目录
1 概述
2 实现文件
3 数据结构
4 初始化
5 加锁
6 死锁检测
6.1 数据结构
6.2 初始化
6.3 工作原理
7 锁的释放
概述
RegularLock锁由LWLock实现,有两种锁方法DEFAULT_LOCKMETHOD,USER_LOCKMETHOD,不同锁方法生产不同锁表,八种锁模式。其特点是有等待队列,有死锁检测,能自动释放。
实现文件
Lock.c Lock.h
数据结构
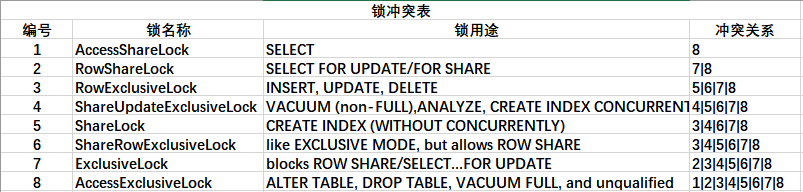
锁模式
/* NoLock is not a lock mode, but a flag value meaning "don't get a lock" */#define NoLock0#define AccessShareLock1/* SELECT */#define RowShareLock2/* SELECT FOR UPDATE/FOR SHARE */#define RowExclusiveLock3/* INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE */#define ShareUpdateExclusiveLock 4/* VACUUM (non-FULL),ANALYZE, CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY */#define ShareLock5/* CREATE INDEX (WITHOUT CONCURRENTLY) */#define ShareRowExclusiveLock6/* like EXCLUSIVE MODE, but allows ROW SHARE */#define ExclusiveLock7/* blocks ROW SHARE/SELECT...FOR UPDATE */#define AccessExclusiveLock8/* ALTER TABLE, DROP TABLE, VACUUM FULL, and unqualified LOCK TABLE */
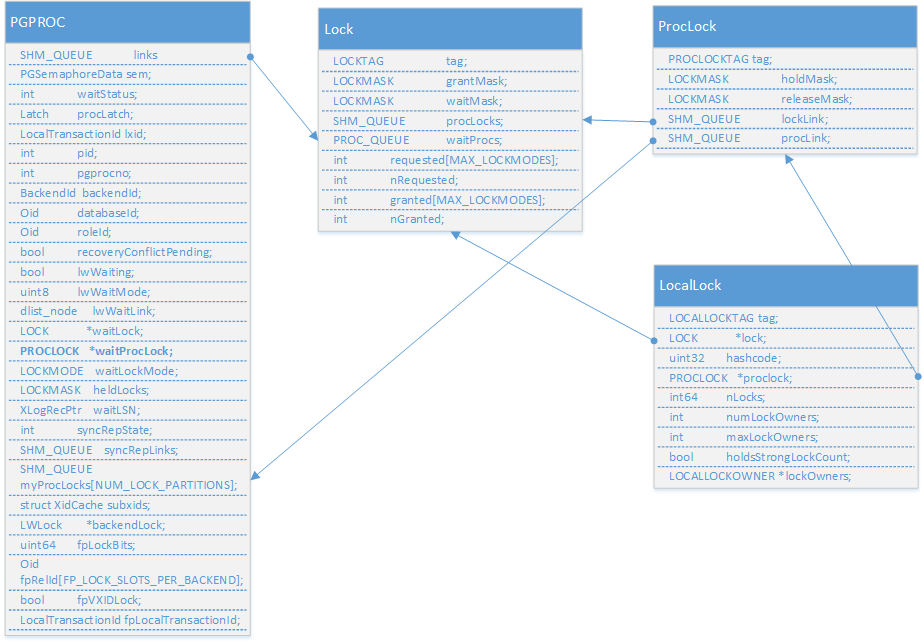
LockConfilicMap.pngtypedef struct LockMethodData{intnumLockModes;const LOCKMASK *conflictTab;const char *const * lockModeNames;const bool *trace_flag;} LockMethodData;typedef struct LOCKTAG{uint32locktag_field1; /* a 32-bit ID field */uint32locktag_field2; /* a 32-bit ID field */uint32locktag_field3; /* a 32-bit ID field */uint16locktag_field4; /* a 16-bit ID field */uint8locktag_type;/* see enum LockTagType */uint8locktag_lockmethodid;/* lockmethod indicator */} LOCKTAG;typedef struct LOCK{/* hash key */LOCKTAGtag;/* unique identifier of lockable object *//* data */LOCKMASKgrantMask;/* bitmask for lock types already granted */LOCKMASKwaitMask;/* bitmask for lock types awaited */SHM_QUEUEprocLocks;/* list of PROCLOCK objects assoc. with lock */PROC_QUEUEwaitProcs;/* list of PGPROC objects waiting on lock */intrequested[MAX_LOCKMODES];/* counts of requested locks */intnRequested;/* total of requested[] array */intgranted[MAX_LOCKMODES]; /* counts of granted locks */intnGranted;/* total of granted[] array */} LOCK;typedef struct PROCLOCKTAG{/* NB: we assume this struct contains no padding! */LOCK *myLock;/* link to per-lockable-object information */PGPROC *myProc;/* link to PGPROC of owning backend */} PROCLOCKTAG;typedef struct PROCLOCK{/* tag */PROCLOCKTAG tag;/* unique identifier of proclock object *//* data */LOCKMASKholdMask;/* bitmask for lock types currently held */LOCKMASKreleaseMask;/* bitmask for lock types to be released */SHM_QUEUElockLink;/* list link in LOCK's list of proclocks */SHM_QUEUEprocLink;/* list link in PGPROC's list of proclocks */} PROCLOCK;typedef struct LOCALLOCKTAG{LOCKTAGlock;/* identifies the lockable object */LOCKMODEmode;/* lock mode for this table entry */} LOCALLOCKTAG;typedef struct LOCALLOCKOWNER{/** Note: if owner is NULL then the lock is held on behalf of the session;* otherwise it is held on behalf of my current transaction.** Must use a forward struct reference to avoid circularity.*/struct ResourceOwnerData *owner;int64nLocks;/* # of times held by this owner */} LOCALLOCKOWNER;typedef struct LOCALLOCK{/* tag */LOCALLOCKTAG tag;/* unique identifier of locallock entry *//* data */LOCK *lock;/* associated LOCK object, if any */PROCLOCK *proclock;/* associated PROCLOCK object, if any */uint32hashcode;/* copy of LOCKTAG's hash value */int64nLocks;/* total number of times lock is held */intnumLockOwners;/* # of relevant ResourceOwners */intmaxLockOwners;/* allocated size of array */boolholdsStrongLockCount;/* bumped FastPathStrongRelationLocks */LOCALLOCKOWNER *lockOwners; /* dynamically resizable array */} LOCALLOCK;static HTAB *LockMethodLockHash;static HTAB *LockMethodProcLockHash;static HTAB *LockMethodLocalHash;typedef struct{slock_tmutex;uint32count[FAST_PATH_STRONG_LOCK_HASH_PARTITIONS];} FastPathStrongRelationLockData;
初始化
在创建共享内存函数:
“CreateSharedMemoryAndSemaphores”中,调用LockShmemSize分配空间Lock Hash 和ProcLock Hash 加上10%的安全考虑,然后调用InitLocks对LockMethodLockHash, LockMethodProcLockHash, LockMethodLocalHash进行初始化。
加锁
LockAcquire(constLOCKTAG*locktag,LOCKMODElockmode,boolsessionLock,booldontWait)中调用LockAcquireExtended(locktag,lockmode,sessionLock, dontWait,true);
LockAcquireExtended(const LOCKTAG *locktag,LOCKMODE lockmode,bool sessionLock,bool dontWait,bool reportMemoryError){/* Identify owner for lock */if (sessionLock)owner = NULL;elseowner = CurrentResourceOwner;/* Find or create a LOCALLOCK entry for this lock and lockmode */在local中查找如果没找到,初始化locallock,找到判断是否锁的owners超过最大值,超过就将最大值*2,并repalloc locallock->lockOwnersMemSet(&localtag, 0, sizeof(localtag));/* must clear padding */localtag.lock = *locktag;localtag.mode = lockmode;locallock = (LOCALLOCK *) hash_search(LockMethodLocalHash, (void *) &localtag, HASH_ENTER, &found);if(!found){locallock->lock = NULL;locallock->proclock = NULL;locallock->hashcode = LockTagHashCode(&(localtag.lock));locallock->nLocks = 0;locallock->numLockOwners = 0;locallock->maxLockOwners = 8;locallock->holdsStrongLockCount = FALSE;locallock->lockOwners = NULL;/* in case next line fails */locallock->lockOwners = (LOCALLOCKOWNER *)MemoryContextAlloc(TopMemoryContext, locallock->maxLockOwners * sizeof(LOCALLOCKOWNER));}else{if (locallock->numLockOwners >= locallock->maxLockOwners){intnewsize = locallock->maxLockOwners * 2;locallock->lockOwners = (LOCALLOCKOWNER *)repalloc(locallock->lockOwners, newsize * sizeof(LOCALLOCKOWNER));locallock->maxLockOwners = newsize;}}/* If we already hold the lock, we can just increase the count locally.*/如果这个进程已经持有这个锁,就将引用计数加1if (locallock->nLocks > 0){GrantLockLocal(locallock, owner);//locallock->lockOwners[i].owner = owner;locallock->lockOwners[i].nLocks = 1;或者如果已经存在就将引用计数locallock->lockOwners[i].nLocks++,并将LocalLock记录到resourceOwner中return LOCKACQUIRE_ALREADY_HELD;}//如果加锁是给表加锁&&采用默认锁方法&&DatabaseId为MyDatabaseId&&MyDatabaseId不等于无效ID&&加锁模式为1,2,3,则采用快速路径加锁,因为模式1,2,3各进程间不存在冲突,即进程A和B之间可以同时对这三个模式加锁,所以就通过快速路径即在PGPROC对象Myproc中存储这三个锁模式的锁,防止加入到Lock Hash中,提高加锁和解锁的速度,在快速路径中的锁不进行死锁检测。{FastPathStrongRelationLocks//定义在共享内存中,大小为1024的hash槽,通过LOCKTAG生成的存储在Lock hash中的hashcode%1024来索引。当存在strong 锁时,即所要加的锁模式为>4时,进程间可能产生锁冲突,这时需要在FastPathStrongRelationLocks中对应位置加1,用以指示此锁不能使用快速路径Myproc中有两个变量{uint64 fpLockBits;/* lock modes held for each fast-path slot */64位分成16份每份用后三位标注模式为1,2,3的锁Oid fpRelId[16];/* slots for rel oids */用于存放对应上面的表ID。}}//检测此锁是否为strong锁,进程间可能产生锁冲突,这时需要将FastPathStrongRelationLocks中对应位置加1,指示这个锁不能使用快速路径了,并在locallock标注持有着这种strong锁,把快速路径的锁加入到Lock hash中。{FastPathStrongRelationLocks->count[fasthashcode]++;locallock->holdsStrongLockCount = TRUE;StrongLockInProgress = locallock;FastPathTransferRelationLocks(lockMethodTable, locktag, hashcode)}//如果不在local中,也不能通过快速加锁,就智能通过lock hash 和proclock hash来实现加锁了LWLockAcquire(partitionLock, LW_EXCLUSIVE);proclock = SetupLockInTable(lockMethodTable, MyProc, locktag,hashcode, lockmode);//查找或创建lock 和proclock对象在各自的hash中,并返回proclock对象。case1://查询所要加锁的模式不和已加锁的模式冲突,也不和等待的锁模式冲突,加锁成功并返回。GrantLock(lock, proclock, lockmode);//设置lock的nGranted++,granted[lockmode]++,lock->grantMask |= LOCKBIT_ON(lockmode);proclock->holdMask |= LOCKBIT_ON(lockmode);分配锁GrantLockLocal(locallock, owner);//记录resourceowner到locallock中,增加owner持有这个lock的次数。case2 //发生冲突,如果不等待dontWait=1的情况,如果proclock所持有的锁为空,清空proclock对象,根据locallock引用情况为0,清空之前设置的locallock对象,否则修改lock对象的状态将申请总计数减1,所申请模式的锁计数减1.return LOCKACQUIRE_NOT_AVAILif (proclock->holdMask == 0){SHMQueueDelete(&proclock->lockLink);SHMQueueDelete(&proclock->procLink);if (!hash_search_with_hash_value(LockMethodProcLockHash,(void *) &(proclock->tag), proclock_hashcode,HASH_REMOVE,NULL))}if (locallock->nLocks == 0)RemoveLocalLock(locallock);lock->nRequested--;lock->requested[lockmode]--;return LOCKACQUIRE_NOT_AVAIL;case3://发生冲突,并等待进入sleep直到被唤醒WaitOnLock(locallock, owner);//调用ProcSleep-->ProcSleep{1, 将本进程插入到等待队列lock->waitProcs,如果本进程持有锁,将本进程插入到所有等待本进程所持有锁的进程之前。如果本进程没有持有锁,则将本进程插入到等待队列的最后面。如果存在互相等待情况即死锁现象则 return STATUS_ERROR并唤醒等待队列中可以唤醒的锁。2, 调用waitLatch进入sleep3, 当进程wakeup,根据设置的DeadlockTimeout,(默认值1000ms)触发死锁检测 checkDeadLock();4, GrantLockLocal添加信息到locallock(指定锁的owner,这个owner所持有锁的数量加1,锁的owner总数加1)}LWLockRelease(partitionLock);}
死锁检测
在DeadLock.c 中定义了死锁检测相关的操作,调用接口为CheckDeadLock-->DeadLockCheck.调用DeadLockCheck之前要锁住整个锁表。
for (i = 0; i < NUM_LOCK_PARTITIONS; i++)LWLockAcquire(LockHashPartitionLockByIndex(i), LW_EXCLUSIVE);
1. 数据结构
/* One edge in the waits-for graph */typedef struct{PGPROC *waiter;/* the waiting process */PGPROC *blocker;/* the process it is waiting for */intpred;/* workspace for TopoSort */intlink;/* workspace for TopoSort */} EDGE;/* One potential reordering of a lock's wait queue */typedef struct{LOCK *lock;/* the lock whose wait queue is described */PGPROC **procs;/* array of PGPROC *'s in new wait order */intnProcs;} WAIT_ORDER;/** Information saved about each edge in a detected deadlock cycle. This* is used to print a diagnostic message upon failure.** Note: because we want to examine this info after releasing the lock* manager's partition locks, we can't just store LOCK and PGPROC pointers;* we must extract out all the info we want to be able to print.*/typedef struct{LOCKTAGlocktag;/* ID of awaited lock object */LOCKMODElockmode;/* type of lock we're waiting for */intpid;/* PID of blocked backend */} DEADLOCK_INFO;
在每个子进程启动时候InitProcess中调用InitDeadLockChecking实现。
voidInitDeadLockChecking(void){MemoryContext oldcxt;/* Make sure allocations are permanent */oldcxt = MemoryContextSwitchTo(TopMemoryContext);/** FindLockCycle needs at most MaxBackends entries in visitedProcs[] and* deadlockDetails[].*/visitedProcs = (PGPROC **) palloc(MaxBackends * sizeof(PGPROC *));deadlockDetails = (DEADLOCK_INFO *) palloc(MaxBackends * sizeof(DEADLOCK_INFO));/** TopoSort needs to consider at most MaxBackends wait-queue entries, and* it needn't run concurrently with FindLockCycle.*/topoProcs = visitedProcs;/* re-use this space */beforeConstraints = (int *) palloc(MaxBackends * sizeof(int));afterConstraints = (int *) palloc(MaxBackends * sizeof(int));/** We need to consider rearranging at most MaxBackends/2 wait queues* (since it takes at least two waiters in a queue to create a soft edge),* and the expanded form of the wait queues can't involve more than* MaxBackends total waiters.*/waitOrders = (WAIT_ORDER *)palloc((MaxBackends 2) * sizeof(WAIT_ORDER));waitOrderProcs = (PGPROC **) palloc(MaxBackends * sizeof(PGPROC *));/** Allow at most MaxBackends distinct constraints in a configuration. (Is* this enough? In practice it seems it should be, but I don't quite see* how to prove it. If we run out, we might fail to find a workable wait* queue rearrangement even though one exists.) NOTE that this number* limits the maximum recursion depth of DeadLockCheckRecurse. Making it* really big might potentially allow a stack-overflow problem.*/maxCurConstraints = MaxBackends;curConstraints = (EDGE *) palloc(maxCurConstraints * sizeof(EDGE));/** Allow up to 3*MaxBackends constraints to be saved without having to* re-run TestConfiguration. (This is probably more than enough, but we* can survive if we run low on space by doing excess runs of* TestConfiguration to re-compute constraint lists each time needed.) The* last MaxBackends entries in possibleConstraints[] are reserved as* output workspace for FindLockCycle.*/maxPossibleConstraints = MaxBackends * 4;possibleConstraints =(EDGE *) palloc(maxPossibleConstraints * sizeof(EDGE));MemoryContextSwitchTo(oldcxt);}
possibleConstraints//按照递归顺序记录每次递归调用TestConfiguration 返回的soft edge,按顺序存放,序号代表递归次数。
NPossibleConstraints.png CurConstraints//按照递归顺序记录每次递归调用所采用调整的边,这个边是nPossibleConstraints中对应soft edges中的一个,从这个递归中的返回的soft edges中第一个开始试,如果解决了死锁就记录这一个,否则试下一个,直到找到。如果找不到就代表死锁。
waitOrders//按照调整的边记录调整好顺序的这个边中的lock的waitprocs即这条边的锁的等待队列并按照这条边的约束进行排序。最后对用waitOrders中的调整完顺序的waitProcs替换lock原来的waitProcs,然后在调用ProcLockWakeup对waitProcs中等待的进程按顺序唤醒。
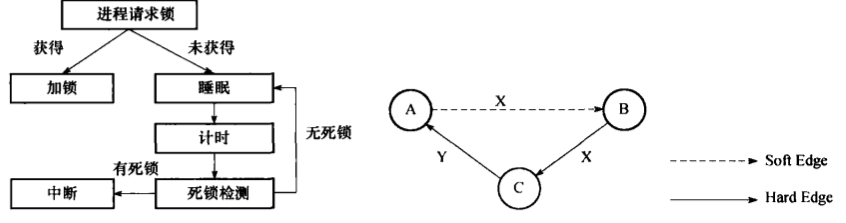
在DeadLockCheck{DeadLockCheckRecurse(proc)-->TestConfiguration(proc)//测试是否deadlock,如果存在,是hard deadlock还是soft deadlock ,返回值-1代表hard deadlock,0代表无死锁,>1代表死锁环中soft edge的数量-->ExpandConstraints(curConstraints, nCurConstraints)-->调用TopoSort对curConstraints边中的lock的waitProcs进行排列,将curConstraints中的waiter拍到blocker的前面,其他顺序不变。-->对curConstraints中的所有边,分别以这条边的waiter和blocker作为起点调用FindLockCycle查找是否存在死锁环。最后对测试起始点的Proc调用FindLockCycle查找是否存在死锁环。返回-->if (nEdges < 0)return true;/*硬死锁*/if (nEdges == 0)return false;/* good configuration found */if (nCurConstraints >= maxCurConstraints)return true;/* out of room for active constraints? *///从软死锁环中按顺序取soft edge,作为constraint然后递归调用DeadLockCheckRecursefor (i = 0; i < nEdges; i++){if (!savedList && i > 0){/* Regenerate the list of possible added constraints */if (nEdges != TestConfiguration(proc))elog(FATAL, "inconsistent results during deadlock check");}curConstraints[nCurConstraints] =possibleConstraints[oldPossibleConstraints + i];nCurConstraints++;if (!DeadLockCheckRecurse(proc))return false;/* found a valid solution! *//* give up on that added constraint, try again */nCurConstraints--;}}
锁的释放
LockRelease(const LOCKTAG *locktag, LOCKMODE lockmode, bool sessionLock){locallock = (LOCALLOCK *) hash_search(LockMethodLocalHash,(void *) &localtag,HASH_FIND, NULL);//查找locallock--locallock->lockOwners.nLocks//Decrease the count for the resource owner,如果到0 就调用ResourceOwnerForgetLock(owner, locallock);把owner中这个localLock的信息去除。并locallock->numLockOwners--;locallock->nLocks--;//如果引用计数依然>0,直接return true.//如果这个锁满足快速加锁条件,则调用LWLockAcquire(MyProc->backendLock, LW_EXCLUSIVE);released = FastPathUnGrantRelationLock(locktag->locktag_field2,lockmode);LWLockRelease(MyProc->backendLock);if (released){RemoveLocalLock(locallock);return TRUE;}//否则我们认为这个锁在共享锁表里,LWLockAcquire(partitionLock, LW_EXCLUSIVE);wakeupNeeded = UnGrantLock(lock, lockmode, proclock, lockMethodTable);//对lock中的信息进行修改。如果此锁为block锁,wakeupNeeded = true.CleanUpLock(lock, proclock,lockMethodTable, locallock->hashcode,wakeupNeeded);-->if (proclock->holdMask == 0){在proclock hash中清除这个proclock}-->if (lock->nRequested == 0){在lock hash中清除这个lock}-->if (wakeupNeeded) ProcLockWakeup(lockMethodTable, lock);//按顺序唤醒-->SetLatch(&proc->procLatch);//在ProcLockWakeup-->ProcWakeup中调用。//唤醒的核心,参考进程间锁LatchLWLockRelease(partitionLock);}








