本文主要是对Aws在 SIGMOD 2017上发表的论文Amazon Aurora: Design Considerations for High Throughput CloudNative Relational Databases的学习和总结。
aurora有几个关键词:存储与计算分离、Quorum模型、分段存储、the log is the database
存储与计算分离
怎么理解存储与计算分离?
我们知道mysql分为Server层和存储引擎(storage engine)层两部分。
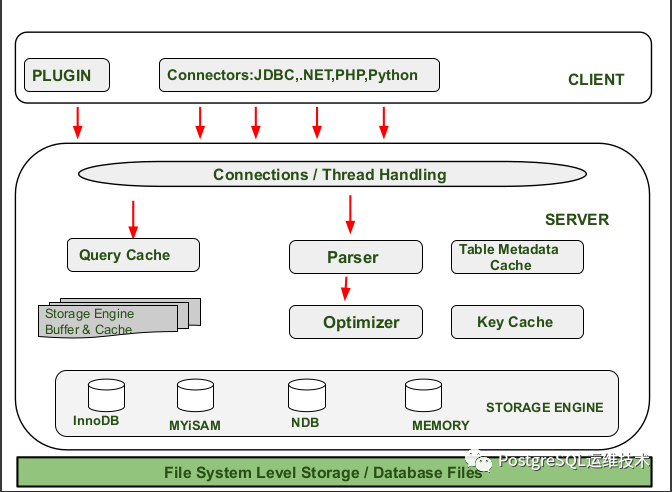 图片来源:https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/architecture-of-mysql/
图片来源:https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/architecture-of-mysql/
Server层: 包括连接器、查询缓存、分析器、优化器、执行器。
存储引擎层: mysql是可插拔的存储引擎架构,常用的存储引擎有innodb、MyISAM、Memory等。存储引擎层除了提供数据的存取功能外,可能还会包括更多的功能,比如事务、锁、备份和恢复等等。
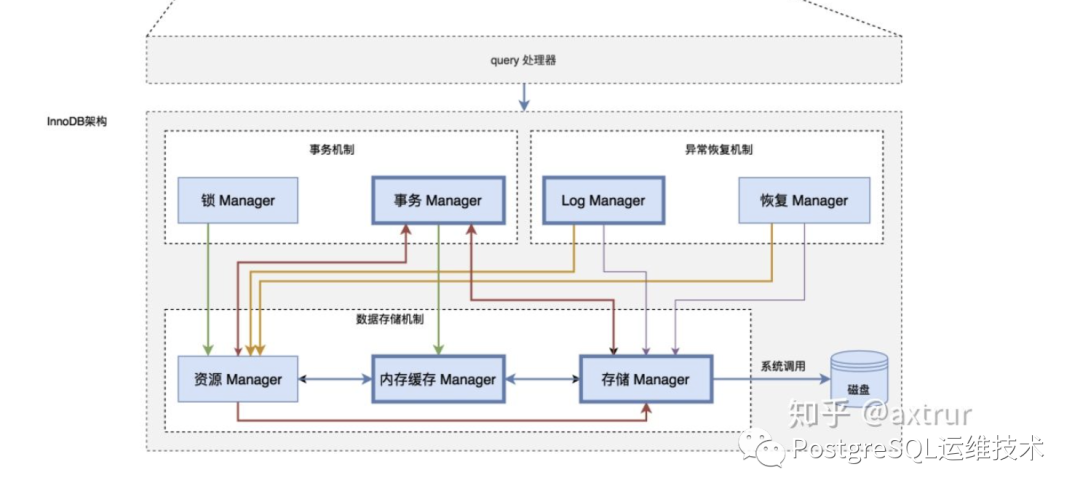 图片来源:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/262570892
图片来源:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/262570892
而aurora所说的存储与计算分离,其实是将日志部分(log manager)的逻辑下推到一个独立的分布式存储服务中,达到存储节点与数据库实例(计算节点)松耦合。这里说的log manager是指与redo log关联的功能,包括redo logging、durable storage、crash recovery、backup/restore等功能。
如下图所示:
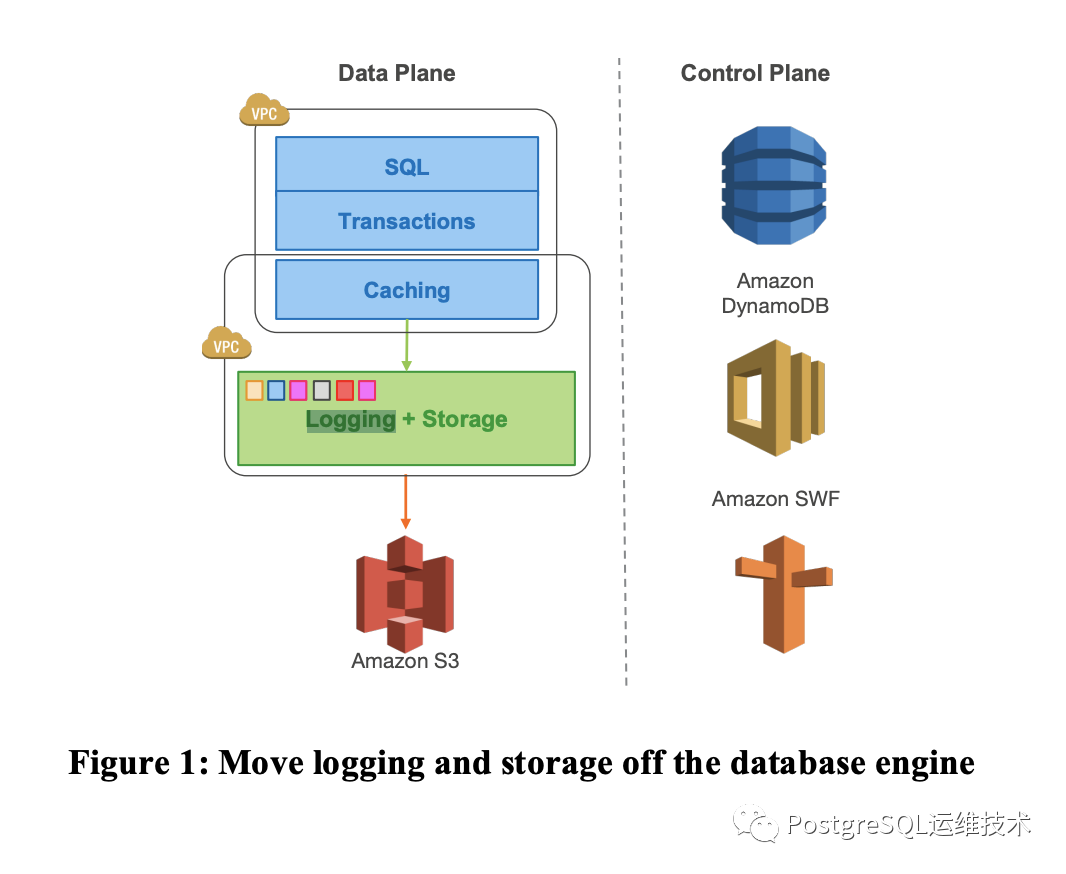
paper原文:
In this paper, we describe Amazon Aurora, a new database service that addresses the above issues by more aggressively leveraging the redo log across a highly-distributed cloud environment. We use a novel service-oriented architecture (see Figure 1) with a multi-tenant scale-out storage service that abstracts a virtualized segmented redo log and is loosely coupled to a fleet of database instances. Although each instance still includes most of the components of a traditional kernel (query processor, transactions, locking, buffer cache, access methods and undo management) several functions (redo logging, durable storage, crash recovery, and backup/restore) are off-loaded to the storage service.
这种分离架构有个特点是,服务所涉及的io都需要通过网络,网络IO负担将会是服务最大的瓶颈。
另外分布式存储层需要做数据复制(同步或异步), 通常来说,同步复制面临性能问题,异步复制又有丢数据的风险。
aurora采取的是基于Quorum模型的复制方案。
Quorum模型
paper原文
One approach to tolerate failures in a replicated system is to use a quorum-based voting protocol as described in [6]. If each of the V copies of a replicated data item is assigned a vote, a read or write operation must respectively obtain a read quorum of Vr votes or a write quorum of Vw votes. To achieve consistency, the quorums must obey two rules. First, each read must be aware of the most recent write, formulated as Vr + Vw > V. This rule ensures the set of nodes used for a read intersects with the set of nodes used for a write and the read quorum contains at least one location with the newest version. Second, each write must be aware of the most recent write to avoid conflicting writes, formulated as Vw > V/2.
Aurora 使用quorum模型,假设复制拓扑中有V个节点,每个节点都有一个投票权,读和写需要分别拿到Vr和Vw个投票才能返回。
同时为了满足一致性,quorum模型需要遵循两个原则:
每次读都要读到包含最新数据的副本,也就是读取的副本集合Vr 和写入的副本集合Vw,二者必须有交集(至少一个副本重叠),因此必须满足:Vr + Vw >V。 每次写都要保证能获取到上次写的最新数据,也就是两次写操作的副本集合也必须有交集,因此必须满足:Vw > V/2。
假设设置复制节点为3(V = 3), 那么为了满足上述条件,Vr=2,Vw=2。这种情况下可以可以容忍一个节点故障。
aws有可用区(Availability Zone,后简称Az)的概念, Az是region的一个子集,与Region内的其他Azs通过低延迟网络连接。但是单个az部署无法应对单个az级别的故障,所以云上一般是跨az部署。如果是3个副本,它会将3个副本分别放到3个不同的az中。这样其实也可以正常工作,但是它只能容忍一个故障节点。aws认为这种3副本模型的可用性是不足的。
为了提高可用性,aurora使用跨三个Az的6副本模型, 每个az两个副本,Vw是4, Vr是3。这种架构下,当2个节点故障时,集群不会失去写入能力,当3个节点故障时,不会丢失读取最新数据的能力。确保读仲裁可以使我们能够通过添加额外的副本来重新构建写仲裁。aurora跨三个az的6副本模型可以保证实例有Az+1的故障容错能力。
paper原文
In Aurora, we have chosen a design point of tolerating (a) losing an entire AZ and one additional node (AZ+1) without losing data, and (b) losing an entire AZ without impacting the ability to write data. We achieve this by replicating each data item 6 ways across 3 AZs with 2 copies of each item in each AZ. We use a quorum model with 6 votes (V = 6), a write quorum of 4/6 (Vw = 4), and a read quorum of 3/6 (Vr = 3). With such a model, we can (a) lose a single AZ and one additional node (a failure of 3 nodes) without losing read availability, and (b) lose any two nodes, including a single AZ failure and maintain write availability. Ensuring read quorum enables us to rebuild write quorum by adding additional replica copies.
让我们考虑一下Az+1是否提供了足够的可用性,为了在此模型下保证服务提供足够的可用性,就必须确保Az级别的故障与节点故障不同时发生。也就是说,问题变成如何降低这两类故障发生的概率。论文中的表述是,必须确保在不相关故障(Mean Time to Failure-MTTF)上出现双故障的概率在服务在修复其中一个故障(Mean Time To repair)时间内足够低(这句话有点拗口)。
上面提到两个名词MTTF和MTTR。MTTF表示平均两次故障间隔时间,MTTR表示平均修复时间。
降低不相关故障发生的概率(MTTF)很困难,所以aurora专注于改善MTTR,也即想办法减少故障的修复时间。出于这个考虑,Aurora将存储进行分段管理。
分段管理
Aurora将数据划分为固定10G大小的单元,叫Segment, 这些segement会被存储到6个副本上,6个副本合称一个PG(protection Group)。segement是服务故障修复的基本单元,在10Gbps的网络链路上,10G的段可以在10秒内被修复。在如此短的时间内,服务同时出现4个副本故障的概率是非常低的。服务的可用性得到进一步提高。另外,基于分段管理,系统可以更灵活地应对故障和运维操作。
paper原文
It is difficult, past a point, to reduce the probability of MTTF on independent failures. We instead focus on reducing MTTR to shrink the window of vulnerability to a double fault. We do so by partitioning the database volume into small fixed size segments, currently 10GB in size. These are each replicated 6 ways into Protection Groups (PGs) so that each PG consists of six 10GB segments, organized across three AZs, with two segments in each AZ. A storage volume is a concatenated set of PGs, physically implemented using a large fleet of storage nodes that are provisioned as virtual hosts with attached SSDs using Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2).
the log is the database
aurora存储层的设计理念,体现了“the log is the database”的思想,其含义是日志(redo log)包含了数据的信息,可以从日志中恢复出数据,所以数据不需要再单独存储。
要理解这句话,需要理解传统mysql中写数据的流程。以单机mysql为例,执行写操作会先将日志落盘,同时后台线程异步将脏页刷盘,另外为了避免页的部分写,刷脏页面的过程还需要将数据页写入double-write区。如果是生产场景下的主备复制环境,则情况会更复杂。
如下图所示,展示了aws上一个跨可用区的主备实例,它的写操作所需要写入的数据,及其io流。图中,AZ1和AZ2分别部署一个mysql实例做同步复制,底层存储采用EBS(Elastic Block Store),同时每个EBS还有自己的镜像。另外还需要传送binlog到S3(Amazon Simple Storage Service)以支持point-in-time恢复。图中列出了引擎写操作所需要操作的各种类型数据:redo log、binlog、data、double-write、Frm。
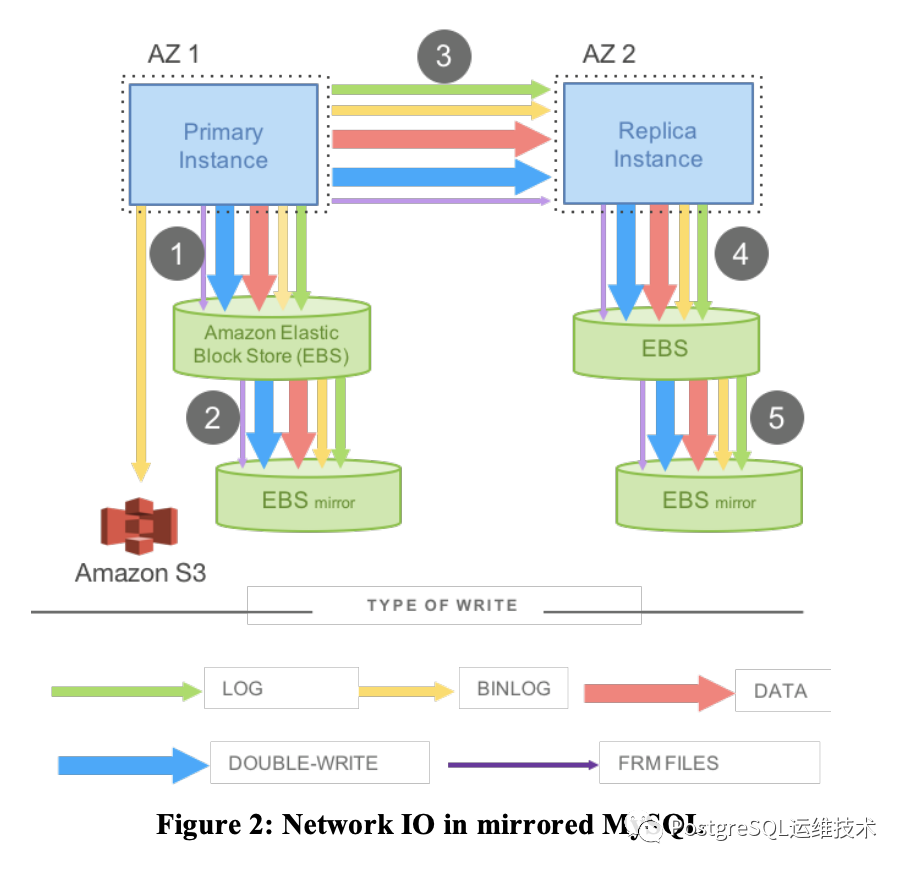
我们看到图中这种架构模型,首先写入的数据类型非常多,网络IO的负担很大,同时如果是同步复制,响应需要等待5完成才能返回,服务性能很差。
基于此,Aurora采取的方案是只写redo log到存储层,不会从数据库层写入任何页面,这里的写入包括异步刷脏页、checkpoint、缓存回收。
那么页面是什么时候被写入呢?
答案是,日志应用程序也被推到了存储层,存储层接受了redo日志,由日志应用程序基于旧版本数据页回放日志,得到新版本数据页。这个过程是异步的,持续的。为了避免每次都从头开始回放数据页变更产生的redo log,存储层会持续地materialize数据页。
这种架构下Aurora 集群的网络 IO如下图所示:
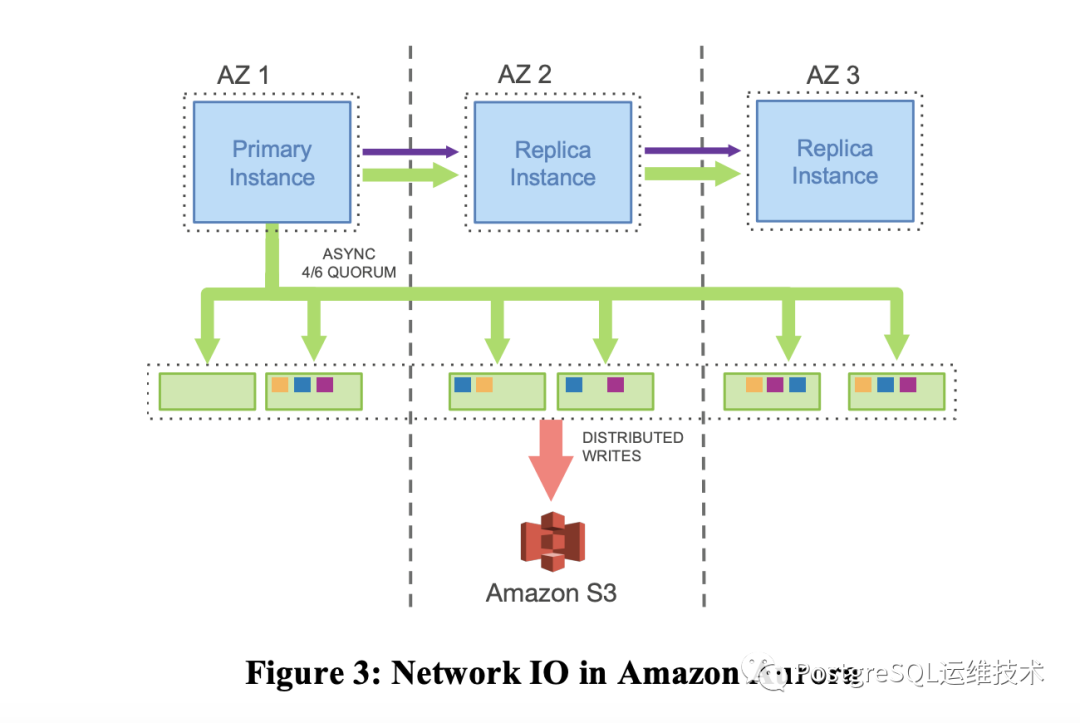
paper原文
In Aurora, the only writes that cross the network are redo log records. No pages are ever written from the database tier, not for background writes, not for checkpointing, and not for cache eviction. Instead, the log applicator is pushed to the storage tier where it can be used to generate database pages in background or on demand. Of course, generating each page from the complete chain of its modifications from the beginning of time is prohibitively expensive. We therefore continually materialize database pages in the background to avoid regenerating them from scratch on demand every time.
这种方法大大降低了网络IO,尽管增加了用于复制的写操作,并提高了性能和持久性。
怎么理解增加了用于复制的写操作?
答:之前写binlog到replica, 现在要写redo log, 放大了用于replication的IO。
对于网络IO, 论文提供了一份基于SysBench的测试报告。100G的数据量,只写、压测30分钟。测试结果如下表所示:
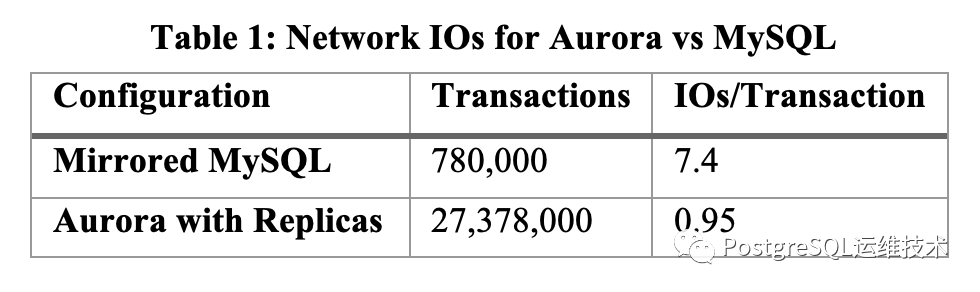
可以看到,在30分钟内,aurora能处理的事务数是mysql的2737800/780000=35.1倍,而每个事务的io,mysql是aurora的7.4/0.95=7.8倍。
除了减少网络io,aurora架构还有其他的优点:
最小化崩溃恢复时间; 消除checkpoint、数据页写入和备份等后台进程引起的抖动;
怎么理解最小化崩溃恢复时间?
传统数据库宕机重启时,恢复从最近一个检查点开始,读取检查点后的所有redo日志进行回放。在aurora中,redo相关的功能下推到存储层,回放日志的工作一直在存储层的后台在做。而且,任何一次读磁盘io的操作,如果数据页不是最新版本,都会触发存储节点回放日志。所以在真正进行故障恢复时,需要恢复的日志可能很少,所以故障恢复的速度非常快。
对于存储服务的设计,核心的原则即是减少前台用户写的响应时间,因此就把能异步做的事情都放到后台做。如下图所示:
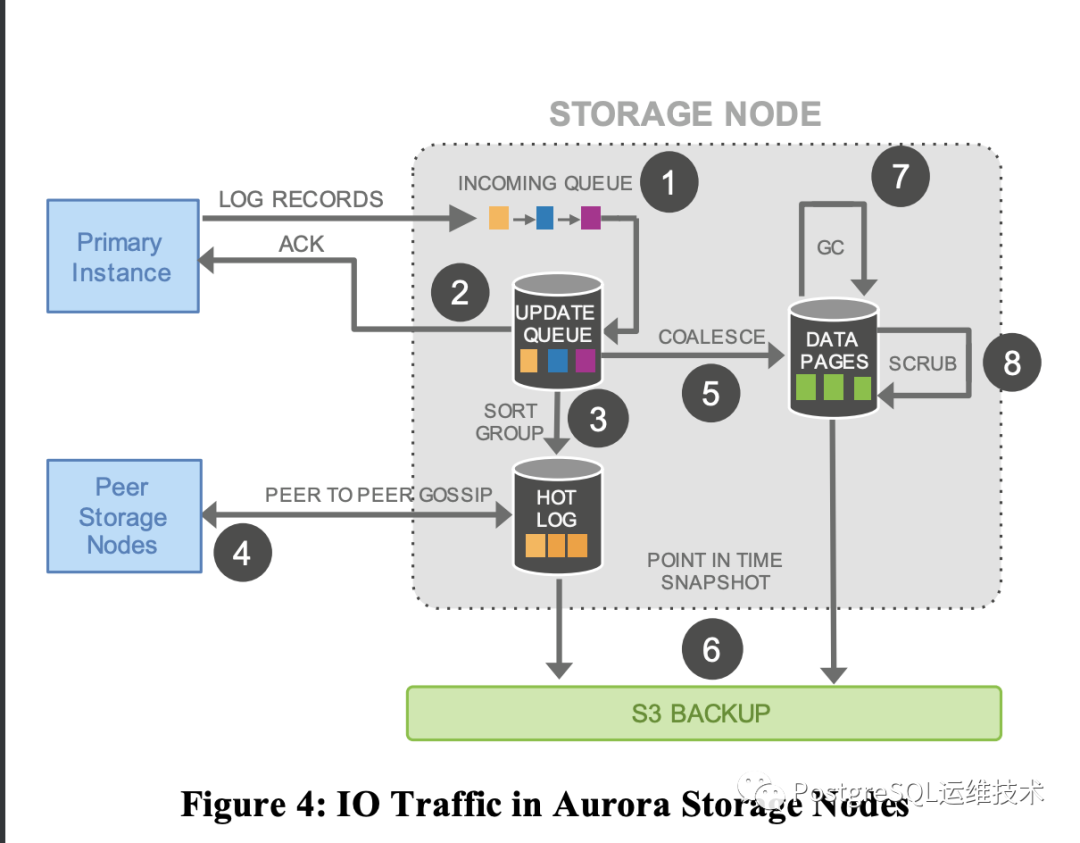
图中,primary写redo日志到6个storage node,Storage node接受到日志,将其加入一个队列等待被处理,对应图中步骤1。日志持久化到物理存储设备,并立即给主机回应(ack),对应图中步骤二。一和二之后的其他操作都是异步操作。当primary收到6个storage node中的四个节点的ack后,就认为日志成功写入。
注:4是通过Gossip协议,与其他peer通信,修复数据。
本篇文章就先写到这里,到这里基本上是论文中前3节的内容,后面比较重要的是第4节,讲数据一致性,会放到下篇文章中去梳理,下次见。
参考文档:
https://aws.amazon.com/cn/blogs/database/amazon-aurora-under-the-hood-quorum-and-correlated-failure/
https://blog.csdn.net/joy0921/article/details/80131085






