一、背景
公司最近搞服务器迁移,其中包括我负责的一个网站登陆系统,该系统中有一个小程序登陆的功能,小程序登陆流程中有一步是code兑换用户信息,需要https请求腾讯的https://api.weixin.qq.com/sns/jscode2session?grant_type=authorization_code接口去获取code,问题来了,迁移完后的新服务器在请求这个接口的时候报错了,具体异常如下:
javax.net.ssl.SSLException: java.lang.RuntimeException: java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException: EC AlgorithmParameters not availableat sun.security.ssl.Alerts.getSSLException(Alerts.java:208)at sun.security.ssl.SSLSocketImpl.fatal(SSLSocketImpl.java:1949)at sun.security.ssl.SSLSocketImpl.fatal(SSLSocketImpl.java:1906)at sun.security.ssl.SSLSocketImpl.handleException(SSLSocketImpl.java:1889)at sun.security.ssl.SSLSocketImpl.startHandshake(SSLSocketImpl.java:1410)at sun.security.ssl.SSLSocketImpl.startHandshake(SSLSocketImpl.java:1387)at org.apache.http.conn.ssl.SSLConnectionSocketFactory.createLayeredSocket(SSLConnectionSocketFactory.java:275)at org.apache.http.conn.ssl.SSLConnectionSocketFactory.connectSocket(SSLConnectionSocketFactory.java:254)at org.apache.http.impl.conn.HttpClientConnectionOperator.connect(HttpClientConnectionOperator.java:117)at org.apache.http.impl.conn.PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager.connect(PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager.java:314)at org.apache.http.impl.execchain.MainClientExec.establishRoute(MainClientExec.java:363)at org.apache.http.impl.execchain.MainClientExec.execute(MainClientExec.java:219)at org.apache.http.impl.execchain.ProtocolExec.execute(ProtocolExec.java:195)at org.apache.http.impl.execchain.RetryExec.execute(RetryExec.java:86)at org.apache.http.impl.execchain.RedirectExec.execute(RedirectExec.java:108)at org.apache.http.impl.client.InternalHttpClient.doExecute(InternalHttpClient.java:186)at org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient.execute(CloseableHttpClient.java:82)at org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient.execute(CloseableHttpClient.java:106)at com.gome.loginFront.web.controller.quicklogin.weapp.service.WeAppLoginService.doGet(WeAppLoginService.java:130)at com.gome.loginFront.web.controller.quicklogin.weapp.service.WeAppLoginService.doWeAppLogin(WeAppLoginService.java:53)at com.gome.loginFront.web.controller.quicklogin.weapp.WeAppLoginController.weAppLogin(WeAppLoginController.java:166)at sun.reflect.GeneratedMethodAccessor182.invoke(Unknown Source)at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43)at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:498)at org.springframework.web.method.support.InvocableHandlerMethod.invoke(InvocableHandlerMethod.java:219)at org.springframework.web.method.support.InvocableHandlerMethod.invokeForRequest(InvocableHandlerMethod.java:132)at org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ServletInvocableHandlerMethod.invokeAndHandle(ServletInvocableHandlerMethod.java:100)at org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.invokeHandlerMethod(RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.java:604)at org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.handleInternal(RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.java:565)at org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter.handle(AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter.java:80)at org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.doDispatch(DispatcherServlet.java:923)at org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.doService(DispatcherServlet.java:852)at org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.processRequest(FrameworkServlet.java:882)at org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.doGet(FrameworkServlet.java:778)at javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet.service(HttpServlet.java:635)at javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet.service(HttpServlet.java:742)at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.internalDoFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:231)at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.doFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:166)at org.apache.tomcat.websocket.server.WsFilter.doFilter(WsFilter.java:52)at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.internalDoFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:193)at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.doFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:166)--at org.apache.tomcat.util.threads.TaskThread$WrappingRunnable.run(TaskThread.java:61)at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:745)Caused by: java.lang.RuntimeException: java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException: EC AlgorithmParameters not availableat sun.security.util.ECUtil.getECParameters(ECUtil.java:100)at sun.security.util.ECUtil.getECParameterSpec(ECUtil.java:149)at sun.security.ssl.JsseJce.getECParameterSpec(JsseJce.java:385)at sun.security.ssl.HandshakeMessage$ECDH_ServerKeyExchange.<init>(HandshakeMessage.java:1067)at sun.security.ssl.ClientHandshaker.processMessage(ClientHandshaker.java:284)at sun.security.ssl.Handshaker.processLoop(Handshaker.java:979)at sun.security.ssl.Handshaker.process_record(Handshaker.java:914)at sun.security.ssl.SSLSocketImpl.readRecord(SSLSocketImpl.java:1062)at sun.security.ssl.SSLSocketImpl.performInitialHandshake(SSLSocketImpl.java:1375)at sun.security.ssl.SSLSocketImpl.startHandshake(SSLSocketImpl.java:1403)... 80 common frames omittedCaused by: java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException: EC AlgorithmParameters not availableat sun.security.jca.GetInstance.getInstance(GetInstance.java:159)at java.security.Security.getImpl(Security.java:695)at java.security.AlgorithmParameters.getInstance(AlgorithmParameters.java:146)at sun.security.util.ECUtil.getECParameters(ECUtil.java:98)... 89 common frames omitted
当时看到这个异常的时候有点蒙圈,毕竟是jdk底层的问题,当时第一时间就是去问度娘,不问还好,一问给整歪了,问度娘:EC AlgorithmParameters not available,这个问题的答案只有几条,但是后N-1条要么是抄第一条的,要么就是翻译第一条的,然后就一直怀疑是JDK版本的问题,就让运维换JDK7,但是依旧不行,然后就怀疑网络部是不是有啥限制,因为是在发送https请求底层socket握手的时候报的错,但是curl接口https://api.weixin.qq.com/sns/jscode2session?grant_type=authorization_code后发现没问题,也就很快推翻了这个可能,然后就是十一假期,回家happy,回来之后决定再重头捋一遍,不问度娘,自己啃,终于解决。
二、解决过程
分析异常信息可以发现,报的错的文件是java.security,就去看看这个文件里是什么东西,打开后发现(新服务器上的):
## This is the "master security properties file".## In this file, various security properties are set for use by# java.security classes. This is where users can statically register# Cryptography Package Providers ("providers" for short). The term# "provider" refers to a package or set of packages that supply a# concrete implementation of a subset of the cryptography aspects of# the Java Security API. A provider may, for example, implement one or# more digital signature algorithms or message digest algorithms.## Each provider must implement a subclass of the Provider class.# To register a provider in this master security properties file,# specify the Provider subclass name and priority in the format## security.provider.<n>=<className>## This declares a provider, and specifies its preference# order n. The preference order is the order in which providers are# searched for requested algorithms (when no specific provider is# requested). The order is 1-based; 1 is the most preferred, followed# by 2, and so on.## <className> must specify the subclass of the Provider class whose# constructor sets the values of various properties that are required# for the Java Security API to look up the algorithms or other# facilities implemented by the provider.## There must be at least one provider specification in java.security.# There is a default provider that comes standard with the JDK. It# is called the "SUN" provider, and its Provider subclass# named Sun appears in the sun.security.provider package. Thus, the# "SUN" provider is registered via the following:## security.provider.1=sun.security.provider.Sun## (The number 1 is used for the default provider.)## Note: Providers can be dynamically registered instead by calls to# either the addProvider or insertProviderAt method in the Security# class.## List of providers and their preference orders (see above):#security.provider.1=sun.security.provider.Sunsecurity.provider.2=sun.security.rsa.SunRsaSignsecurity.provider.3=com.sun.net.ssl.internal.ssl.Providersecurity.provider.4=com.sun.crypto.provider.SunJCEsecurity.provider.5=sun.security.jgss.SunProvidersecurity.provider.6=com.sun.security.sasl.Providersecurity.provider.7=org.jcp.xml.dsig.internal.dom.XMLDSigRIsecurity.provider.8=sun.security.smartcardio.SunPCSC## Select the source of seed data for SecureRandom. By default an# attempt is made to use the entropy gathering device specified by# the securerandom.source property. If an exception occurs when# accessing the URL then the traditional system/thread activity# algorithm is used.## On Solaris and Linux systems, if file:/dev/urandom is specified and it# exists, a special SecureRandom implementation is activated by default.# This "NativePRNG" reads random bytes directly from dev/urandom.## On Windows systems, the URLs file:/dev/random and file:/dev/urandom# enables use of the Microsoft CryptoAPI seed functionality.#securerandom.source=file:/dev/./urandom## The entropy gathering device is described as a URL and can also# be specified with the system property "java.security.egd". For example,# -Djava.security.egd=file:/dev/urandom# Specifying this system property will override the securerandom.source# setting.## Class to instantiate as the javax.security.auth.login.Configuration# provider.#login.configuration.provider=com.sun.security.auth.login.ConfigFile## Default login configuration file##login.config.url.1=file:${user.home}/.java.login.config## Class to instantiate as the system Policy. This is the name of the class# that will be used as the Policy object.#policy.provider=sun.security.provider.PolicyFile# The default is to have a single system-wide policy file,# and a policy file in the user's home directory.policy.url.1=file:${java.home}/lib/security/java.policypolicy.url.2=file:${user.home}/.java.policy# whether or not we expand properties in the policy file# if this is set to false, properties (${...}) will not be expanded in policy# files.policy.expandProperties=true# whether or not we allow an extra policy to be passed on the command line# with -Djava.security.policy=somefile. Comment out this line to disable# this feature.policy.allowSystemProperty=true# whether or not we look into the IdentityScope for trusted Identities# when encountering a 1.1 signed JAR file. If the identity is found# and is trusted, we grant it AllPermission.policy.ignoreIdentityScope=false## Default keystore type.#keystore.type=jks## Class to instantiate as the system scope:#system.scope=sun.security.provider.IdentityDatabase## List of comma-separated packages that start with or equal this string# will cause a security exception to be thrown when# passed to checkPackageAccess unless the# corresponding RuntimePermission ("accessClassInPackage."+package) has# been granted.package.access=sun.,com.sun.xml.internal.ws.,com.sun.xml.internal.bind.,com.sun.imageio.## List of comma-separated packages that start with or equal this string# will cause a security exception to be thrown when# passed to checkPackageDefinition unless the# corresponding RuntimePermission ("defineClassInPackage."+package) has# been granted.## by default, no packages are restricted for definition, and none of# the class loaders supplied with the JDK call checkPackageDefinition.##package.definition=## Determines whether this properties file can be appended to# or overridden on the command line via -Djava.security.properties#security.overridePropertiesFile=true## Determines the default key and trust manager factory algorithms for# the javax.net.ssl package.#ssl.KeyManagerFactory.algorithm=SunX509ssl.TrustManagerFactory.algorithm=PKIX## The Java-level namelookup cache policy for successful lookups:## any negative value: caching forever# any positive value: the number of seconds to cache an address for# zero: do not cache## default value is forever (FOREVER). For security reasons, this# caching is made forever when a security manager is set. When a security# manager is not set, the default behavior in this implementation# is to cache for 30 seconds.## NOTE: setting this to anything other than the default value can have# serious security implications. Do not set it unless# you are sure you are not exposed to DNS spoofing attack.##networkaddress.cache.ttl=-1# The Java-level namelookup cache policy for failed lookups:## any negative value: cache forever# any positive value: the number of seconds to cache negative lookup results# zero: do not cache## In some Microsoft Windows networking environments that employ# the WINS name service in addition to DNS, name service lookups# that fail may take a noticeably long time to return (approx. 5 seconds).# For this reason the default caching policy is to maintain these# results for 10 seconds.##networkaddress.cache.negative.ttl=10## Properties to configure OCSP for certificate revocation checking## Enable OCSP## By default, OCSP is not used for certificate revocation checking.# This property enables the use of OCSP when set to the value "true".## NOTE: SocketPermission is required to connect to an OCSP responder.## Example,# ocsp.enable=true## Location of the OCSP responder## By default, the location of the OCSP responder is determined implicitly# from the certificate being validated. This property explicitly specifies# the location of the OCSP responder. The property is used when the# Authority Information Access extension (defined in RFC 3280) is absent# from the certificate or when it requires overriding.## Example,# ocsp.responderURL=http://ocsp.example.net:80## Subject name of the OCSP responder's certificate## By default, the certificate of the OCSP responder is that of the issuer# of the certificate being validated. This property identifies the certificate# of the OCSP responder when the default does not apply. Its value is a string# distinguished name (defined in RFC 2253) which identifies a certificate in# the set of certificates supplied during cert path validation. In cases where# the subject name alone is not sufficient to uniquely identify the certificate# then both the "ocsp.responderCertIssuerName" and# "ocsp.responderCertSerialNumber" properties must be used instead. When this# property is set then those two properties are ignored.## Example,# ocsp.responderCertSubjectName="CN=OCSP Responder, O=XYZ Corp"## Issuer name of the OCSP responder's certificate## By default, the certificate of the OCSP responder is that of the issuer# of the certificate being validated. This property identifies the certificate# of the OCSP responder when the default does not apply. Its value is a string# distinguished name (defined in RFC 2253) which identifies a certificate in# the set of certificates supplied during cert path validation. When this# property is set then the "ocsp.responderCertSerialNumber" property must also# be set. When the "ocsp.responderCertSubjectName" property is set then this# property is ignored.## Example,# ocsp.responderCertIssuerName="CN=Enterprise CA, O=XYZ Corp"## Serial number of the OCSP responder's certificate## By default, the certificate of the OCSP responder is that of the issuer# of the certificate being validated. This property identifies the certificate# of the OCSP responder when the default does not apply. Its value is a string# of hexadecimal digits (colon or space separators may be present) which# identifies a certificate in the set of certificates supplied during cert path# validation. When this property is set then the "ocsp.responderCertIssuerName"# property must also be set. When the "ocsp.responderCertSubjectName" property# is set then this property is ignored.## Example,# ocsp.responderCertSerialNumber=2A:FF:00## Policy for failed Kerberos KDC lookups:## When a KDC is unavailable (network error, service failure, etc), it is# put inside a blacklist and accessed less often for future requests. The# value (case-insensitive) for this policy can be:## tryLast# KDCs in the blacklist are always tried after those not on the list.## tryLess[:max_retries,timeout]# KDCs in the blacklist are still tried by their order in the configuration,# but with smaller max_retries and timeout values. max_retries and timeout# are optional numerical parameters (default 1 and 5000, which means once# and 5 seconds). Please notes that if any of the values defined here is# more than what is defined in krb5.conf, it will be ignored.## Whenever a KDC is detected as available, it is removed from the blacklist.# The blacklist is reset when krb5.conf is reloaded. You can add# refreshKrb5Config=true to a JAAS configuration file so that krb5.conf is# reloaded whenever a JAAS authentication is attempted.## Example,# krb5.kdc.bad.policy = tryLast# krb5.kdc.bad.policy = tryLess:2,2000krb5.kdc.bad.policy = tryLast
看不懂,那就再看下老服务器上的对比下看看是否一样:
## This is the "master security properties file".## An alternate java.security properties file may be specified# from the command line via the system property## -Djava.security.properties=<URL>## This properties file appends to the master security properties file.# If both properties files specify values for the same key, the value# from the command-line properties file is selected, as it is the last# one loaded.## Also, if you specify## -Djava.security.properties==<URL> (2 equals),## then that properties file completely overrides the master security# properties file.## To disable the ability to specify an additional properties file from# the command line, set the key security.overridePropertiesFile# to false in the master security properties file. It is set to true# by default.# In this file, various security properties are set for use by# java.security classes. This is where users can statically register# Cryptography Package Providers ("providers" for short). The term# "provider" refers to a package or set of packages that supply a# concrete implementation of a subset of the cryptography aspects of# the Java Security API. A provider may, for example, implement one or# more digital signature algorithms or message digest algorithms.## Each provider must implement a subclass of the Provider class.# To register a provider in this master security properties file,# specify the Provider subclass name and priority in the format## security.provider.<n>=<className>## This declares a provider, and specifies its preference# order n. The preference order is the order in which providers are# searched for requested algorithms (when no specific provider is# requested). The order is 1-based; 1 is the most preferred, followed# by 2, and so on.## <className> must specify the subclass of the Provider class whose# constructor sets the values of various properties that are required# for the Java Security API to look up the algorithms or other# facilities implemented by the provider.## There must be at least one provider specification in java.security.# There is a default provider that comes standard with the JDK. It# is called the "SUN" provider, and its Provider subclass# named Sun appears in the sun.security.provider package. Thus, the# "SUN" provider is registered via the following:## security.provider.1=sun.security.provider.Sun## (The number 1 is used for the default provider.)## Note: Providers can be dynamically registered instead by calls to# either the addProvider or insertProviderAt method in the Security# class.## List of providers and their preference orders (see above):#security.provider.1=sun.security.provider.Sunsecurity.provider.2=sun.security.rsa.SunRsaSignsecurity.provider.3=sun.security.ec.SunECsecurity.provider.4=com.sun.net.ssl.internal.ssl.Providersecurity.provider.5=com.sun.crypto.provider.SunJCEsecurity.provider.6=sun.security.jgss.SunProvidersecurity.provider.7=com.sun.security.sasl.Providersecurity.provider.8=org.jcp.xml.dsig.internal.dom.XMLDSigRIsecurity.provider.9=sun.security.smartcardio.SunPCSC## Sun Provider SecureRandom seed source.## Select the primary source of seed data for the "SHA1PRNG" and# "NativePRNG" SecureRandom implementations in the "Sun" provider.# (Other SecureRandom implementations might also use this property.)## On Unix-like systems (for example, Solaris/Linux/MacOS), the# "NativePRNG" and "SHA1PRNG" implementations obtains seed data from# special device files such as file:/dev/random.## On Windows systems, specifying the URLs "file:/dev/random" or# "file:/dev/urandom" will enable the native Microsoft CryptoAPI seeding# mechanism for SHA1PRNG.## By default, an attempt is made to use the entropy gathering device# specified by the "securerandom.source" Security property. If an# exception occurs while accessing the specified URL:## SHA1PRNG:# the traditional system/thread activity algorithm will be used.## NativePRNG:# a default value of dev/random will be used. If neither# are available, the implementation will be disabled.# "file" is the only currently supported protocol type.## The entropy gathering device can also be specified with the System# property "java.security.egd". For example:## % java -Djava.security.egd=file:/dev/random MainClass## Specifying this System property will override the# "securerandom.source" Security property.## In addition, if "file:/dev/random" or "file:/dev/urandom" is# specified, the "NativePRNG" implementation will be more preferred than# SHA1PRNG in the Sun provider.#securerandom.source=file:/dev/random## A list of known strong SecureRandom implementations.## To help guide applications in selecting a suitable strong# java.security.SecureRandom implementation, Java distributions should# indicate a list of known strong implementations using the property.## This is a comma-separated list of algorithm and/or algorithm:provider# entries.#securerandom.strongAlgorithms=NativePRNGBlocking:SUN## Class to instantiate as the javax.security.auth.login.Configuration# provider.#login.configuration.provider=sun.security.provider.ConfigFile## Default login configuration file##login.config.url.1=file:${user.home}/.java.login.config## Class to instantiate as the system Policy. This is the name of the class# that will be used as the Policy object.#policy.provider=sun.security.provider.PolicyFile# The default is to have a single system-wide policy file,# and a policy file in the user's home directory.policy.url.1=file:${java.home}/lib/security/java.policypolicy.url.2=file:${user.home}/.java.policy# whether or not we expand properties in the policy file# if this is set to false, properties (${...}) will not be expanded in policy# files.policy.expandProperties=true# whether or not we allow an extra policy to be passed on the command line# with -Djava.security.policy=somefile. Comment out this line to disable# this feature.policy.allowSystemProperty=true# whether or not we look into the IdentityScope for trusted Identities# when encountering a 1.1 signed JAR file. If the identity is found# and is trusted, we grant it AllPermission.policy.ignoreIdentityScope=false## Default keystore type.#keystore.type=jks## Controls compatibility mode for the JKS keystore type.## When set to 'true', the JKS keystore type supports loading# keystore files in either JKS or PKCS12 format. When set to 'false'# it supports loading only JKS keystore files.#keystore.type.compat=true## List of comma-separated packages that start with or equal this string# will cause a security exception to be thrown when# passed to checkPackageAccess unless the# corresponding RuntimePermission ("accessClassInPackage."+package) has# been granted.package.access=sun.,\com.sun.xml.internal.,\com.sun.imageio.,\com.sun.istack.internal.,\com.sun.jmx.,\com.sun.media.sound.,\com.sun.naming.internal.,\com.sun.proxy.,\com.sun.corba.se.,\com.sun.org.apache.bcel.internal.,\com.sun.org.apache.regexp.internal.,\com.sun.org.apache.xerces.internal.,\com.sun.org.apache.xpath.internal.,\com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.extensions.,\com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.lib.,\com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.res.,\com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.templates.,\com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.utils.,\com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xslt.,\com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.cmdline.,\com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.compiler.,\com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.,\com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.util.,\com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.res.,\com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.security.,\com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.serializer.utils.,\com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.utils.,\com.sun.org.glassfish.,\com.oracle.xmlns.internal.,\com.oracle.webservices.internal.,\oracle.jrockit.jfr.,\org.jcp.xml.dsig.internal.,\jdk.internal.,\jdk.nashorn.internal.,\jdk.nashorn.tools.,\com.sun.activation.registries.,\com.sun.browser.,\com.sun.glass.,\com.sun.javafx.,\com.sun.media.,\com.sun.openpisces.,\com.sun.prism.,\com.sun.scenario.,\com.sun.t2k.,\com.sun.pisces.,\com.sun.webkit.,\jdk.management.resource.internal.## List of comma-separated packages that start with or equal this string# will cause a security exception to be thrown when# passed to checkPackageDefinition unless the# corresponding RuntimePermission ("defineClassInPackage."+package) has# been granted.## by default, none of the class loaders supplied with the JDK call# checkPackageDefinition.#package.definition=sun.,\com.sun.xml.internal.,\com.sun.imageio.,\com.sun.istack.internal.,\com.sun.jmx.,\com.sun.media.sound.,\com.sun.naming.internal.,\com.sun.proxy.,\com.sun.corba.se.,\com.sun.org.apache.bcel.internal.,\com.sun.org.apache.regexp.internal.,\com.sun.org.apache.xerces.internal.,\com.sun.org.apache.xpath.internal.,\com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.extensions.,\com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.lib.,\com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.res.,\com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.templates.,\com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.utils.,\com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xslt.,\com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.cmdline.,\com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.compiler.,\com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.,\com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.util.,\com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.res.,\com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.security.,\com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.serializer.utils.,\com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.utils.,\com.sun.org.glassfish.,\com.oracle.xmlns.internal.,\com.oracle.webservices.internal.,\oracle.jrockit.jfr.,\org.jcp.xml.dsig.internal.,\jdk.internal.,\jdk.nashorn.internal.,\jdk.nashorn.tools.,\com.sun.activation.registries.,\com.sun.browser.,\com.sun.glass.,\com.sun.javafx.,\com.sun.media.,\com.sun.openpisces.,\com.sun.prism.,\com.sun.scenario.,\com.sun.t2k.,\com.sun.pisces.,\com.sun.webkit.,\jdk.management.resource.internal.## Determines whether this properties file can be appended to# or overridden on the command line via -Djava.security.properties#security.overridePropertiesFile=true## Determines the default key and trust manager factory algorithms for# the javax.net.ssl package.#ssl.KeyManagerFactory.algorithm=SunX509ssl.TrustManagerFactory.algorithm=PKIX## The Java-level namelookup cache policy for successful lookups:## any negative value: caching forever# any positive value: the number of seconds to cache an address for# zero: do not cache## default value is forever (FOREVER). For security reasons, this# caching is made forever when a security manager is set. When a security# manager is not set, the default behavior in this implementation# is to cache for 30 seconds.## NOTE: setting this to anything other than the default value can have# serious security implications. Do not set it unless# you are sure you are not exposed to DNS spoofing attack.##networkaddress.cache.ttl=-1# The Java-level namelookup cache policy for failed lookups:## any negative value: cache forever# any positive value: the number of seconds to cache negative lookup results# zero: do not cache## In some Microsoft Windows networking environments that employ# the WINS name service in addition to DNS, name service lookups# that fail may take a noticeably long time to return (approx. 5 seconds).# For this reason the default caching policy is to maintain these# results for 10 seconds.##networkaddress.cache.negative.ttl=10## Properties to configure OCSP for certificate revocation checking## Enable OCSP## By default, OCSP is not used for certificate revocation checking.# This property enables the use of OCSP when set to the value "true".## NOTE: SocketPermission is required to connect to an OCSP responder.## Example,# ocsp.enable=true## Location of the OCSP responder## By default, the location of the OCSP responder is determined implicitly# from the certificate being validated. This property explicitly specifies# the location of the OCSP responder. The property is used when the# Authority Information Access extension (defined in RFC 3280) is absent# from the certificate or when it requires overriding.## Example,# ocsp.responderURL=http://ocsp.example.net:80## Subject name of the OCSP responder's certificate## By default, the certificate of the OCSP responder is that of the issuer# of the certificate being validated. This property identifies the certificate# of the OCSP responder when the default does not apply. Its value is a string# distinguished name (defined in RFC 2253) which identifies a certificate in# the set of certificates supplied during cert path validation. In cases where# the subject name alone is not sufficient to uniquely identify the certificate# then both the "ocsp.responderCertIssuerName" and# "ocsp.responderCertSerialNumber" properties must be used instead. When this# property is set then those two properties are ignored.## Example,# ocsp.responderCertSubjectName="CN=OCSP Responder, O=XYZ Corp"## Issuer name of the OCSP responder's certificate## By default, the certificate of the OCSP responder is that of the issuer# of the certificate being validated. This property identifies the certificate# of the OCSP responder when the default does not apply. Its value is a string# distinguished name (defined in RFC 2253) which identifies a certificate in# the set of certificates supplied during cert path validation. When this# property is set then the "ocsp.responderCertSerialNumber" property must also# be set. When the "ocsp.responderCertSubjectName" property is set then this# property is ignored.## Example,# ocsp.responderCertIssuerName="CN=Enterprise CA, O=XYZ Corp"## Serial number of the OCSP responder's certificate## By default, the certificate of the OCSP responder is that of the issuer# of the certificate being validated. This property identifies the certificate# of the OCSP responder when the default does not apply. Its value is a string# of hexadecimal digits (colon or space separators may be present) which# identifies a certificate in the set of certificates supplied during cert path# validation. When this property is set then the "ocsp.responderCertIssuerName"# property must also be set. When the "ocsp.responderCertSubjectName" property# is set then this property is ignored.## Example,# ocsp.responderCertSerialNumber=2A:FF:00## Policy for failed Kerberos KDC lookups:## When a KDC is unavailable (network error, service failure, etc), it is# put inside a blacklist and accessed less often for future requests. The# value (case-insensitive) for this policy can be:## tryLast# KDCs in the blacklist are always tried after those not on the list.## tryLess[:max_retries,timeout]# KDCs in the blacklist are still tried by their order in the configuration,# but with smaller max_retries and timeout values. max_retries and timeout# are optional numerical parameters (default 1 and 5000, which means once# and 5 seconds). Please notes that if any of the values defined here is# more than what is defined in krb5.conf, it will be ignored.## Whenever a KDC is detected as available, it is removed from the blacklist.# The blacklist is reset when krb5.conf is reloaded. You can add# refreshKrb5Config=true to a JAAS configuration file so that krb5.conf is# reloaded whenever a JAAS authentication is attempted.## Example,# krb5.kdc.bad.policy = tryLast# krb5.kdc.bad.policy = tryLess:2,2000krb5.kdc.bad.policy = tryLast# Algorithm restrictions for certification path (CertPath) processing## In some environments, certain algorithms or key lengths may be undesirable# for certification path building and validation. For example, "MD2" is# generally no longer considered to be a secure hash algorithm. This section# describes the mechanism for disabling algorithms based on algorithm name# and/or key length. This includes algorithms used in certificates, as well# as revocation information such as CRLs and signed OCSP Responses.## The syntax of the disabled algorithm string is described as this Java# BNF-style:# DisabledAlgorithms:# " DisabledAlgorithm { , DisabledAlgorithm } "## DisabledAlgorithm:# AlgorithmName [Constraint]## AlgorithmName:# (see below)## Constraint:# KeySizeConstraint## KeySizeConstraint:# keySize Operator DecimalInteger## Operator:# <= | < | == | != | >= | >## DecimalInteger:# DecimalDigits## DecimalDigits:# DecimalDigit {DecimalDigit}## DecimalDigit: one of# 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0## The "AlgorithmName" is the standard algorithm name of the disabled# algorithm. See "Java Cryptography Architecture Standard Algorithm Name# Documentation" for information about Standard Algorithm Names. Matching# is performed using a case-insensitive sub-element matching rule. (For# example, in "SHA1withECDSA" the sub-elements are "SHA1" for hashing and# "ECDSA" for signatures.) If the assertion "AlgorithmName" is a# sub-element of the certificate algorithm name, the algorithm will be# rejected during certification path building and validation. For example,# the assertion algorithm name "DSA" will disable all certificate algorithms# that rely on DSA, such as NONEwithDSA, SHA1withDSA. However, the assertion# will not disable algorithms related to "ECDSA".## A "Constraint" provides further guidance for the algorithm being specified.# The "KeySizeConstraint" requires a key of a valid size range if the# "AlgorithmName" is of a key algorithm. The "DecimalInteger" indicates the# key size specified in number of bits. For example, "RSA keySize <= 1024"# indicates that any RSA key with key size less than or equal to 1024 bits# should be disabled, and "RSA keySize < 1024, RSA keySize > 2048" indicates# that any RSA key with key size less than 1024 or greater than 2048 should# be disabled. Note that the "KeySizeConstraint" only makes sense to key# algorithms.## Note: This property is currently used by Oracle's PKIX implementation. It# is not guaranteed to be examined and used by other implementations.## Example:# jdk.certpath.disabledAlgorithms=MD2, DSA, RSA keySize < 2048##jdk.certpath.disabledAlgorithms=MD2, MD5, RSA keySize < 1024# Algorithm restrictions for Secure Socket Layer/Transport Layer Security# (SSL/TLS) processing## In some environments, certain algorithms or key lengths may be undesirable# when using SSL/TLS. This section describes the mechanism for disabling# algorithms during SSL/TLS security parameters negotiation, including# protocol version negotiation, cipher suites selection, peer authentication# and key exchange mechanisms.## Disabled algorithms will not be negotiated for SSL/TLS connections, even# if they are enabled explicitly in an application.## For PKI-based peer authentication and key exchange mechanisms, this list# of disabled algorithms will also be checked during certification path# building and validation, including algorithms used in certificates, as# well as revocation information such as CRLs and signed OCSP Responses.# This is in addition to the jdk.certpath.disabledAlgorithms property above.## See the specification of "jdk.certpath.disabledAlgorithms" for the# syntax of the disabled algorithm string.## Note: This property is currently used by Oracle's JSSE implementation.# It is not guaranteed to be examined and used by other implementations.## Example:# jdk.tls.disabledAlgorithms=MD5, SSLv3, DSA, RSA keySize < 2048jdk.tls.disabledAlgorithms=SSLv3, RC4, MD5withRSA, DH keySize < 768# Legacy algorithms for Secure Socket Layer/Transport Layer Security (SSL/TLS)# processing in JSSE implementation.## In some environments, a certain algorithm may be undesirable but it# cannot be disabled because of its use in legacy applications. Legacy# algorithms may still be supported, but applications should not use them# as the security strength of legacy algorithms are usually not strong enough# in practice.## During SSL/TLS security parameters negotiation, legacy algorithms will# not be negotiated unless there are no other candidates.## The syntax of the disabled algorithm string is described as this Java# BNF-style:# LegacyAlgorithms:# " LegacyAlgorithm { , LegacyAlgorithm } "## LegacyAlgorithm:# AlgorithmName (standard JSSE algorithm name)## See the specification of security property "jdk.certpath.disabledAlgorithms"# for the syntax and description of the "AlgorithmName" notation.## Per SSL/TLS specifications, cipher suites have the form:# SSL_KeyExchangeAlg_WITH_CipherAlg_MacAlg# or# TLS_KeyExchangeAlg_WITH_CipherAlg_MacAlg## For example, the cipher suite TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA uses RSA as the# key exchange algorithm, AES_128_CBC (128 bits AES cipher algorithm in CBC# mode) as the cipher (encryption) algorithm, and SHA-1 as the message digest# algorithm for HMAC.## The LegacyAlgorithm can be one of the following standard algorithm names:# 1. JSSE cipher suite name, e.g., TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA# 2. JSSE key exchange algorithm name, e.g., RSA# 3. JSSE cipher (encryption) algorithm name, e.g., AES_128_CBC# 4. JSSE message digest algorithm name, e.g., SHA## See SSL/TLS specifications and "Java Cryptography Architecture Standard# Algorithm Name Documentation" for information about the algorithm names.## Note: This property is currently used by Oracle's JSSE implementation.# It is not guaranteed to be examined and used by other implementations.# There is no guarantee the property will continue to exist or be of the# same syntax in future releases.## Example:# jdk.tls.legacyAlgorithms=DH_anon, DES_CBC, SSL_RSA_WITH_RC4_128_MD5#jdk.tls.legacyAlgorithms= \K_NULL, C_NULL, M_NULL, \DHE_DSS_EXPORT, DHE_RSA_EXPORT, DH_anon_EXPORT, DH_DSS_EXPORT, \DH_RSA_EXPORT, RSA_EXPORT, \DH_anon, ECDH_anon, \RC4_128, RC4_40, DES_CBC, DES40_CBC# The pre-defined default finite field Diffie-Hellman ephemeral (DHE)# parameters for Transport Layer Security (SSL/TLS/DTLS) processing.## In traditional SSL/TLS/DTLS connections where finite field DHE parameters# negotiation mechanism is not used, the server offers the client group# parameters, base generator g and prime modulus p, for DHE key exchange.# It is recommended to use dynamic group parameters. This property defines# a mechanism that allows you to specify custom group parameters.## The syntax of this property string is described as this Java BNF-style:# DefaultDHEParameters:# DefinedDHEParameters { , DefinedDHEParameters }## DefinedDHEParameters:# "{" DHEPrimeModulus , DHEBaseGenerator "}"## DHEPrimeModulus:# HexadecimalDigits## DHEBaseGenerator:# HexadecimalDigits## HexadecimalDigits:# HexadecimalDigit { HexadecimalDigit }## HexadecimalDigit: one of# 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F a b c d e f## Whitespace characters are ignored.## The "DefinedDHEParameters" defines the custom group parameters, prime# modulus p and base generator g, for a particular size of prime modulus p.# The "DHEPrimeModulus" defines the hexadecimal prime modulus p, and the# "DHEBaseGenerator" defines the hexadecimal base generator g of a group# parameter. It is recommended to use safe primes for the custom group# parameters.## If this property is not defined or the value is empty, the underlying JSSE# provider's default group parameter is used for each connection.## If the property value does not follow the grammar, or a particular group# parameter is not valid, the connection will fall back and use the# underlying JSSE provider's default group parameter.## Note: This property is currently used by OpenJDK's JSSE implementation. It# is not guaranteed to be examined and used by other implementations.## Example:# jdk.tls.server.defaultDHEParameters=# { \# FFFFFFFF FFFFFFFF C90FDAA2 2168C234 C4C6628B 80DC1CD1 \# 29024E08 8A67CC74 020BBEA6 3B139B22 514A0879 8E3404DD \# EF9519B3 CD3A431B 302B0A6D F25F1437 4FE1356D 6D51C245 \# E485B576 625E7EC6 F44C42E9 A637ED6B 0BFF5CB6 F406B7ED \# EE386BFB 5A899FA5 AE9F2411 7C4B1FE6 49286651 ECE65381 \# FFFFFFFF FFFFFFFF, 2}
WTF!虽然我看不懂,但是这里面的内容明显不一样,然后又对比了一下大小:
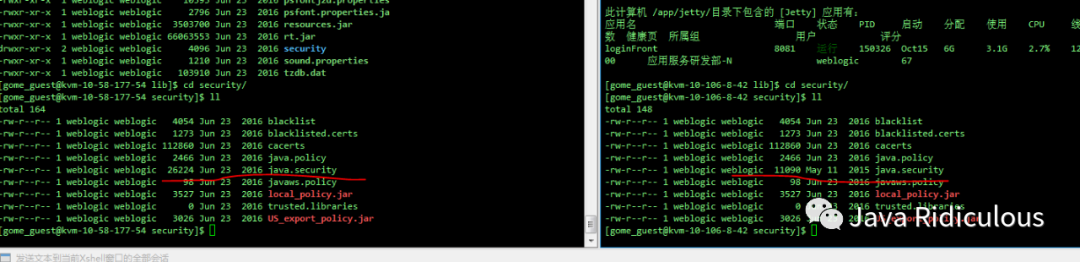
然后赶紧找运维同事重新安装了下jdk后解决~~
三、总结(重要)
发生异常不要第一时间去百度上找答案,很容易走歪路,静下心来分析异常信息,定位异常信息的位置,逐步分析其实很容易发现问题所在,就像这次异常,本来很简单的一个问题,结果搞了好几天。






