上一篇基本概念中简单的介绍了sql的分类和增删改操作,今天聊聊常用复杂SQL查询。

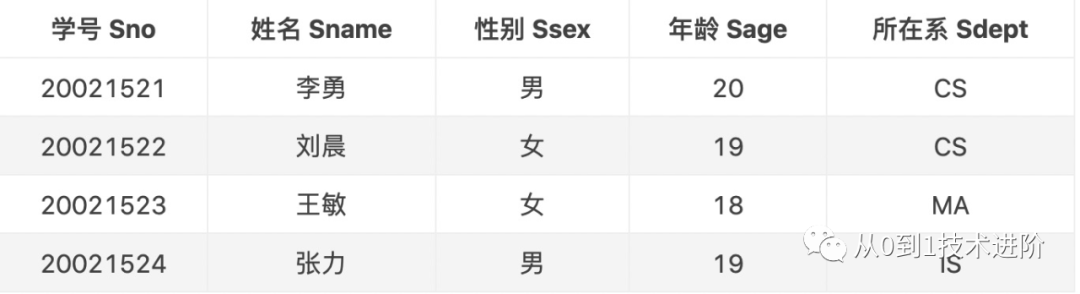
Student
(1)选择指定的列
【例】查询全体学生的学号和姓名
select Sno as 学号,Sname as 姓名 from student;
select Sno,Sname from student;
(2)查询全部列
【例】查询全体学生的详细信息
select * from student;
(3)对查询后的指定列进行命名
【例】查询全部学生的“姓名”及其“出生年”两列
select Sname as 姓名,(2014-Sage) as 出生年 from student;
(4)消除取值重复的行
【例】查询选修了课程的学生学号
select distinct Sno as 选修了课程的学生学号 from SC;
(5)选择表中若干元组(满足条件的)
【例】查询全体20岁以下的学生姓名和年龄
select Sname as 姓名,Sage as 年龄 from student where Sage<20
select Sname as 姓名,Sdept as 系别,Sage as 年龄 from student where Sage between20 and 23;
注意between 小数 and 大数。
select Sname as 姓名,Ssex as 性别 from student where Sdept='IS' or Sdept='CS';
select Sname as 姓名,Ssex as 性别 from student where Sdept in ('IS','CS');
【例】查询既不属于IS系,也不属于MA系的学生姓名和年龄
select Sname as 姓名,Sage as 年龄 from student where Sdept !='IS'and Sdept!='CS';
select Sname as 姓名,Sage as 年龄 from student where Sdept not in('IS','MA');
select Sname as 姓名,Ssex as 性别 from student where Sname like '李%';
【例】查询所有“2002”年入学的学生学号、姓名和系别
select Sno as 学号,Sname as 姓名,Sdept as 系别 from student where Sno like'2002%';
【例】查询所有不姓“刘”的学生信息
select * from student where Sname not like'刘%';
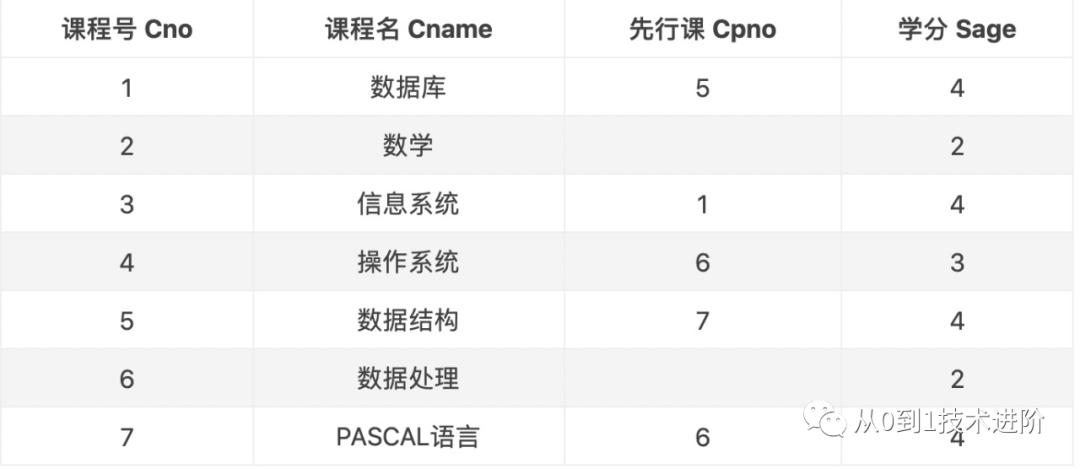
【例】查询名称含有“数据”的课程号、课程名及学分
总结:
select * from course where cname like '%数据%';包含数据的字符串
select * from course where cname like '数据%';以数据开头的字符串
select * from course where cname like '%数据'; 以数据结尾的字符串
select Cno as 课程号,Cname as 课程名,Cpno from course where Cpno is null;
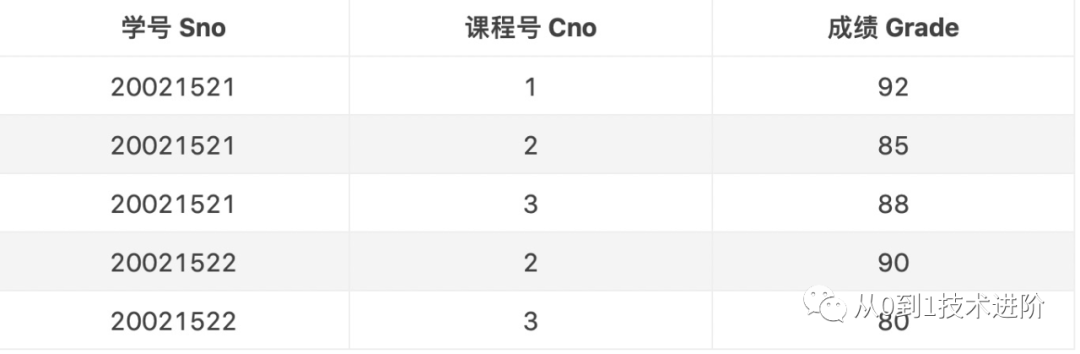
【例】查询所有有成绩的学生学号、课程号及成绩
select Sno as 学号,Cno as 课程号,Grade as 成绩 from SC where Grade is not null;
select Sno as 学号,Grade as 成绩 from SC where Cno=3 order by Grade desc;
【例】查询选修了3号课程的学生学号和成绩,结果按成绩升序排列。
select Sno as 学号,Grade as 成绩 from SC where Cno=3 order by Grade asc;
【例】查询学生总数
select count(*) as 学生总数 from student;
【例】查询所有课程的总学分
select sum(Ccredit) as 所有课程总学分 from course;
【例】查询全体学生平均年龄
select avg(Sage) as 平均年龄 from student;
【例】查询1号课程的最高分
select max(Grade) as 1号课程的最高分 from SC where Cno=1;
select Ssex as 性别,count(*) as 人数 from student group by Ssex;
【例】查询每个课程的课程号和平均分。
select Cno as 课程号,avg(Grade) as 平均分 from SC group by Cno;
【例】查询选修了3门课程以上(含3门)的学生学号和选修课程数。
select Sno as 学号 ,count(course.Cno) as 选修课程数
From SC,course
Where course.Cno=SC.Cno
Group by Sno
Having Count(course.Cno)>=3;
having 关键字后面直接跟聚集函数
在 SQL 中增加 HAVING 子句原因是,WHERE 关键字无法与合计函数一起使用。
SELECT column_name, aggregate_function(column_name)
FROM table_name
WHERE column_name operator valueGROUP BY column_name
HAVING aggregate_function(column_name) operator value
【例】查询选修了2门课程以上(含2门,但不含1号课程),学生学号和选修课程数。
select Sno as 学号 ,count(course.Cno) as 选修课程数
From SC,course
Where course.Cno=SC.Cno and course.Cno !=1
Group by Sno
Having Count(course.Cno)>=2;
【例】查询不及格门数2门以上的学生学号。
Select Sno
from sc
Where sc.Grade<60
Group by Sno
Having count(Cno)>=2;
【例】查询有2名以上(含2名)学生选修了的课程号和选修人数。
Select Cno,count(Sno)
From SC
Group by Cno
Having count(sno)>=2
from student,course,SC
where student.Sno=SC.Sno and course.Cno=SC.Cno ;
(2)自身连接
【例】查询每个学生的间接选修课
select SC.Sno as 学号,
FIRST.Cname as 直接选修课,
SECOND.Cname as 间接选修课
from SC,
course as FIRST,
course as SECOND
where FIRST.Cno=SC.Cno
and FIRST.Cpno=SECOND.Cno;
(3)外连接
【例】查询所有学生选修课程情况(含没选修课程的学生)
select student.Sno as 学号,
Sname as 姓名,
sc.Cno as 选修课程号
from student
LEFT OUTER JOIN SC ON student.Sno=SC.Sno;
join 用于根据两个或多个表中的列之间的关系,从这些表中查询数据
JOIN: 如果表中有至少一个匹配,则返回行
LEFT JOIN: 即使右表中没有匹配,也从左表返回所有的行
RIGHT JOIN: 即使左表中没有匹配,也从右表返回所有的行
FULL JOIN: 只要其中一个表中存在匹配,就返回行
UNION 操作符用于合并两个或多个 SELECT 语句的结果集。
请注意,UNION 内部的 SELECT 语句必须拥有相同数量的列。列也必须拥有相似的数据类型。同时,每条 SELECT 语句中的列的顺序必须相同。
(1)带有IN谓词的子查询( 属性 in (子查询的查询结果) )
【例】查询与王敏同学在同一个系的学生信息。
select *
from student
where Sdept in (
select Sdept
from student
where Sname='王敏'
);
【例】查询不与王敏同学不在同一个系的学生信息。
select *
from student
where Sdept not in (
select Sdept
from student
whereSname='王敏'
);
【例】查询选修了课程名是“信息系统”的学生学号和姓名。
select student.Sno as 学号, Sname as 姓名
from student,SC
where student.Sno=SC.Sno and Cno in (
select Cno
from course
where Cname='信息系统'
)
【例】查询曾与刘晨一同上课的学生学号和姓名。(假设:一个课程只有一个上课班)
select distinct student.Sno as 学号, Sname as 姓名
from student,SC
where student.Sno=SC.Sno and Cno in (
select Cno
from SC,student
where SC.Sno=student.Sno and student.Sno in (
select Sno
from student
where student.Sname='刘晨'
)
)
内层in 查出刘晨的学号sno,外层in查出刘晨所上课程的课程号。
(2)带有比较运算符的子查询(=,>=,<=,<>或!=)
【例】查询与王敏同学在同一个系的所有学生信息 (=判断)
select *
from student
where Sdept=(
select Sdept
from student
where Sname='王敏'
)
【例】查询每个学生超过该课程最低分的课程号。(同类课程不是最低分的),子查询的结果返回一个数的时候,这个子查询就可以当一个数用?可以使用in符号,或者大于小于符号。
select Cno
from SC a
where Grade> (
select min(Grade)
from SC b
where a.Cno=b.Cno
)
【例】查询每个学生超过他选修课程平均成绩的课程号。
select Cno
from SC a
where Grade> (
select avg(Grade)
from SC b
where a.Sno=b.Sno
)
(3)带有ANY或ALL谓词的子查询
ANY表示任何一个,ALL表示所有,可以用在子查询的括号前面
【例】查询其他系中比计算机系某一学生年龄小的学生姓名,性别、年龄和所在系。
select Sname as 姓名,Ssex as 性别, Sage as 年龄, Sdept as 所在系
from student
where Sage <(
select Sage
from student
where Sdept='CS'
);
【例】查询其他系中比计算机系所有年龄都小的学生姓名和年龄。
select Sname as 姓名, Sage as 年龄
from student
where Sdept<>'CS' and Sage
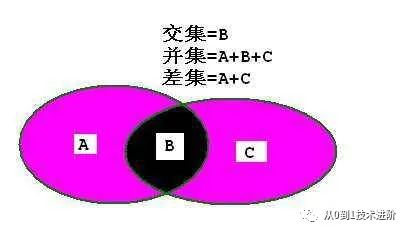
04 集合查询
(1)并UNION
【例】查询计算机系的学生及年龄不大于19岁的学生详细信息。
select *
from student
where student.Sdept='CS'
union
select *
from student
where student.Sage<=19;
(2)交INTERSECT
【例】查询选修了1号课程的与年龄不大于19岁的 学生 详细信息 的交集。
Select *
from student,SC
where student.Sno=SC.Sno and SC.Cno=1
INTERSECT
Select *
from student
where student.Sage<=19;
(3)差EXCEPT
【例】查询计算机科学系的学生与年龄不大于19岁的学生详细信息的差集。
select *
from student
where student.Sdept='SC'
EXCEPT
select *
from student
where student.Sage<=19;