union [all]用于合并两个或多个select语句的结果集
这里需要注意的是:
1.union [all]内部的select语句必须拥有相同数量的列,列也必须拥有相似的数据类型,同时,每条select语句中列的顺序必须相同
2.结果集中的列名总等于union [all]中第一个select语句中的列名。
union和union all的区别:
union操作符合并的结果集,不会允许重复值,如果允许有重复值的话,使用union all
union和union all的语法:
select column_name(s) from table_name1
union [all]
select column_name(s) from table_name2
示例:
表的定义如下:
create table [dbo].[Students](
[StuId] [int]not null,
[StuName] [nvarchar](50) not null,
[StuDept] [nvarchar](50) not null,
[StuAge] [int] not null,)
create table [dbo].[Students2](
[StuID ] [int] not null,
[Stuname] [nvarchar](50) not null,
[StuDept] [nvarchar](50) not null,
[StuAge] [int] not null,)
1.普通查询如下:
select * from dbo.Students
select * from dbo.Students2
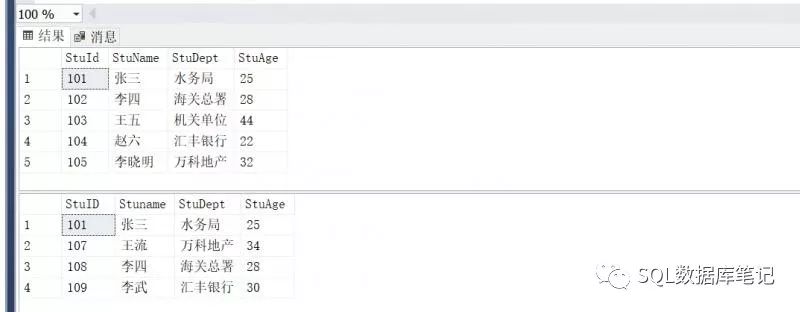 2.找出Students表和Students2表所有学生的信息:
2.找出Students表和Students2表所有学生的信息:
select * from dbo.Students union all
select * from dbo.Students2
 其中张三同学有两条数据,且列名是第一条select语句中的列名
其中张三同学有两条数据,且列名是第一条select语句中的列名
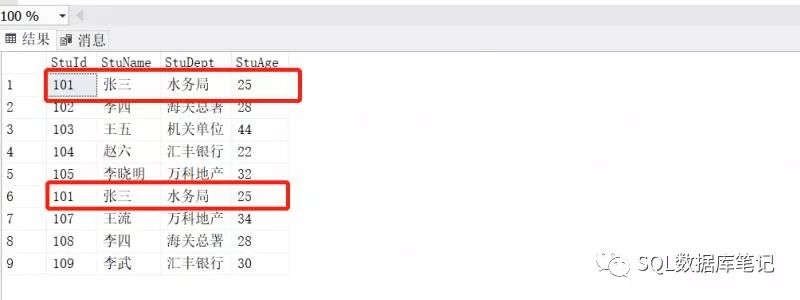
3.找出Students表和Students2表所有学生的信息,相同的学生只返回一条数据:
select * from dbo.Students union
select * from dbo.Students2
 在这里’张三‘同学的数据已经被去重
在这里’张三‘同学的数据已经被去重
如有错误欢迎留言指正
有兴趣的小伙伴可以关注“SQL数据库笔记”公众号,一起学习吧!
最后修改时间:2019-12-16 10:02:45
文章转载自SQL数据库笔记,如果涉嫌侵权,请发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。






