);}else#endif/* shouldn't happen */elog(ERROR, "unsupported collprovider: %c", mylocale->provider);}PG_FREE_IF_COPY(key, 0);rowHash = hash_combine64(rowHash, DatumGetUInt64(hash));PG_RETURN_UINT64(rowHash % modulus);}PG_FUNCTION_INFO_V1(hash_partition_int2);Datumhash_partition_int2(PG_FUNCTION_ARGS){int16 val = PG_GETARG_INT16(0);int modulus = PG_GETARG_INT32(1);if (val < 0 || modulus < 0)ereport(ERROR, (errcode(ERRCODE_INVALID_PARAMETER_VALUE),errmsg("function ""%s"" fail(""%s"")!", "hash_partition_int2","val < 0 or modulus < 0")));Datum hash;uint64 rowHash = 0;hash = hash_uint32_extended((int32) val, HASH_PARTITION_SEED);rowHash = hash_combine64(rowHash, DatumGetUInt64(hash));PG_RETURN_UINT64(rowHash % modulus);}PG_FUNCTION_INFO_V1(hash_partition_int4);Datumhash_partition_int4(PG_FUNCTION_ARGS){int val = PG_GETARG_INT32(0);int modulus = PG_GETARG_INT32(1);if (val < 0 || modulus < 0)ereport(ERROR, (errcode(ERRCODE_INVALID_PARAMETER_VALUE),errmsg("function ""%s"" fail(""%s"")!", "hash_partition_int4","val < 0 or modulus < 0")));Datum hash;uint64 rowHash = 0;hash = hash_uint32_extended(val, HASH_PARTITION_SEED);rowHash = hash_combine64(rowHash, DatumGetUInt64(hash));PG_RETURN_UINT64(rowHash % modulus);}PG_FUNCTION_INFO_V1(hash_partition_int8);Datumhash_partition_int8(PG_FUNCTION_ARGS){int64 val = PG_GETARG_INT64(0);int modulus = PG_GETARG_INT32(1);if (val < 0 || modulus < 0)ereport(ERROR, (errcode(ERRCODE_INVALID_PARAMETER_VALUE),errmsg("function ""%s"" fail(""%s"")!", "hash_partition_int8","val < 0 or modulus < 0")));uint32 lohalf = (uint32) val;uint32 hihalf = (uint32) (val >> 32);lohalf ^= (val >= 0) ? hihalf : ~hihalf;Datum hash;uint64 rowHash = 0;hash = hash_uint32_extended(lohalf, HASH_PARTITION_SEED);rowHash = hash_combine64(rowHash, DatumGetUInt64(hash));PG_RETURN_UINT64(rowHash % modulus);}
postgres@~$ pwd/home/postgrespostgres@~$ gcc -fPIC -c compute_hash_partition_value.c -I `pg_config --includedir-server`postgres@~$ cc -shared -o compute_hash_partition_value.so compute_hash_partition_value.opostgres@~$ ls |grep compute_hash_partition_valuecompute_hash_partition_value.ccompute_hash_partition_value.ocompute_hash_partition_value.sopostgres@~$ psqlpsql (12.3)Type "help" for help.postgres=# CREATE or replace FUNCTION hash_partition_value(oid, modulus int, VARIADIC "any")RETURNS BIGINT/*依赖于partition table oid, 适用于任意列数hash分区表*/AS '/home/postgres/compute_hash_partition_value', 'hash_partition_value'LANGUAGE C STRICT;CREATE FUNCTIONpostgres=#postgres=# CREATE or replace FUNCTION hash_partition_int2(val int2, modulus int)RETURNS bigint /*不依赖于partition table oid, 适用于计算单列smallint的分区*/AS '/home/postgres/compute_hash_partition_value', 'hash_partition_int2'LANGUAGE C STRICT;CREATE FUNCTIONpostgres=#postgres=# CREATE or replace FUNCTION hash_partition_int4(val int,modulus int)RETURNS bigint /*不依赖于partition table oid, 适用于计算单列int的分区*/AS '/home/postgres/compute_hash_partition_value', 'hash_partition_int4'LANGUAGE C STRICT;CREATE FUNCTIONpostgres=#postgres=# CREATE or replace FUNCTION hash_partition_int8(val int8, modulus int)RETURNS bigint /*不依赖于partition table oid, 适用于计算单列bigint的分区*/AS '/home/postgres/compute_hash_partition_value', 'hash_partition_int8'LANGUAGE C STRICT;CREATE FUNCTIONpostgres=#postgres=# CREATE or replace FUNCTION hash_partition_text(val text, modulus int)RETURNS BIGINT /*不依赖于partition table oid, 适用于计算单列text的分区*/AS '/home/postgres/compute_hash_partition_value', 'hash_partition_text'LANGUAGE C STRICT;CREATE FUNCTIONpostgres=#
验证数据量一致,hash 值正确。
postgres=# select count(*) from test_hash where substring(tableoid::Regclass::text, 11, 1) = hash_partition_value('test_hash'::regclass, 10, location)::text;count-------10000(1 row)postgres=# select count(*) from test_hash where substring(tableoid::Regclass::text, 11, 1) = hash_partition_text(location, 10)::text;count-------10000(1 row)
八、Qunar 表分区实践
Qunar 的酒店基础数据,全司 Watcher 监控数据,全司的 Hive 元数据等业务中的性能存在瓶颈的大表改造为分区表后,性能都得到了大幅提升。
下面以酒店的 1 个 list 分区表为例,看一下分区前后性能对比。
vim/home/postgres/compute_hash_partition_value.c
未分表之前:
hotel_beta=# \dt+ public.xds_entity_index_oldList of relationsSchema | Name | Type | Owner | Size | Description--------+----------------------+-------+----------+-------+-------------public | xds_entity_index_old | table | postgres | 23 GB |(1 row)hotel_beta=# explain analyze select count(1) from xds_entity_index_old;QUERY PLAN--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Finalize Aggregate (cost=813988.87..813988.88 rows=1 width=8) (actual time=27947.494..27947.495 rows=1 loops=1)-> Gather (cost=813988.45..813988.86 rows=4 width=8) (actual time=27947.421..27949.412 rows=5 loops=1)Workers Planned: 4Workers Launched: 4-> Partial Aggregate (cost=812988.45..812988.46 rows=1 width=8) (actual time=27943.837..27943.837 rows=1 loops=5)-> Parallel Seq Scan on xds_entity_index_old (cost=0.00..800032.76 rows=5182276 width=0) (actual time=1.246..27554.475 rows=4145821 loops=5)Planning Time: 0.109 msExecution Time: 27949.453 ms(8 rows)
hotel_beta=# \d xds_entity_indexTable "public.xds_entity_index"Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default--------------+-----------------------------+-----------+----------+----------------------------------------------id | integer | | not null | nextval('xds_entity_index_id_seq'::regclass)entity_type | integer | | not null |......create_time | timestamp(6) with time zone | | not null | now()Partition key: LIST (entity_type)Indexes:......Number of partitions: 128 (Use \d+ to list them.)hotel_beta=# explain analyze select count(1) from xds_entity_index;QUERY PLAN---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Finalize Aggregate (cost=267790.55..267790.56 rows=1 width=8) (actual time=1376.571..1376.571 rows=1 loops=1)-> Gather (cost=267790.13..267790.54 rows=4 width=8) (actual time=1376.053..1381.522 rows=5 loops=1)Workers Planned: 4Workers Launched: 4-> Partial Aggregate (cost=266790.13..266790.14 rows=1 width=8) (actual time=1364.338..1364.338 rows=1 loops=5)-> Parallel Append (cost=0.30..253348.19 rows=5376776 width=0) (actual time=0.084..1080.768 rows=4293129 loops=5)-> Parallel Index Only Scan using xds_entity_index_list_2_data_version_idx on xds_entity_index_list_2 (cost=0.43..99652.70 rows=3333755 width=0) (actual time=0.055..382.835 rows=2066928 loops=5)Heap Fetches: 0-> ......-> Parallel Seq Scan on xds_entity_index_list_0 (cost=0.00..13.06 rows=306 width=0) (actual time=0.000..0.000 rows=0 loops=1)-> ......-> Parallel Seq Scan on xds_entity_index_list_106 (cost=0.00..1.01 rows=1 width=0) (actual time=0.008..0.009 rows=1 loops=1)Planning Time: 5.336 msExecution Time: 1381.910 ms(169 rows)
hotel_beta=# select round(27949.453/1381.910);round-------20(1 row)
参考文献:
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/ddl-partitioning.html
https://www.postgresql.org/about/featurematrix/
https://pgdash.io/blog/partition-postgres-11.html
https://postgres.fun/20180920155600.html
https://severalnines.com/database-blog/guide-partitioning-data-postgresql
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/110927990
PostgreSQL中文社区欢迎广大技术人员投稿
投稿邮箱:press@postgres.cn






