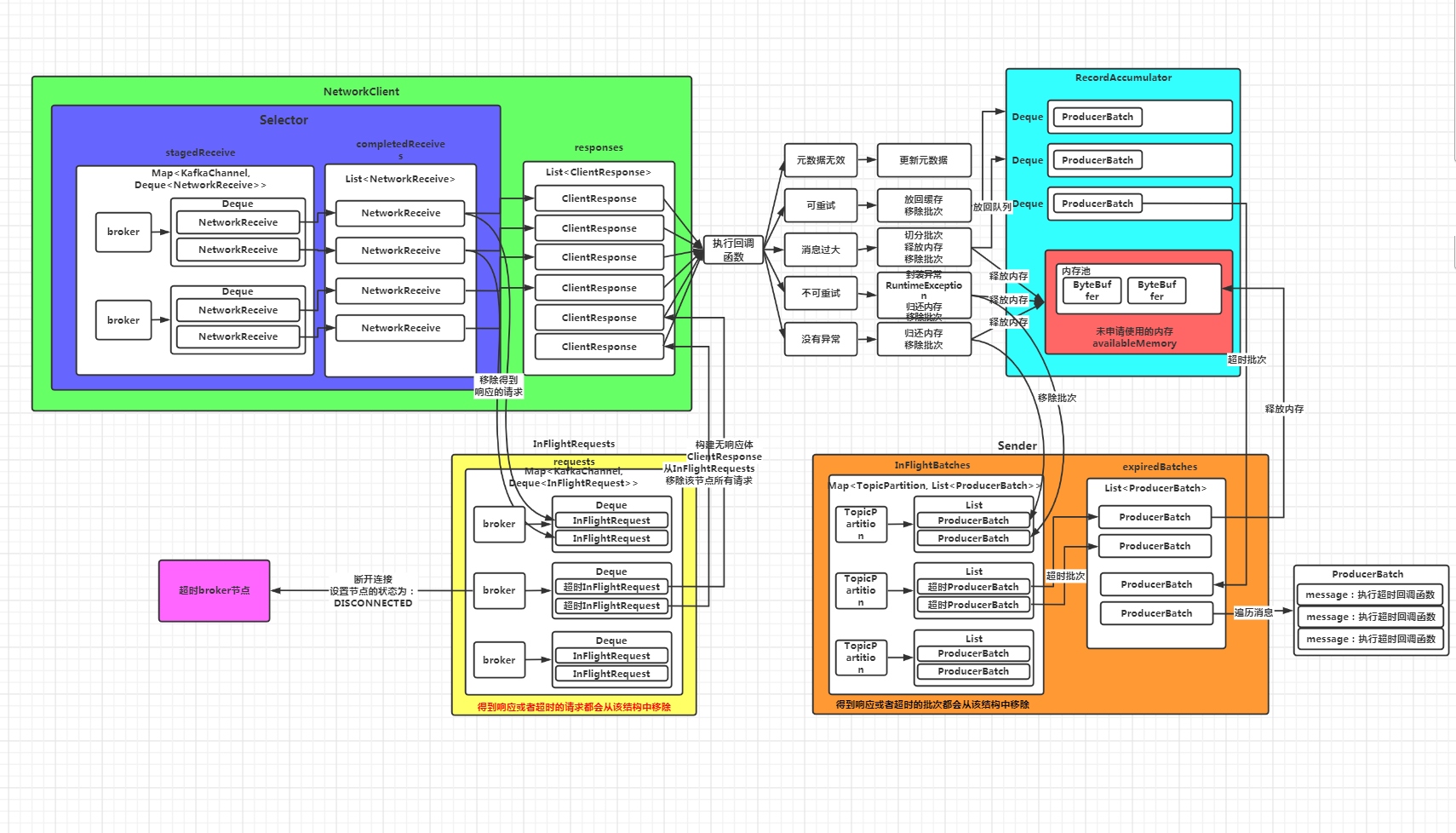
一、场景分析
首先更正一下《深入理解Kafka客户端之服务端响应及超时请求的处理》中的流程图,图中少画了一个数据结构:InFlightBatches,这个结构保存的是正在发送的批次。当Sender线程将缓存中的批次拿出来封装成请求的同时,会将这个批次放到InFlightBatches结构中,即标记这些批次正在发送,当发送成功,会将这个批次从InFlightBatches中移除,同样,如果批次超时,也会将该批次移除。
超时批次的处理主要在右下角Sender线程这块:
三、过程源码分析
还是从Sender的runOnce方法看起,主要看下面的代码:
long pollTimeout = sendProducerData(currentTimeMs);
private long sendProducerData(long now) {...//TODO 步骤六:对超时批次对处理(由于没有建立网络连接,第一次这里的代码也不执行)这里的超时指生成的批次超过120s未发送或者发送了未返回响应//获取inflightBatches集合中已经超时的批次,// inflightBatches记录的是从缓存中取出来的批次,上面进行合并时,将批次从Deque中取出来List<ProducerBatch> expiredInflightBatches = getExpiredInflightBatches(now);//获取缓存中已经过期的批次,这里指还未发送就已经超时的批次List<ProducerBatch> expiredBatches = this.accumulator.expiredBatches(now);//获取总的过期的批次expiredBatches.addAll(expiredInflightBatches);if (!expiredBatches.isEmpty())log.trace("Expired {} batches in accumulator", expiredBatches.size());//遍历处理过期的批次for (ProducerBatch expiredBatch : expiredBatches) {String errorMessage = "Expiring " + expiredBatch.recordCount + " record(s) for " + expiredBatch.topicPartition+ ":" + (now - expiredBatch.createdMs) + " ms has passed since batch creation";//TODO 处理超时的批次failBatch(expiredBatch, -1, NO_TIMESTAMP, new TimeoutException(errorMessage), false);if (transactionManager != null && expiredBatch.inRetry()) {// This ensures that no new batches are drained until the current in flight batches are fully resolved.transactionManager.markSequenceUnresolved(expiredBatch.topicPartition);}}...}
List<ProducerBatch> expiredInflightBatches = getExpiredInflightBatches(now);
private List<ProducerBatch> getExpiredInflightBatches(long now) {List<ProducerBatch> expiredBatches = new ArrayList<>();for (Iterator<Map.Entry<TopicPartition, List<ProducerBatch>>> batchIt = inFlightBatches.entrySet().iterator(); batchIt.hasNext();) {Map.Entry<TopicPartition, List<ProducerBatch>> entry = batchIt.next();//获取每个分区对应的List<ProducerBatch>集合List<ProducerBatch> partitionInFlightBatches = entry.getValue();//说明指定的分区存在正在发送的批次if (partitionInFlightBatches != null) {Iterator<ProducerBatch> iter = partitionInFlightBatches.iterator();//遍历所有的批次while (iter.hasNext()) {ProducerBatch batch = iter.next();//判断批次是否超时//超时的标准:now - createMs > deliveryTimeoutMS 即当前时间 - 批次的创建时间 > 过期时间(默认120秒)if (batch.hasReachedDeliveryTimeout(accumulator.getDeliveryTimeoutMs(), now)) {//如果该批次已经超时了,就从inFlightBatches集合中移除iter.remove();//如果done方法还未执行,即还未标记该批次是成功了还是失败了if (!batch.isDone()) {//添加到超时批次到集合中expiredBatches.add(batch);} else {throw new IllegalStateException(batch.topicPartition + " batch created at " +batch.createdMs + " gets unexpected final state " + batch.finalState());}} else {//如果没有超时,则更新超时的具体时间accumulator.maybeUpdateNextBatchExpiryTime(batch);break;}}if (partitionInFlightBatches.isEmpty()) {batchIt.remove();}}}return expiredBatches;}
判断批次是否超时:
batch.hasReachedDeliveryTimeout(accumulator.getDeliveryTimeoutMs(), now))
boolean hasReachedDeliveryTimeout(long deliveryTimeoutMs, long now) {return deliveryTimeoutMs <= now - this.createdMs;}
这里判断批次是否超时调用的是ProducerBatch.hasReachedDeliveryTimeout方法。如果当前时间-批次的创建时间>deliveryTimeoutMs,则超时。deliveryTimeoutMs的默认值为120秒。
如果批次超时,则从inFlightBatches数据结构中将该批次移除,同时将该批次放入expiredBatches集合。
如果批次未超时,则更新批次超时的具体时间nextBatchExpiryTimeMs
if (batch.hasReachedDeliveryTimeout(accumulator.getDeliveryTimeoutMs(), now)) {//如果该批次已经超时了,就从inFlightBatches集合中移除iter.remove();//如果done方法还未执行,即还未标记该批次是成功了还是失败了if (!batch.isDone()) {//添加到超时批次到集合中expiredBatches.add(batch);} else {throw new IllegalStateException(batch.topicPartition + " batch created at " +batch.createdMs + " gets unexpected final state " + batch.finalState());}} else {//如果没有超时,则更新超时的具体时间accumulator.maybeUpdateNextBatchExpiryTime(batch);break;}
这里注意batch.isDone()方法,该方法判断批次是否执行了done()方法,即是否已经标记了批次的状态(FAILED、ABORTED或者SUCCEEDED),关于done()方法,后面进行具体的分析。
List<ProducerBatch> expiredBatches = this.accumulator.expiredBatches(now);
public List<ProducerBatch> expiredBatches(long now) {List<ProducerBatch> expiredBatches = new ArrayList<>();for (Map.Entry<TopicPartition, Deque<ProducerBatch>> entry : this.batches.entrySet()) {//获取每个分区对应的批次队列Deque<ProducerBatch> deque = entry.getValue();synchronized (deque) {//如果队列中存在批次对象while (!deque.isEmpty()) {//获取队列中头部的批次对象(为什么只取头部批次?因为是按时间顺序进入队列的,如果头部批次没超时,后面的肯定也没有超时)ProducerBatch batch = deque.getFirst();//判断批次是否超时了if (batch.hasReachedDeliveryTimeout(deliveryTimeoutMs, now)) {//如果超时把这个批次从队列中移除deque.poll();//终止批次的写入(假设批次还未写满)batch.abortRecordAppends();//将这个批次放到过期集合中expiredBatches.add(batch);} else {//如果没有超时,则更新批次超时的具体时间maybeUpdateNextBatchExpiryTime(batch);break;}}}}return expiredBatches;}
这里的逻辑比较简单,就是判断所有Deque队列中的批次是否超时,判断标准和上面一样,即批次创建的时间超过了deliveryTimeoutMs(默认120秒)。如果超时,则将这个批次从Deque中移除,同时终止该批次的写入(有时候该批次还未写满),然后将该批次放入过期批次的集合。
expiredBatches.addAll(expiredInflightBatches);
for (ProducerBatch expiredBatch : expiredBatches) {String errorMessage = "Expiring " + expiredBatch.recordCount + " record(s) for " + expiredBatch.topicPartition+ ":" + (now - expiredBatch.createdMs) + " ms has passed since batch creation";//TODO 处理超时的批次failBatch(expiredBatch, -1, NO_TIMESTAMP, new TimeoutException(errorMessage), false);if (transactionManager != null && expiredBatch.inRetry()) {// This ensures that no new batches are drained until the current in flight batches are fully resolved.transactionManager.markSequenceUnresolved(expiredBatch.topicPartition);}}
这里主要调用了failBatch方法进行,注意此时RuntimeException参数传入的是一个new TimeoutException(errorMessage):
failBatch(expiredBatch, -1, NO_TIMESTAMP, new TimeoutException(errorMessage), false);
failBatch方法具体代码如下:
private void failBatch(ProducerBatch batch,long baseOffset,long logAppendTime,RuntimeException exception,boolean adjustSequenceNumbers) {if (transactionManager != null) {transactionManager.handleFailedBatch(batch, exception, adjustSequenceNumbers);}this.sensors.recordErrors(batch.topicPartition.topic(), batch.recordCount);//给这个批次标记状态,(失败或者成功)if (batch.done(baseOffset, logAppendTime, exception)) {//归还内存池的内存并从inFlightBatches集合中移除maybeRemoveAndDeallocateBatch(batch);}}
这里我们详细分析一下batch.done方法,首先看一下方法的注释:
/*** Finalize the state of a batch. Final state, once set, is immutable. This function may be called* once or twice on a batch. It may be called twice if* 1. An inflight batch expires before a response from the broker is received. The batch's final* state is set to FAILED. But it could succeed on the broker and second time around batch.done() may* try to set SUCCEEDED final state.* 2. If a transaction abortion happens or if the producer is closed forcefully, the final state is* ABORTED but again it could succeed if broker responds with a success.*/
翻译如下:
该方法用来标记批次的最终执行状态,这个状态一旦设置,就无法更改。这个方法可能被每个批次调用1次或者两次,调用2次的情况有:1。一个inFlight批次在服务端返回响应之前超时了。这个批次的状态被设置为FAILED。但是第二次调用该方法时最终状态设置为SUCCEEDED2。如果发生了事务回滚或者生产者关闭,状态为ABORTED,但是如果服务端返回success这个状态会被设置为SUCCEEDED
假设有批次正在发送,那么该批次保存在InFlightBatches结构中,如果此时该批次被判断为已超时,那么就会将该批次标记为FAILED。但是,如果后面发现这个批次发送成功了(因为该批次已经封装了发送的请求,正在发送),服务端返回了正常的响应,那么该方法还会被调用1次,但是批次的状态不会再修改。 假设发送了事务回滚或者生产者关闭,状态会先被标记为ABORTED,如果后续服务端针对该批次返回了成功的响应,那么还会调用该方法1次。同样,批次的状态不会再修改。
public boolean done(long baseOffset, long logAppendTime, RuntimeException exception) {//如果有异常,状态暂时设为FAILED,否则设置为SUCCEEDEDfinal FinalState tryFinalState = (exception == null) ? FinalState.SUCCEEDED : FinalState.FAILED;if (tryFinalState == FinalState.SUCCEEDED) {log.trace("Successfully produced messages to {} with base offset {}.", topicPartition, baseOffset);} else {log.trace("Failed to produce messages to {} with base offset {}.", topicPartition, baseOffset, exception);}//如果当前finalState状态为null,则更新为tryFinalState,并执行回调函数并返回if (this.finalState.compareAndSet(null, tryFinalState)) {//遍历批次中的消息,执行回调函数逻辑,这里的回调函数就是我们生产消息时绑定的那个回调函数completeFutureAndFireCallbacks(baseOffset, logAppendTime, exception);return true;}//如果finalState状态不为SUCCEEDEDif (this.finalState.get() != FinalState.SUCCEEDED) {//但是tryFinalState为SUCCEEDED,这种场景就是该批次先被标记为FAILED,然后第二次调用时被标记为SUCCEEDEDif (tryFinalState == FinalState.SUCCEEDED) {// Log if a previously unsuccessful batch succeeded later on.log.debug("ProduceResponse returned {} for {} after batch with base offset {} had already been {}.",tryFinalState, topicPartition, baseOffset, this.finalState.get());} else {// FAILED --> FAILED and ABORTED --> FAILED transitions are ignored.log.debug("Ignored state transition {} -> {} for {} batch with base offset {}",this.finalState.get(), tryFinalState, topicPartition, baseOffset);}//如果finalState为SUCCEEDED则抛异常,状态不允许修改} else {// A SUCCESSFUL batch must not attempt another state change.throw new IllegalStateException("A " + this.finalState.get() + " batch must not attempt another state change to " + tryFinalState);}return false;}
当传入的exception对象为null时,tryFinalState 变量会被赋值为SUCCEEDED,否则赋值为FAILED。 然后判断this.finalState属性的值: 如果为null,说明是第一次设置批次的状态,那么就将this.finalState属性的值设置为tryFinalState 变量的值,然后遍历批次中的消息,执行回调函数,并最终返回true。 如果不为null,说明之前已经设置过一次批次状态。 此时如果第一次设置状态不为SUCCEEDED,且本次准备将批次状态设置为SUCCEEDED,那么该方法最终返回false。 如果第一次设置为SUCCEEDED,则抛出异常:SECCEEDED状态的批次不允许修改状态
private void completeFutureAndFireCallbacks(long baseOffset, long logAppendTime, RuntimeException exception) {produceFuture.set(baseOffset, logAppendTime, exception);//一个thunk就是批次中的一条消息for (Thunk thunk : thunks) {try {//如果没有异常if (exception == null) {RecordMetadata metadata = thunk.future.value();if (thunk.callback != null)//调用我们生产消息的回调函数thunk.callback.onCompletion(metadata, null);//如果有异常} else {if (thunk.callback != null)thunk.callback.onCompletion(null, exception);}} catch (Exception e) {log.error("Error executing user-provided callback on message for topic-partition '{}'", topicPartition, e);}}//将produceFuture标记为已处理,并解除等待该请求完成的所有线程的阻塞状态produceFuture.done();}
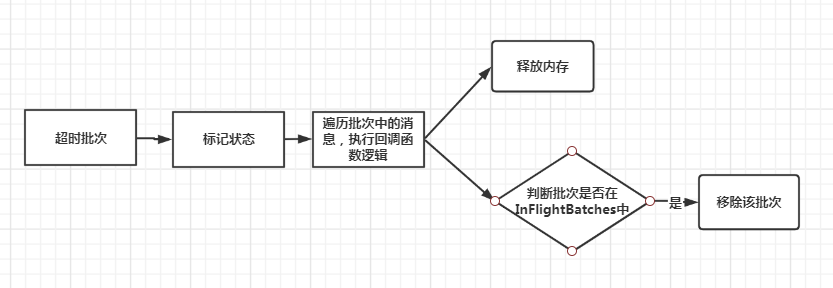
获取InFlightBatches中超时的批次 获取缓存队列Deque中超时的批次 合并超时批次 遍历批次进行处理 标记批次状态为FAILED,遍历批次中的消息执行生产时绑定的回调函数 再次判断该批次是否在InFlightBatches中,如果在,则移除 释放批次占用的内存






