一、场景分析
羊群效应:Zookeeper 中被监听的节点发生变化,大量的 Watcher 通知被发送到客户端,导致在通知期间的其他操作被延迟,也可能发生类似死锁的情况。
脑裂问题:消费者组进行 Rebalance 操作时每个消费者都与 Zookeeper 进行通信以判断消费者或 Broker 变化的情况,由于 Zookeeper 本身的特性,可能导致同一时刻各个消费者获取的状态不一致,这样会导致异常。
二、图示说明
三、源码分析
class GroupMetadataManager(brokerId: Int,//当前节点idinterBrokerProtocolVersion: ApiVersion,//Broker端参数inter.broker.protocol.version值config: OffsetConfig,//内部位移主题的配置类replicaManager: ReplicaManager,//副本管理器对象zkClient: KafkaZkClient,//zk客户端对象time: Time//时间工具类) extends Logging with KafkaMetricsGroup {//位移主题消息的压缩格式private val compressionType: CompressionType = CompressionType.forId(config.offsetsTopicCompressionCodec.codec)//消费组元数据缓存,key是消费组group.id,value是组元数据对象private val groupMetadataCache = new Pool[String, GroupMetadata]private val partitionLock = new ReentrantLock()// 位移主题下正在执行加载操作的分区private val loadingPartitions: mutable.Set[Int] = mutable.Set()// 位移主题下完成加载操作的分区private val ownedPartitions: mutable.Set[Int] = mutable.Set()private val shuttingDown = new AtomicBoolean(false)// 位移主题总分区数,默认为50private val groupMetadataTopicPartitionCount = getGroupMetadataTopicPartitionCount//初始化一个调度器private val scheduler = new KafkaScheduler(threads = 1, threadNamePrefix = "group-metadata-manager-")...}
重点介绍下面几个变量:
groupMetadataCache:管理的所有消费者组的元数据,key表示消费者组id,即消费者指定的 group.id 参数;value 是 GroupMetadata 类型,表示该消费者组的元数据信息对象。这个变量是 GroupMetadataManager 中最重要的一个变量,加入消费者组或者移除消费者组都会操作这个变量
loadingPartitions:位移主题__consumer_offsets 下正在执行加载操作的分区号的集合。所谓的加载,是指读取位移主题消息数据,填充 groupMetadataCache 变量的操作。
ownedPartitions:位移主题__consumer_offsets 下完成加载操作的分区号的集合。
groupMetadataTopicPartitionCount:位移主题__consumer_offsets 的分区数量,默认为 50.
scheduler:调度器对象,用于调度定时任务,如 主题分区中过期消息的定期清理任务
2. 重要方法简介
GroupMetadataManager 定义的重要方法可以分为以下三类
2.1 对消费者组元数据的管理。包括
①查询消费者组元数据
②添加消费者组元数据
③移除消费者组元数据
④将消费者组元数据对应的注册消息写入 __consumer_offsets 主题
2.2 对消费者组消费位移的管理
①将位移提交消息写入 __consumer_offsets 主题
②查询消费者组已提交位移。(注意:这里是从 GroupMetadata 组元数据信息的缓存中进行查询)
2.3 读取 __consumer_offsets 主题的消息,填充消费者组元数据缓存。
为什么把这个操作单独拿出来呢?因为消费者程序在获取消费位移时,并不是去直接读取位移主题的消息,而是从对应消费者组的元数据缓存 GroupMetadata 中进行读取。而元数据缓存中的位移消息,是在消费者组被当前节点的 GroupCoordinator 管理时进行填充的。换句话说,就是消费者组注册消息所在的位移主题分区的 Leader 副本切换到当前节点上时,会将分区中所有消费者组的位移提交信息加载到元数据缓存。
3.1对管辖内所有消费者组元数据的管理:主要就是操作 groupMetadataCache 变量
3.1.1 查询消费者组元数据
getGroup:根据给定的 group.id ,获取对应的消费者组元数据对象。如果没有则返回None
def getGroup(groupId: String): Option[GroupMetadata] = {Option(groupMetadataCache.get(groupId))}
addGroup:将给定的消费者组元数据添加到 groupMetadataCache 变量中
def addGroup(group: GroupMetadata): GroupMetadata = {val currentGroup = groupMetadataCache.putIfNotExists(group.groupId, group)if (currentGroup != null) {currentGroup} else {group}}
removeGroupsForPartition:移除给定位移主题分区中存储的所有消费者组元数据。当 Broker 卸任某些消费者组的 Coordinator 角色时,它需要将这些消费者组的信息从 groupMetadataCache 中全部移除掉
def removeGroupsForPartition(offsetsPartition: Int,//消费者组元数据消息所在的分区号onGroupUnloaded: GroupMetadata => Unit) {//获取位移主题分区对象val topicPartition = new TopicPartition(Topic.GROUP_METADATA_TOPIC_NAME, offsetsPartition)info(s"Scheduling unloading of offsets and group metadata from $topicPartition")//创建异步任务,移除组信息和位移信息scheduler.schedule(topicPartition.toString, () => removeGroupsAndOffsets)//定义了一个内部方法,用于移除组信息和位移信息def removeGroupsAndOffsets() {var numOffsetsRemoved = 0var numGroupsRemoved = 0inLock(partitionLock) {// 移除已加载分区集合ownedPartitions中给定位移主题分区的记录ownedPartitions.remove(offsetsPartition)//遍历所有消费者组信息for (group <- groupMetadataCache.values) {//如果该消费者组元数据消息保存在给定的位移主题分区中if (partitionFor(group.groupId) == offsetsPartition) {//进行消费者组的卸载逻辑,这个逻辑是在上层调用时传入的,具体逻辑在GroupCoordinator.onGroupUnloaded方法中onGroupUnloaded(group)//将该组信息从元数据缓存中移除groupMetadataCache.remove(group.groupId, group)//把消费者组从producer对应的组集合中移除removeGroupFromAllProducers(group.groupId)//更新移除组数量numGroupsRemoved += 1//更新移除位移值数量numOffsetsRemoved += group.numOffsets}}}info(s"Finished unloading $topicPartition. Removed $numOffsetsRemoved cached offsets " +s"and $numGroupsRemoved cached groups.")}}
该方法的逻辑是:
第一步:根据给定的待移除分区号,封装位移主题分区对象
第二步:创建一个异步的调度任务,将组信息和位移信息进行移除
调度任务的流程是:
首先,将给定的待移除分区号从已加载分区号集合中移除
接着,遍历所有的消费者组元数据,选出元数据在待移除分区上的消费者组,执行下面的逻辑:
① 执行消费者组的卸载逻辑,该逻辑是在上层调用时传入的,具体逻辑在GroupCoordinator.onGroupUnloaded方法中,主要做两件事:①将消费者组状态变更到 Dead 状态;②封装异常表示 Coordinator 已发生变更,然后调用回调函数返回。
② 将该消费者组元数据从 groupMetadataCache 变量中移除
③ 把消费者组从producer对应的组集合中移除,这里的producer是事务中使用的
④ 更新移除的消费者组数量和移除的主题分区提交位移数量(即 GroupMetadata 的 offsets 变量对应集合的大小)
3.1.4 将注册消息写入位移主题
def storeGroup(group: GroupMetadata,groupAssignment: Map[String, Array[Byte]],responseCallback: Errors => Unit): Unit = {//判断当前Broker是否是该消费者组的CoordinatorgetMagic(partitionFor(group.groupId)) match {//如果是该消费者组的Coordinatorcase Some(magicValue) =>//定义写入消息的时间戳类型val timestampType = TimestampType.CREATE_TIMEval timestamp = time.milliseconds()//构建写入消息的key,是一个字节数组val key = GroupMetadataManager.groupMetadataKey(group.groupId)//构建写入消息的value,也是一个字节数组val value = GroupMetadataManager.groupMetadataValue(group, groupAssignment, interBrokerProtocolVersion)//封装待写入的消费者组注册消息集合val records = {val buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(AbstractRecords.estimateSizeInBytes(magicValue, compressionType,Seq(new SimpleRecord(timestamp, key, value)).asJava))val builder = MemoryRecords.builder(buffer, magicValue, compressionType, timestampType, 0L)builder.append(timestamp, key, value)builder.build()}//根据消费者组名称获取注册消息所在主题分区对象val groupMetadataPartition = new TopicPartition(Topic.GROUP_METADATA_TOPIC_NAME, partitionFor(group.groupId))val groupMetadataRecords = Map(groupMetadataPartition -> records)val generationId = group.generationId//回调函数,用于将消息写入位移主题后更新缓存中的消费者组元数据def putCacheCallback(responseStatus: Map[TopicPartition, PartitionResponse]) {if (responseStatus.size != 1 || !responseStatus.contains(groupMetadataPartition))throw new IllegalStateException("Append status %s should only have one partition %s".format(responseStatus, groupMetadataPartition))//获取主题分区的响应状态val status = responseStatus(groupMetadataPartition)//如果没有错误val responseError = if (status.error == Errors.NONE) {Errors.NONE//如果有错误,根据错误信息获取对象的错误响应状态} else {debug(s"Metadata from group ${group.groupId} with generation $generationId failed when appending to log " +s"due to ${status.error.exceptionName}")status.error match {case Errors.UNKNOWN_TOPIC_OR_PARTITION| Errors.NOT_ENOUGH_REPLICAS| Errors.NOT_ENOUGH_REPLICAS_AFTER_APPEND =>//Coordinator不可用Errors.COORDINATOR_NOT_AVAILABLEcase Errors.NOT_LEADER_FOR_PARTITION| Errors.KAFKA_STORAGE_ERROR =>//未找到CoordinatorErrors.NOT_COORDINATORcase Errors.REQUEST_TIMED_OUT =>//执行RebalanceErrors.REBALANCE_IN_PROGRESScase Errors.MESSAGE_TOO_LARGE| Errors.RECORD_LIST_TOO_LARGE| Errors.INVALID_FETCH_SIZE =>error(s"Appending metadata message for group ${group.groupId} generation $generationId failed due to " +s"${status.error.exceptionName}, returning UNKNOWN error code to the client")//未知的服务端错误Errors.UNKNOWN_SERVER_ERRORcase other =>error(s"Appending metadata message for group ${group.groupId} generation $generationId failed " +s"due to unexpected error: ${status.error.exceptionName}")other}}//执行上层调用传入的回调函数responseCallback(responseError)}//向位移主题写入消费者组注册消息appendForGroup(group, groupMetadataRecords, putCacheCallback)//如果当前Broker不是该消费者组的Coordinator,则返回一个 NOT_COORDINATOR 错误case None =>responseCallback(Errors.NOT_COORDINATOR)None}}
该方法的逻辑是:
第一步:判断当前节点是否是管理该消费者组的 GroupCoordinator。判断依据是:尝试去获取位移主题目标分区的底层日志对象。如果能够获取到,就说明当前 Broker 是 Coordinator,程序进入到下一步;反之,则表明当前 Broker 不是 Coordinator,就构造一个 NOT_COORDINATOR 异常返回。
第二步:设置时间戳类型,封装注册消息的 key 和 value,构建待写入的消费者组注册消息集合,即 MemoryRecords 对象
第三步:根据消费者组名称,计算注册消息要写入的分区号,并构建 TopicPartition 主题分区对象
第四步:调用 appendForGroup 方法,向位移主题写入第二步构建的消费者组注册消息集合
对于 appendForGroup 方法,其作用就是将构建的消息集合写入位移主题,和写入普通主题一样,调用的就是 ReplicaManager.appendRecords 方法
private def appendForGroup(group: GroupMetadata,records: Map[TopicPartition, MemoryRecords],callback: Map[TopicPartition, PartitionResponse] => Unit): Unit = {//调用副本管理器的appendRecords方法向位移主题写入消息replicaManager.appendRecords(timeout = config.offsetCommitTimeoutMs.toLong,requiredAcks = config.offsetCommitRequiredAcks,internalTopicsAllowed = true,isFromClient = false,entriesPerPartition = records,delayedProduceLock = Some(group.lock),responseCallback = callback)}
3.2 对管辖内所有消费者组消费位移的管理
def storeOffsets(group: GroupMetadata,//消费者组元数据consumerId: String,//消费者组中消费者成员IDoffsetMetadata: immutable.Map[TopicPartition, OffsetAndMetadata],//待保存的位移值,按照分区分组responseCallback: immutable.Map[TopicPartition, Errors] => Unit,//处理完成后的回调函数producerId: Long = RecordBatch.NO_PRODUCER_ID,//事务型Producer IDproducerEpoch: Short = RecordBatch.NO_PRODUCER_EPOCH//事务型Producer Epoch值): Unit = {//过滤出满足特定条件的待保存位移数据//特定条件:metadata为null或者长度小于4kb,metadata为自定义元数据,如果不手动设置的话为nullval filteredOffsetMetadata = offsetMetadata.filter { case (_, offsetAndMetadata) =>validateOffsetMetadataLength(offsetAndMetadata.metadata)}...val isTxnOffsetCommit = producerId != RecordBatch.NO_PRODUCER_ID//如果没有任何分区的待保存位移满足特定条件if (filteredOffsetMetadata.isEmpty) {// 构造OFFSET_METADATA_TOO_LARGE异常并调用responseCallback返回val commitStatus = offsetMetadata.mapValues(_ => Errors.OFFSET_METADATA_TOO_LARGE)responseCallback(commitStatus)None} else {//查看当前Broker是否为给定消费者组的CoordinatorgetMagic(partitionFor(group.groupId)) match {//如果是Coordinatorcase Some(magicValue) =>//设置消息的时间戳类型val timestampType = TimestampType.CREATE_TIMEval timestamp = time.milliseconds()//构造位移主题的位移提交消息val records = filteredOffsetMetadata.map { case (topicPartition, offsetAndMetadata) =>val key = GroupMetadataManager.offsetCommitKey(group.groupId, topicPartition)val value = GroupMetadataManager.offsetCommitValue(offsetAndMetadata, interBrokerProtocolVersion)new SimpleRecord(timestamp, key, value)}//获取指定消费者组位移提交消息所在的主题分区对象val offsetTopicPartition = new TopicPartition(Topic.GROUP_METADATA_TOPIC_NAME, partitionFor(group.groupId))//为写入消息申请内存Bufferval buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(AbstractRecords.estimateSizeInBytes(magicValue, compressionType, records.asJava))if (isTxnOffsetCommit && magicValue < RecordBatch.MAGIC_VALUE_V2)throw Errors.UNSUPPORTED_FOR_MESSAGE_FORMAT.exception("Attempting to make a transaction offset commit with an invalid magic: " + magicValue)//封装待写入消息集合MemoryRecordsval builder = MemoryRecords.builder(buffer, magicValue, compressionType, timestampType, 0L, time.milliseconds(),producerId, producerEpoch, 0, isTxnOffsetCommit, RecordBatch.NO_PARTITION_LEADER_EPOCH)records.foreach(builder.append)val entries = Map(offsetTopicPartition -> builder.build())//在位移提交消息写入日志后,调用该回调函数来更新消费者组元数据,// 即将多个消费者组位移值填充到 GroupMetadata 的 offsets 元数据缓存中。def putCacheCallback(responseStatus: Map[TopicPartition, PartitionResponse]) {//确保消息写入到指定位移主题分区,否则抛出异常if (responseStatus.size != 1 || !responseStatus.contains(offsetTopicPartition))throw new IllegalStateException("Append status %s should only have one partition %s".format(responseStatus, offsetTopicPartition))val status = responseStatus(offsetTopicPartition)val responseError = group.inLock {//如果写入结果没有错误if (status.error == Errors.NONE) {//如果消费者组不是Dead状态if (!group.is(Dead)) {filteredOffsetMetadata.foreach { case (topicPartition, offsetAndMetadata) =>if (isTxnOffsetCommit)group.onTxnOffsetCommitAppend(producerId, topicPartition, CommitRecordMetadataAndOffset(Some(status.baseOffset), offsetAndMetadata))else//调用GroupMetadata的onOffsetCommitAppend方法填充元数据// 也就是更新消费者组订阅的主题分区具体消费到哪个地方了,以及更新位移提交消息在_consumer_offsets主题中对应分区的偏移量group.onOffsetCommitAppend(topicPartition, CommitRecordMetadataAndOffset(Some(status.baseOffset), offsetAndMetadata))}}Errors.NONE//如果写入结果存在异常} else {//且消费者组的状态不是Deadif (!group.is(Dead)) {if (!group.hasPendingOffsetCommitsFromProducer(producerId))removeProducerGroup(producerId, group.groupId)filteredOffsetMetadata.foreach { case (topicPartition, offsetAndMetadata) =>if (isTxnOffsetCommit)group.failPendingTxnOffsetCommit(producerId, topicPartition)elsegroup.failPendingOffsetWrite(topicPartition, offsetAndMetadata)}}//确认写入结果中的异常类型status.error match {case Errors.UNKNOWN_TOPIC_OR_PARTITION| Errors.NOT_ENOUGH_REPLICAS| Errors.NOT_ENOUGH_REPLICAS_AFTER_APPEND =>Errors.COORDINATOR_NOT_AVAILABLEcase Errors.NOT_LEADER_FOR_PARTITION| Errors.KAFKA_STORAGE_ERROR =>Errors.NOT_COORDINATORcase Errors.MESSAGE_TOO_LARGE| Errors.RECORD_LIST_TOO_LARGE| Errors.INVALID_FETCH_SIZE =>Errors.INVALID_COMMIT_OFFSET_SIZEcase other => other}}}//利用异常类型构建提交返回状态val commitStatus = offsetMetadata.map { case (topicPartition, offsetAndMetadata) =>if (validateOffsetMetadataLength(offsetAndMetadata.metadata))(topicPartition, responseError)else(topicPartition, Errors.OFFSET_METADATA_TOO_LARGE)}//调用回调函数responseCallback(commitStatus)}if (isTxnOffsetCommit) {group.inLock {addProducerGroup(producerId, group.groupId)group.prepareTxnOffsetCommit(producerId, offsetMetadata)}} else {group.inLock {group.prepareOffsetCommit(offsetMetadata)}}//写入消息到位移主题,同时调用putCacheCallback方法更新消费者元数据appendForGroup(group, entries, putCacheCallback)//如果不是Coordinatorcase None =>//构造NOT_COORDINATOR异常并提交给responseCallback方法val commitStatus = offsetMetadata.map { case (topicPartition, _) =>(topicPartition, Errors.NOT_COORDINATOR)}responseCallback(commitStatus)None}}}
第一步:筛选出满足条件的待写入主题分区和已提交位移信息。这里的条件是:已提交位移对象中的 metadata 为 null ,或者长度小于服务端参数offset.metadata.max.bytes 的值,即 4 KB。这个 metadata 是自定义的元数据,字符串类型,如果没有指定则为 null。
第二步:如果没有满足条件的待写入主题分区消费位移信息,则构造OFFSET_METADATA_TOO_LARGE异常,调用 responseCallback 并返回 None
第三步:如果存在满足条件的待写入主题分区消费位移信息,则判断当前节点是否为给定消费者组的 GroupCoordinator ,如果不是则构造 NOT_COORDINATOR异常,调用 responseCallback 并返回 None
第四步:如果当前节点是给定消费者组的 GroupCoordinator,则根据给定的主题分区和对应的消费位移信息构建已提交位移消息,并封装成待写入消息集合 MemoryRecords
第五步:定义 putCacheCallback 回调函数并调用 appendForGroup 方法将上面封装好消息集合写入位移主题,并更新消费者组元数据
第一步:要确保位移消息写入到指定位移主题分区,否则就抛出异常。
第二步:判断写入结果是否有错误。(这里先不考虑事务相关的处理)
如果没有错误,只要组状态不是 Dead 状态,就遍历给定的主题分区,调用 GroupMetadata 的 onOffsetCommitAppend 方法填充元数据。onOffsetCommitAppend 方法的主体逻辑,是将消费者组订阅分区的位移值写入到 offsets 字段保存的集合中。如果状态是 Dead,则什么都不做。
如果有错误,只要组状态不是 Dead 状态,就遍历给定的主题分区,通过 failPendingOffsetWrite 方法取消未完成的位移消息写入。也就是将主题分区从等待进行位移提交的分区集合中移除
第三步:将日志写入的异常类型转换成表征提交状态错误的异常类型。然后再将转换后的异常封装进 commitStatus 字段中传给回调函数。
第四步:调用回调函数返回
def getOffsets(groupId: String, topicPartitionsOpt: Option[Seq[TopicPartition]]): Map[TopicPartition, OffsetFetchResponse.PartitionData] = {trace("Getting offsets of %s for group %s.".format(topicPartitionsOpt.getOrElse("all partitions"), groupId))//第一步:获取给定消费者组的元数据信息val group = groupMetadataCache.get(groupId)//如果没有获取到,则返回空数据if (group == null) {topicPartitionsOpt.getOrElse(Seq.empty[TopicPartition]).map { topicPartition =>val partitionData = new OffsetFetchResponse.PartitionData(OffsetFetchResponse.INVALID_OFFSET,Optional.empty(), "", Errors.NONE)topicPartition -> partitionData}.toMap//第二步:如果获取到了} else {group.inLock {//如果消费者组状态为Dead,同样返回空数据if (group.is(Dead)) {topicPartitionsOpt.getOrElse(Seq.empty[TopicPartition]).map { topicPartition =>val partitionData = new OffsetFetchResponse.PartitionData(OffsetFetchResponse.INVALID_OFFSET,Optional.empty(), "", Errors.NONE)topicPartition -> partitionData}.toMap//如果组状态不为Dead} else {//第三步:看是否指定了要读取的主题分区topicPartitionsOpt match {//如果没有指定case None =>// Return offsets for all partitions owned by this consumer group. (this only applies to consumers// that commit offsets to Kafka.)//获取指定消费者组对所有订阅主题分区的消费位移group.allOffsets.map { case (topicPartition, offsetAndMetadata) =>//按照主题分区封装PartitionDatatopicPartition -> new OffsetFetchResponse.PartitionData(offsetAndMetadata.offset,offsetAndMetadata.leaderEpoch, offsetAndMetadata.metadata, Errors.NONE)}//第四步:如果指定了要读取的主题分区case Some(topicPartitions) =>//遍历指定的所有主题分区topicPartitions.map { topicPartition =>//获取对应的OffsetAndMetadata对象val partitionData = group.offset(topicPartition) match {//如果没有获取到,则返回空数据case None =>new OffsetFetchResponse.PartitionData(OffsetFetchResponse.INVALID_OFFSET,Optional.empty(), "", Errors.NONE)//如果获取到了,根据获取的OffsetAndMetadata信息封装PartitionData对象case Some(offsetAndMetadata) =>new OffsetFetchResponse.PartitionData(offsetAndMetadata.offset,offsetAndMetadata.leaderEpoch, offsetAndMetadata.metadata, Errors.NONE)}topicPartition -> partitionData}.toMap}}}}}
第一步:获取给定消费者组的元数据信息,如果没有获取到,返回空数据集
第二步:如果获取到了,判断消费者组的状态,如果是 Dead,说明消费者组已经被销毁了,位移数据也被视为不可用了,依然返回空数据集
第三步:如果消费者组状态不是 Dead,看方法调用时是否指定了主题分区。如果没有指定,那么就获取该消费者组订阅的所有主题分区的消费位移
第四步:如果指定了主题分区,则遍历这些分区,从消费者组元数据中获取该分区的消费位移信息。如果没有获取到,还是返回空数据集;如果获取到了,则将消费位移信息封装到 OffsetFetchResponse.PartitionData 对象中
第五步:返回结果集
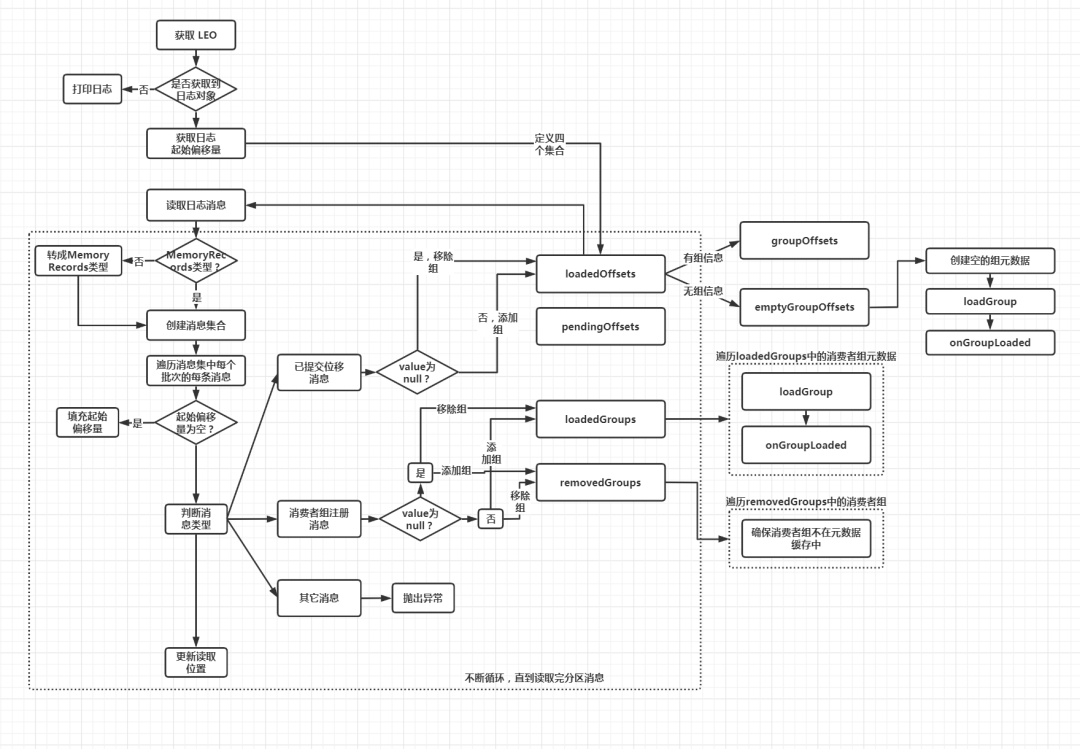
3.3 读取位移主题消息,填充元数据缓存
def scheduleLoadGroupAndOffsets(offsetsPartition: Int, onGroupLoaded: GroupMetadata => Unit) {//根据给定的分区号封装主题分区对象val topicPartition = new TopicPartition(Topic.GROUP_METADATA_TOPIC_NAME, offsetsPartition)//如果将该分区号成功添加到 loadingPartitions 集合if (addLoadingPartition(offsetsPartition)) {info(s"Scheduling loading of offsets and group metadata from $topicPartition")//创建调度任务,从位移主题中读取主题分区的消费位移scheduler.schedule(topicPartition.toString, () => loadGroupsAndOffsets(topicPartition, onGroupLoaded))} else {info(s"Already loading offsets and group metadata from $topicPartition")}}
private[group] def loadGroupsAndOffsets(topicPartition: TopicPartition, onGroupLoaded: GroupMetadata => Unit) {try {val startMs = time.milliseconds()//最重要的逻辑都在这个方法里面doLoadGroupsAndOffsets(topicPartition, onGroupLoaded)info(s"Finished loading offsets and group metadata from $topicPartition in ${time.milliseconds() - startMs} milliseconds.")} catch {case t: Throwable => error(s"Error loading offsets from $topicPartition", t)} finally {inLock(partitionLock) {//将分区添加到完成加载的分区集合ownedPartitions.add(topicPartition.partition)//并将分区从正在执行加载的分区集合中移除loadingPartitions.remove(topicPartition.partition)}}}
private def doLoadGroupsAndOffsets(topicPartition: TopicPartition, onGroupLoaded: GroupMetadata => Unit) {//第一步:获取位移主题指定分区的LEO值,如果当前节点不是该分区的Leader副本,则返回-1def logEndOffset: Long = replicaManager.getLogEndOffset(topicPartition).getOrElse(-1L)...
//获取该分区本地副本日志replicaManager.getLog(topicPartition) match {//如果没有获取到,则只打印日志case None =>warn(s"Attempted to load offsets and group metadata from $topicPartition, but found no log")//如果获取到了日志对象case Some(log) =>核心逻辑...
定义四个集合,用于存储读取位移主题时获取到的重要信息,然后读取位移主题的消息
处理读取到的消息,填充四个集合
处理四个集合中的数据
//获取分区日志的起始偏移量var currOffset = log.logStartOffset//申请一个ByteBuffer对象,容量为0var buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(0)//定义已完成位移值加载的分区列表val loadedOffsets = mutable.Map[GroupTopicPartition, CommitRecordMetadataAndOffset]()//定义处于位移加载中的分区列表,只用于Kafka事务val pendingOffsets = mutable.Map[Long, mutable.Map[GroupTopicPartition, CommitRecordMetadataAndOffset]]()//定义已完成组信息加载的消费者组列表val loadedGroups = mutable.Map[String, GroupMetadata]()//定义待移除的消费者组列表val removedGroups = mutable.Set[String]()//循环读取分区的所有消息while (currOffset < logEndOffset && !shuttingDown.get()) {//读取消息val fetchDataInfo = log.read(currOffset, config.loadBufferSize, maxOffset = None,minOneMessage = true, includeAbortedTxns = false)//创建消息集合val memRecords = fetchDataInfo.records match {//如果读出的是MemoryRecords类型,直接返回case records: MemoryRecords => records//如果是FileRecords类型,需要转成MemoryRecords类型,然后返回case fileRecords: FileRecords =>val sizeInBytes = fileRecords.sizeInBytesval bytesNeeded = Math.max(config.loadBufferSize, sizeInBytes)if (buffer.capacity < bytesNeeded) {if (config.loadBufferSize < bytesNeeded)warn(s"Loaded offsets and group metadata from $topicPartition with buffer larger ($bytesNeeded bytes) than " +s"configured offsets.load.buffer.size (${config.loadBufferSize} bytes)")buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(bytesNeeded)} else {buffer.clear()}fileRecords.readInto(buffer, 0)MemoryRecords.readableRecords(buffer)}
第一步:获取分区日志的起始偏移量,并申请一个容量为 0 的 ByteBuffer对象
第二步:定义四个集合:
loadedOffsets:已完成位移值加载的分区列表
pendingOffsets:位移值正在加载中的分区列表,只用于 Kafka 事务
loadedGroups:已完成组信息加载的消费者组列表
removedGroups:待移除的消费者组列表。
第三步:当读取偏移量小于 LEO,且组件未关闭,说明位移主题下该分区的消息没有读取完,不断地进行读取
第四步:根据读取到的消息创建内存中的消息集合对象,即 MemoryRecords 对象,如果读取到的是 FileRecords 类型,需要转成 MemoryRecords 类型。
第二部分:根据读取的数据,填充四个集合
//遍历消息集中的批次对象memRecords.batches.asScala.foreach { batch =>val isTxnOffsetCommit = batch.isTransactional//控制类消息批次,属于事务的范畴if (batch.isControlBatch) {...} else {//定义一个变量,用于保存消息批次第一条消息的偏移量var batchBaseOffset: Option[Long] = None//遍历批次中的每条消息for (record <- batch.asScala) {require(record.hasKey, "Group metadata/offset entry key should not be null")//填充起始消息偏移量if (batchBaseOffset.isEmpty)batchBaseOffset = Some(record.offset)//根据消息的key,判断是哪种类型GroupMetadataManager.readMessageKey(record.key) match {//如果是已提交位移消息case offsetKey: OffsetKey =>if (isTxnOffsetCommit && !pendingOffsets.contains(batch.producerId))pendingOffsets.put(batch.producerId, mutable.Map[GroupTopicPartition, CommitRecordMetadataAndOffset]())//从key中获取(消费者组名,主题,分区号)三元组val groupTopicPartition = offsetKey.key//如果消息没有value,也就是墓碑消息if (!record.hasValue) {if (isTxnOffsetCommit)pendingOffsets(batch.producerId).remove(groupTopicPartition)else//由于是墓碑消息,所以这个主题分区对应的消息已经过期//之前如果加载了,应该从已完成位移值加载的分区列表中移除loadedOffsets.remove(groupTopicPartition)//如果有value} else {//获取value中的信息val offsetAndMetadata = GroupMetadataManager.readOffsetMessageValue(record.value)if (isTxnOffsetCommit)pendingOffsets(batch.producerId).put(groupTopicPartition, CommitRecordMetadataAndOffset(batchBaseOffset, offsetAndMetadata))else//将从消息中读取的主题分区消费信息放入已完成位移值加载的分区列表loadedOffsets.put(groupTopicPartition, CommitRecordMetadataAndOffset(batchBaseOffset, offsetAndMetadata))}//如果是消费者组注册类消息case groupMetadataKey: GroupMetadataKey =>//获取消费者组名val groupId = groupMetadataKey.key//根据消息的value封装消费者组元数据对象val groupMetadata = GroupMetadataManager.readGroupMessageValue(groupId, record.value, time)//如果value有值//TODO 由于是按照偏移量读取的,墓碑消息的偏移量会比对应过期消息的大,所有墓碑消息一定是后读取的if (groupMetadata != null) {//把该消费者组从待移除消费者组列表中移除removedGroups.remove(groupId)//把该消费者组添加到已完成组信息加载的列表loadedGroups.put(groupId, groupMetadata)//如果value为空,说明是墓碑消息} else {//把该消费者组从已完成组信息加载列表中移除loadedGroups.remove(groupId)//把该消费者组添加到待移除消费者组列表中removedGroups.add(groupId)}//如果是未知类型的Key,抛出异常case unknownKey =>throw new IllegalStateException(s"Unexpected message key $unknownKey while loading offsets and group metadata")}}}//更新读取位置到消息批次最后一条消息的位移值+1currOffset = batch.nextOffset}
遍历消息集合中的批次对象,如果不是控制类的消息批次,执行下面的逻辑:
第一步:记录消息批次中第一条消息的偏移量
第二步:根据消息的 key,判断消息的类型:
如果是已提交位移消息,从 key 中或者(消费者组名称,订阅主题,分区号)三元组信息,然后判断是否有 value。如果没有,说明是墓碑消息,需要将该分区从已完成位移值加载的分区列表中移除;如果有,则将目标分区加入到已完成位移值加载的分区列表中。
如果是消费者组注册消息,先从 key 中获取消费者组名称,然后判断是否有 value。如果有,把该消费者组从待移除消费者组列表中移除,并加入到已完成加载的消费者组列表;如果没有,同样是墓碑消息,把该消费者组从已完成加载的消费者组列表中移除,并加入到待移除消费组列表。
如果是未知类型的 key,则直接抛异常
第三步:更新读取位置到消息批次的最后一条消息的偏移量 + 1
//对loadedOffsets 进行分组,将完成信息加载的组对应的消费者组位移值保存到groupOffsets//将有消费者组消费位移,却没有消费者组信息的保存到emptyGroupOffsetsval (groupOffsets, emptyGroupOffsets) = loadedOffsets//按照消费者组名进行分组.groupBy(_._1.group).mapValues(_.map { case (groupTopicPartition, offset) => (groupTopicPartition.topicPartition, offset) }).partition { case (group, _) => loadedGroups.contains(group) }val pendingOffsetsByGroup = mutable.Map[String, mutable.Map[Long, mutable.Map[TopicPartition, CommitRecordMetadataAndOffset]]]()//属于事务范畴pendingOffsets.foreach { case (producerId, producerOffsets) =>producerOffsets.keySet.map(_.group).foreach(addProducerGroup(producerId, _))producerOffsets.groupBy(_._1.group).mapValues(_.map { case (groupTopicPartition, offset) => (groupTopicPartition.topicPartition, offset)}).foreach { case (group, offsets) =>val groupPendingOffsets = pendingOffsetsByGroup.getOrElseUpdate(group, mutable.Map.empty[Long, mutable.Map[TopicPartition, CommitRecordMetadataAndOffset]])val groupProducerOffsets = groupPendingOffsets.getOrElseUpdate(producerId, mutable.Map.empty[TopicPartition, CommitRecordMetadataAndOffset])groupProducerOffsets ++= offsets}}val (pendingGroupOffsets, pendingEmptyGroupOffsets) = pendingOffsetsByGroup.partition { case (group, _) => loadedGroups.contains(group)}//遍历完成信息加载的组的元数据loadedGroups.values.foreach { group =>//提取消费者组的已提交位移val offsets = groupOffsets.getOrElse(group.groupId, Map.empty[TopicPartition, CommitRecordMetadataAndOffset])val pendingOffsets = pendingGroupOffsets.getOrElse(group.groupId, Map.empty[Long, mutable.Map[TopicPartition, CommitRecordMetadataAndOffset]])debug(s"Loaded group metadata $group with offsets $offsets and pending offsets $pendingOffsets")//为已完成加载的组执行加载组操作loadGroup(group, offsets, pendingOffsets)//为已完成加载的组执行加载组操作之后的逻辑onGroupLoaded(group)}(emptyGroupOffsets.keySet ++ pendingEmptyGroupOffsets.keySet).foreach { groupId =>val group = new GroupMetadata(groupId, Empty, time)//创建空的消费者组元数据val offsets = emptyGroupOffsets.getOrElse(groupId, Map.empty[TopicPartition, CommitRecordMetadataAndOffset])val pendingOffsets = pendingEmptyGroupOffsets.getOrElse(groupId, Map.empty[Long, mutable.Map[TopicPartition, CommitRecordMetadataAndOffset]])debug(s"Loaded group metadata $group with offsets $offsets and pending offsets $pendingOffsets")//为空的消费者组执行加载组操作loadGroup(group, offsets, pendingOffsets)//为空的消费者执行加载组操作之后的逻辑onGroupLoaded(group)}//处理removedGroups,检查 removedGroups中的所有消费者组,确保它们不能出现在消费者组元数据缓存中,否则将抛出异常。removedGroups.foreach { groupId =>if (groupMetadataCache.contains(groupId) && !emptyGroupOffsets.contains(groupId))throw new IllegalStateException(s"Unexpected unload of active group $groupId while " +s"loading partition $topicPartition")}
第一步:对 loadedOffsets 进行分组,将完成信息加载的组对应的消费者组位移值保存到groupOffsets;将有消费者组消费位移,却没有消费者组信息的保存到emptyGroupOffsets
第二步:遍历完成信息加载的消费者组元数据,提取已提交消费位移,调用 loadGroup 方法,将获取到的已提交消费位移更新到 GroupMetadata 组元数据的 offsets 变量中,同时将这些消费者组元数据添加到 GroupMetadataManager的 groupMetadataCache 变量中(调用 addGroup 方法)。之后执行上层调用传入的 onGroupLoaded 函数,其作用是处理消费者组下所有成员的心跳超时设置,并指定下一次心跳的超时时间。
第三步:为 emptyGroupOffsets 中的所有消费者组,创建空的消费者组元数据,然后执行和上一步相同的组加载逻辑以及加载后的逻辑。
第四步:遍历待移除的消费者组列表,确保它们不能出现在消费者组元数据缓存中,否则将抛出异常。
pendingOffsets属于事务范畴,这里不进行分析
1. 为了解决强依赖 zk 进行 rebalance 操作带来的问题,和统一协调消费者组中所有消费者成员,引入了 Coordinator 机制。
2. GroupMetadataManager 组件管理了当前节点 GroupCoordinator 管辖的所有消费者组元数据,并定义了一些列方法供 GroupCoordinator 调用
3. GroupMetadataManager 定义的方法主要分为三大类:
管理消费者组元数据
管理消费者组消费位移
读取位移主题消息,填充消费者组元数据缓存
4. 消费者程序获取主题分区的消费位移时,并不会直接读取位移主题,而是读取消费者组元数据缓存中的信息。该信息由 GroupCoordinator 读取位移主题并填充元数据缓存






