CUDA的Thread index是GPU硬件和软件的唯一标识,在一些2D/3D场景下的内存操作会和thread index相关,因此,如何根据grid、block和thread的dim3来确定唯一的全局thread index是了解cuda编程模型的基础。
dim3的结构:
1、基于uint3的矢量类型(cuda-10.0/include/vector_types.h),
struct __device_builtin__ uint3{unsigned int x, y, z;};... ...struct __device_builtin__ dim3{unsigned int x, y, z;#if defined(__cplusplus)#if __cplusplus >= 201103L__host__ __device__ constexpr dim3(unsigned int vx = 1, unsigned int vy = 1, unsigned int vz = 1) : x(vx), y(vy), z(vz) {}#else__host__ __device__ dim3(unsigned int vx = 1, unsigned int vy = 1, unsigned int vz = 1) : x(vx), y(vy), z(vz) {}#endif__host__ __device__ dim3(uint3 v) : x(v.x), y(v.y), z(v.z) {}__host__ __device__ operator uint3(void) { uint3 t; t.x = x; t.y = y; t.z = z; return t; }#endif * __cplusplus */};typedef __device_builtin__ struct dim3 dim3;
2、dim3是通过kernel函数<<<,>>>使用的,如上例中的hello<<<B, T>>>()。B,blocks,即每个grid在每个维度中包含的block的数目,T,threads,即每个block在每个维度中包含的thread的数目;
3、threadIdx是指thread在block内的位置(索引),如果是一维的就是threadIdx.x,二维的就是threadIdx.y,三维的就是threadIdx.z;blockIdx同理,是指在grid中的位置;
4、blockDim,gridDim是指block和grid各自的维度,本篇文章的主旨就是通过gridDim、blockDim、blockIdx以及threadIdx来计算全局唯一的thread index;
5、对于一维的block,thread index = threadIdx.x,对于最复杂的情况也就是三维grid、block和thread。
如图1所示,展示的是grid和block都是一维的情况,对应的kernel的调用为:kernel<<<4096, 255>>>(),其线程总数为gridDim.x * gridDim.y:
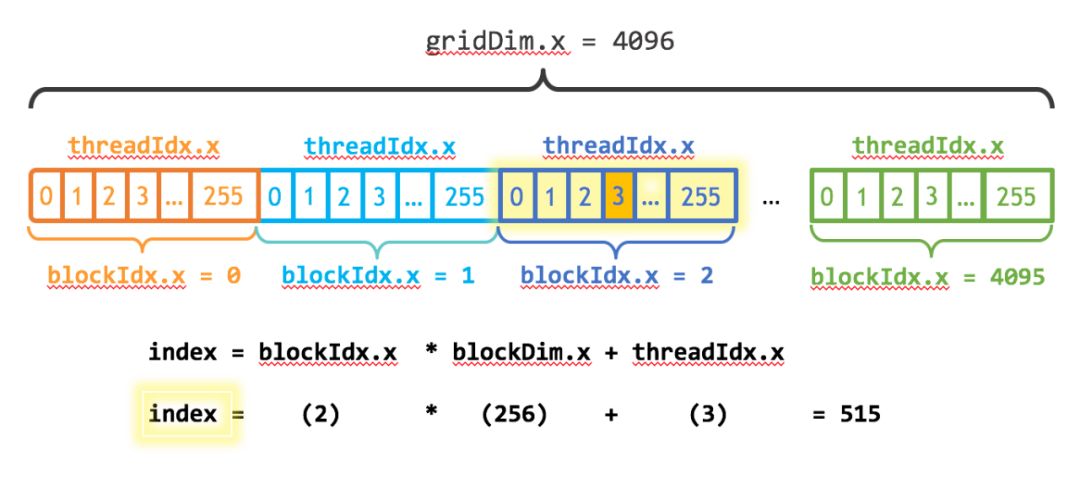
图1 gridDim.x为4096和blockDim.x为256的情况
在不同grid和block维数情况下,全局唯一线程索引的计算也略有不同。以下是grid和block不同维数下线程索引的计算公式:
// 1D grid of 1D blocks__device__ int getGlobalIdx_1D_1D() {return blockIdx.x *blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;}// 1D grid of 2D blocks__device__ int getGlobalIdx_1D_2D() {return blockIdx.x * blockDim.x * blockDim.y +threadIdx.y * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;}// 1D grid of 3D blocks__device__ int getGlobalIdx_1D_3D() {return blockIdx.x * blockDim.x * blockDim.y * blockDim.z +threadIdx.z * blockDim.y * blockDim.x +threadIdx.y * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;}// 2D grid of 1D blocks__device__ int getGlobalIdx_2D_1D() {int blockId = blockIdx.y * gridDim.x + blockIdx.x;int threadId = blockId * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;return threadId;}// 2D grid of 2D blocks__device__ int getGlobalIdx_2D_2D() {int blockId = blockIdx.x + blockIdx.y * gridDim.x;int threadId = blockId * (blockDim.x * blockDim.y) +(threadIdx.y * blockDim.x) + threadIdx.x;return threadId;}// 2D grid of 3D blocks__device__ int getGlobalIdx_2D_3D() {int blockId = blockIdx.x + blockIdx.y * gridDim.x;int threadId = blockId * (blockDim.x * blockDim.y * blockDim.z) +(threadIdx.z * (blockDim.x * blockDim.y)) +(threadIdx.y * blockDim.x) + threadIdx.x;return threadId;}// 3D grid of 1D blocks__device__ int getGlobalIdx_3D_1D() {int blockId = blockIdx.x + blockIdx.y * gridDim.x +gridDim.x * gridDim.y * blockIdx.z;int threadId = blockId * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;return threadId;}// 3D grid of 2D blocks__device__ int getGlobalIdx_3D_2D() {int blockId = blockIdx.x + blockIdx.y * gridDim.x +gridDim.x * gridDim.y * blockIdx.z;int threadId = blockId * (blockDim.x * blockDim.y) +(threadIdx.y * blockDim.x) + threadIdx.x;return threadId;}// 3D grid of 3D blocks__device__ int getGlobalIdx_3D_3D() {int blockId = blockIdx.x + blockIdx.y * gridDim.x +gridDim.x * gridDim.y * blockIdx.z;int threadId = blockId * (blockDim.x * blockDim.y * blockDim.z) +(threadIdx.z * (blockDim.x * blockDim.y)) +(threadIdx.y * blockDim.x) + threadIdx.x;return threadId;}
按照上面的公式,我们来计算下grid和block都是2D的情况:
// gridDim.x = 3, gridDim.y = 2, gridDim.z = 1dim3 blocks(3, 2);// blockDim.x = 4, blockDim.y = 4, blockDim.z = 1dim3 threads(4, 4);// threadIdx.x = 2, threadIdx.y = 1// blockIdx.x = 2, blockIdx.y = 0getGlobalIdx_2D_2D<<<blocks, threads>>>()
根据getGlobalIdx_2D_2D()的返回结果是38(blockId = 2 + 0 * 3 = 2;
threadId = 2 * (4 * 4) + (1 * 4) + 2 = 38),其实际情况如图2所示:
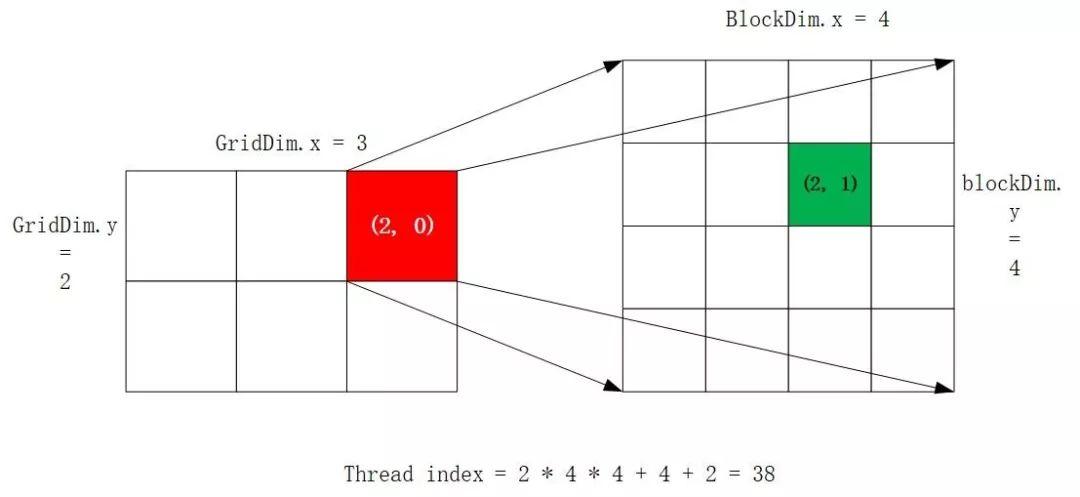
图2 2D-2D的thread index计算
注:
1、index由0开始,故只需增加block(2, 1)前的两个threads即可






