在阅读本文之前,需要对列存表的存储结构有基本的了解,可以参考列存表的介绍文章:openGauss存储技术(二)——列存储引擎和内存引擎
概述
列存表 B-tree 索引结构与行存表并无大的差别,列存表的 B-tree 索引在存储引擎侧是以行存形式组织。对于一般用于应对大数据批量分析性负载的列存储引擎来说,B-tree 索引有助于帮助列存储提升自身的点查效率,更好地适应混合负载。
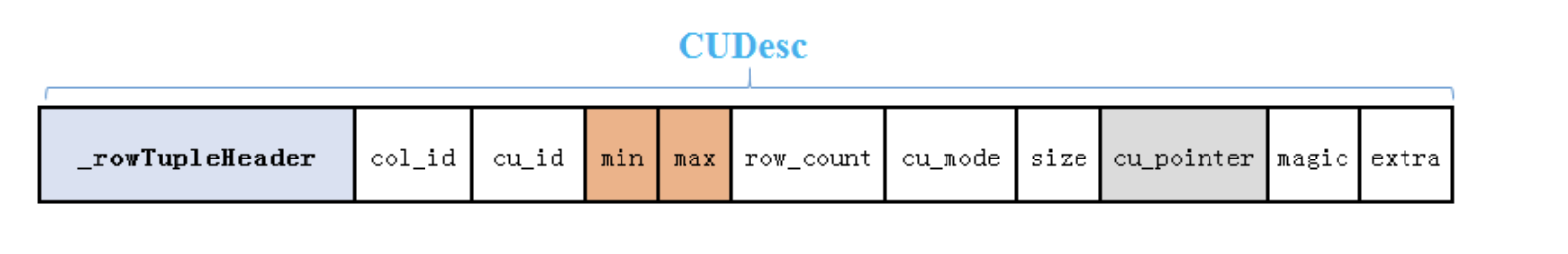
行存储的 B-tree 索引数据中存储的是 key→ctid (键→行号)的映射,在列存储的场景下,这个映射依旧为 key→ctid。但列存储的结构并不能像行存储一样,通过ctid中的块号(block number)和偏移量(offset)直接找到此行数据在数据文件页面中的位置。列存储ctid中记录的是(cu_id,offset),要通过 CUDesc 结构来进行查找。
在基于 B-tree 索引的扫描中,从索引中拿到 ctid 后,需要在对应的 CUDesc表中,根据 CUDesc 在 cu_id 列的索引找到对应的 CUDesc 记录,并由此打开对应的 CU 文件,根据偏移量找到数据。
此操作涉及大量的存储层性能开销,因此列存储的 B树索引,与列存储的其他操作一样,统一都会批量操作,会根据 B-tree 索引找到 ctid 的集合,然后对此集合进行排序,再批量地对排序后的 ctid 进行 CU 文件级别的查找与操作。这样可以做到顺序单调地进行索引遍历,大大减少了反复操作文件带来的 CPU 以及IO 开销。
列存表的 B-btree 索引实现主要在 src/gausskernel/storage/access/cbtree 下
先在 pg_am 中查询 cbtree 索引对应的处理函数:
| 功能 | 处理函数 |
|---|---|
| aminsert | btinsert |
| ambeginscan | btbeginscan |
| amgettuple | cbtreegettuple |
| amgetbitmap | cbtreegetbitmap |
| amrescan | btrescan |
| amendscan | btendscan |
| ambuild | cbtreebuild |
| ambuildempty | btbuildempty |
| amcanreturn | cbtreecanreturn |
| amcostestimate | cbtreecostestimate |
| amoptions | cbtreeoptions |
构建 B-tree 索引
cbtreebuild
{
_bt_spoolinit // 初始化一个 BTSpool, 行存表也有
// scan 列存表
CStoreBeginScan
do {
vecScanBatch = CStoreGetNextBatch(scanstate); // 读取一批数据
InsertToBtree(vecScanBatch, buildstate, indexInfo, reltuples, values, isnull, transferFuncs); // 将这批数据插入 BTSPool,过程中会生成 index tuple
} while(!CStoreIsEndScan(scanstate))
_bt_leafbuild // 根据扫描出来的数据开始构建 btree,此函数 行存 btree 索引和列存 btree 索引共用,可以参考行存 btree 索引构建
返回结果
}
行存和列存差异
行存表构建BTSpool的时候,如果是 unique index 会额外初始化一个 BTSpool , 列存表中没有此逻辑。因为目前OpenGauss中只有行存表的 Btree 索引支持唯一索引,其他索引都不支持唯一索引。
行存表和列存表的 index tuple 中, t_tid 的设置不同:
列存表
{
tid = (ItemPointer)(&sysVec->m_vals[rowIdx]);
_bt_spool(buildstate.spool, tid, values, isnulls);
}
行存表
{
_bt_spool(buildstate->spool, &htup->t_self, values, isnull);
}
行存表的 t_tid直接指向 heap tuple,而列存表的 t_tid 指向(CU_id, offset),使用时还需要通过 CU_id 先找到 CUDesc记录,再打开对应的CU文件,根据 offset 读取数据。由于列存中数据按照列组织,因此拿到(CU_id, offset)后,还需要按列去获取数据。
行存索引实现中的重要数据结构:
ScalarVector:表示一列数据的数据结构,其中可能包含一列数据的多个值
VectorBatch:表示多行数据的数据结构,其中一行可能有多列。其中包含一个 ScalarVector 类型的数组,数组的长度为每一行包含的列数。
向 BTSPool 中插入一批数据:
static void InsertToBtree(VectorBatch *vecScanBatch, BTBuildState &buildstate, IndexInfo *indexInfo, double &reltuples,
Datum *values, bool *isnulls, ScalarToDatum *transferFuncs)
{
int rows = vecScanBatch->m_rows;
ScalarVector *vec = vecScanBatch->m_arr;
ScalarVector *sysVec = vecScanBatch->GetSysVector(SelfItemPointerAttributeNumber);
reltuples += rows;
for (int rowIdx = 0; rowIdx < rows; rowIdx++) {
int i;
ItemPointer tid;
for (i = 0; i < indexInfo->ii_NumIndexAttrs; i++) {
int32 colIdx = indexInfo->ii_KeyAttrNumbers[i] - 1;
if (vec[colIdx].IsNull(rowIdx)) {
isnulls[i] = true;
} else {
isnulls[i] = false;
values[i] = transferFuncs[i](vec[colIdx].m_vals[rowIdx]);
}
}
tid = (ItemPointer)(&sysVec->m_vals[rowIdx]);
/* Fill btree spool */
_bt_spool(buildstate.spool, tid, values, isnulls);
buildstate.indtuples += 1;
}
}
列存表的 Btree 索引插入、查询流程基本和行存表的 Btree 索引一致,不一样的是叶子节点的 tid 是(CU_id, offset)。查找流程得到 tid 后需要根据 CUDesc 去找到 CU 再读取数据。






