LLVM Obfuscator是一个基于LLVM框架实现的一个开源代码混淆器,整个项目包含了三个相对独立的LLVM pass, 每个pass实现了一种混淆方式,通过这些混淆手段,可以模糊原程序的流程或者某一部分的算法,给逆向分析带来一些困难。指令变换:https://github.com/obfuscator-llvm/obfuscator/wiki/Instructions-Substitution流程伪造:https://github.com/obfuscator-llvm/obfuscator/wiki/Bogus-Control-Flow流程平坦化:https://github.com/obfuscator-llvm/obfuscator/wiki/Control-Flow-FlatteningGithub文档上有说,指令变换的混淆技术,在功能等效的指令序列替换标准的二进制运算符,当有很多个等效的指令序列随机选取一个,这种混淆很简单,可以很轻松的就将其删除。
- `-mllvm -sub`: activateinstructions substitution- `-mllvm -sub_loop=3`: if thepass is activated, applies it 3 times on a function. Default : 1前置的一点点知识:其中全局变量用@,局部变量用%,%1指的是第一个寄存器(抽象意义上的寄存器,不同于CPU的寄存器), alloca 是声明, align是字节对齐位数,store是存储,load是加载
Addition
a = b - (-c)
%0 = load i32* %a, align 4%1 = load i32* %b, align 4%a,%b四字节对齐( i32 代表的就是32位转化就是4字节 ), %a - 0-%b = %a + %b
%0 = load i32* %a, align 4%1 = load i32* %b, align 4%5 = 0- (0 - %a + 0 - %b)
r = rand (); a = b + r; a = a + c; a = a - r%0 = load i32* %a, align 4%1 = load i32* %b, align 4%2 = add i32 %0, 1107414009%4 = sub nsw i32 %3, 1107414009rand() 随机数定义 %4 = %a + rand() + %b - rand()
r = rand (); a = b - r; a = a + b; a = a + r
%0 = load i32* %a, align 4%1 = load i32* %b, align 4%2 = sub i32 %0, 1108523271c%4 = add nsw i32 %3, 1108523271%4 = %a - rand() + %b + rand()
%0 = load i32* %a, align 4%1 = load i32* %b, align 4%3 = %a + 0 - %b
r = rand (); a = b + r; a = a - c; a = a - r
%0 = load i32* %a, align 4%1 = load i32* %b, align 4%2 = add i32 %0, 1571022666c%4 = sub nsw i32 %3, 1571022666%4 = %a + rand() - %b - rand()
r = rand (); a = b - r; a = a - c; a = a + r
%0 = load i32* %a, align 4%1 = load i32* %b, align 4%2 = sub i32 %0, 1057193181c%4 = add nsw i32 %3, 1057193181%4 = %a - rand() - %b + rand()
a = b & c -> a = (b ^ ~c) & b%0 = load i32* %a, align 4%1 = load i32* %b, align 4%4 = (%a xor not(%b)) and %aa = b | c -> a = (b & c) | (b ^ c)
%0 = load i32* %a, align 4%1 = load i32* %b, align 4%4 = (%a xor %b) or (%a and %b)
a = a ^ b -> a = (~a & b) | (a & ~b)%0 = load i32* %a, align 4%1 = load i32* %b, align 4%6 = (not %a and %b) or (not %b and %a)
这里看完以后ollvm的指令变换特别像数电模电中的一些东西,如果慢点分析还是可以分析出来的,可以这里全部改成与非门,之前在看雪也有看过这样的题,所以感觉与非门来说相对复杂度大一些,而且在ida中会有一个big function的限定,可以稍微卡一下不懂这方面修改的人,而且看起来会比较复杂一些。
流程伪造
该方法通过在当前基本块之前添加一个基本块来修改函数调用图。这个新的基本块包含一个不透明的谓词,然后有条件地跳转到原始基本块。原始的基本块也将被克隆并填充以随机选择的垃圾指令,这里和我在CTF中的一些看到的很多if...else...语句相对应了,中间会有很多的分支,有一个是正确的。- `-mllvm -bcf`: activates thebogus control flow pass- `-mllvm -bcf_loop=3`: if thepass is activated, applies it 3 times on a function. Default: 1- `-mllvm -bcf_prob=40`: if thepass is activated, a basic bloc will be obfuscated with a probability of 40%.Default: 30这里原作者给了很详细的一个说明来说明这个流程伪造:
int main(int argc, char** argv){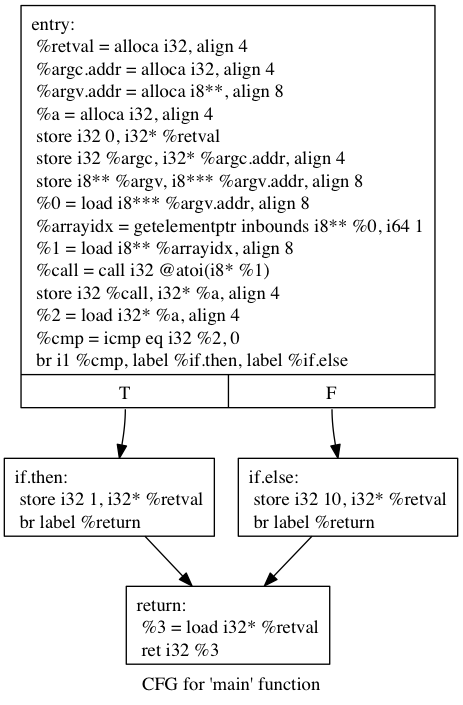
我们进行了流程伪造会变成:
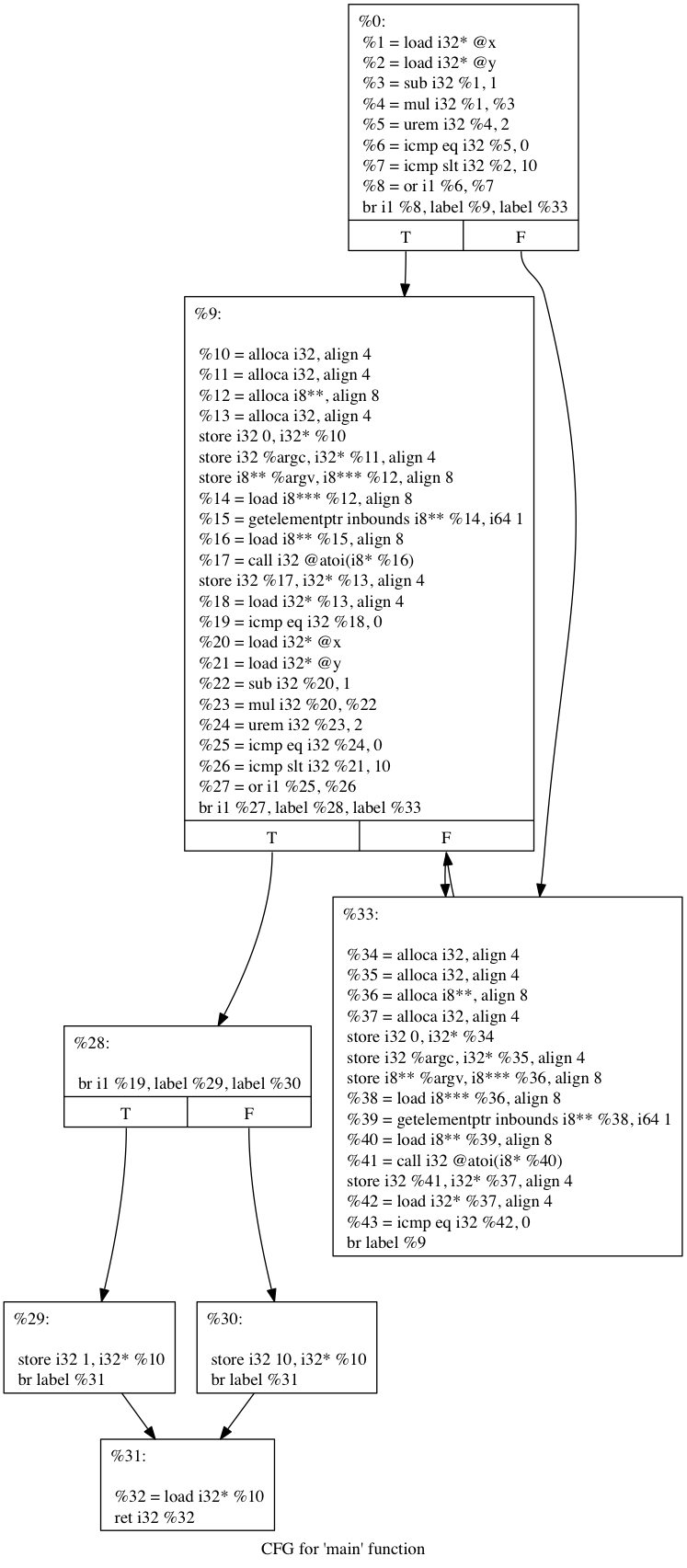
就是创建很多的分支来去混淆我们原先的代码,从而达到一个安全的角度,避免被分析出来,不过一般的话这里也是可以慢慢分析出来的。
<<OBFUSCATING C++ PROGRAMS VIA CONTROL FLOW FLATTENING>> 这本文献里面详细的介绍了流程平坦化。
给了几个例子来理解:
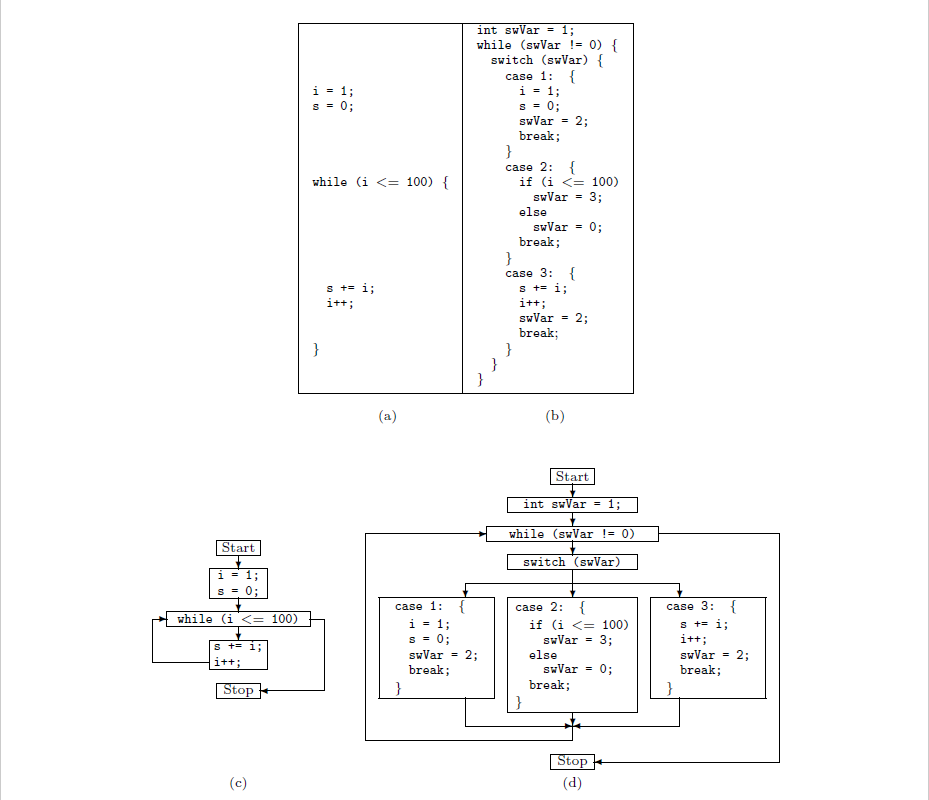

- `-mllvm -fla`: activatescontrol flow flattening- `-mllvm -split`: activatesbasic block splitting. Improve the flattening when applied together.- `-mllvm -split_num=3`: if thepass is activated, applies it 3 times on each basic block. Default: 1大概这里也给了我们源代码的问题的对应,一个是平坦化之前,一个是平坦化之后的:
int main(int argc, char** argv){
int main(int argc, char** argv){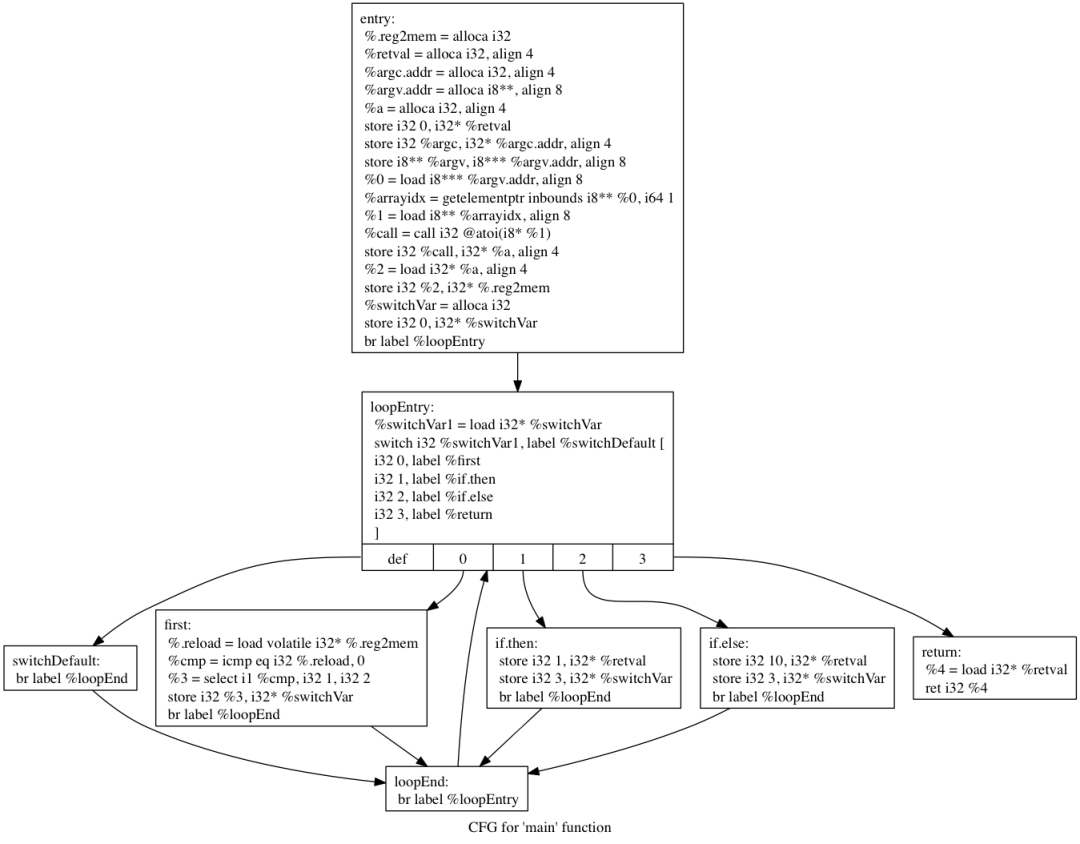
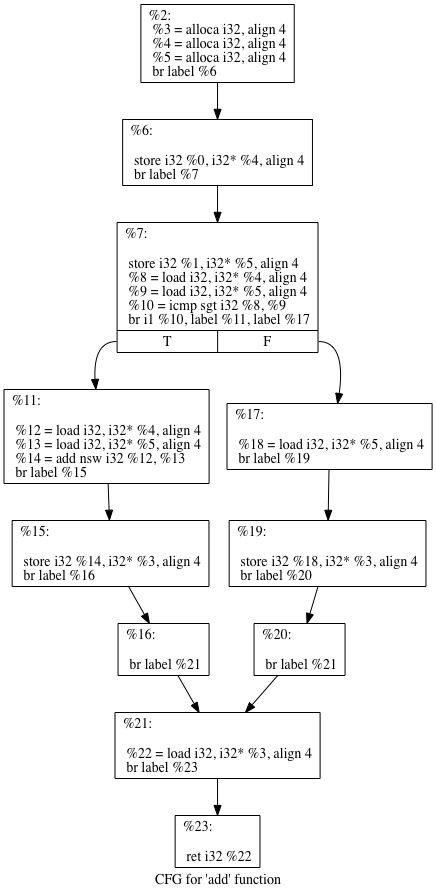
总体来说,控制流程平坦化这个特性,抽象下来,主要是通过这几个步骤来实现的:1. 在整个代码流程中,分析搜集出所有的基本代码块(Basic Block)(译者注:遇到条件分支就算是一个新的代码块了)2. 把基本代码块放到控制流图的最底部,然后删除掉原来的基本块之间的跳转关系3. 添加混淆器的流程控制分发逻辑,通过新的复杂分发逻辑还原原来程序块之间的逻辑关系就跟我们上面说举的例子一样,我们通过用更复杂的逻辑关系从而去等同于现在的逻辑关系,我们去搭建一下ollvm的环境,然后用ida去测试一下。clang -c -emit-llvm *.c -o *.bc编译产生字节码clang -S -emit-llvm *.c -o *.ll编译产生可视化字节码llvm-dis *.bc -o *.ll 将字节码转换为可视化字节码llvm-as *.ll - o *.bc 将可视化字节码转换为字节码 3 sudo apt-get install g++ cmake git 4 cdollvm && git clone -b llvm-4.0https://github.com/obfuscator-llvm/obfuscator.git 9 cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release ../obfuscator/ 10 cmake-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release ../../obfuscator/ 13 cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release ../../obfuscator/ 14 cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DLLVM_INCLUDE_TESTS=OFF../../obfuscator/我们平坦化后的代码:
int __cdecl main(int argc,const char **argv, const char **envp) signed int v4; [rsp+20h] [rbp-10h] signed int v5; [rsp+24h] [rbp-Ch] while ( v4 == 602246107 ) printf("hello ollvm", argv,envp); else if ( v4 == 1923071755 ) printf("hello word!", argv,envp);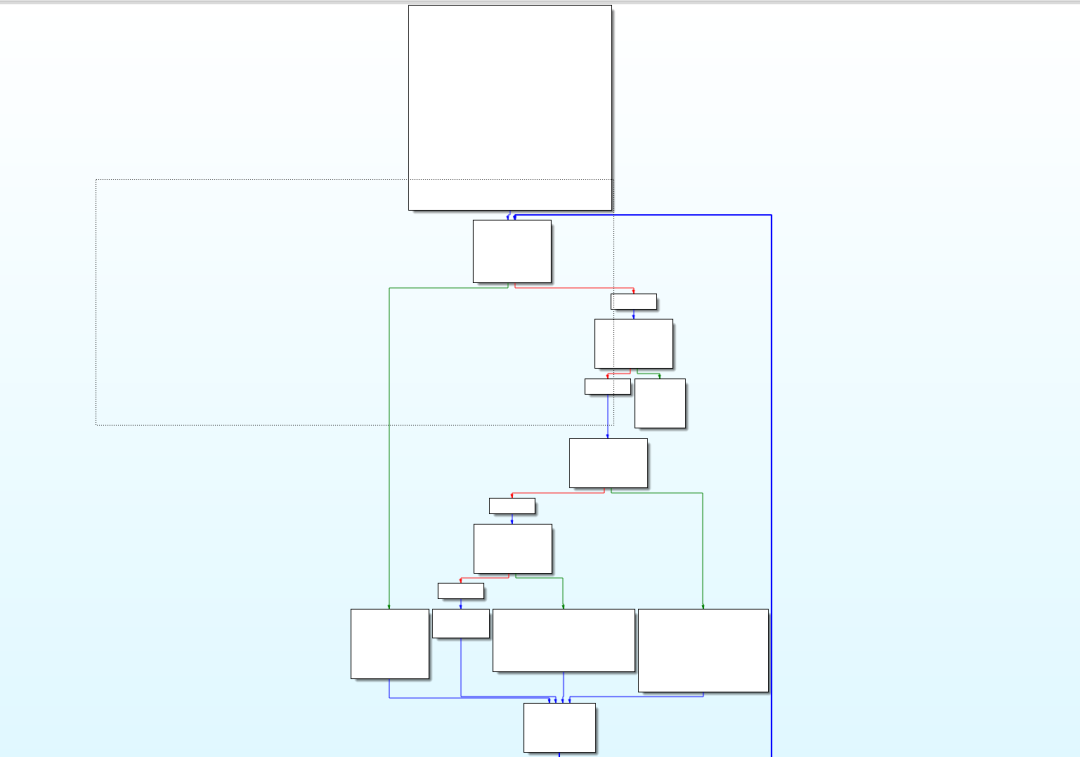
可执⾏流程块:
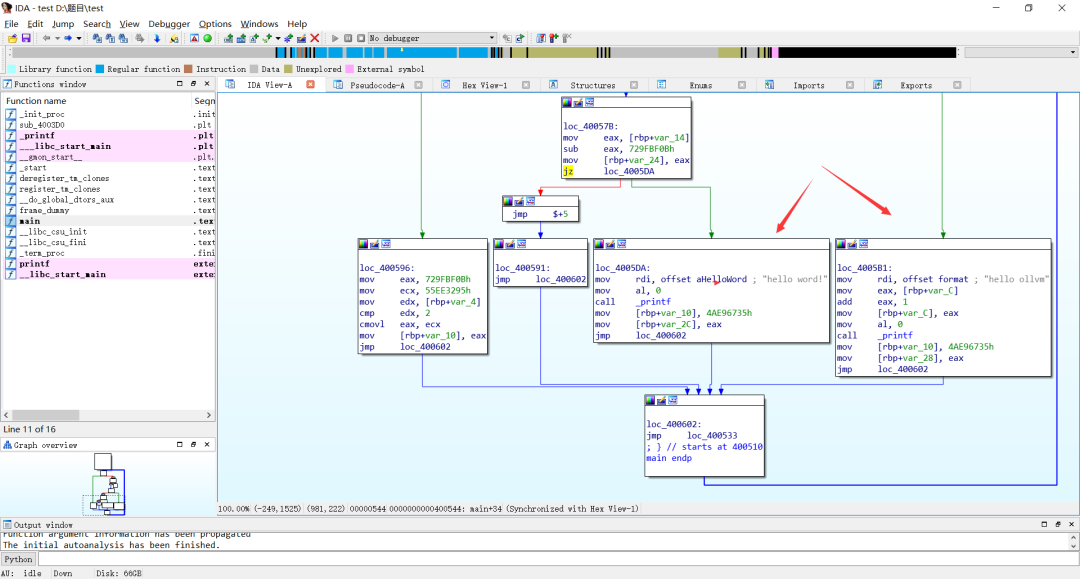
源码分析
这里还是比较推荐看一下相关文档的源码,可以看看是怎么实现的,为什么这么实现的,直接去解读一下:https://github.com/obfuscator-llvm/obfuscator/tree/llvm-4.0/lib/Transforms/Obfuscation对于我们的OLLVM的每个pass,主要是继承对应的pass类,对应的方法进行重写。
IR基本结构:
IR代码是由一个个Module组成的,每个Module(块)之间互相联系,而Module又是由一个个Function(函数)组成,Function又是由一个个BasicBlock(基本快)组成,在BasicBlock中又包含了一条条Instruction(指令)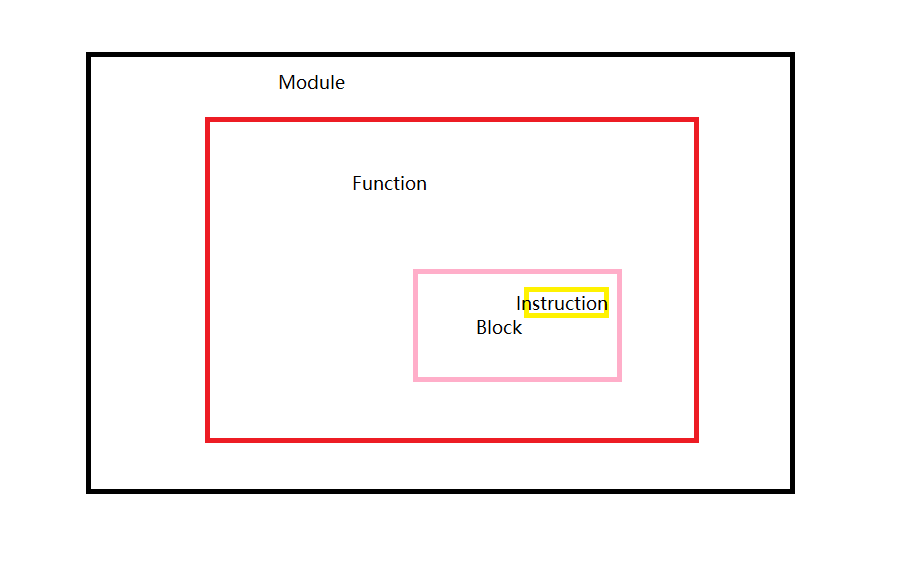
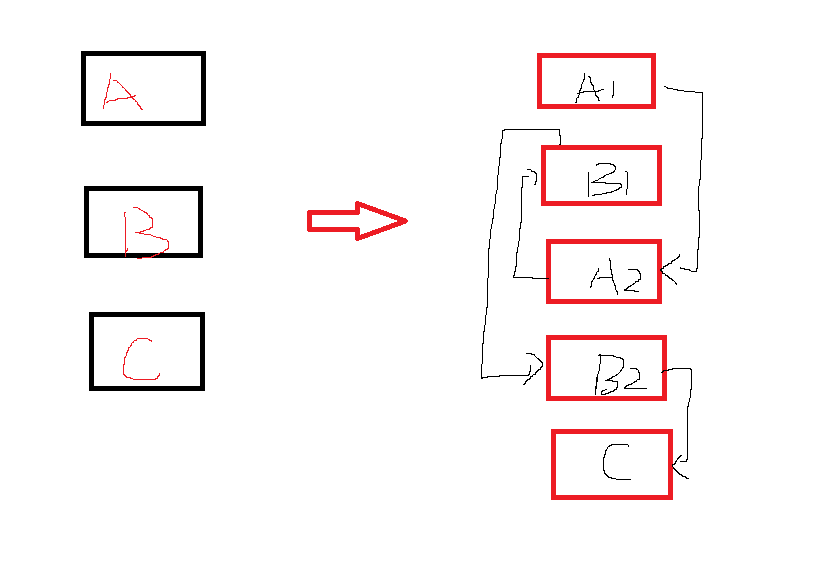
如果我们把ABC三个代码快每个都再进行细粒度的切割,变成A1,A2...Ax, B1,B2,Bx, C1,C2,Cx这样,那再按照流程平坦化的逻辑去进行一次代码重组,重组之后的画面,重组之后的代码会充斥着switch case,而且case的顺序还是随机的,结果是大大的降低了整个代码逻辑的可读性。
指令分割实现与:SplitBasicBlock.cpp中:struct SplitBasicBlock : publicFunctionPass { static char ID; Pass identification,replacement for typeid SplitBasicBlock() : FunctionPass(ID) {} SplitBasicBlock(bool flag) : FunctionPass(ID){ bool runOnFunction(Function &F); bool containsPHI(BasicBlock *b); void shuffle(std::vector<int>&vec);这里面我们继承了FunctionPass,去实现runOnFunction函数
STATISTIC(Split,"Basicblock splitted");static cl::opt<int>SplitNum("split_num", cl::init(2), cl::desc("Split <split_num> time each BB"));struct SplitBasicBlock : publicFunctionPass { static char ID; / Pass identification,replacement for typeid SplitBasicBlock() : FunctionPass(ID) {} SplitBasicBlock(bool flag) : FunctionPass(ID){ bool runOnFunction(Function &F); bool containsPHI(BasicBlock *b); void shuffle(std::vector<int>&vec);char SplitBasicBlock::ID = 0;staticRegisterPass<SplitBasicBlock> X("splitbbl", "BasicBlocksplitting");Pass*llvm::createSplitBasicBlock(bool flag) { return new SplitBasicBlock(flag);//继承FunctionPass,重新写一下runOnFunction的功能boolSplitBasicBlock::runOnFunction(Function &F) { // Check if the number of applications iscorrect if (!((SplitNum > 1) && (SplitNum<= 10))) { errs()<<"Split application basicblock percentage\ -split_num=x must be 1 < x <= 10";//切割次数必须要在1到10次之间,如果再这个范围之外就会flase,这里的代码用来判断切割次数 if (toObfuscate(flag, tmp,"split")) {//如果我们的SplitNum符合,我们会进行toObfuscate进行处理,在我们的Utils.h的头文件里面,之后执行我们的split函数clang -mllvm -split test.cclang -mllvm -split_num=3test.c默认次数是1,第二个是告诉我们分割次数是3,源码中写了必须再1-10次之内
bool toObfuscate(bool flag,Function *f, std::string attribute) { std::string attr = attribute; std::string attrNo = "no" + attr; if (f->isDeclaration()) { // Check external linkage if(f->hasAvailableExternallyLinkage() !=0) { // We have to check the nofla flag first // Because .find("fla") is true fora string like "fla" or if (readAnnotate(f).find(attrNo) !=std::string::npos) { if (readAnnotate(f).find(attr) !=std::string::npos) { /* Check if the number of applications iscorrect if (!((Percentage > 0) &&(Percentage <= 100))) { LLVMContext &ctx =llvm::getGlobalContext(); ctx.emitError(Twine("Flatteningapplication function\ percentage -perFLA=x must be 0< x <= 100")); else if (func.size() != 0 &&func.find(f->getName()) != std::string::npos) { if((((int)llvm::cryptoutils->get_range(100))) < Percentage) {这是判断是否启用了split功能,bool flag, Function *f, std::string attribute 是我们的依据
voidSplitBasicBlock::split(Function *f) { std::vector<BasicBlock *> origBB; for (Function::iterator I = f->begin(), IE= f->end(); I != IE; ++I) { for (std::vector<BasicBlock*>::iterator I = origBB.begin(), // No need to split a 1 inst bb // Or ones containing a PHI node if (curr->size() < 2 ||containsPHI(curr)) { // Check splitN and current BB size if ((size_t)splitN > curr->size()) { splitN = curr->size() - 1; for (unsigned i = 1; i <curr->size(); ++i) { std::sort(test.begin(), test.begin() +splitN); BasicBlock::iterator it = curr->begin(); BasicBlock *toSplit = curr; for (int i = 0; i < splitN; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < test[i] - last;++j) { toSplit = toSplit->splitBasicBlock(it,toSplit->getName() + ".split");vector数组origBB用于保存所有的block块,遍历origBB,每一个curr,如果它包含的指令数只有1个或者包含PHI节点,则不分割该block, 对于待分割的block,首先生成分割点,用test数组存放分割点,用shuffle打乱指令的顺序,使sort函数排序前splitN个数能尽量随机, 最后分割block是调用splitBasicBlock函数分割基本块总结起来就是:按照 -mllvm -split_num=x 指定的参数值,把原BaiscBlock切割成x+1块,新老块之间用无条件跳转指令连起来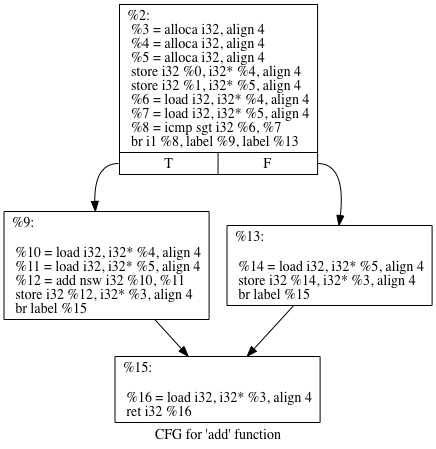
指令替换功能实现在Substitution.cpp,可以看到这边里的函数swtich case只对我们的加 减 或 与 异或进行了操作
bool Substitution::substitute(Function*f) { // Loop for the number of time we run thepass on the function for (Function::iterator bb =tmp->begin(); bb != tmp->end(); ++bb) { for (BasicBlock::iterator inst =bb->begin(); inst != bb->end(); ++inst) { if (inst->isBinaryOp()) { switch (inst->getOpcode()) { case BinaryOperator::Add: // case BinaryOperator::FAdd: // Substitute with random addoperation (this->*funcAdd[llvm::cryptoutils->get_range(NUMBER_ADD_SUBST)])( cast<BinaryOperator>(inst)); case BinaryOperator::Sub: // case BinaryOperator::FSub: // Substitute with random suboperation (this->*funcSub[llvm::cryptoutils->get_range(NUMBER_SUB_SUBST)])( cast<BinaryOperator>(inst)); case BinaryOperator::Mul: case BinaryOperator::FMul: case BinaryOperator::UDiv: case BinaryOperator::SDiv: case BinaryOperator::FDiv: case BinaryOperator::URem: case BinaryOperator::SRem: case BinaryOperator::FRem: funcAnd[llvm::cryptoutils->get_range(2)])(cast<BinaryOperator>(inst)); funcOr[llvm::cryptoutils->get_range(2)])(cast<BinaryOperator>(inst)); funcXor[llvm::cryptoutils->get_range(2)])(cast<BinaryOperator>(inst)); } while (--times > 0); // for times这里面操作的方法会有对应的函数的跳转操作,一般我们的case的位置跳转会在我们上面进行了定义
// Implementation of a = b -(-c)voidSubstitution::addNeg(BinaryOperator *bo) { BinaryOperator *op = NULL; if (bo->getOpcode() == Instruction::Add) { op =BinaryOperator::CreateNeg(bo->getOperand(1), "", bo); BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Sub, bo->getOperand(0), op,"", bo); //op->setHasNoSignedWrap(bo->hasNoSignedWrap()); //op->setHasNoUnsignedWrap(bo->hasNoUnsignedWrap()); bo->replaceAllUsesWith(op); op =BinaryOperator::CreateFNeg(bo->getOperand(1), "", bo); op =BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::FSub, bo->getOperand(0), op,"",// Implementation of a = -(-b +(-c))voidSubstitution::addDoubleNeg(BinaryOperator *bo) { BinaryOperator *op, *op2 = NULL; if (bo->getOpcode() == Instruction::Add) { op = BinaryOperator::CreateNeg(bo->getOperand(0),"", bo); op2 =BinaryOperator::CreateNeg(bo->getOperand(1), "", bo); op =BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Add, op, op2, "", bo); op = BinaryOperator::CreateNeg(op,"", bo); //op->setHasNoSignedWrap(bo->hasNoSignedWrap()); //op->setHasNoUnsignedWrap(bo->hasNoUnsignedWrap()); op =BinaryOperator::CreateFNeg(bo->getOperand(0), "", bo); op2 =BinaryOperator::CreateFNeg(bo->getOperand(1), "", bo); op =BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::FAdd, op, op2, "", bo); op = BinaryOperator::CreateFNeg(op,"", bo); bo->replaceAllUsesWith(op);// Implementation of r = rand (); a = b + r; a = a + c; a = a - rvoidSubstitution::addRand(BinaryOperator *bo) { BinaryOperator *op = NULL; if (bo->getOpcode() == Instruction::Add) { Type *ty = bo->getType(); (ConstantInt *)ConstantInt::get(ty,llvm::cryptoutils->get_uint64_t()); BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Add,bo->getOperand(0), co, "", bo); BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Add, op, bo->getOperand(1),"", bo); op =BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Sub, op, co, "", bo); //op->setHasNoSignedWrap(bo->hasNoSignedWrap()); //op->setHasNoUnsignedWrap(bo->hasNoUnsignedWrap()); bo->replaceAllUsesWith(op); Type *ty = bo->getType(); (ConstantFP*)ConstantFP::get(ty,(float)llvm::cryptoutils->get_uint64_t()); op =BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::FAdd,bo->getOperand(0),co,"",bo); op =BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::FAdd,op,bo->getOperand(1),"",bo); op = BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::FSub,op,co,"",bo);// Implementation of r = rand(); a = b - r; a = a + b; a = a + rvoidSubstitution::addRand2(BinaryOperator *bo) { BinaryOperator *op = NULL; if (bo->getOpcode() == Instruction::Add) { Type *ty = bo->getType(); (ConstantInt *)ConstantInt::get(ty,llvm::cryptoutils->get_uint64_t()); BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Sub, bo->getOperand(0), co,"", bo); BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Add,op, bo->getOperand(1), "", bo); op =BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Add, op, co, "", bo); //op->setHasNoSignedWrap(bo->hasNoSignedWrap()); //op->setHasNoUnsignedWrap(bo->hasNoUnsignedWrap()); bo->replaceAllUsesWith(op); Type *ty = bo->getType(); (ConstantFP*)ConstantFP::get(ty,(float)llvm::cryptoutils->get_uint64_t()); op =BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::FAdd,bo->getOperand(0),co,"",bo); op =BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::FAdd,op,bo->getOperand(1),"",bo); op =BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::FSub,op,co,"",bo);// Implementation of a = b +(-c)voidSubstitution::subNeg(BinaryOperator *bo) { BinaryOperator *op = NULL; if (bo->getOpcode() == Instruction::Sub) { op =BinaryOperator::CreateNeg(bo->getOperand(1), "", bo); BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Add, bo->getOperand(0), op,"", bo); //op->setHasNoSignedWrap(bo->hasNoSignedWrap()); //op->setHasNoUnsignedWrap(bo->hasNoUnsignedWrap()); op =BinaryOperator::CreateFNeg(bo->getOperand(1), "", bo); op =BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::FAdd, bo->getOperand(0), op,"", bo->replaceAllUsesWith(op);// Implementation of r = rand (); a = b + r; a = a - c; a = a - rvoidSubstitution::subRand(BinaryOperator *bo) { BinaryOperator *op = NULL; if (bo->getOpcode() == Instruction::Sub) { Type *ty = bo->getType(); (ConstantInt *)ConstantInt::get(ty,llvm::cryptoutils->get_uint64_t()); BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Add, bo->getOperand(0), co,"", bo); BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Sub,op, bo->getOperand(1), "", bo); op =BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Sub, op, co, "", bo); //op->setHasNoSignedWrap(bo->hasNoSignedWrap()); //op->setHasNoUnsignedWrap(bo->hasNoUnsignedWrap()); bo->replaceAllUsesWith(op); Type *ty = bo->getType(); (ConstantFP*)ConstantFP::get(ty,(float)llvm::cryptoutils->get_uint64_t()); op =BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::FAdd,bo->getOperand(0),co,"",bo); op =BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::FSub,op,bo->getOperand(1),"",bo); op =BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::FSub,op,co,"",bo);// Implementation of r = rand (); a = b - r; a = a - c; a = a + rvoidSubstitution::subRand2(BinaryOperator *bo) { BinaryOperator *op = NULL; if (bo->getOpcode() == Instruction::Sub) { Type *ty = bo->getType(); (ConstantInt *)ConstantInt::get(ty,llvm::cryptoutils->get_uint64_t()); BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Sub, bo->getOperand(0), co,"", bo); BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Sub, op, bo->getOperand(1),"", bo); op = BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Add,op, co, "", bo); //op->setHasNoSignedWrap(bo->hasNoSignedWrap()); //op->setHasNoUnsignedWrap(bo->hasNoUnsignedWrap()); bo->replaceAllUsesWith(op); Type *ty = bo->getType(); (ConstantFP*)ConstantFP::get(ty,(float)llvm::cryptoutils->get_uint64_t()); op =BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::FSub,bo->getOperand(0),co,"",bo); op =BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::FSub,op,bo->getOperand(1),"",bo); op =BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::FAdd,op,co,"",bo);// Implementation of a = b& c => a = (b^~c)& bvoidSubstitution::andSubstitution(BinaryOperator *bo) { BinaryOperator *op = NULL; // Create NOT on second operand => ~c op =BinaryOperator::CreateNot(bo->getOperand(1), "", bo); BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Xor,bo->getOperand(0), op, "", bo); // Create AND => (b^~c) & b op = BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::And,op1, bo->getOperand(0), "", bo); bo->replaceAllUsesWith(op);// Implementation of a = a&& b <=> !(!a | !b) && (r | !r)voidSubstitution::andSubstitutionRand(BinaryOperator *bo) { // Copy of the BinaryOperator type to createthe random number with the // same type of the operands Type *ty = bo->getType(); (ConstantInt *)ConstantInt::get(ty,llvm::cryptoutils->get_uint64_t()); BinaryOperator *op =BinaryOperator::CreateNot(bo->getOperand(0), "", bo); BinaryOperator *op1 =BinaryOperator::CreateNot(bo->getOperand(1), "", bo); BinaryOperator *opr =BinaryOperator::CreateNot(co, "", bo); BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Or,op, op1, "", bo); opr = BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Or,co, opr, "", bo); op = BinaryOperator::CreateNot(opa,"", bo); // !(!a | !b) && (r | !r) op = BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::And,op, opr, "", bo); // We replace all the old AND operators withthe new one transformed bo->replaceAllUsesWith(op);// Implementation of a = b | c=> a = (b & c) | (b ^ c)voidSubstitution::orSubstitutionRand(BinaryOperator *bo) { Type *ty = bo->getType(); (ConstantInt *)ConstantInt::get(ty,llvm::cryptoutils->get_uint64_t()); BinaryOperator *op =BinaryOperator::CreateNot(bo->getOperand(0), "", bo); BinaryOperator *op1 =BinaryOperator::CreateNot(bo->getOperand(1), "", bo); BinaryOperator *op2 =BinaryOperator::CreateNot(co, "", bo); BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::And,op, co, "", bo); BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::And,bo->getOperand(0), op2, "", bo); BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::And,op1, co, "", bo); BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::And,bo->getOperand(1), op2, "", bo); // (!a && r) || (a && !r) op3 = BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Or,op3, op4, "", bo); op4 = BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Or,op5, op6, "", bo); // (!a && r) || (a && !r) ^(!b && r) ||(b && !r) op5 = BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Xor,op3, op4, "", bo); op3 = BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Or,op, op1, "", bo); op3 = BinaryOperator::CreateNot(op3,"", bo); op4 = BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Or,co, op2, "", bo); // !(!a|| !b) && (r || !r) op4 =BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::And, op3, op4, "", bo); // [(!a && r) || (a && !r) ^(!b && r) ||(b && !r) ] || [!(!a || !b) && (r || op = BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Or,op5, op4, "", bo); bo->replaceAllUsesWith(op);voidSubstitution::orSubstitution(BinaryOperator *bo) { BinaryOperator *op = NULL; // Creating first operand (b & c) op = BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::And,bo->getOperand(0), bo->getOperand(1),"", bo); // Creating second operand (b ^ c) BinaryOperator *op1 = BinaryOperator::Create( Instruction::Xor, bo->getOperand(0),bo->getOperand(1), "", bo); op = BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Or,op, op1, "", bo); bo->replaceAllUsesWith(op);// Implementation of a = a ~ b=> a = (!a && b) || (a && !b)voidSubstitution::xorSubstitution(BinaryOperator *bo) { BinaryOperator *op = NULL; // Create NOT on first operand op = BinaryOperator::CreateNot(bo->getOperand(0),"", bo); // !a op = BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::And,bo->getOperand(1), op, "", // Create NOT on second operand BinaryOperator::CreateNot(bo->getOperand(1), "", bo); // !b op1 =BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::And, bo->getOperand(0), op1,"", op = BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Or,op, op1, "", bo); // (!a&& b) || (a && !b) bo->replaceAllUsesWith(op);// implementation of a = a ^ b<=> (a ^ r) ^ (b ^ r) <=> (!a && r || a && !r) ^// note : r is a random numbervoidSubstitution::xorSubstitutionRand(BinaryOperator *bo) { BinaryOperator *op = NULL; Type *ty = bo->getType(); (ConstantInt *)ConstantInt::get(ty,llvm::cryptoutils->get_uint64_t()); op = BinaryOperator::CreateNot(bo->getOperand(0),"", bo); op = BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::And,co, op, "", bo); BinaryOperator *opr =BinaryOperator::CreateNot(co, "", bo); BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::And,bo->getOperand(0), opr, "", bo); BinaryOperator *op2 =BinaryOperator::CreateNot(bo->getOperand(1), "", bo); op2 =BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::And, op2, co, "", bo); BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::And,bo->getOperand(1), opr, "", bo); // (!a && r) || (a && !r) op = BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Or,op, op1, "", bo); // (!b && r) || (b && !r) op1 = BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Or,op2, op3, "", bo); // (!a && r) || (a && !r) ^(!b && r) || (b && !r) op = BinaryOperator::Create(Instruction::Xor,op, op1, "", bo); bo->replaceAllUsesWith(op);这个就是我们的指令替换的一个转换
控制流平坦功能
控制流平坦功能实现在Flattening.cpp中可以看到还是继承了FunctionPass,可以直接去看一下runOnFunctionstruct Flattening : publicFunctionPass { static char ID; // Pass identification, replacement fortypeid Flattening() : FunctionPass(ID) {} Flattening(bool flag) : FunctionPass(ID) {this->flag = flag; } bool runOnFunction(Function &F); bool flatten(Function *f);我们和原来的toObfuscate的函数调用一样,还是去看是否传入了 -mllvm -fla参数
boolFlattening::runOnFunction(Function &F) { if (toObfuscate(flag, tmp, "fla")){功能实现在flatten函数
boolFlattening::flatten(Function *f) { vector<BasicBlock *> origBB; //llvm::cryptoutils->get_bytes产生一个随机种子 llvm::cryptoutils->get_bytes(scrambling_key, 16); //调用了一个外部Pass,LowerSwitch这个Pass,内部逻辑是消除了当前函数中的switch方式组织的代码,抓换成if else这种分支调用,方便后面进行代码块分割,从而进行平坦化操作 FunctionPass *lower =createLowerSwitchPass(); lower->runOnFunction(*f); //遍历当前函数中的所有BasicBlock,并保存到origBB vector数组 for (Function::iterator i = f->begin(); i!= f->end(); ++i) { if (isa<InvokeInst>(bb->getTerminator())){ if (origBB.size() <= 1) { //把第一块BasicBlock从origBB这个vector中移除了,因为按照流程平坦化的设计,第一块是单独处理的,作为整个混淆流程的开始逻辑 origBB.erase(origBB.begin()); // Get a pointer on the first BB Function::iterator tmp = f->begin(); //++tmp; BasicBlock *insert = &*tmp; // If main begin with an if //查第一块中是否包含条件跳转分支,如果包含条件跳转分支,则按照条件分支的位置进行代码块分割,分割逻辑跟SplitBasicBlock的逻辑一致 if(isa<BranchInst>(insert->getTerminator())) { br =cast<BranchInst>(insert->getTerminator()); if ((br != NULL &&br->isConditional()) || insert->getTerminator()->getNumSuccessors() > 1) { BasicBlock::iterator i = insert->end(); if (insert->size() > 1) { BasicBlock *tmpBB =insert->splitBasicBlock(i, "first"); origBB.insert(origBB.begin(), tmpBB); insert->getTerminator()->eraseFromParent(); // Create switch variable and set as it //创建了一个switch用的变量,相当于switch(caseVar) 这个语句中的caseVar, 并通过StoreInst赋予初始值,初始值通过llvm::cryptoutils->scramble32(0,scrambling_key))生成,其中scrambling_key就是函数开头生成的随机种子 newAllocaInst(Type::getInt32Ty(f->getContext()), 0, "switchVar",insert); ConstantInt::get(Type::getInt32Ty(f->getContext()), llvm::cryptoutils->scramble32(0, scrambling_key)), //创建了一个代码块loopEntry, 空代码块 loopEntry =BasicBlock::Create(f->getContext(), "loopEntry", f, insert); loopEnd =BasicBlock::Create(f->getContext(), "loopEnd", f, insert); //创建了一条load指令,load是上面创建的switchVar, 并把这句代码放入loopEntry load = new LoadInst(switchVar,"switchVar", loopEntry); //把函数第一个BasicBlock和loopEntry用一个无条件跳转指令连起来 insert->moveBefore(loopEntry); BranchInst::Create(loopEntry, insert); // loopEnd jump to loopEntry // loopEntry, loopEnd用无条件跳转连接起来 BranchInst::Create(loopEntry, loopEnd); //创建了一个BasicBlock, 并用无条件跳转指令连接起来 BasicBlock::Create(f->getContext(),"switchDefault", f, loopEnd); BranchInst::Create(loopEnd, swDefault); //Create switch instruction itself and set condition //创建了一个switch结构,并放入到loopEntry代码块中 switchI =SwitchInst::Create(&*f->begin(), swDefault, 0, loopEntry); switchI->setCondition(load); // Remove branch jump from 1st BB and make ajump to the while f->begin()->getTerminator()->eraseFromParent(); BranchInst::Create(loopEntry,&*f->begin()); // Put all BB in the switch for (vector<BasicBlock *>::iterator b =origBB.begin(); b != origBB.end(); ConstantInt *numCase = NULL; // Move the BB inside the switch (onlyvisual, no code logic) numCase =cast<ConstantInt>(ConstantInt::get( switchI->getCondition()->getType(), llvm::cryptoutils->scramble32(switchI->getNumCases(),scrambling_key))); switchI->addCase(numCase, i); for (vector<BasicBlock *>::iterator b =origBB.begin(); b != origBB.end(); ConstantInt *numCase = NULL; if(i->getTerminator()->getNumSuccessors() == 0) { // If it's a non-conditional jump if(i->getTerminator()->getNumSuccessors() == 1) { // Get successor and delete terminator BasicBlock *succ =i->getTerminator()->getSuccessor(0); i->getTerminator()->eraseFromParent(); numCase = switchI->findCaseDest(succ); // If next case == default case(switchDefault) numCase = cast<ConstantInt>( ConstantInt::get(switchI->getCondition()->getType(), llvm::cryptoutils->scramble32( switchI->getNumCases() - 1, scrambling_key))); // Update switchVar and jump to the endof loop new StoreInst(numCase,load->getPointerOperand(), i); BranchInst::Create(loopEnd, i); // If it's a conditional jump if(i->getTerminator()->getNumSuccessors() == 2) { ConstantInt *numCaseTrue = switchI->findCaseDest(i->getTerminator()->getSuccessor(0)); ConstantInt *numCaseFalse = switchI->findCaseDest(i->getTerminator()->getSuccessor(1)); // Check if next case == default case(switchDefault) if (numCaseTrue == NULL) { numCaseTrue = cast<ConstantInt>( ConstantInt::get(switchI->getCondition()->getType(), llvm::cryptoutils->scramble32( switchI->getNumCases() - 1, scrambling_key))); if (numCaseFalse == NULL) { numCaseFalse = cast<ConstantInt>( ConstantInt::get(switchI->getCondition()->getType(), llvm::cryptoutils->scramble32( switchI->getNumCases() - 1, scrambling_key))); BranchInst *br =cast<BranchInst>(i->getTerminator()); SelectInst::Create(br->getCondition(), numCaseTrue, numCaseFalse,"", i->getTerminator()->eraseFromParent(); // Update switchVar and jump to the endof loop new StoreInst(sel,load->getPointerOperand(), i); BranchInst::Create(loopEnd, i);最后的形成就是上面的平坦化的功能


















