启动 HttpServer,对外开放 50070 端口 启动 RPCServer,对外开放 9000 端口 加载元数据信息到内存 启动公共服务:包括资源监测,安全模式检查,块管理、心跳管理等服务
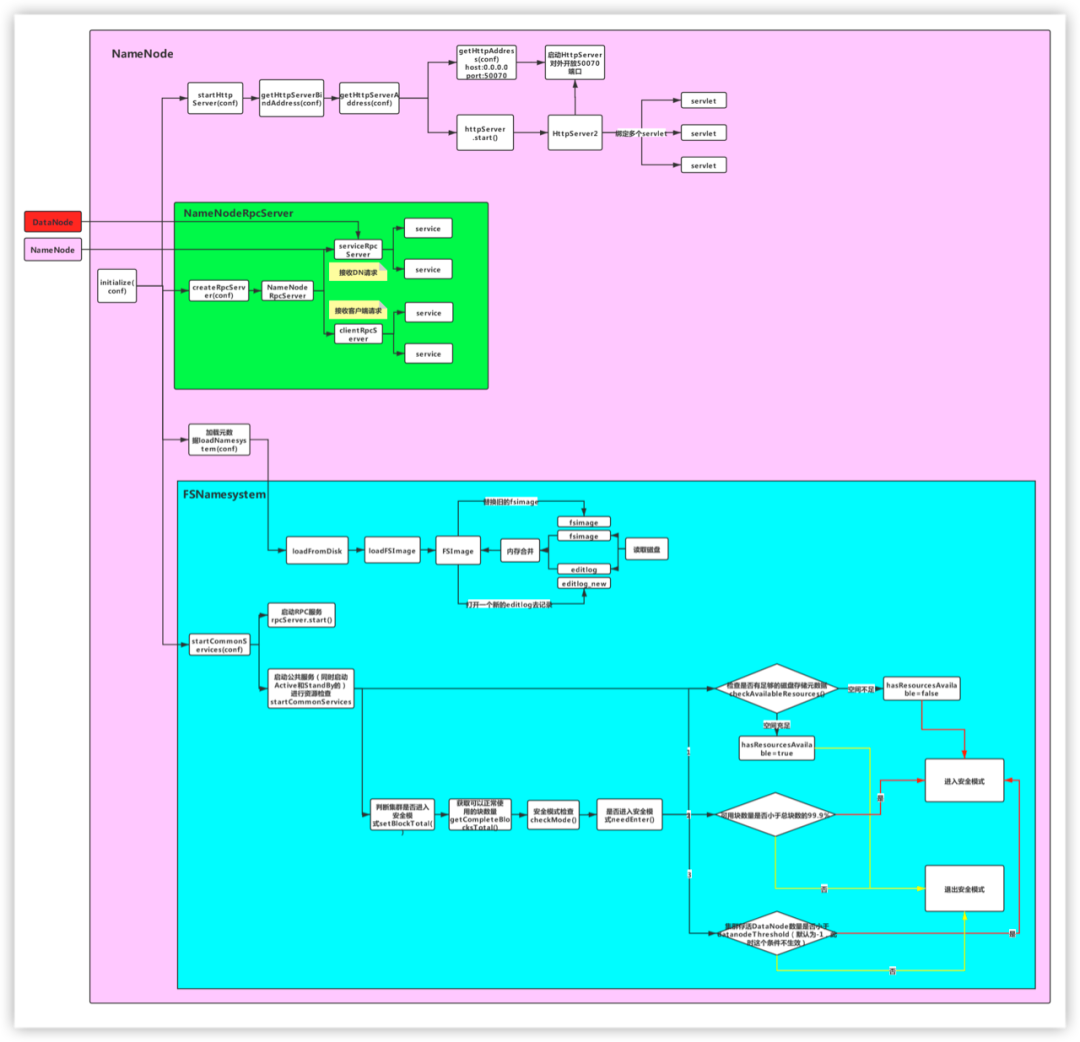
对于 NameNode,首先需要重点关注该类的注释信息:
* NameNode serves as both directory namespace manager and* "inode table" for the Hadoop DFS. There is a single NameNode* running in any DFS deployment. (Well, except when there* is a second backup/failover NameNode, or when using federated NameNodes.)* NameNode服务既管理了HDFS集群的命名空间(即目录树),同时管理了一个inode table* 一个集群只有一个NameNode(除了HA和联邦)** The NameNode controls two critical tables: NameNode维护了两张表* 1) filename->blocksequence (namespace) 文件和文件块的关系* 2) block->machinelist ("inodes") 文件块和节点的关系** The first table is stored on disk and is very precious.* 第一张表存在磁盘(因为一个文件的切块情况是固定的,不会发生变化)* The second table is rebuilt every time the NameNode comes up.* 第二张表存在内存(文件块和节点的对应关系可能发生变化,比如进行负载均衡)** 'NameNode' refers to both this class as well as the 'NameNode server'.* The 'FSNamesystem' class actually performs most of the filesystem* management. The majority of the 'NameNode' class itself is concerned* with exposing the IPC interface and the HTTP server to the outside world,* plus some configuration management.** NameNode服务由三个重要的类支撑:* 1)NameNode:管理配置的参数 hdfs-site.xml core-site.xml* 2)NameNode server* RPC Server:* NameNodeRPCServer:开放端口,等待别人调用,比如:8020/9000* HTTP Server* NameNodeHttpServer:开放50070界面,我们可以通过这个界面了解HDFS的情况* 3)FSNameSystem:管理了HDFS的元数据(目录树的信息)
NameNode服务既管理了HDFS集群的命名空间(即目录树),同时管理了一个inode table,一个集群只有一个NameNode(除了HA和联邦)
NameNode维护了两张表:
文件和文件块的关系,这张表存在磁盘,因为一个文件的切块情况是固定的
文件块和节点的关系,这张表存在内存,因为文件块和节点的对应关系可能发生变化,如执行 start-balancer.sh 脚本进行负载均衡
NameNode服务有三个重要的类支撑:
NameNode:管理配置的参数,通过 hdfs-site.xml 、core-site.xml配置文件配置
NameNodeServer,包括:
RPC Server:RPC服务,开放端口等到其它服务调用,如8020、9000端口
HTTP Server:HTTP服务,开放50070端口,通过该端口可以在页面查看集群情况
FSNameSystem:管理了HDFS的元数据(目录树信息)
解析参数
通过createNameNode()方法创建NameNode实例对象
public static void main(String argv[]) throws Exception {//解析参数if (DFSUtil.parseHelpArgument(argv, NameNode.USAGE, System.out, true)) {//参数异常退出System.exit(0);}try {StringUtils.startupShutdownMessage(NameNode.class, argv, LOG);//TODO 创建NameNode的核心代码//RPC的服务端NameNode namenode = createNameNode(argv, null);if (namenode != null) {namenode.join();}} catch (Throwable e) {LOG.error("Failed to start namenode.", e);terminate(1, e);}}
执行createNameNode方法
在该方法中,首先会解析argv参数,然后根据解析结果执行不同的switch-case分支,这里重点看default分支,返回一个 NameNode 对象
public static NameNode createNameNode(String argv[], Configuration conf)throws IOException {LOG.info("createNameNode " + Arrays.asList(argv));if (conf == null)conf = new HdfsConfiguration();/*** 解析参数:我们操作HDFS的时候会传进来如下的参数:* hdfs namenode -format* hadoop-deamon.sh start namenode*/StartupOption startOpt = parseArguments(argv);if (startOpt == null) {printUsage(System.err);return null;}setStartupOption(conf, startOpt);//根据具体参数类型进行处理switch (startOpt) {...default: {//初始化指标监控系统DefaultMetricsSystem.initialize("NameNode");//TODO 关键代码return new NameNode(conf);}}
执行NameNode的构造方法:
主要执行了 initialize() 方法
protected NameNode(Configuration conf, NamenodeRole role)throws IOException {...try {initializeGenericKeys(conf, nsId, namenodeId);//分析源码的时候,初始化的方法一定要留意//TODO 初始化的方法initialize(conf);try {haContext.writeLock();state.prepareToEnterState(haContext);state.enterState(haContext);} finally {haContext.writeUnlock();}}...this.started.set(true);}
1.启动HttpServer服务
对应流程图中的如下部分:
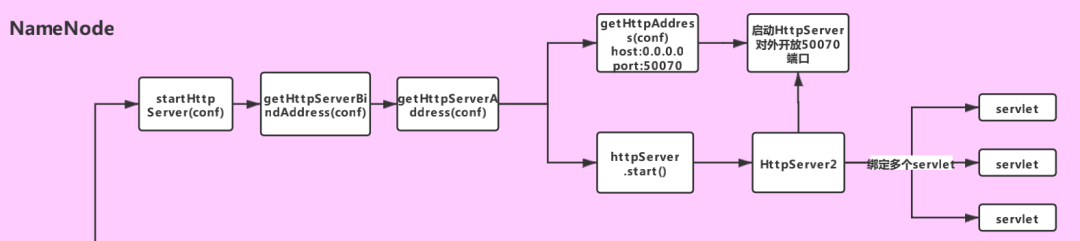
if (NamenodeRole.NAMENODE == role) {//TODO 步骤一:启动HttpServer,开放50070端口startHttpServer(conf);}
private void startHttpServer(final Configuration conf) throws IOException {//TODO 里面设置了主机名和端口号httpServer = new NameNodeHttpServer(conf, this, getHttpServerBindAddress(conf));httpServer.start();httpServer.setStartupProgress(startupProgress);}
在 start() 方法中,给HttpServer2对象绑定了一堆servlet(其中HttpServer2是Hadoop对HttpServer的封装)
//TODO 绑定一堆servlet// servlet就是一个规范,servlet必须放到容器里面才能和客户端交互,而这里的HttpServer2就是servlet容器setupServlets(httpServer, conf);//TODO 启动HttpServer2,对外开放50070端口httpServer.start();
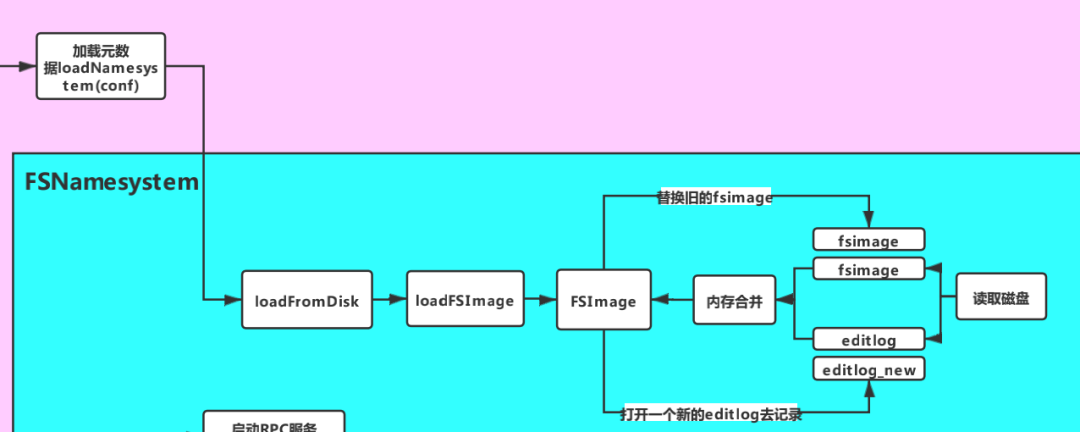
//TODO 步骤二:加载元数据loadNamesystem(conf);
方法内部调用了 loadFromDisk 方法,其中主要执行了 loadFSImage 方法
static FSNamesystem loadFromDisk(Configuration conf) throws IOException {...try {//TODO 加载元数据,读取fsimage,并执行editlognamesystem.loadFSImage(startOpt);} catch (IOException ioe) {LOG.warn("Encountered exception loading fsimage", ioe);fsImage.close();throw ioe;}...return namesystem;}
loadFSImage 方法
private void loadFSImage(StartupOption startOpt) throws IOException {final FSImage fsImage = getFSImage();if (startOpt == StartupOption.FORMAT) {fsImage.format(this, fsImage.getStorage().determineClusterId());startOpt = StartupOption.REGULAR;}boolean success = false;//获取写锁writeLock();try {MetaRecoveryContext recovery = startOpt.createRecoveryContext();final boolean staleImage//TODO (1)合并元数据//fsImage+editLog=new fsImage= fsImage.recoverTransitionRead(startOpt, this, recovery);if (RollingUpgradeStartupOption.ROLLBACK.matches(startOpt) ||RollingUpgradeStartupOption.DOWNGRADE.matches(startOpt)) {rollingUpgradeInfo = null;}final boolean needToSave = staleImage && !haEnabled && !isRollingUpgrade();LOG.info("Need to save fs image? " + needToSave+ " (staleImage=" + staleImage + ", haEnabled=" + haEnabled+ ", isRollingUpgrade=" + isRollingUpgrade() + ")");if (needToSave) {//TODO (2)把合并出来的fsimage文件写到磁盘文件fsImage.saveNamespace(this);} else {updateStorageVersionForRollingUpgrade(fsImage.getLayoutVersion(),startOpt);// No need to save, so mark the phase done.StartupProgress prog = NameNode.getStartupProgress();prog.beginPhase(Phase.SAVING_CHECKPOINT);prog.endPhase(Phase.SAVING_CHECKPOINT);}if (!haEnabled || (haEnabled && startOpt == StartupOption.UPGRADE)|| (haEnabled && startOpt == StartupOption.UPGRADEONLY)) {//TODO (3)打开一个新的editLog记录操作日志fsImage.openEditLogForWrite();}success = true;} finally {if (!success) {fsImage.close();}writeUnlock();}imageLoadComplete();}
该方法主要做了以下三件事:
合并磁盘文件中的 FsImage 和 EditLog,合并后会生成新的 FsImage
如果合并完成,且未启动HA,且不处于滚动升级状态,则将合并生成的 FsImage 持久化到磁盘文件
打开一个新的 EditLog 用于记录合并之后的操作日志
3.初始化RpcServer对象
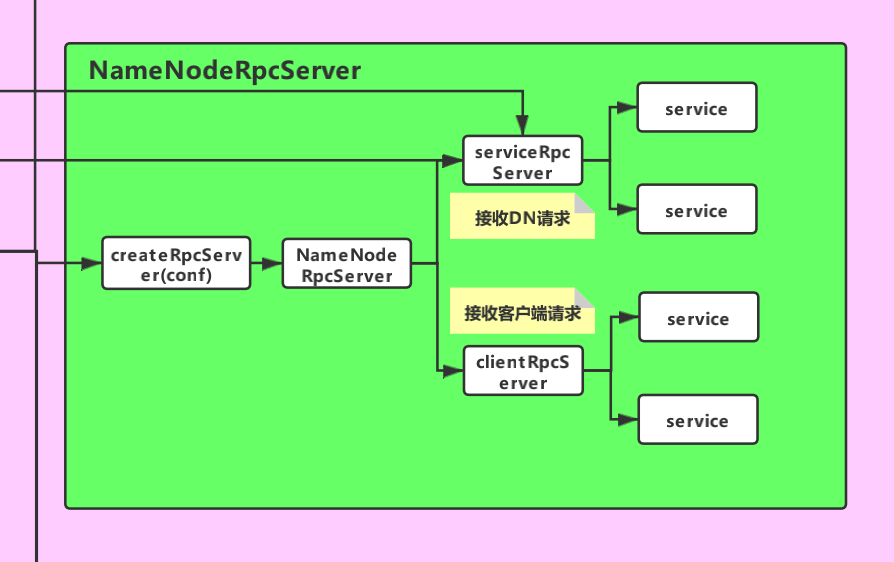
//TODO 重要!!这个就是Hadoop RPC,rpcServer就是Hadoop RPC服务端对象rpcServer = createRpcServer(conf);
//TODO 通过建造者模式来初始化serviceRpcServer 和 clientRpcServer// 注意:这里只是进行了初始化,还没有启动// 这个服务就是用来监听DataNode发送过来的请求的this.serviceRpcServer = new RPC.Builder(conf).setProtocol(org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.protocolPB.ClientNamenodeProtocolPB.class).setInstance(clientNNPbService).setBindAddress(bindHost).setPort(serviceRpcAddr.getPort()).setNumHandlers(serviceHandlerCount).setVerbose(false).setSecretManager(namesystem.getDelegationTokenSecretManager()).build();...// 这个服务用来监听Client发送过来的请求this.clientRpcServer = new RPC.Builder(conf).setProtocol(org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.protocolPB.ClientNamenodeProtocolPB.class).setInstance(clientNNPbService).setBindAddress(bindHost).setPort(rpcAddr.getPort()).setNumHandlers(handlerCount).setVerbose(false).setSecretManager(namesystem.getDelegationTokenSecretManager()).build();
4.启动公共服务
进行资源的监测,检查是否有足够的磁盘空间存储元数据 进入安全模式检查,检查是否可以退出安全模式 启动RPC服务的服务端 rpcServer
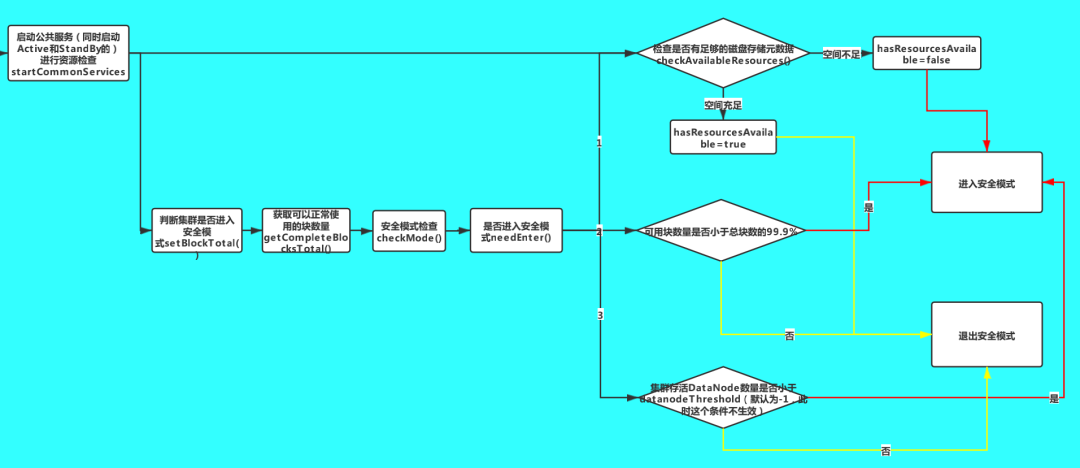
//TODO 启动一些公共服务,NameNode RPC的服务就是在这里面启动的// (1)进行资源监测,检查是否有足够的磁盘空间存储元数据// (2)进入安全模式检查,检查是否可以退出安全模式startCommonServices(conf);
NameNode.startCommonServices(conf) 方法,
调用了FSNamesystem.startCommonServices 方法
调用了rpcServer.start() 方法启动 RPC 服务端
private void startCommonServices(Configuration conf) throws IOException {//TODO 启动公共服务,进行资源检查namesystem.startCommonServices(conf, haContext);registerNNSMXBean();if (NamenodeRole.NAMENODE != role) {startHttpServer(conf);httpServer.setNameNodeAddress(getNameNodeAddress());httpServer.setFSImage(getFSImage());}//TODO 启动RPC服务rpcServer.start();plugins = conf.getInstances(DFS_NAMENODE_PLUGINS_KEY,ServicePlugin.class);for (ServicePlugin p: plugins) {try {p.start(this);} catch (Throwable t) {LOG.warn("ServicePlugin " + p + " could not be started", t);}}...}
这里重点看一下 FSNamesystem.startCommonServices 方法,该方法会同时启动Active和StandBy状态的NameNode的公共服务
获取资源检查对象
检查各个目录是否有足够的空间存储元数据
HDFS安全模式检查
启动其它重要服务
void startCommonServices(Configuration conf, HAContext haContext) throws IOException {this.registerMBean(); // register the MBean for the FSNamesystemState//获取写锁writeLock();this.haContext = haContext;try {/*** NameNode资源检查,通过core-site.xml,hdfs-site.xml两个文件,就知道了元数据保存在哪儿。* 加载配置文件,配置文件里面有存储元数据的目录* NameNode的两个目录,存储fsimage的目录和存储editLog的目录* 一般情况下,默认这两个目录是一个目录*/nnResourceChecker = new NameNodeResourceChecker(conf);//TODO 检查是否有足够的磁盘空间存储元数据checkAvailableResources();assert safeMode != null && !isPopulatingReplQueues();StartupProgress prog = NameNode.getStartupProgress();prog.beginPhase(Phase.SAFEMODE);prog.setTotal(Phase.SAFEMODE, STEP_AWAITING_REPORTED_BLOCKS,getCompleteBlocksTotal());//getCompleteBlocksTotal() 计算可以正常使用的块数量//TODO HDFS的安全模式setBlockTotal();//TODO 启动其它重要服务blockManager.activate(conf);} finally {//释放写锁writeUnlock();}registerMXBean();DefaultMetricsSystem.instance().register(this);if (inodeAttributeProvider != null) {inodeAttributeProvider.start();dir.setINodeAttributeProvider(inodeAttributeProvider);}snapshotManager.registerMXBean();}
a.获取资源检查对象:
nnResourceChecker = new NameNodeResourceChecker(conf);
public NameNodeResourceChecker(Configuration conf) throws IOException {this.conf = conf;volumes = new HashMap<String, CheckedVolume>();//NameNode服务器上面的多个目录,到底应该监测哪些目录?//TODO 资源阈值,通过dfs.namenode.resource.du.reserved 参数配置,默认是100MduReserved = conf.getLong(DFSConfigKeys.DFS_NAMENODE_DU_RESERVED_KEY,DFSConfigKeys.DFS_NAMENODE_DU_RESERVED_DEFAULT);//获取需要额外监控的目录,通过dfs.namenode.resource.checked.volumes参数配置Collection<URI> extraCheckedVolumes = Util.stringCollectionAsURIs(conf.getTrimmedStringCollection(DFSConfigKeys.DFS_NAMENODE_CHECKED_VOLUMES_KEY));//获取需要监控资源的目录,也就是FsImage和EditLog的存放目录Collection<URI> localEditDirs = Collections2.filter(FSNamesystem.getNamespaceEditsDirs(conf),new Predicate<URI>() {@Overridepublic boolean apply(URI input) {if (input.getScheme().equals(NNStorage.LOCAL_URI_SCHEME)) {return true;}return false;}});//TODO 将需要监控的EditLog和FsImage磁盘目录放入volumes集合// localEditDirs -> core-site.xml,hdfs-site.xmlfor (URI editsDirToCheck : localEditDirs) {//对指定目录进行监控addDirToCheck(editsDirToCheck,FSNamesystem.getRequiredNamespaceEditsDirs(conf).contains(editsDirToCheck));}//将额外需要监控的目录放入volumes集合for (URI extraDirToCheck : extraCheckedVolumes) {addDirToCheck(extraDirToCheck, true);}minimumRedundantVolumes = conf.getInt(//参数dfs.namenode.resource.checked.volumes.minimum,所需的冗余namenode存储卷的最小数量。DFSConfigKeys.DFS_NAMENODE_CHECKED_VOLUMES_MINIMUM_KEY,DFSConfigKeys.DFS_NAMENODE_CHECKED_VOLUMES_MINIMUM_DEFAULT);//默认为1}
在构造方法中,通过调用 addDirToCheck方法,将所有需要检查的目录(主要是保存FsImage和EditLog的目录)都放入了 volumes 变量中,该变量是一个Map<String,CheckedVolume>集合
private void addDirToCheck(URI directoryToCheck, boolean required)throws IOException {File dir = new File(directoryToCheck.getPath());if (!dir.exists()) {throw new IOException("Missing directory "+dir.getAbsolutePath());}//一个目录对应一个CheckedVolume对象CheckedVolume newVolume = new CheckedVolume(dir, required);CheckedVolume volume = volumes.get(newVolume.getVolume());if (volume == null || !volume.isRequired()) {//将多个目录保存到volumes(Map)里面volumes.put(newVolume.getVolume(), newVolume);}}
b.检查各个目录是否有足够的空间
//TODO 检查是否有足够的磁盘空间存储元数据checkAvailableResources();
void checkAvailableResources() {Preconditions.checkState(nnResourceChecker != null,"nnResourceChecker not initialized");//检查是否有足够的磁盘空间,如果空间不足则hasResourcesAvailable为falsehasResourcesAvailable = nnResourceChecker.hasAvailableDiskSpace();}
如果空间不足,hasResourcesAvailable 变量的值为 false,否则为 true。后面在安全模式的检查中会用到这个变量。
static boolean areResourcesAvailable(Collection<? extends CheckableNameNodeResource> resources,int minimumRedundantResources) {...//遍历每一个目录for (CheckableNameNodeResource resource : resources) {...//TODO 判断磁盘资源是否充足,如果空间不足返回falseif (!resource.isResourceAvailable()) {return false;}}}if (redundantResourceCount == 0) {return requiredResourceCount > 0;} else {return redundantResourceCount - disabledRedundantResourceCount >=minimumRedundantResources;}}
c.HDFS安全模式检查
//TODO HDFS的安全模式setBlockTotal();
public void setBlockTotal() {// safeMode is volatile, and may be set to null at any timeSafeModeInfo safeMode = this.safeMode;if (safeMode == null)return;//TODO 设置安全模式safeMode.setBlockTotal((int)getCompleteBlocksTotal());}
其中,getCompleteBlocksTotal 方法用来获取Complete状态的块数量,在HDFS中,块状态有两种:
complete:正常可用的block
underconstuction:正在构建的block,不可用
setBlockTotal 方法
private synchronized void setBlockTotal(int total) {this.blockTotal = total;//正常的块数量//TODO 计算阈值// threshold默认为 0.999f,即阈值是block总数的99.9%,只有正常block的数量达到这个阈值,才能退出安全模式this.blockThreshold = (int) (blockTotal * threshold);this.blockReplQueueThreshold =(int) (blockTotal * replQueueThreshold);if (haEnabled) {this.shouldIncrementallyTrackBlocks = true;}if(blockSafe < 0)this.blockSafe = 0;//TODO 检查安全模式checkMode();}
checkMode 方法
private void checkMode() {//确认持有写锁assert hasWriteLock();if (inTransitionToActive()) {return;}//TODO 判断是否进入安全模式if (smmthread == null && needEnter()) {//TODO 进入安全模式enter();if (canInitializeReplQueues() && !isPopulatingReplQueues()&& !haEnabled) {initializeReplQueues();}reportStatus("STATE* Safe mode ON.", false);return;}if (!isOn() || // safe mode is offextension <= 0 || threshold <= 0) { // don't need to waitthis.leave(); // leave safe modereturn;}if (reached > 0) { // threshold has already been reached beforereportStatus("STATE* Safe mode ON.", false);return;}// start monitorreached = monotonicNow();reachedTimestamp = now();if (smmthread == null) {smmthread = new Daemon(new SafeModeMonitor());smmthread.start();reportStatus("STATE* Safe mode extension entered.", true);}if (canInitializeReplQueues() && !isPopulatingReplQueues() && !haEnabled) {initializeReplQueues();}}
这里通过 needEnter() 方法判断是否进入安全模式
private boolean needEnter() {/*** TODO 进入安全模式的三个条件:* (1)threshold!=0且DataNode已经汇报的block的数量(blockSafe)小于阈值(block总数的99.9%)* (2)集群存活的DataNode数量小于datanodeThreshold;datanodeThreshold默认为0,这个条件默认不生效,只有配置了该参数不为0才会生效* (3)监控的保存元数据的目录资源不足(存放fsimage和editLog的目录)*/return (threshold != 0 && blockSafe < blockThreshold) ||(datanodeThreshold != 0 && getNumLiveDataNodes() < datanodeThreshold) || //datanodeThreshold默认值为0(!nameNodeHasResourcesAvailable());}
当满足三个条件之一时,就会进入安全模式:
threshold!=0 且 DataNode已经汇报的block的数量小于阈值(block总数的99.9%)
集群存活的DataNode数量小于datanodeThreshold;datanodeThreshold默认为0,这个条件默认不生效,只有配置了该参数不为0才会生效
监控的保存元数据的目录资源不足(存放fsimage和editLog的目录)
//TODO 启动文件块管理服务blockManager.activate(conf);
public void activate(Configuration conf) {//启动等待块复制的线程pendingReplications.start();//TODO 启动了管理DataNode心跳的服务datanodeManager.activate(conf);this.replicationThread.start();}
启动 HttpServer,对外开放 50070 端口 启动 RPCServer,对外开放 9000 端口 加载元数据信息到内存 启动公共服务:包括资源监测,安全模式检查,块管理、心跳管理等服务
hreshold!=0 且 DataNode已经汇报的block的数量小于阈值(block总数的99.9%) 集群存活的DataNode数量小于datanodeThreshold;datanodeThreshold默认为0,这个条件默认不生效,只有配置了该参数不为0才会生效 监控的保存元数据的目录资源不足(存放fsimage和editLog的目录)






