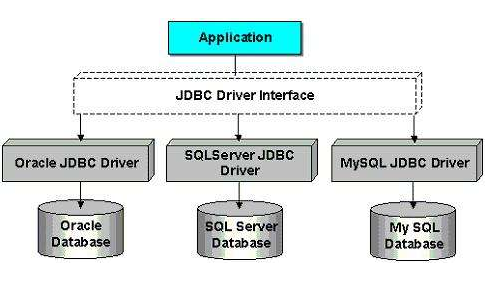
JDBC
概念
Java数据库连接,(Java Database Connectivity
,简称JDBC
)是Java语言中用来规范客户端程序如何来访问数据库的[应用程序接口,提供了诸如查询和更新数据库中数据的方法。JDBC
也是Sun Microsystems
的商标。我们通常说的JDBC
是面向关系型数据库的。(面向接口编程)
数据的持久化
像IO
流文件就是属于持久文件,企业级应用,数据持久化意味着将内存中的数据保存到硬盘上加以“固化”,而持久的实现过程大多通过各种关系数据库来完成
持久化的主要应用层是将内存中的数据存储在关系型数据库中,当然也可以存储在硬盘文件,XML
数据文件中
Java中的数据存储技术
JDBC:直接访问数据库;JDBC就是一组规范(类似抽象类或接口)、接口;它可以实现连接多套数据库接口
JDO(Java Data Object
)技术
第三方O/R
工具,如Hibernate
、MyBatis
等只是更好的封装了JDBC
总的来说,JDBC是sun公司提供一套用于数据库操作的接口,不同数据库的厂商根据这套接口提供不同实现,不同的实现的集合,即为不同数据库的驱动
这里先说明一些类或者接口是干什么用,方便理解代码
DriverManager类
DriverManager
作用
管理和注册驱动 创建数据库的连接
常用方法
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Connection getConnection (String url, String user, String password) | 通过连接字符串,用户,密码来得到数据库的连接对象 |
| Connection getConnection (String url, Properties info) | 通过连接字符串,属性对象来得到连接对象 |
Conection接口
Connection 作用
与特定数据库的连接(会话)。在连接上下文中执行 SQL
语句并返回结果。Connection
对象的数据库能够提供描述其表、所支持的SQL
语法、存储过程、此连接功能等等的信息。此信息是使用getMetaData
方法获得的。
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Statement createStatement() | 创建一条 SQL 语句对象 |
statement接口
statement
:用于执行静态SQL语句并返回它所生成结果的对象
JDBC访问数据库实现步骤
准备数据库的驱动包,加载到项目中(不同数据库需要不同的jar包)
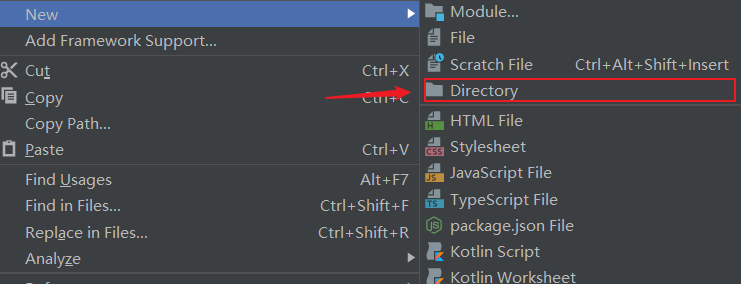
然后
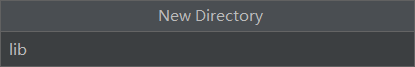
接着

或者以这种方式导包
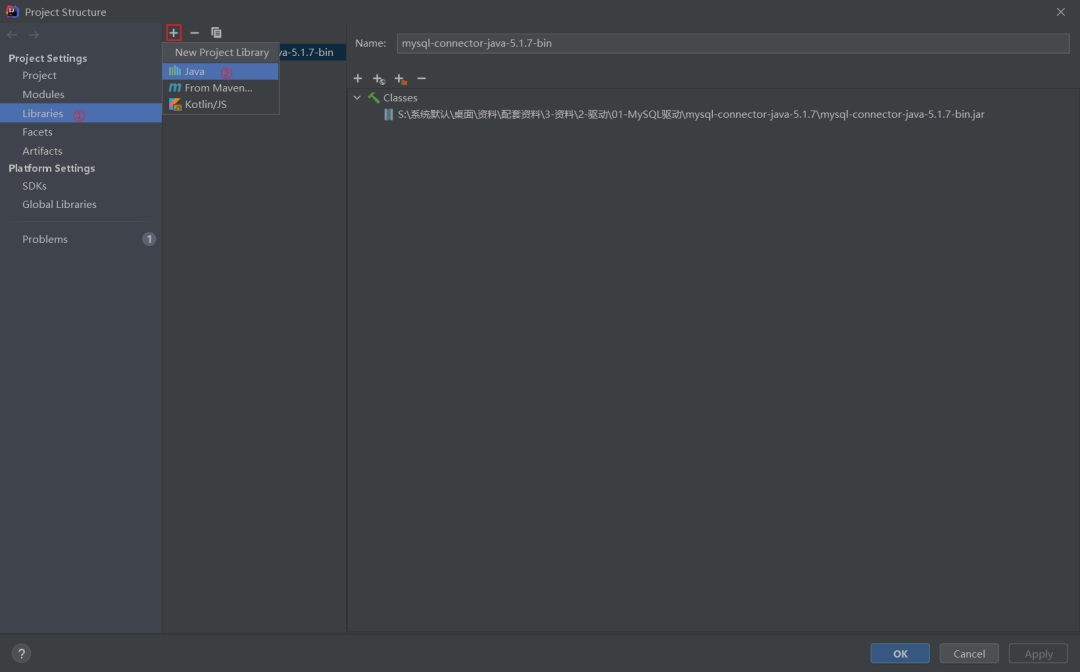
然后
初始化驱动
和数据库之间的
Connection
连接(这一步相当于连接(例如数据库登录,先登录,然后进行增删改查))然后创建
Statement
或者PreparedStatement
对象(下面会说到),执行sql
对象。如果是查询语句的话,返回的是ResultSet
结果集;如果是增删改,则不需要结果集最后就是处理和显示结果,然后释放资源
先获取数据库连接
Java.sql.Driver
接口是所有 JDBC
驱动程序需要实现的接口。这个接口是提供给数据库厂商使用的,不同数据库厂商提供不同的实现;在程序中不需要直接去访问实现了 Driver
接口的类,而是由驱动程序管理器类(java.sql.DriverManager
)去调用这些Driver
实现,通过Driver
接口获取数据连接Driver
接口
/*
1.加载驱动;Class.forName() 方法要求JVM查找并加载指定的类到内存中;
将"com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" 当做参数传入,就是告诉JVM,去"com.mysql.jdbc"这个路径下找Driver类,将其加载到内存中。由于JVM加载类文件时会执行其中的静态代码块,从Driver类的源码中可以看到该静态代码块执行的操作是:将mysql的driver注册到系统的DriverManager中
*/
//通过反射获取Driver实现类对象
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
提供连接的基本信息
/*
2.jdbc:mysql:协议
127.0.0.1:3306:ip地址和数据库端口号
myemployees:数据库名
连接信息(用户信息和url;useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true";//第一个支持中文编码;第二个设置字符集编码utf—8;第三个使用安全连接)
*/
String url= "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/myemployees?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true";
String username="root";
String password="111";
获取连接
DriverManager.getConnection
创建数据库对象
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
获得执行sql的对象 Statement(不安全)
Statement
对象用于执行sql
语句,增删改查(CURD操作)必须通过statement
对向数据库发送
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| executeQuery() | 查询操作,返回一个结果集 |
| executeUpdate() | 主要执行更新、插入、删除语句,返回受影响的行数 |
| execute() | 执行任何任何SQL语句 |
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
String sql="SELECT * FROM `employees`";//编写SQL语句
executeUpdate() :主要执行增、删、改操作
String sql="insert into user (……) values(……)";
int num=statement.executeUpdate(sql);//返回受影响的行数
if (num>0){//如果有受影响的行数,则插入成功
System.out.println("插入成功");
}
executeQuery() :主要执行查询操作
String sql="insert into user (……) values(……)";
int num=statement.executeQuery(sql);//返回受影响的行数
if (num>0){//如果有受影响的行数,则插入成功
System.out.println("插入成功");
}
返回结果集对象
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);//返回结果集,结果集封装了我们所有的查询出来的结果
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| getObject() | 在不知道列类型的情况下使用 |
| getString() | 如果知道列的类型就使用指定的类型 |
| getDate() | 将此 ResultSet对象的当前行中的指定列的值作为Java编程语言中的 java.sql.Date对象检索。 |
| afterLast() | 移动到最后面的数据 |
| beforeFirst() | 移动到最前面的数据 |
| next() | 移动到下一个数据 |
| previous() | 移动到前一行 |
| absolute(rwo) | 移动到指定行 |
释放连接
释放原则:先开的后关,后开的先关。 放在 Finally
代码块中
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
大致基本写法如下
import java.sql.*;
public class JdbcTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
/*
1.加载驱动;Class.forName() 方法要求JVM查找并加载指定的类到内存中;
将"com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" 当做参数传入,就是告诉JVM,去"com.mysql.jdbc"这个路径下找Driver类,将其加载到内存中。由于JVM加载类文件时会执行其中的静态代码块,从Driver类的源码中可以看到该静态代码块执行的操作是:将mysql的driver注册到系统的DriverManager中
*/
//通过反射获取Driver实现类对象
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
/*
2.jdbc:mysql:协议
127.0.0.1:3306:ip地址和数据库端口号
myemployees:数据库名
连接信息(用户信息和url;useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true";//第一个支持中文编码;第二个设置字符集编码utf—8;第三个使用安全连接)
*/
String url= "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/myemployees?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true";
String username="root";
String password="111";
//3.连接成功,返回数据库对象(固定一个类(驱动管理));Connection代表数据库
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//4.执行SQL对象 Statement执行sql对象
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
//5.执行SQL对象去执行SQL,可能存在结果,查看返回结果
String sql="SELECT * FROM `employees`";
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);//返回结果集,结果集封装了我们全部的查询出来的结果
while(resultSet.next()){
System.out.println("first_name="+resultSet.getObject("first_name"));
System.out.println("last_name="+resultSet.getObject("last_name"));
System.out.println("email="+resultSet.getObject("email"));
System.out.println("phone_number="+resultSet.getObject("phone_number"));
System.out.println();
}
//6.释放连接
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
由于上面代码过于冗余,于是将数据库连接需要的4个基本信息声明在配置文件里(推荐这种写法),通过读取配置文件获取连接
#jdbc.properties文件里面的内容
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/数据库?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true
#第一个参数是支持中文编码;第二个参数设置字符编码utf—8;第三个参数使用安全连接
username=root
password=111
代码如下
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class DriverTest {
@Test
public void test() throws Exception {
//1.读取配置文件。自定义的类是系统类加载器自己加载的
InputStream is = DriverTest.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(is);
String d = properties.getProperty("driver");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String username = properties.getProperty("username");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
//2.加载驱动
Class.forName(d);
//3.获取连接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
System.out.println(connection);
}
}
把上面的代码再进行优化
#配置文件
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/bank?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true
username=root
password=111
import mysql_1.utils.jdbc.Utils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JdbcTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection c=null;
Statement st=null;
ResultSet re=null;
try {
c = JdbcUtils.getConnection();//获取数据库连接
st = c.createStatement();//获取SQL的执行对象
String sql="INSERT INTO `boy`VALUES(NULL,'狂十郎','张三老婆')";
int i = st.executeUpdate(sql);
if (i>0){
System.out.println("插入成功");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(c,st,re);
}
}
}
//把所有重复冗余的代码进行封装,然后直接调用即可
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JdbcUtils {
public static String driver=null;
public static String url=null;
public static String username=null;
public static String password=null;
static {
try {
//加载配置文件
InputStream in = JdbcUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(in);
//获取配置文件的信息
driver=properties.getProperty("driver");
url=properties.getProperty("url");
username=properties.getProperty("username");
password=properties.getProperty("password");
//加载驱动
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//连接信息,连接成功,返回数据库对象(固定一个类(驱动管理));Connection代表数据库
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
}
//释放连接
public static void release(Connection c, Statement s, ResultSet r){
try {
if (c!=null){
c.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}try {
if (s!=null){
s.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}try {
if (r!=null){
r.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
SQL注入问题
SQL
注入即是指web
应用程序对用户输入数据的合法性没有判断或过滤不严,攻击者可以在web应用程序中事先定义好的查询语句的结尾上添加额外的[SQL语句,在管理员不知情的情况下实现非法操作,以此来实现欺骗数据库服务器执行非授权的任意查询,从而进一步得到相应的数据信息
简单来说就是SQL注入是比较常见的网络攻击方式之一,它不是利用操作系统的BUG来实现攻击,而是针对程序员编写时的疏忽,通过SQL语句,实现无账号登录,甚至篡改数据库。
String sql = "select * from user_table where username=
' "+userName+" ' and password=' "+password+" '";
//当输入了上面的用户名和密码,上面的SQL语句变成:
SELECT * FROM user_table WHERE username=
''or 1 = 1 -- and password=''
//或者
SELECT * FROM user_table WHERE username=
'1' or ' AND password='=1 or '1'='1'
/*
分析SQL语句:
条件后面username=”or 1=1 用户名等于 ” 或1=1 那么这个条件为true;
*/
/*
然后后面加两个-,这意味着注释,它将后面的语句注释,让他们不起作用,这样语句永远都--能正确执行,用户轻易骗过系统,获取合法身份。
这还是比较温柔的,如果是执行
*/
SELECT * FROM user_table WHERE
username='' ;DROP DATABASE (DB Name) --' and password=''
PreparedStatement接口(安全)
PreparedStatement
是Statement
接口的子接口,继承于父接口中所有的方法。prepareStatement
会先将SQL
语句发送给数据库==预编译==。PreparedStatement
会引用着==预编译==后的结果。可多次传不同的参数给
PreparedStatement
对象并执行。减少 SQL 编译次数,提高效率。防止
SQL
语句注入编写
SQL
语句,未知内容使用?
占位:"SELECT * FROM user WHERE name=? AND password=?";获得
PreparedStatement
对象设置实际参数:
setXxx
(占位符的位置, 真实的值)执行参数化 SQL 语句
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| int executeUpdate() | 执行 DML,增删改的操作,返回影响的行数。 |
| ResultSet executeQuery() | 执行 DQL,查询的操作,返回结果集 |
关闭资源
PreparedStatement使用具体步骤
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
public class PreparedTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection c=null;
PreparedStatement ps=null;
try {
c = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
//区别,使用?占位符代替参数
String sql="INSERT INTO `boy`VALUES(?,?,?)";
ps = c.prepareStatement(sql);//预编译SQL,先写sql然后不执行
//手动给参数赋值
ps.setInt(1,1);//第一个参数代表第几个占位符,然后第二个参数是赋值
ps.setString(2,"张三");
ps.setString(3,"张三老婆");
//执行
int i = ps.executeUpdate();
if (i>0){
System.out.println("插入成功");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(c,ps,null);
}
}
}
//JdbcUtils类在上面,这里就不重复写了
典型的用户登录案例
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
//大概写法
public class TestUpdate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
login("'' or 1=1","123465");
}
public static void login(String username,String password){
Connection c=null;
PreparedStatement ps=null;
ResultSet r=null;
try {
c = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
//prepareStatement防止SQL注入本质,把传递进来的参数当作字符
//假设其中存在转义字符,就直接忽略 ' 会被直接转义
String sql="select * from boy where `boyname`=?and `PASSWORD`=?";
ps= c.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1,username);
ps.setString(2,password);
r = ps.executeQuery();
while (r.next()){
System.out.println(r.getString("boyname"));
System.out.println(r.getString("password"));
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(c,ps,null);
}
}
}
//用户登录
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.ResultSetMetaData;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Scanner;
import org.junit.Test;
public class StatementTest {
// 使用Statement的弊端:需要拼写sql语句,并且存在SQL注入的问题
@Test
public void testLogin() {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("用户名:");
String userName = scan.nextLine();
System.out.print("密 码:");
String password = scan.nextLine();
// SELECT user,password FROM user_table WHERE USER = '1' or ' AND PASSWORD = '
// ='1' or '1' = '1';
String sql = "SELECT user,password FROM user_table WHERE USER = '" + userName + "' AND PASSWORD = '" + password
+ "'";
User user = get(sql, User.class);
if (user != null) {
System.out.println("登陆成功!");
} else {
System.out.println("用户名或密码错误!");
}
}
小结
PreparedStatement
具有预编译机制,性能比statement
更快PreparedStatement
可以解决SQL
注入问题PreparedStatement
可以操作Blob
的数据,而Statement
做不到PreparedStatement
可以实现更高效的批量操作(比如要插入1w条数据,PreparedStatement
只校验一次,然后缓存起来,之后添加数据只是对占位符进行填充)
针对具体某张表进行增删改查操作
ORM
对象关系映射(
Object Relational Mapping
,简称ORM
,或O/RM
,或O/R mapping
),是一种程序技术,用于实现面向对象编程语言里不同类型系统的数据之间的转换。从效果上说,它其实是创建了一个可在编程语言里使用的“虚拟对象数据库”
一张数据表对应一个Java类 表中的一条记录对应Java类的一个对象 表中的一个字段对应Java类的一个属性
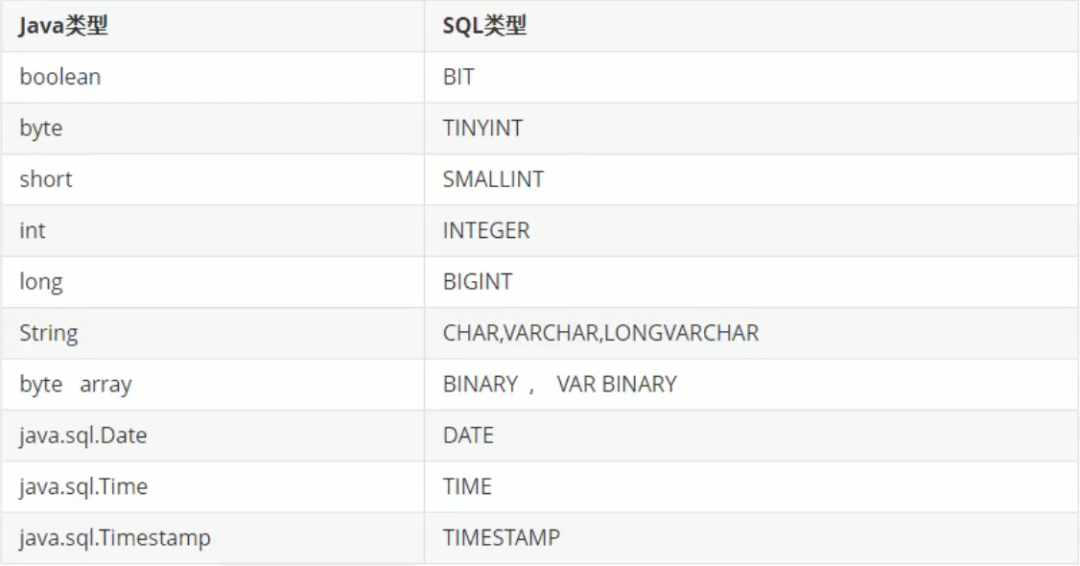
Java
数据类型与SQL
数据类型对应关系
通用的增删改操作
针对这张表

#配置文件
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/bank?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true
username=root
password=111
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JdbcUt {
public static String driver=null;
public static String url=null;
public static String username=null;
public static String password=null;
static {
try {
//类的加载器的一个主要方法是getResourceAsStream()获取类路径下的指定文件的输入流
InputStream in = JdbcUt.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(in);
driver=properties.getProperty("driver");
url=properties.getProperty("url");
username=properties.getProperty("username");
password=properties.getProperty("password");
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
}
public static void release(Connection c, Statement s){
try {
if (c!=null){
c.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}try {
if (s!=null){
s.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//针对固定表通用增删改(这里只演示了增操作)
import mysql_3.JdbcUt;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.sql.*;
public class JDBCUtils {
@Test
public void test1(){
String sql="insert into `account` (name,money) values (?,?)";
update(sql,"王五",2100);
}
public void update(String sql, Object...args) {
//获取数据库连接
Connection con =null;
PreparedStatement ps=null;
try {
con = JdbcUt.getConnection();
//预编译sql语句,返回PreparedStatement的实例
ps=con.prepareStatement(sql);
//填充占位符
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
//占位符和要传参的个数要一致
ps.setObject(i+1,args[i]);
}
//执行
ps.execute();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUt.release(con,ps);
}
}
}
通用查询操作
//这里的配置文件就不在写了;只不过这里略有不同,把查询结果集封装到类里
//连接、关闭资源的封装
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JdbcUt {
static {
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
properties.load(JdbcUt.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static String driver=null;
public static String url=null;
public static String username=null;
public static String password=null;
static {
try {
InputStream in = JdbcUt.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(in);
driver=properties.getProperty("driver");
url=properties.getProperty("url");
username=properties.getProperty("username");
password=properties.getProperty("password");
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
}
public static void release(Connection c, Statement s, ResultSet r){
try {
if (c!=null){
c.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}try {
if (s!=null){
s.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}try {
if (r!=null){
r.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class BankDemo {
private int id;
private String name;
private BigDecimal money;//因为money字段的数据类型是decimal,对应的java数据类型是BigDecimal(java.math.BigDecimal)
public BankDemo() {
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public BigDecimal getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(BigDecimal money) {
this.money = money;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "BankDemo{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", money=" + money +
'}';
}
}
将查询到的结果集封装进类
import org.junit.Test;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.sql.*;
public class Query {
@Test
public void test() {
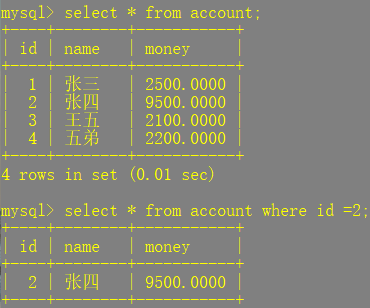
String sql = "select * from account where id=?";
BankDemo bankDemo = testQuery(sql, 2);
System.out.println(bankDemo);
}
public BankDemo testQuery(String sql, Object... args) {
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
con = JdbcUt.getConnection();
ps = con.prepareStatement(sql);
//处理结果集一行数据中的每一个列
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);
}
//获取结果集
resultSet = ps.executeQuery();
//获取结果集的元数据
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = resultSet.getMetaData();
//if只针对查询一条数据的时候,如果需要查询多条数据使用while循环
//next()判断结果集的下一条是否有数据,如果有数据返回true,并指针下移,如果返回false,指针不下移
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
if (resultSet.next()) {
BankDemo b = new BankDemo();
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
Object columnvalue = resultSet.getObject(i + 1);
//获取每个列的列名
//String columnName = rsmd.getColumnName(i + 1);
//获取列的列名:getColumnName()
//获取列的别名:getColumnLabel(),一般直接用这个
String columnLabel = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1);
//给BankDemo对象指定的columnName属性赋值为columnvalue
Field declaredField = BankDemo.class.getDeclaredField(columnLabel);
declaredField.setAccessible(true);
//指定类的对象,获取指定的属性并赋值
declaredField.set(b, columnvalue);
}
return b;
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUt.release(con, ps, resultSet);
}
return null;
}
}
//输出结果:BankDemo{id=2, name='张四', money=9500.0000}
注意
getColumnLabel()
:这个方法针对于表的字段名与类的属性名不相同的情况(如果sql
没有给字段起别名,getColumnLabel()
这个方法仍然可以获取列名,所以一般使用这个)
必须声明sql
时,使用类的属性名来命名字段的别名。
这里附上康老师的图方便理解
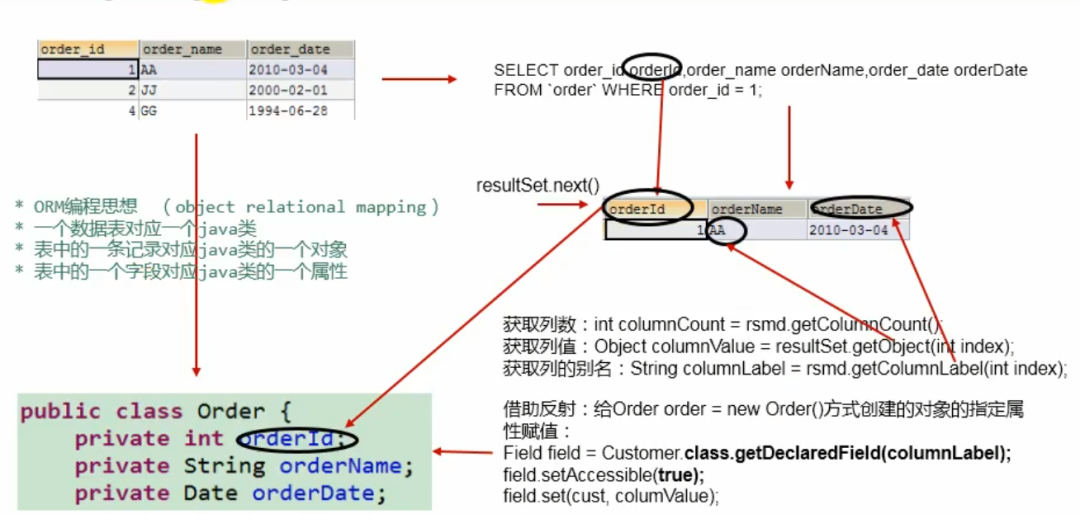
针对不同表的查询操作
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JdbcUt {
static {
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
properties.load(JdbcUt.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static String driver=null;
public static String url=null;
public static String username=null;
public static String password=null;
static {
try {
InputStream in = JdbcUt.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(in);
driver=properties.getProperty("driver");
url=properties.getProperty("url");
username=properties.getProperty("username");
password=properties.getProperty("password");
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
}
public static void release(Connection c, PreparedStatement s, ResultSet r){
try {
if (c!=null){
c.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}try {
if (s!=null){
s.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}try {
if (r!=null){
r.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class BankDemo {
private int id;
private String name;
private BigDecimal money;
public BankDemo() {
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public BigDecimal getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(BigDecimal money) {
this.money = money;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "BankDemo{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", money=" + money +
'}';
}
}
import org.junit.Test;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.ResultSetMetaData;
public class UniversalQuery {
@Test
public void test(){
String sql="select * from account where id=?";
BankDemo bankDemo = get(BankDemo.class, sql, 2);
System.out.println(bankDemo);
}
public <T> T get(Class<T> clazz,String sql, Object...args) {
Connection c=null;
PreparedStatement ps=null;
ResultSet r=null;
try {
c= JdbcUt.getConnection();
ps= c.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
ps.setObject(i+1,args[i]);
}
r= ps.executeQuery();
// 获取结果集的元数据(元数据里面有个方法专门存储列名)(rs.getMetaData() 获得表结构)
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = r.getMetaData();
// 获取结果集的列数(获取列数)
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
//if是查询一条记录,如果想查询多条记录的话,使用while循环
if (r.next()) {
//通过反射获取属性,然后赋值给列名
T t = clazz.newInstance();
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
// 1. 根据列名获取对应数据表中的数据
Object columnVal = r.getObject(i+1);
// 2. 获取列的别名(从元数据获取列名)
String columnLabel = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1);
// 3. 将数据表中得到的数据,封装进对象
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(columnLabel);
field.setAccessible(true);
//设置当前属性的值(参数1时是设置哪个对象的属性;参数2是将此属性值设置为多少)
field.set(t, columnVal);
}
return t;
}
} catch (Exception throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUt.release(c,ps,r);
}
return null;
}
}
//输出结果:BankDemo{id=2, name='张四', money=9500.0000}
查询多条记录
import org.junit.Test;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.ResultSetMetaData;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class UniversalQuery {
@Test
public void test(){
String sql="select * from account where id<?";
ArrayList<BankDemo> bankDemo = get(BankDemo.class, sql, 4);
for (Object o : bankDemo) {
System.out.println(o);
}
}
public <T> ArrayList get(Class<T> clazz, String sql, Object...args) {
Connection c=null;
PreparedStatement ps=null;
ResultSet r=null;
try {
c= JdbcUt.getConnection();
ps= c.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
ps.setObject(i+1,args[i]);
}
r= ps.executeQuery();
// 获取结果集的元数据(元数据里面有个方法专门存储列名)(rs.getMetaData() 获得表结构)
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = r.getMetaData();
// 获取结果集的列数(获取列数)
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
while (r.next()) {
//通过反射获取属性,然后赋值给列名
T t = clazz.newInstance();
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
// 1. 根据列名获取对应数据表中的数据
Object columnVal = r.getObject(i+1);
// 2. 获取列的别名(从元数据获取列名)
String columnLabel = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1);
// 3. 将数据表中得到的数据,封装进对象
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(columnLabel);
field.setAccessible(true);
//设置当前属性的值(参数1时是设置哪个对象的属性;参数2是将此属性值设置为多少)
field.set(t, columnVal);
}
list.add(t);
}
return list;
} catch (Exception throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUt.release(c,ps,r);
}
return null;
}
}
批量插入数据
当需要成批插入或者更新记录数据时,可以采用 Java
的批量更新机制,这一机制允许多条语句一次性提交给数据库批量处理。通常情况下比单独提交处理更有效率
#配置文件
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/bank?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true&rewriteBatchedStatements=true
username=root
password=111
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JdbcUt {
static {
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
properties.load(JdbcUt.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static String driver=null;
public static String url=null;
public static String username=null;
public static String password=null;
static {
try {
InputStream in = JdbcUt.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(in);
driver=properties.getProperty("driver");
url=properties.getProperty("url");
username=properties.getProperty("username");
password=properties.getProperty("password");
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
}
public static void release(Connection c, PreparedStatement s){
try {
if (c!=null){
c.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}try {
if (s!=null){
s.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
import org.junit.Test;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class BatchInsertTest {
@Test
public void test() {
Connection c = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
c = JdbcUt.getConnection();
c.setAutoCommit(false);
String sql = "insert into account (name,money) values(?,?)";
ps = c.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {
ps.setObject(1, "张" + i);
ps.setObject(2, 9600);
//“攒”sql
ps.addBatch();
if (i % 500 == 0) {
//执行batch
ps.executeBatch();
//清空batch
ps.clearBatch();
}
}
c.commit();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("用时:" + (end - start));
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//用时:548
数据库事务
事务概念
由一条或多条SQL语句组成,要么都成功,要么都失败
事务原则(ACID)
原子性(Atomicity):事务是最小的执行单位,不允许分割。事务的原子性确保动作要么全部完成,要么完全不起作用
一致性(Consistency)): 执行事务前后,数据保持一致(例如,完整性约束了a+b=10,一个事务改变了a,那么b也应该随之改变)多个事务对同一个数据读取的结果是相同的
隔离性(独立性)(Isolation): 并发访问数据库时,一个用户的事务不被其他事务所干扰,各并发事务之间数据库是独立的
事务的隔离级别又分为
脏读:指一个事务读取了另外一个事务未提交 的数据
不可重复读:在一个事务内读取表中的某一行数据,多次读取的结果不同(不一定错误,只是某些场合不对)
幻读:指在一个事务内读取到了别的事务插入的数据 ,导致前后读取不一样
四种隔离级别
| 隔离级别 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| READ UNCOMMITTED(Read Uncommitted)读未提交数据 | 允许事务读取未被其他事务提交的数据,也被称之为脏读(Dirty Read)脏读、不可重复读和幻读都会出现 |
| READ COMMITED(Read Committed)读已提交数据 | 这是Oracle的默认事务隔离级别。它满足了隔离的简单定义:一个事务只能看见已经提交事务所做的改变。可以避免脏读,但不可重复读和幻读问题仍然存在 |
| REPEATABLE READ(Repeatable Read)可重复读 | 这是Mysql的默认事务隔离级别,它确保同一事务的多个实例在并发读取数据时,在这个事务持续期间,禁止其他事务对这个实例进行更新。但幻读仍然存在。 InnoDB和 Falcon存储引擎通过多版本并发控制(MVCC,Multiversion Concurrency Control)机制解决了该问题 |
| SERIALIZABLE(Serializable)串行化 | 这是最高的隔离级别,但是性能也是最差的,确保事务可以从一个表中读取相同的行,在这个事务的持续期间,禁止其他事务对该表执行插入、更新和删除操作,从而解决幻读问题。总的来说,它是在每个读的数据行上加上共享锁。在这个级别,可能导致大量的超时现象和锁竞争。 |
Oracle
支持的2种事务隔离级别:READ COMMITED
和SERIALIZABLE
。Oracle
默认的事务隔离级别是READ COMMITED
持久性(Durability):一个事务被提交之后。它对数据库中数据的改变是持久的,即使数据库发生故障也不应该对其有任何影响
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| connection.setAutoCommit(); | 数据库设置自动提交 |
| connection.commit(); | 事务提交 |
| connection.rollback(); | 事务回滚(回滚到原来的状态) |
用Java代码模拟转账
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class ACIDtext {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection c=null;
PreparedStatement ps=null;
ResultSet r=null;
try {
c=JdbcUtils.getConnection();
//关闭自动提交(这一步不仅关闭事务提交,同时自动开启一个事务(也就是说不用另外开启一个事务))
c.setAutoCommit(false);
//编写事务需要的SQL语句
String sql="update account set money=money-500 where id=2";
ps= c.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.executeUpdate();
String sql1="update account set money=money+500 where id=1";
ps= c.prepareStatement(sql1);
ps.executeUpdate();
//提交事务
c.commit();
System.out.println("成功");
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
try {
c.rollback();//如果失败则回滚(回滚到原来的位置)
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(c,ps);
}
}
}
使用Java
代码设置数据库的隔离级别
@Test
public void test(){
try {
Connection connection = DBCPTest.getConnection();
//设置数据库的隔离级别
System.out.println(connection.getTransactionIsolation());
//设置数据库的隔离级别
connection.setTransactionIsolation(Connection.TRANSACTION_READ_COMMITTED);
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
数据连接池(池化技术)
为什么要有数据库连接池?
在开发过程中,存在很多问题:首先,普通的JDBC数据库连接使用DriverManager来获取,每一次web请求都要建立一次数据库连接。这个过程将会消耗大量的资源和时间,而且系统还要分配内存资源。这个时间对于一次或几次数据库操作,或许感觉不出系统有多大的开销。可是对于现在的web应用,尤其是大型电子商务网站,同时有几百人甚至几千人在线是很正常的事。在这种情况下,频繁的进行数据库连接操作势必占用很多的系统资源。所有就有了数据库连接池。 还有对于每一次使用数据库连接,使用完都得断开,否则会存在内存泄漏,使得重启数据库 这种开发不能控制被创建的连接对象数,系统资源会毫无顾及的分配出去,如连接过多,也可能导致内存泄漏,服务器崩溃
数据库连接池作用?
数据库连接池负责分配、管理和释放数据库连接,它允许应用程序重复使用一个现有的数据库连接,而不是再重新建立一个;释放空闲时间超过最大空闲时间的数据库连接来避免因为没有释放数据库连接而引起的数据库连接遗漏。这项技术能明显提高对数据库操作的性能。
数据连接概念
JDBC
的数据库连接使用,有专门的包javax.sql.Data.Source来表示,DataSource是一个接口,该接口通常由服务器(Weblogic
,Websphere
,Tomcat
)提供实现,因为数据库连接然后执行完毕后释放是非常浪费系统资源,所以也就有池化技术。DataSource
通常被称为数据源,它包含连接池和连接池管理两个部分,习惯上也经常把DataSource
称为连接池;DataSource
用来取代了DataManager
来获取Connection
,获取速度快,同时可以大幅度提高数据库访问速度
什么是池化技术?
在请求量大时能明显优化应用 性能,降低系统频繁建连的资源开销,规定其最小连接数(常用连接数设置多少,最小连接数也一样)、最大连接数、阻塞队列(等待超时)等配置,方便进行统一管理和复用(有这些数据库连接池之后,我们在以后开发中就不用编写连接数据库的代码)
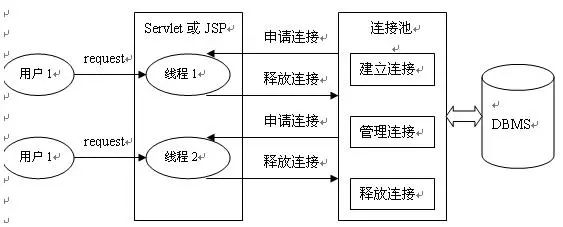
常规数据库连接由以下六个步骤组成
加载数据库驱动; 建立数据库连接 创建数据库操作对象 操作数据库,执行 sql
语句处理返回结果集 释放数据库连接(注意如果是事务操作,要记得修改其为自动提交数据)
DBCP
DBCP
:一般就是指 Apache commons DBCP
(Data Base Connection Pool
)数据库连接池。是一个储存Java
数据库连接对象的池子。(是Apache
提供的数据库连接池)应用程序需要建立数据库连接时直接到连接池中申请一个就行,用完再放回。单线程,并发量低,性能不好,适用于小型系统。
| 配置信息 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| dbcp | 连接池常用基本配置属性 |
| initialSize | 连接池启动时创建的初始化连接数量(默认值为0) |
| maxActive | 连接池中可同时连接的最大的连接数(默认值为8,调整为20,高峰单机器在20并发左右,自己根据应用场景定) |
| maxIdle | 连接池中最大的空闲的连接数,超过的空闲连接将被释放,如果设置为负数表示不限制(默认为8个,maxIdle不能设置太小,因为假如在高负载的情况下,连接的打开时间比关闭的时间快,会引起连接池中idle的个数 上升超过maxIdle,而造成频繁的连接销毁和创建,类似于jvm参数中的Xmx设置) |
| minIdle | 连接池中最小的空闲的连接数,低于这个数量会被创建新的连接(默认为0,调整为5,该参数越接近maxIdle,性能越好,因为连接的创建和销毁,都是需要消耗资源的;但是不能太大,因为在机器很空闲的时候,也会创建低于minidle个数的连接,类似于jvm参数中的Xmn设置) |
| maxWait | 最大等待时间,当没有可用连接时,连接池等待连接释放的最大时间,超过该时间限制会抛出异常,如果设置-1表示无限等待(默认为无限,调整为60000ms,避免因线程池不够用,而导致请求被无限制挂起) |
| poolPreparedStatements | 开启池的prepared(默认是false,未调整,经过测试,开启后的性能没有关闭的好) |
| maxOpenPreparedStatements | 开启池的prepared 后的同时最大连接数(默认无限制,同上,未配置) |
| minEvictableIdleTimeMillis | 连接池中连接,在时间段内一直空闲, 被逐出连接池的时间 |
| removeAbandonedTimeout | 超过时间限制,回收没有用(废弃)的连接(默认为 300秒,调整为180) |
| removeAbandoned | 超过removeAbandonedTimeout时间后,是否进 行没用连接(废弃)的回收(默认为false,调整为true) |
连接DBCP数据池大致步骤
导入jar包 从配置文件中获取输入流,进行加载 有了 BasicDataSoureFactory
,那我们也不需要将配置文件中的属性值一个一个读取出来了,它有个方法createDataSource()
能自动获取到数据源 ,然后创建数据库连接池
import org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSourceFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class DBCPTest {
private static DataSource dataSource=null;
//因为每次连接都需要创建数据库连接池,所以使用静态代码块
static {
try {
//方式一
Properties ps = new Properties();
InputStream is = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("dbcp.properties");
/*方式二:只识别的话是当前工程
FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream(new File("dbcp.properties"));*/
ps.load(is);
//创建DBCP数据库连接池
dataSource= BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(ps);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//获取dbcp连接
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
Connection con = dataSource.getConnection();
return con;
}
}
C3P0
C3P0
是一个开源的JDBC
连接池,它实现了数据源和JNDI
绑定,支持JDBC3
规范和JDBC2
的标准扩展。目前使用它的开源项目有Hibernate
、Spring
等。
这里直接展示配置文件然后进行连接
<!-- c3p0-config.xml -->
<c3p0-config>
<!-- This app is massive! -->
<named-config name="C3p0Test">
<!-- 提供获取连接的4个信息-->
<property name="driverClass">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="jdbcUrl">jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/bank</property>
<property name="user">root</property>
<property name="password">111</property>
<!-- 进行数据库连接池管理的基本信息-->
<!-- 当数据库连接池中的连接数不够时,c3p0一次性向数据库服务器申请的连接数-->
<property name="acquireIncrement">5</property>
<!-- c3p0数据库连接池中初始化的连接数-->
<property name="initialPoolSize">10</property>
<!-- c3p0数据库连接池维护的最少连接数-->
<property name="minPoolSize">10</property>
<!-- c3p0数据库连接池维护的最多连接数-->
<property name="maxPoolSize">100</property>
<!-- c3p0数据库连接池最多维护的Statement的个数-->
<property name="maxStatements">50</property>
<!-- 每个连接中可以最多使用的Statement的个数-->
<property name="maxStatementsPerConnection">2</property>
</named-config>
</c3p0-config>
import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class C3p0Jtils {
//提供数据库连接池
private static ComboPooledDataSource cp = new ComboPooledDataSource("C3p0Test");//这里写配置文件里面的配置名字
public static Connection test() {
Connection con = null;
try {
con = cp.getConnection();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
return con;
}
public static void release(Connection c, Statement s, ResultSet r){
try {
if (c!=null){
c.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}try {
if (s!=null){
s.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}try {
if (r!=null){
r.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
CP30
与DBCP
区别?
DBCP
默认不自动回收空闲连接,需要手动开启CP30
默认自动回收空闲连接功能
Druid
Druid
首先是一个数据库连接池。Druid
是目前最好的数据库连接池,在功能、性能、扩展性方面,都超过其他数据库连接池,包括DBCP
、C3P0
、BoneCP
、Proxool
、JBoss
DataSource
。Druid
已经在阿里巴巴部署了超过600个应用。可以监控数据库的访问性能 数据库密码加密 监控 SQL
执行日志扩展JDBC
<!-- 配置文件(常见参数)-->
#连接设置 是DBCP数据源已经定义好的,不能瞎改名字
driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/bookstore?rewriteBatchedStatements=true
#url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mysqldb
username=root
password=111
#初始化默认连接大小
initialSize=10
#最大空闲连接对象(池子最少有5个空闲)
minIdle=5
#最大的连接数是20
maxActive=20
#超过等待时间以毫秒为单位(等待时间最长不能超过5000豪秒)
maxWait=5000
配置文件
url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/bank
username=root
password=111
driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
#初始化连接数
initialSize=5
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class DruidTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//读取配置文件
Properties ps = new Properties();
InputStream is = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties");
//加载配置文件
ps.load(is);
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(ps);
Connection con = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(con);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class DruidTest {
private static DataSource dataSource = null;
static {
Properties ps = new Properties();
InputStream is = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties");
try {
dataSource= DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(ps);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static Connection getDruidConnection(){
Connection con = null;
try {
con = dataSource.getConnection();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
return con;
}
}
DbUtils
Dbutils
:主要是封装了JDBC
的代码, DbUtils
是一个为简化JDBC
操作的小类库(连接数据库对象,jdbc辅助方法的集合类,线程安全),相当于简化Dao
层的操作。
为什么需要Dbutils ?
在使用Dbutils
之前,我们Dao
层使用的技术是JDBC
,那么分析一下JDBC
的弊端:
数据库链接对象、
sql
语句操作对象,封装结果集对象,这三大对象会重复定义封装数据的代码重复,而且操作复杂,代码量大
释放资源的代码重复
import mysql_11.DBCPTest;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanListHandler;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.MapHandler;
import org.junit.Test;
import javax.swing.plaf.basic.BasicListUI;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/*
* Dbutils封装了对数据库的增删改查操作
* */
public class Dbutils {
@Test
public void test1() {
Connection connection = null;
try {
//QueryRunner():SQL语句的操作对象,可以设置查询结果集的封装策略,线程安全。QueryRunner():创建一个与数据库无关的QueryRunner对象,后期再操作数据库的会后,需要手动给一个Connection对象,它可以手动控制事务。
QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner();
connection = DBCPTest.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from account where id<?";
//BeanListHandler是ResultSetHandler接口的实现类,用来封装表中的多条记录构成集合
BeanListHandler<BankDemo> beanListHandler = new BeanListHandler<>(BankDemo.class);
List<BankDemo> query = runner.query(connection, sql, beanListHandler, 10);
query.forEach(System.out::println);
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBCPTest.release(connection, null, null);
}
}
//使用DBCP数据连接池获得连接然后使用DbUtils封装好的功能插入一条记录
@Test
public void test3() {
Connection druidConnection= null;
try {
QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner();
druidConnection = DruidTest.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into account(name,money)values(?,?)";
runner.update(druidConnection, sql, "张三", 2000);
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DbUtils.closeQuietly(druidConnection);//DbUtils提供释放资源的操作
}
}
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.MapHandler;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Map;
/*
* 封装了对数据库的增删改查操作
*/
public class Dbutils {
@Test
public void test1() {
Connection dc = null;
try {
QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner();
dc = DruidTest.getDruidConnection();
String sql = "select * from account where id<?";
MapHandler mapHandler = new MapHandler();
//MapHandler是ResultSetHandler接口的实现类,对应表中的一条记录;而MapListHandlerd对应的是数据库的多条记录(这里就不举例了,都一样的)将字段及相应的值作为map的key和value
Map<String, Object> query = runner.query(dc, sql, mapHandler, 10);
System.out.println(query);
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DruidTest.release(dc, null, null);
}
}
}






