AWS ALB Ingress Controller
设计原理
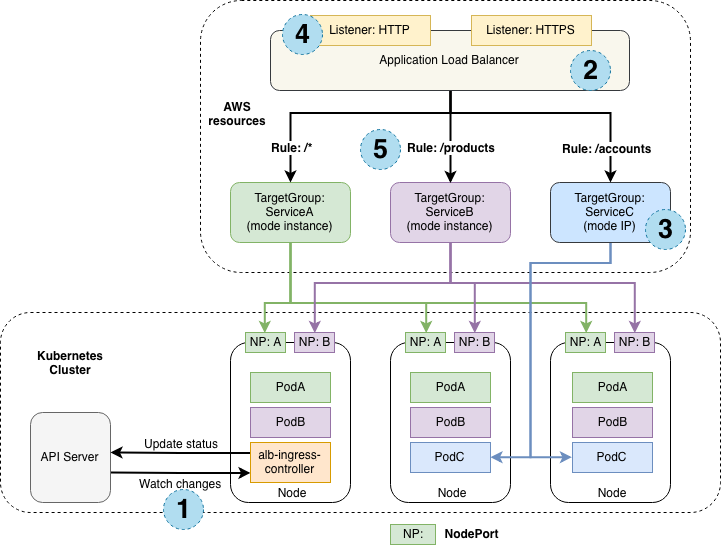
控制器监视来自API服务器的入口事件。当发现满足其要求的Ingress 资源时,它将开始创建AWS资源。
在AWS中为新的当发现满足其要求的Ingress资源创建了一个 ALB(ELBv2)。该ALB可以面向互联网或内部。您也可以使用annotations指定其创建的子网
在AWS中为Ingress资源中描述的每个唯一的Kubernetes服务创建目标组。
为Ingress资源注释中详细说明的每个端口创建侦听器。如果未指定端口,则使用合理的默认值(80或443)。证书也可以通过注释附加。
为Ingress资源中指定的每个路径创建规则。这样可以确保将到特定路径的流量路由到正确的Kubernetes服务。
除了上述内容外,控制器还可以
从k8s中删除Ingress资源后,将删除AWS组件。
当Ingress资源在k8s中更改时,修改AWS组件。
在启动时会组装一个与现有与Ingress相关的现有AWS组件的列表,使您可以恢复是否要重新启动控制器。
Ingress流量
ALB Ingress控制器支持两种流量模式:
Instance
IP
默认情况下,Instance mode使用,用户可以通过 alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/target-type 选择模式。
Instance
Ingress流量从ALB开始,并通过每个服务的NodePort到达Kubernetes节点。这意味着从Ingress资源引用的服务必须公开,以便ALB能够访问。type:NodePort
IP
Ingress流量从ALB开始,直接到达Kubernetes窗格。CNI必须通过ENI上的辅助IP地址支持可直接访问的POD ip
部署ALB控制器
部署RBAC权限
kubectl apply -f rbac.yaml
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: alb-ingress-controller
name: alb-ingress-controller
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
- extensions
resources:
- configmaps
- endpoints
- events
- ingresses
- ingresses/status
- services
verbs:
- create
- get
- list
- update
- watch
- patch
- apiGroups:
- ""
- extensions
resources:
- nodes
- pods
- secrets
- services
- namespaces
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: alb-ingress-controller
name: alb-ingress-controller
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: alb-ingress-controller
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: alb-ingress-controller
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: alb-ingress-controller
name: alb-ingress-controller
namespace: kube-system
部署deployment
kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml
# Application Load Balancer (ALB) Ingress Controller Deployment Manifest.
# This manifest details sensible defaults for deploying an ALB Ingress Controller.
# GitHub: https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/aws-alb-ingress-controller
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: alb-ingress-controller
name: alb-ingress-controller
# Namespace the ALB Ingress Controller should run in. Does not impact which
# namespaces it's able to resolve ingress resource for. For limiting ingress
# namespace scope, see --watch-namespace.
namespace: kube-system
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: alb-ingress-controller
template:
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: alb-ingress-controller
spec:
containers:
- name: alb-ingress-controller
args:
- --ingress-class=alb
- --cluster-name=xxx # cluster name
- --aws-vpc-id=vpc-xxx # vpc-id
- --aws-region=xx # cluster region
# Enables logging on all outbound requests sent to the AWS API.
# If logging is desired, set to true.
# - --aws-api-debug
# Maximum number of times to retry the aws calls.
# defaults to 10.
# - --aws-max-retries=10
# env:
# AWS key id for authenticating with the AWS API.
# This is only here for examples. It's recommended you instead use
# a project like kube2iam for granting access.
#- name: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
# value: KEYVALUE
# AWS key secret for authenticating with the AWS API.
# This is only here for examples. It's recommended you instead use
# a project like kube2iam for granting access.
#- name: AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
# value: SECRETVALUE
# Repository location of the ALB Ingress Controller.
image: docker.io/amazon/aws-alb-ingress-controller:v1.1.4
serviceAccountName: alb-ingress-controller
部署一个2048测试一下alb
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: "2048-game"
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: "2048-deployment"
namespace: "2048-game"
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: "2048"
replicas: 5
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: "2048"
spec:
containers:
- image: alexwhen/docker-2048
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: "2048"
ports:
- containerPort: 80
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: "service-2048"
namespace: "2048-game"
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
protocol: TCP
type: NodePort
selector:
app: "2048"
---
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: "2048-ingress"
namespace: "2048-game"
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: alb
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme: internet-facing
labels:
app: 2048-ingress
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /*
backend:
serviceName: "service-2048"
servicePort: 80
部署成功了以后,查询alb 的负载均衡器
kubectl get ingress/2048-ingress -n 2048-game
NAME HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
2048-ingress * example-2048game-2048ingr-6fa0-352729433.region-code.elb.amazonaws.com 80 24h
等待 alb状态为active 时 访问地址example-2048game-2048ingr-6fa0-352729433.region-code.elb.amazonaws.com 就可以玩2048了
aws-alb-ingress-controller 配置详解
查看
https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/aws-alb-ingress-controller/guide/ingress/annotation/ 官方文档
说一下我常用的配置
kind: Ingress
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
metadata:
name: test-prod-ingress
namespace: test-prod
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: alb
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme: internet-facing # 外网ALB
#alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme: internal # 内网ALB
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-ports: '[{"HTTPS":443}]' # ALB 开放端口
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/certificate-arn: arn:aws:acm:xxxcertificate/xxx # ALB证书arn
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/target-type: ip # ALB模式ip或者instance
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: HTTP # ALB连接后端的协议
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-path: /heartbeat # 后端心跳地址,如果心跳不正常,那么ALB会随便选择一个目标组的机器发送流量
external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/hostname: xxx.xxx.com # 这个是通过external-dns 进行r53 域名管理的方法
labels:
k8s-app: test-prod-ingress
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /1*
backend:
serviceName: test-1-service
servicePort: 30000
- path: /2*
backend:
serviceName: test-2-service
servicePort: 30000
部署external-dns 管理Route53
如果我们的域名用了AWS 的Route53进行管理,那么我们可以通过一个插件external-dns 来对Route53进行管理
部署external-dns
创建一个IAM权限
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"route53:ChangeResourceRecordSets"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:route53:::hostedzone/*"
]
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"route53:ListHostedZones",
"route53:ListResourceRecordSets"
],
"Resource": [
"*"
]
}
]
}
可以附加大的IAM(目前来说external-dns无法删除R53的name记录,所以给最小的就可以 )
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"route53:*"
],
"Resource": [
"*"
]
}
]
}
列出 OIDC issuer URL
aws eks describe-cluster --name <cluster name> --query "cluster.identity.oidc.issuer" --output text
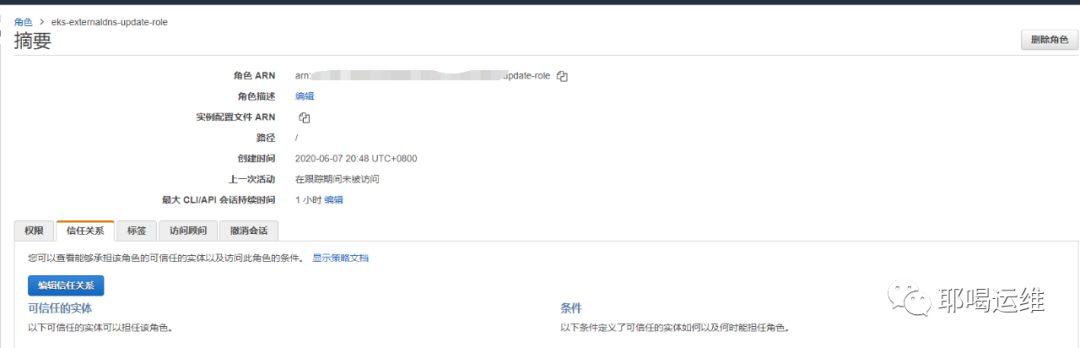
创建角色(role)并且把IAM附加给这个角色
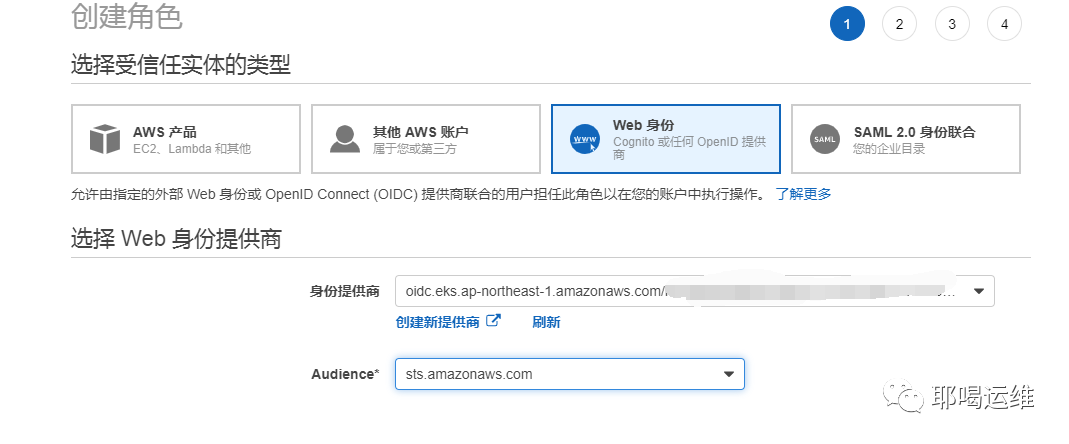
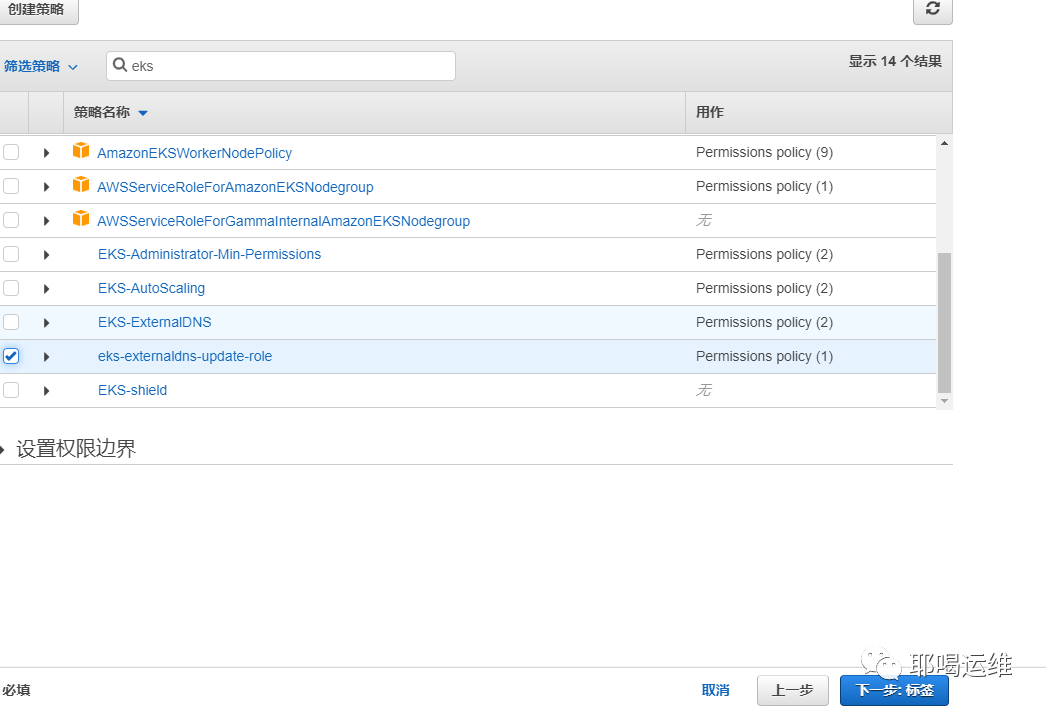
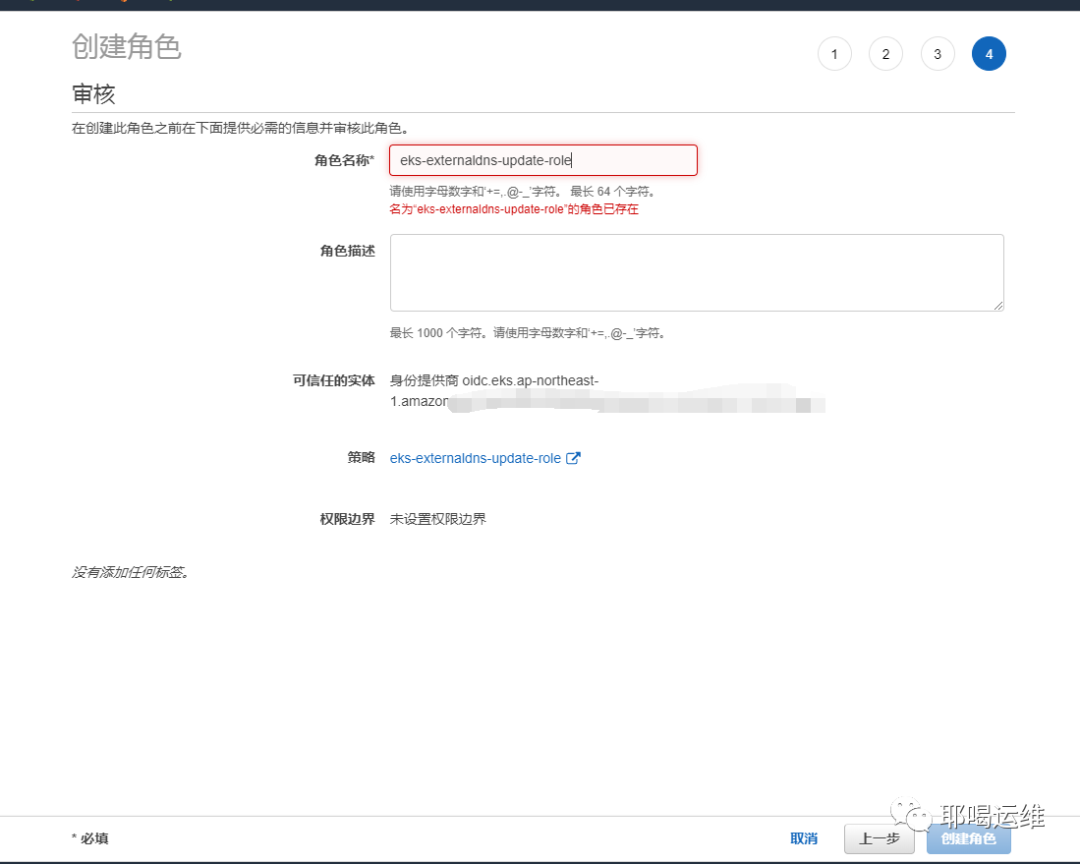
编辑信任关系,并记录ROLE的ARN 地址
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: external-dns
namespace: kube-system
# If you're using Amazon EKS with IAM Roles for Service Accounts, specify the following annotation.
# Otherwise, you may safely omit it.
annotations:
# Substitute your account ID and IAM service role name below.
eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn: arn:aws:iam::xxx:role/xxxxxxx
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: external-dns
namespace: kube-system
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["services","endpoints","pods"]
verbs: ["get","watch","list"]
- apiGroups: ["extensions"]
resources: ["ingresses"]
verbs: ["get","watch","list"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["nodes"]
verbs: ["list","watch"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: external-dns-viewer
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: external-dns
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: external-dns
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: external-dns
namespace: kube-system
spec:
strategy:
type: Recreate
selector:
matchLabels:
app: external-dns
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: external-dns
# If you're using kiam or kube2iam, specify the following annotation.
# Otherwise, you may safely omit it.
annotations:
iam.amazonaws.com/role: arn:aws:iam::xxx:role/xxxxxxx
spec:
serviceAccountName: external-dns
containers:
- name: external-dns
image: registry.opensource.zalan.do/teapot/external-dns:latest
args:
- --source=service
- --source=ingress
# - --domain-filter=nuclearport.com # will make ExternalDNS see only the hosted zones matching provided domain, omit to process all available hosted zones
- --provider=aws
- --policy=upsert-only # would prevent ExternalDNS from deleting any records, omit to enable full synchronization
- --aws-zone-type=public # only look at public hosted zones (valid values are public, private or no value for both)
- --registry=txt
- --txt-owner-id=my-hostedzone-identifier
securityContext:
fsGroup: 65534 # For ExternalDNS to be able to read Kubernetes and AWS token files
tolerations:
- key: "uessystem"
value: "true"
effect: "NoSchedule"
我们用上一个2048的项目测试R53是否生效
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: "2048-ingress"
namespace: "2048-game"
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: alb
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme: internet-facing
external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/hostname: testyehe.xxx.com
labels:
app: 2048-ingress
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /*
backend:
serviceName: "service-2048"
servicePort: 80
监控日志
kubectl logs deployment.apps/external-dns -n kube-system -f
当日志出现
CREATE testyehe.xxx.com A [Id: /hostedzone/xxx]"
time="2020-06-07T13:13:01Z" level=info msg="Desired change: CREATE testyehe.xxx.com TXT [Id: /hostedzone/xxx]"
现在,ALB+R53 已经部署完毕
接下来我们会说一下如何在EKS上使用autoscaler来进行worker节点的动态扩容,并且实现从0开始的动态扩容







