
一.基本概念和原理
智能推荐的方法有很多,包括基于内容推荐,协同过滤推荐,基于关联规则,基于知识推荐,基于效用推荐和组合推荐。
基于内容推荐,就是根据用户过去的行为记录来向用户进行推荐相似的产品。
缺点:由于内容高度匹配,导致内容的精准度比较差,而且有冷启动的问题,对于新用户不能提供可靠的结果,对于新用户需要积累一段时间后的内容才能够推荐。而且只有维度增加才能增加推荐的精度,但是维度增加会导致计算量巨大。
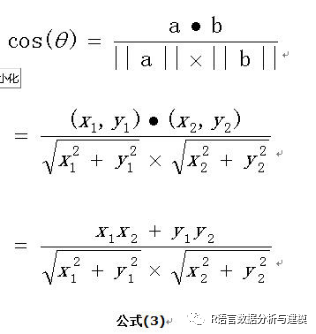
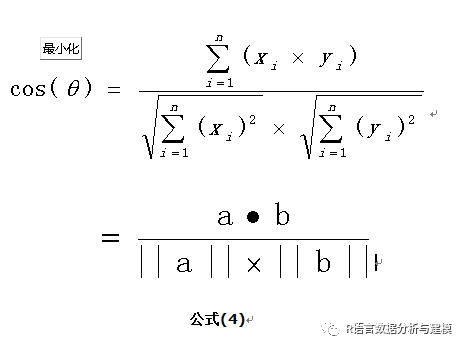
协同过滤算法,主要是找出和你口味相近的用户,根据他的喜好来预测你的喜好。这个方法可能可以挖掘用户的潜在喜好,但是也存在无法向新用户推荐的问题。一个重要环节就是如何选择合适的相似度计算方法。常用的方法是余玄相似度法和皮尔逊相关系数。
皮尔逊相关系数:
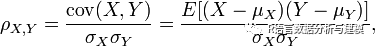
余玄相似度计算
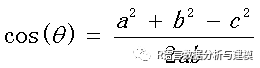
二.recommenderlab包的介绍
1.rating Matrix有两种,realRatingMatrix和binaryRatingMatrix,realRatingMatrix是个评分矩阵,以真实的评分数据反映在矩阵当中,binaryRatingMatrix为布尔矩阵。
2.recommender()构建推荐模型
Recommender(data,method,parameter=Null)
method的选项包括IBCF(基于物品的协同过滤推荐),UBCF(基于用户的协同过滤),SVD(矩阵因子化),PCA(主成分分析),RANDOM(随机推荐),POPULAR(基于流行度的推荐)
3.predict()
预测推荐模型,得到模型的topN列表或者用户的预测评分、
predict(object,newdata,n=10,type=,...)
三.具体实例
library(recommenderlab)
library(ggplot2)
data(MovieLense)
as(MovieLense,"matrix")[1:3,1:4]
m.recomm<-Recommender(MovieLense[1:940],method="IBCF")
m.recomm
ml.predict<-predict(m.recomm,MovieLense[941:943],n=3)
as(ml.predict,"list")
ml.predict2<-predict(m.recomm,MovieLense[941:943],type="ratings")
as(ml.predict2,"matrix")[1:3,1:4]
结果如下:
as(MovieLense,"matrix")[1:3,1:4]
Toy Story (1995) GoldenEye (1995) Four Rooms (1995) Get Shorty (1995)
1 5 3 4 3
2 4 NA NA NA
3 NA NA NA NA
> m.recomm<-Recommender(MovieLense[1:940],method="IBCF")
> m.recomm
Recommender of type ‘IBCF’ for ‘realRatingMatrix’
learned using 940 users.
> ml.predict<-predict(m.recomm,MovieLense[941:943],n=3)
> as(ml.predict,"list")
$`941`
[1] "Once Upon a Time in the West (1969)"
[2] "Flower of My Secret, The (Flor de mi secreto, La) (1995)"
[3] "Unzipped (1995)"
$`942`
[1] "Nadja (1994)"
[2] "Brother Minister: The Assassination of Malcolm X (1994)"
[3] "unknown"
$`943`
[1] "Brother Minister: The Assassination of Malcolm X (1994)"
[2] "Horseman on the Roof, The (Hussard sur le toit, Le) (1995)"
[3] "Mrs. Brown (Her Majesty, Mrs. Brown) (1997)"
四.模型评价
recommendre包提供了evalutatingScheme函数创建了一个数据集的评价方案,可以通过evaluate()评估一个或者一系列推荐模型给出一个评价方案。
1.evaluationScheme()创建一个数据评价方案。
evaluationScheme(data,method="spilt",train=0.9,k=NULL,given,goodRating=NA)
2.evaulate()评估一个或者一系列的推荐模型,给出一个评价方案。
evaulate(x,method,type="topNList",n=1:10,parameter=NULL)
3.calcpredictionAccuracy()计算预测精度,均方误差和平均绝对误差。calcpredictionAccuracy(x,data,...)
4.getData()通常与evaluationScheme函数配合使用,用于访问evaluationScheme生成的数据
getData(x,pram)
代码如下:
scheme<-evaluationScheme(MovieLense,method="split",train=0.9,k=1,given=10,goodRating=4)
algorithms<-list(popular=list(name="POPUlAR",param=list(normalize="Z-score")),ubcf=list(name="UBCF",param=list(normalize="Z-score",method="Cosine",nn=25,minRating=3)),ibcf=list(name="IBCF",param=list(normalize="Z-score")))
results<-evaluate(scheme,algorithms,n=c(1,3,5,10,15,20))
plot(results,annotate=1:3,legend="topleft")
plot(results,"prec/rec",annotate=3)
model.popular<-Recommender(getData(scheme,"train"),method="POPULAR",parameter=algorithms[[3]][[2]])
model.ibcf<-Recommender(getData(scheme,"train"),method="UBCF",parameter=algorithms[[2]][[2]])
model.ubcf<-Recommender(getData(scheme,"train"),method="IBCF",parameter=algorithms[[3]][[2]])
predict.popular<-predict(model.popular,getData(scheme,"known"),type="ratings")
predict.ubcf<-predict(model.ubcf,getData(scheme,"known"),type="ratings")
predict.ibcf<-predict(model.ibcf,getData(scheme,"known"),type="ratings")
predict.err<-rbind(calcPredictionAccuracy(predict.popular,getData(scheme,"unknow")),calcPredictionAccuracy(predict.ubcf,getData(scheme,"unknow")),calcPredictionAccuracy(predict.ibcf,getData(scheme,"unknow")))
rownames(predict.err)<-c("POPULAR","UBCF","IBCF")
predict.err
结果如下:
POPUlAR run fold/sample [model time/prediction time]
1 [0.031sec/0.179sec]
UBCF run fold/sample [model time/prediction time]
1 Warning: Unknown parameters: minRating
Available parameter (with default values):
method = cosine
nn = 25
sample = FALSE
normalize = center
verbose = FALSE
[0.032sec/0.366sec]
IBCF run fold/sample [model time/prediction time]
1 [16.51sec/0.032sec]
> plot(results,annotate=1:3,legend="topleft")
> plot(results,"prec/rec",annotate=3)
> model.popular<-Recommender(getData(scheme,"train"),method="POPULAR",parameter=algorithms[[3]][[2]])
> model.ibcf<-Recommender(getData(scheme,"train"),method="UBCF",parameter=algorithms[[2]][[2]])
Warning: Unknown parameters: minRating
Available parameter (with default values):
method = cosine
nn = 25
sample = FALSE
normalize = center
verbose = FALSE
> model.ubcf<-Recommender(getData(scheme,"train"),method="IBCF",parameter=algorithms[[3]][[2]])
>
> predict.popular<-predict(model.popular,getData(scheme,"known"),type="ratings")
> predict.ubcf<-predict(model.ubcf,getData(scheme,"known"),type="ratings")
> predict.ibcf<-predict(model.ibcf,getData(scheme,"known"),type="ratings")
>
> predict.err<-rbind(calcPredictionAccuracy(predict.popular,getData(scheme,"unknow")),calcPredictionAccuracy(predict.ubcf,getData(scheme,"unknow")),calcPredictionAccuracy(predict.ibcf,getData(scheme,"unknow")))
> rownames(predict.err)<-c("POPULAR","UBCF","IBCF")
> predict.err
RMSE MSE MAE
POPULAR 1.004768 1.009559 0.7902080
UBCF 1.395545 1.947545 1.0558036
IBCF 1.089496 1.187002 0.8755411
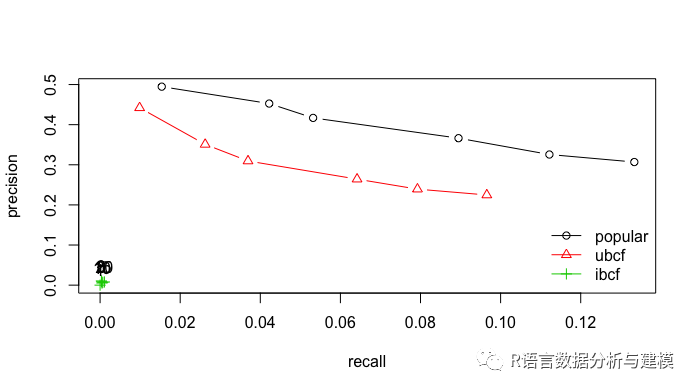
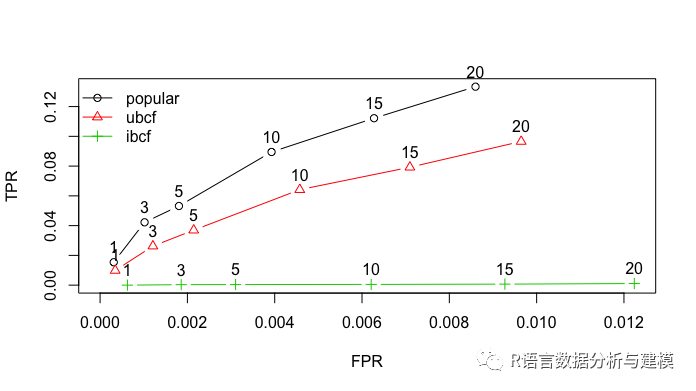
在ROC空间里面,越凸向西北方向,效果越好。因此UBCF的效果是最好的。






