单点故障:NameNode 仅有一个,不支持高可用,一旦 NameNode 所在点节点出现故障,整个 HDFS 就无法提供服务
内存受限:单个 NameNode 的内存有限,当集群规模达到一定程度,单个 NameNode 的内存将无法满足元数据的存储需求
所以从 Hadoop 2.x 版本开始,引入了联邦机制来解决内存受限问题;而针对 NameNode 单点故障的问题,则开始支持高可用(HA),具体的原理如下:
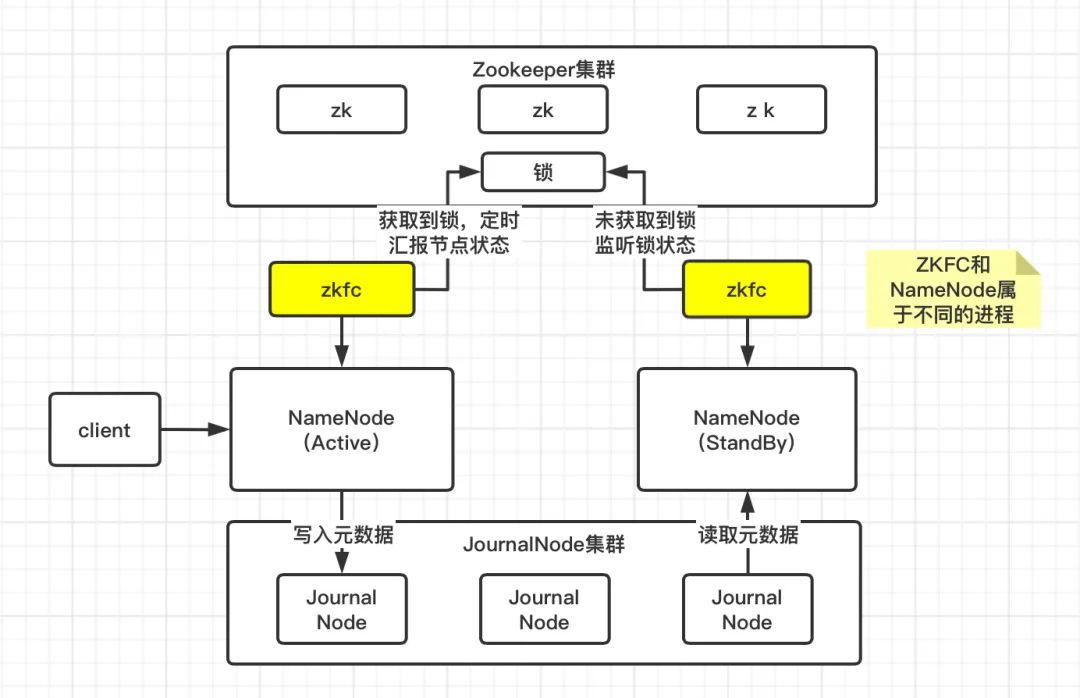
既然 StandBy 状态的 NN 要作为热备节点,那么它的元数据信息必须和 Active 状态的 NN 保持一致。Active 状态的 NN 在更新元数据时,除了会更新本地内存中的元数据信息,同时会将元数据信息写入 JournalNode 集群,而 JournalNode 集群本身具备高可用。之后 StandBy 状态的 NN 从 JournalNode 集群拉取元数据信息并更新自身的状态,从而和 Active 状态的 NN 保持元数据一致。
元数据管理流程
更新本地内存中的元数据信息 将操作日志写入本地磁盘 将操作日志写入 JournalNode 集群 StandBy 状态的 NameNode 拉取 JournalNode 集群中的元数据信息进行同步
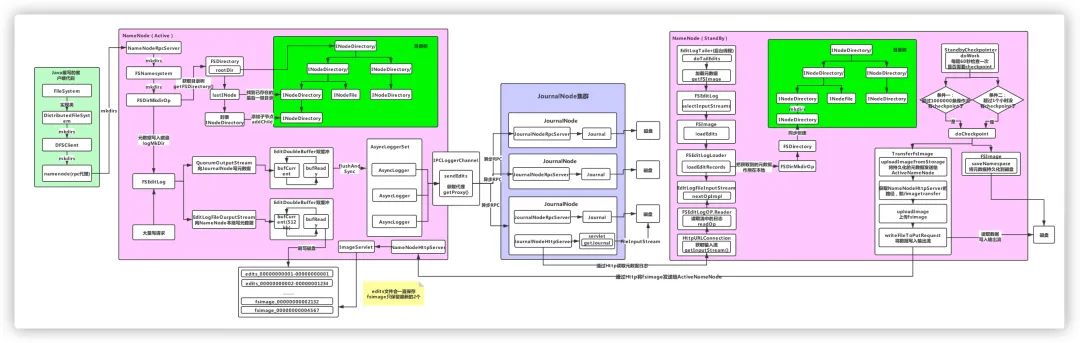
(后台回复HDFS,获取高清流程图)
由于整个流程相对复杂,我们分多篇来进行分析,这篇主要分析 NameNode 如何更新本地内存中的元数据信息。
在编写客户端代码时,通过调用 FileSystem 对象的 mkdirs() 方法来创建目录。这里的 FileSystem 是一个抽象类,如果是 Local 模式,其实例是 LocalFileSystem 对象;如果是分布式模式,其实例是 DistributedFileSystem 对象,这里我们只研究分布式模式。
public boolean mkdirs(String src, FsPermission masked, boolean createParent)throws IOException {//检查NN已启动checkNNStartup();if(stateChangeLog.isDebugEnabled()) {stateChangeLog.debug("*DIR* NameNode.mkdirs: " + src);}//检查给定目录名称的长度if (!checkPathLength(src)) {throw new IOException("mkdirs: Pathname too long. Limit "+ MAX_PATH_LENGTH + " characters, " + MAX_PATH_DEPTH + " levels.");}//TODO 这里的namesystem就是目录树对象,用来管理HDFS目录,创建目录实际调用的是FSNameSystem的mkdirs方法return namesystem.mkdirs(src,new PermissionStatus(getRemoteUser().getShortUserName(),null, masked), createParent);}
boolean mkdirs(String src, PermissionStatus permissions,boolean createParent) throws IOException {HdfsFileStatus auditStat = null;checkOperation(OperationCategory.WRITE);writeLock();try {//操作权限验证checkOperation(OperationCategory.WRITE);//安全模式验证,如果处于安全模式则无法创建checkNameNodeSafeMode("Cannot create directory " + src);//TODO 创建目录auditStat = FSDirMkdirOp.mkdirs(this, src, permissions, createParent);} catch (AccessControlException e) {logAuditEvent(false, "mkdirs", src);throw e;} finally {writeUnlock();}//TODO 元数据日志持久化getEditLog().logSync();logAuditEvent(true, "mkdirs", src, null, auditStat);return true;}
获取写锁
进行安全验证,如操作权限验证及安全模式验证
调用 FSDirMkdirOp.mkdirs() 方法创建目录并写入操作日志
将元数据操作日志持久化到磁盘(NN本地磁盘和JournalNode磁盘),这里将操作日志持久化到磁盘的过程就用到了上篇中提到的双缓冲机制
创建目录:
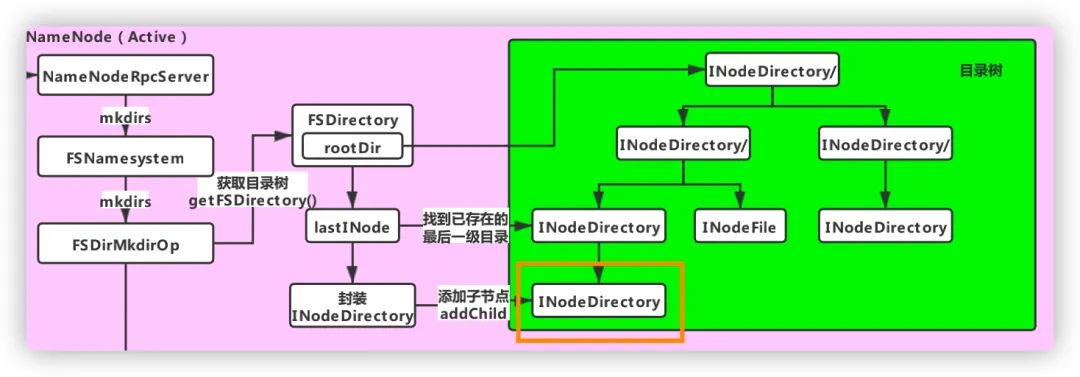
FSDirMkdirOp.mkdirs() 方法
static HdfsFileStatus mkdirs(FSNamesystem fsn, String src,PermissionStatus permissions, boolean createParent) throws IOException {//TODO 获取当前的目录树结构FSDirectory fsd = fsn.getFSDirectory();if(NameNode.stateChangeLog.isDebugEnabled()) {NameNode.stateChangeLog.debug("DIR* NameSystem.mkdirs: " + src);}//验证路径是否有效if (!DFSUtil.isValidName(src)) {throw new InvalidPathException(src);}FSPermissionChecker pc = fsd.getPermissionChecker();byte[][] pathComponents = FSDirectory.getPathComponentsForReservedPath(src);fsd.writeLock();try {//对传入对路径参数进行规范化src = fsd.resolvePath(pc, src, pathComponents);INodesInPath iip = fsd.getINodesInPath4Write(src);if (fsd.isPermissionEnabled()) {fsd.checkTraverse(pc, iip);}//TODO 比如我们现在已经存在的目录是/user/hive/warehouse,要在它下面创建/data/mytable// lastINode就是找到最后一级目录,即 mytablefinal INode lastINode = iip.getLastINode();if (lastINode != null && lastINode.isFile()) {throw new FileAlreadyExistsException("Path is not a directory: " + src);}INodesInPath existing = lastINode != null ? iip : iip.getExistingINodes();if (lastINode == null) {if (fsd.isPermissionEnabled()) {fsd.checkAncestorAccess(pc, iip, FsAction.WRITE);}if (!createParent) {fsd.verifyParentDir(iip, src);}fsn.checkFsObjectLimit();//TODO 假设已存在/user/hive/warehouse// 要创建/user/hive/warehouse/data/mytable目录// 则需要创建的目录就是/data/mytable nonExisting就是需要创建的多级目录,// 即/user/hive/warehouse/data 和 user/hive/warehouse/data/mytableList<String> nonExisting = iip.getPath(existing.length(),iip.length() - existing.length());int length = nonExisting.size();//TODO 如果要创建的目录层级大于1,走这里if (length > 1) {List<String> ancestors = nonExisting.subList(0, length - 1);existing = createChildrenDirectories(fsd, existing, ancestors,addImplicitUwx(permissions, permissions));if (existing == null) {throw new IOException("Failed to create directory: " + src);}}//TODO 如果只有一级目录则走这里if ((existing = createChildrenDirectories(fsd, existing,nonExisting.subList(length - 1, length), permissions)) == null) {throw new IOException("Failed to create directory: " + src);}}return fsd.getAuditFileInfo(existing);} finally {fsd.writeUnlock();}}
获取目录树结构 验证传入的路径是否有效 对路径参数进行规范化 找到待创建的最后一级目录 找到不存在的目录(可能有多级) 根据是否存在多级目录,走不同的分支,但最终都是调用了 createChildrenDirectories() 方法来创建目录
private static INodesInPath createChildrenDirectories(FSDirectory fsd,INodesInPath existing, List<String> children, PermissionStatus perm)throws IOException {assert fsd.hasWriteLock();//TODO 一级一级去创建for (String component : children) {existing = createSingleDirectory(fsd, existing, component, perm);if (existing == null) {return null;}}return existing;}
//创建单个目录private static INodesInPath createSingleDirectory(FSDirectory fsd,INodesInPath existing, String localName, PermissionStatus perm)throws IOException {assert fsd.hasWriteLock();//TODO 更新文件目录树,这棵目录树是存在于内存中的,由FSNamesystem管理的existing = unprotectedMkdir(fsd, fsd.allocateNewInodeId(), existing,localName.getBytes(Charsets.UTF_8), perm, null, now());if (existing == null) {return null;}final INode newNode = existing.getLastINode();NameNode.getNameNodeMetrics().incrFilesCreated();String cur = existing.getPath();//TODO 将创建目录的操作日志写入EditLogfsd.getEditLog().logMkDir(cur, newNode);if (NameNode.stateChangeLog.isDebugEnabled()) {NameNode.stateChangeLog.debug("mkdirs: created directory " + cur);}return existing;}
更新内存中的目录树
将操作日志写入EditLog
private static INodesInPath unprotectedMkdir(FSDirectory fsd, long inodeId,INodesInPath parent, byte[] name, PermissionStatus permission,List<AclEntry> aclEntries, long timestamp)throws QuotaExceededException, AclException, FileAlreadyExistsException {assert fsd.hasWriteLock();assert parent.getLastINode() != null;if (!parent.getLastINode().isDirectory()) {throw new FileAlreadyExistsException("Parent path is not a directory: " +parent.getPath() + " " + DFSUtil.bytes2String(name));}//TODO 封装成一个目录final INodeDirectory dir = new INodeDirectory(inodeId, name, permission,timestamp);//TODO 往文件目录树添加该目录节点INodesInPath iip = fsd.addLastINode(parent, dir, true);if (iip != null && aclEntries != null) {AclStorage.updateINodeAcl(dir, aclEntries, Snapshot.CURRENT_STATE_ID);}return iip;}
(2)将操作日志写入EditLog:调用的是 FSEditLog.logMkDir() 方法
public void logMkDir(String path, INode newNode) {PermissionStatus permissions = newNode.getPermissionStatus();//TODO 创建日志对象MkdirOp op = MkdirOp.getInstance(cache.get()).setInodeId(newNode.getId()).setPath(path).setTimestamp(newNode.getModificationTime()).setPermissionStatus(permissions);AclFeature f = newNode.getAclFeature();if (f != null) {op.setAclEntries(AclStorage.readINodeLogicalAcl(newNode));}XAttrFeature x = newNode.getXAttrFeature();if (x != null) {op.setXAttrs(x.getXAttrs());}//TODO 记录日志,这里只是将操作日志写内存,具体刷写磁盘是由logSync()方法执行的logEdit(op);}






