引言
本文介绍在
Python
中如何与MySQL
数据库交互利用
PyMySQL
数据库驱动,实现MySQL
数据库的增删改查及事务处理
MySQL 简介
MySQL是一个关系型数据库管理系统,由瑞典MySQL AB公司开发,后来被Sun公司收购,Sun公司后来又被Oracle公司收购,目前属于Oracle旗下产品。
特点
开源 免费 不要钱 使用范围广,跨平台支持性好,提供了多种语言调用的 API。
是学习数据库开发的首选。
环境
| 环境名称 | 版本 |
| Python | 3.7.9 |
| PyMySQL | 1.0.2 |
| MySql-Server | 5.7.32 |
首先我们要安装 PyMySQL
数据库驱动
pip install PyMySQL
如要指定版本
pip install PyMySQL==1.0.2
可能默认的源安装第三库会有点慢,可以配置一下其他的镜像源。Pip安装第三方库网速慢(解决方案)[1]
如果只想临时安装第三库快一点,可以临时使用其他镜像源。
pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple PyMySQL==1.0.2
PyMySQL 是在 Python3.x 版本中用于连接 MySQL 服务器的一个库,Python2 中则使用 mysqldb。
准备数据
创建数据库准备数据
# 创建 testdb 数据库create databases testdb charset=utf8;use testdb;# 创建 employee 表create table employee (id int unsigned primary key auto_increment not null,emp_num varchar(10) not null,name varchar(10) not null,age int not null,sex varchar(6) not null,salary float not null);# 插入员工数据insert into employee (emp_num, name, age, sex, salary) values('M001', '张三', 56, '男', 10000),('F002', '李四', 50, '女', 9000),('M003', '王五', 47, '男', 8000),('M004', '赵六', 46, '男', 7000),('F005', '孙七', 36, '女', 6000),('M006', '周八', 28, '男', 5000),('M007', '吴九', 26, '男', 4000),('M008', '郑十', 22, '男', 3000);
Python 访问数据库流程
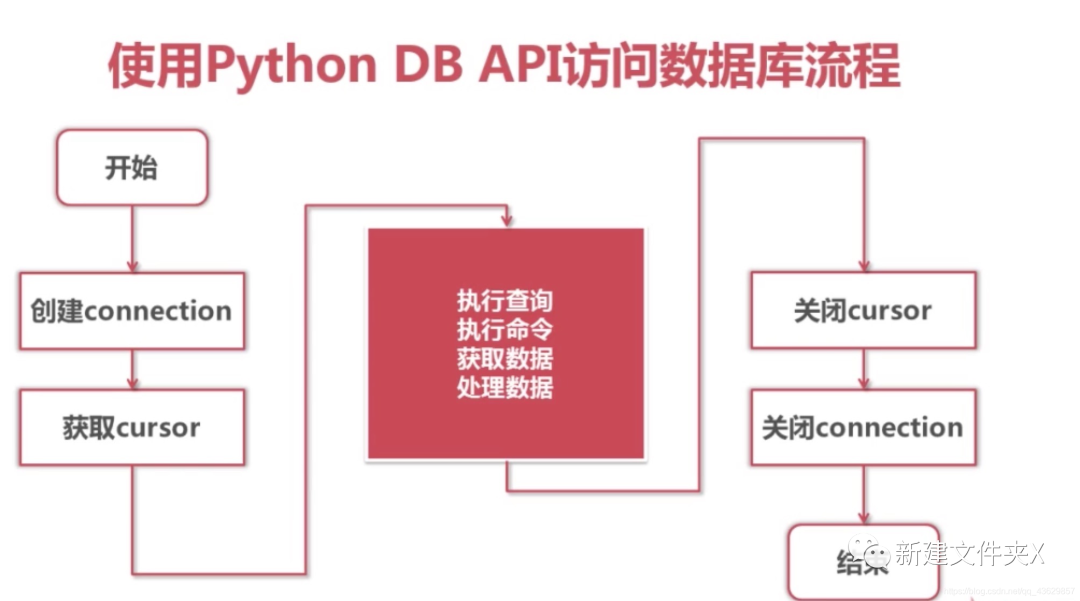
引入模块
•在 py文件 中引入 pymysql
模块
from pymysql import *
Connection 对象
•用于建立与数据库的连接•创建对象:调用connect()方法
conn = connect(参数列表)
•参数 host:连接的 mysql
主机,如果本机就是 localhost
•参数 port:连接的 mysql
主机的端口,默认是 3306
•参数 database:数据库的名称•参数 user:连接的用户名•参数 password:连接的密码•参数 charset:通信采用的编码方式,推荐使用 utf8
对象的方法
•close() 关闭连接•commit() 提交•cursor() 返回 Cursor 对象,用于执行 sql 语句并获得结果
Cursor对象
•用于执行sql语句,使用频度最高的语句为select、insert、update、delete•获取Cursor对象:调用Connection对象的cursor()方法
cursor = conn.cursor()
对象的方法
•close() 关闭•execute(operation [, parameters ]) 执行sql语句,返回受影响的行数,主要用于执行 insert、update、delete
语句,也可以执行 create、alter、drop
等语句•fetchone() 执行查询语句时,获取查询结果集的第一个行数据,返回一个元组•fetchall() 执行查询时,获取结果集的所有行,一行构成一个元组,再将这些元组装入一个元组返回
对象的属性
•rowcount
只读属性,表示最近一次 execute() 执行后受影响的行数•connection
获得当前连接对象
Python操作MySQL数据库
查询 MySQL
服务版本
"""Python与MySQL数据库交互练习"""import pymysqldef mysql_version():"""查询MySQL版本信息"""# 获取数据库连接conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', # mysql服务主机,localhost代表本地user='root',password='123456',database='testdb',port=3306)# 创建游标对象 cursorcursor = conn.cursor()# 查询mysql版本的sql语句sql = 'select version();'# 执行sql语句cursor.execute(sql)data = cursor.fetchone()print ("Database version : %s " % data)# 关闭数据库连接conn.close()def main():mysql_version()if __name__ == '__main__':main()
employee 数据表的增删改
为了方便操作数据库,我把获取数据库连接和游标对象提取到一个函数里了
import pymysqldef get_conn(dbname):"""获取本地 dbname 的数据库连接及游标对象"""conn = pymysql.connect(host = 'localhost',user = 'root',password = '123456',database = dbname,port = 3306)return conn, conn.cursor()
新增员工信息到 employee 数据表
def emp_insert():"""新增员工信息"""conn, cursor = get_conn(dbname='testdb')# 插入数据insert_sql = """insert into employee values (NULL, 'M009', 'hui', 21, '男', 6000);"""# 执行sql语句,返回受响应的行数count = cursor.execute(insert_sql)print(count)# 使用占位符emp_info = ('M010', 'wang', 22, '男', 7000)insert_sql = """insert into employee values (NULL, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s);"""count = cursor.execute(sql, emp_info)print(count)# 更新数据(给每一位员工涨10%工资)update_sql = """update employee set salary=salary * 1.1;"""cursor.execute(update_sql)# 删除数据(删除名字为wang的员工)delete_sql = """delete from employee where name='wang';"""cursor.execute(delete_sql)# 记得提交到数据库执行conn.commit()cursor.close()conn.close()
更新 employee 数据表信息
def emp_update():"""更新employee数据库表数据"""conn, cursor = get_conn(dbname='testdb')# 更新数据(给每一位员工涨10%工资)update_sql = """update employee set salary=salary * 1.1;"""cursor.execute(update_sql)# 记得提交到数据库执行conn.commit()cursor.close()conn.close()
删除 employee 数据表信息
def emp_delete():"""删除employee数据库表数据"""conn, cursor = get_conn(dbname='testdb')# 删除数据(删除名字为wang的员工)delete_sql = """delete from employee where name='wang';"""cursor.execute(delete_sql)# 记得提交到数据库执行conn.commit()cursor.close()conn.close()
原employee数据表
mysql> select * from employee;+----+---------+------+-----+-----+--------+| id | emp_num | name | age | sex | salary |+----+---------+------+-----+-----+--------+| 1 | M001 | 张三 | 56 | 男 | 10000 || 2 | F002 | 李四 | 50 | 女 | 9000 || 3 | M003 | 王五 | 47 | 男 | 8000 || 4 | M004 | 赵六 | 46 | 男 | 7000 || 5 | F005 | 孙七 | 36 | 女 | 6000 || 6 | M006 | 周八 | 28 | 男 | 5000 || 7 | M007 | 吴九 | 26 | 男 | 4000 || 8 | M008 | 郑十 | 22 | 男 | 3000 |+----+---------+------+-----+-----+--------+8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
操作后的
新增后的mysql> select * from employee;+----+---------+------+-----+-----+--------+| id | emp_num | name | age | sex | salary |+----+---------+------+-----+-----+--------+| 1 | M001 | 张三 | 56 | 男 | 10000 || 2 | F002 | 李四 | 50 | 女 | 9000 || 3 | M003 | 王五 | 47 | 男 | 8000 || 4 | M004 | 赵六 | 46 | 男 | 7000 || 5 | F005 | 孙七 | 36 | 女 | 6000 || 6 | M006 | 周八 | 28 | 男 | 5000 || 7 | M007 | 吴九 | 26 | 男 | 4000 || 8 | M008 | 郑十 | 22 | 男 | 3000 || 16 | M009 | hui | 21 | 男 | 6000 || 17 | M010 | wang | 22 | 男 | 7000 |+----+---------+------+-----+-----+--------+10 rows in set (0.00 sec)更新、删除后mysql> select * from employee;+----+---------+------+-----+-----+--------+| id | emp_num | name | age | sex | salary |+----+---------+------+-----+-----+--------+| 1 | M001 | 张三 | 56 | 男 | 11000 || 2 | F002 | 李四 | 50 | 女 | 9900 || 3 | M003 | 王五 | 47 | 男 | 8800 || 4 | M004 | 赵六 | 46 | 男 | 7700 || 5 | F005 | 孙七 | 36 | 女 | 6600 || 6 | M006 | 周八 | 28 | 男 | 5500 || 7 | M007 | 吴九 | 26 | 男 | 4400 || 8 | M008 | 郑十 | 22 | 男 | 3300 || 16 | M009 | hui | 21 | 男 | 6600 |+----+---------+------+-----+-----+--------+9 rows in set (0.00 sec)
employee 数据表的查询
•fetchone() 获取查询结果集的第一个行数据,返回一个元组•fetchall() 获取结果集的所有行,一行构成一个元组,再将这些元组装入一个元组返回
单行查询获取数据
def emp_fetchone():"""单行查询employee数据表信息"""# 单行查询conn, cursor = get_conn('testdb')sql = """select * from employee where id > 3;"""count = cursor.execute(sql)print("查询到%d条数据:" % count)for i in range(count):# 一行一行获取查询结果result = cursor.fetchone()print(result)cursor.close()conn.close()
多行查询获取数据
def emp_fetchall():"""多行查询employee数据表信息"""# 多行查询conn, cursor = get_conn('testdb')sql = """select * from employee;"""count = cursor.execute(sql)print("查询到%d条数据:" % count)results = cursor.fetchall()for ret in results:print(ret)cursor.close()conn.close()
事务处理
为什么要有事务
事务广泛的运用于订单系统、银行系统等多种场景
例如:
A用户和B用户是银行的储户,现在A要给B转账500元,那么需要做以下几件事:
1.检查A的账户余额>500元;2.A 账户中扣除500元;3.B 账户中增加500元;
正常的流程走下来,A账户扣了500,B账户加了500,皆大欢喜。
那如果A账户扣了钱之后,系统出故障了呢?A白白损失了500,而B也没有收到本该属于他的500。
以上的案例中,隐藏着一个前提条件:A扣钱和B加钱,要么同时成功,要么同时失败。事务的需求就在于此
所谓事务,它是一个操作序列,这些操作要么都执行,要么都不执行,它是一个不可分割的工作单位。
例如,银行转帐工作:从一个帐号扣款并使另一个帐号增款,这两个操作要么都执行,要么都不执行。所以,应该把他们看成一个事务。事务是数据库维护数据一致性的单位,在每个事务结束时,都能保持数据一致性
事务机制可以确保数据一致性。
事务应该具有4个属性:原子性、一致性、隔离性、持久性。这四个属性通常称为 ACID 特性。
•原子性(atomicity)。一个事务是一个不可分割的工作单位,事务中包括的诸操作要么都做,要么都不做。•一致性(consistency)。事务必须是使数据库从一个一致性状态变到另一个一致性状态。一致性与原子性是密切相关的。•隔离性(isolation)。一个事务的执行不能被其他事务干扰。即一个事务内部的操作及使用的数据对并发的其他事务是隔离的,并发执行的各个事务之间不能互相干扰。•持久性(durability)。持续性也称永久性(permanence),指一个事务一旦提交,它对数据库中数据的改变就应该是永久性的。接下来的其他操作或故障不应该对其有任何影响。
Python DB API 2.0 的事务提供了两个方法 commit()
或 rollback()
。
小实例
def transaction_test():"""事务演示"""conn, cursor = get_conn('testdb')sql = "delete from employee where age > %s" % (20)try:# 执行SQL语句cursor.execute(sql)# 这里以除0异常,来演示现实场景n = 1 0# 向数据库提交conn.commit()except:# 发生错误时回滚print('事务回滚')conn.rollback()cursor.close()conn.close()
delete from employee where age > 20
这条sql语句并没有把员工年龄20岁以上的给删掉,说明事务回滚。
References
[1]
Pip安装第三方库网速慢(解决方案): https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43629857/article/details/105117129






