前言
ORACLE 10g中crsd管理集群中的资源,通过相关的racg脚本产生racg进程实现资源管理,本质上是进程在管理资源。从11g r2开始,ORACLE使用agent来管理资源,当然是因为racg管理不善喽。
ORACLE对于racg有如下描述,racg是集群件的扩展,能够满足ORACLE特定的需求和复杂的资源,当有FAN事件发生时,racg运行服务标注脚本。

关于FAN,ORACLE有如下描述

01
Agent是什么
当应用程序被当成资源注册到集群时,集群才能管理这些应用程序,集群可以启动、关闭资源,也能监控资源,集群是怎么实现对资源的管理的呢?就是通过agent来执行管理命令。
Oracle Clusterware manages applications when they are registered as resources with Oracle Clusterware. Oracle Clusterware has access to application-specific primitives that have the ability to start, stop, and monitor a specific resource. Oracle Clusterware runs all resource-specific commands through an entity called an agent.
An agent is a process that contains the agent framework and user code to manage resources. The agent framework is a library that enables you to plug in your application-specific code to manage customized applications. You program all of the actual application management functions, such as starting, stopping and checking the health of an application, into the agent. These functions are referred to as entry points.
The agent framework is responsible for invoking these entry point functions on behalf of Oracle Clusterware. Agent developers can use these entry points to plug in therequired functionality for a specific resource regarding how to start, stop, and monitor a resource. Agents are capable of managing multiple resources.
Agent是常驻内存的进程,有很多个,其中两个最重要的是oracle agent和oracle root agent,这个两个agent对应的操作系统的进程名是:oraagent、orarootagent
oracle agent是以oracle用户身份运行,这里的oracle用户也可以是grid,根据自身场景变化
oracle root agent是以root用户身份运行。
Agent & 资源 关系如图
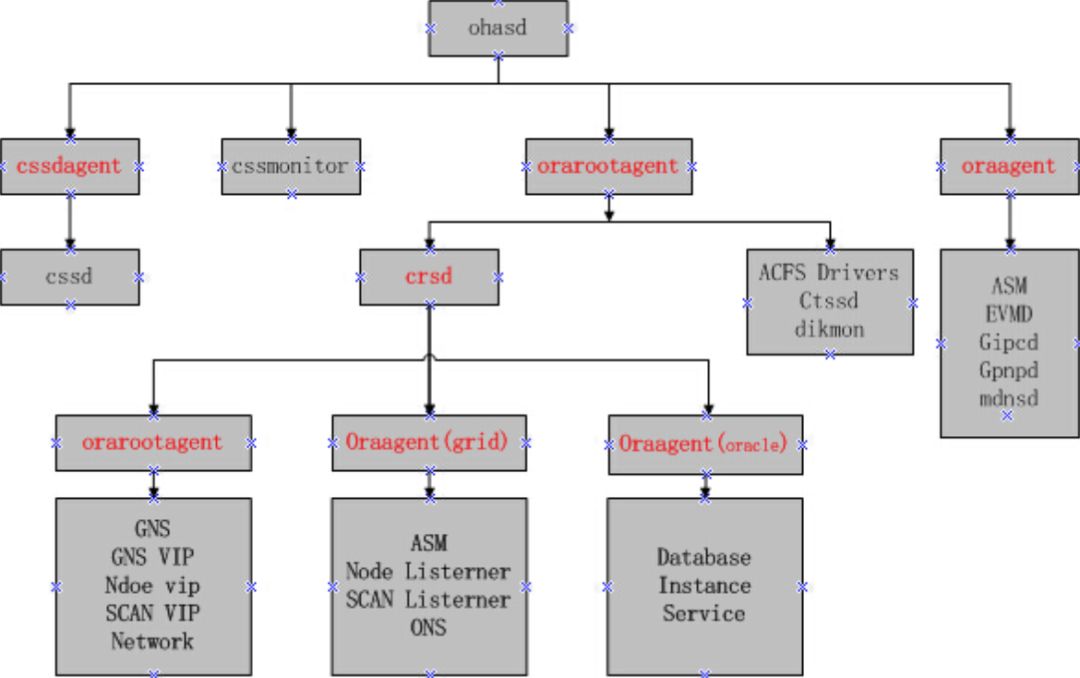
Agent管理了几乎所有的资源和守护进程,例如ohasd产生的oraagent管理gipc,gpnp
ohasd 会产生下面的agent
cssdagent(agent就是执行crsctl stat res –t –init出现的资源ora.cssd )
orarootagent
oraagent
cssdmonitor
crsd 会产生下面的agent
orarootagent
oraagent
用户自定义的agent
用户oracle和grid都会产生各自对应的oraagent来管理各自的资源。例如 oraagent_grid管理资源ora.asm,oraagent_oracle管理ora.<database_name>.db资源。
02
Agent如何工作
Agent 有一些EP(Entry Point),EP表示可以对资源执行的动作。
Start:启动资源
Stop:停止资源
Check:检查资源的状态,如果发现资源状态改变,agent会通知GI资源状态发生了改变
Clean:清理资源,当资源存在问题时,需要重新启动或failover,发生这个EP
Abort:中止资源
ORACLE官方文档描述如下
Agent developers can set the following entry points as callbacks to their code:
START: The START entry point acts to bring a resource online. The agent framework calls this entry point whenever it receives the start command from Oracle Clusterware.
STOP: The STOP entry points acts to gracefully bring down a resource. The agent framework calls this entry point whenever it receives the stop command from Oracle Clusterware.
CHECK: The CHECK (monitor) entry point acts to monitor the health of a resource. The agent framework periodically calls this entry point. If it notices any state change during this action, then the agent framework notifies Oracle Clusterware about the change in the state of the specific resource.
CLEAN: The CLEAN entry point acts whenever there is a need to clean up a resource. It is a non-graceful operation that is invoked when users must forcefully terminate a resource. This command cleans up the resource-specific environment so that the resource can be restarted.
ABORT: If any of the other entry points hang, the agent framework calls the ABORT entry point to abort the ongoing action. If the agent developer does not supply an abort function, then the agent framework exits the agent program.
START, STOP, CHECK, and CLEAN are mandatory entry points and the agent developer must provide these entry points when building an agent. Agent developers have several options to implement these entry points, including using C, C++, or scripts. It is also possible to develop agents that use both C or C++ and script-type entry points. When initializing the agent framework, if any of the mandatory entry points are not provided, then the agent framework invokes a script pointed to by the ACTION_SCRIPT resource attribute.
每一个EP结束之后,会返回资源对应的状态,这些状态有:
ONLINE <==== 对应资源的online状态
OFFLINE <==== 对应资源的offline状态
对于offline状态,可以细分为planed offline 和unplaned offline。Planed offline是指GI倾 向于这个资源处在offline状态,例如我们使用GI相关的工具(srvctl, crsctl)停止了一个资源,这种情况,GI就认为资源应该处于offline状态,因为停止资源的操作是通过GI来实现的。同时,对于planed offline的资源,它的target状态也会被修改为offline状态,这意味着,如果在资源的target状态为offline时重启GI stacks,除非资源的auto_start属性设置为always,否则,该资源不会被自动启动。
对于unplaned offline,是指资源被GI以外的工具停止,例如使用sqlplus手动关闭数据库,在这种情况下,GI并不认为该资源应该处于offline状态,资源的target状态仍然为online,所以,资源在重新启动GI时仍然会被启动,当然除非资源的auto_start属性设置为never。
UNKNOWN <==== 未知,对应资源的unknown状态。在这种状态下,agent会继续对该资源进行check
PARTIAL <==== 资源部分在线,对应资源的intermediate状态。 在这种情况下agent会继续对该资源进行check,并及时更新资源状态
FAILED <==== 失败,该返回值说明资源存在问题,不能正常工作,agent会首先执行clean,之后根据资源的相关属性进行failover或restart操作
有关AUTO_START的描述
Indicates whether Oracle Clusterware automatically starts a resource after a cluster server restart. Valid AUTO_START values are:
always: Restarts the resource when the server restarts regardless of the state of the resource when the server stopped.
restore: Restores the resource to the same state that it was in when the server stopped. Oracle Clusterware attempts to restart the resource if the value of TARGET was ONLINE before the server stopped.
never: Oracle Clusterware never restarts the resource regardless of the state of the resource when the server stopped.
03
Agent日志文件
agent与负责管理的资源的对应关系
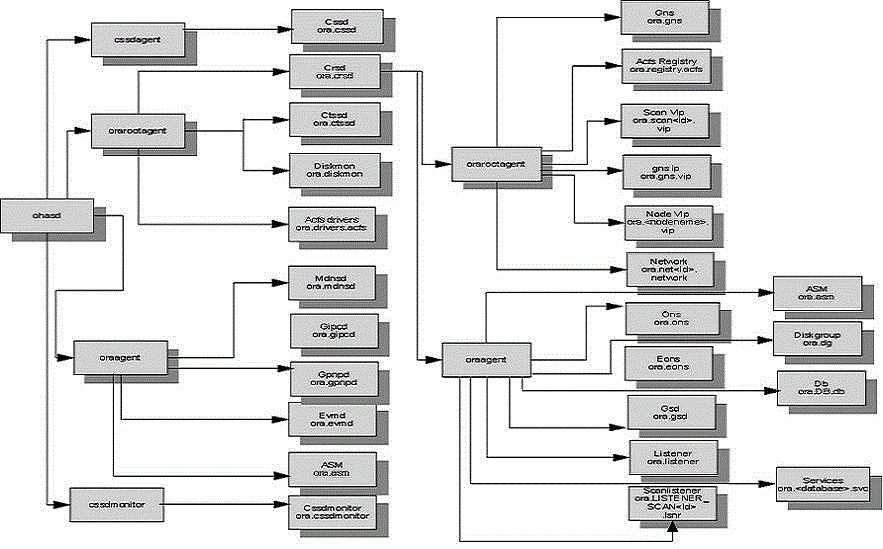
>>>>ohasd产生的orarootagent日志
GRID_HOME/log/<host>/agent ohasd/orarootagent_root
>>>>ohasd产生的oraagent日志
GRID_HOME/log/<host>/agent/ohasd/oraagent_grid
>>>>ohasd产生的cssdagent日志
GRID_HOME/log/<host>/agent/ohasd/oracssdagent_root
>>>>ohasd产生的cssdmonitor日志
GRID_HOME/log/<host>/agent/ohasd/oracssdmonitor_root
>>>>crsd产生的oraagent日志,owner为grid
GRID_HOME/log/<host>/agent/crsd/oraagent_grid
>>>>crsd产生的oraagent日志,owner为oracle
GRID_HOME/log/<host>/agent/crsd/oraagent_oracle
>>>>crsd产生的orarootagent日志
GRID_HOME/log/<host>/agent/crsd/orarootagent_root
>>>>集群alert log
Grid_home/log/<hostname>/alert<hostname>.log
Grid_home/log/<hostname>/ohasd/ohasd.log
Grid_home/log/<hostname>/crsd/crsd.log
由于每个agent管理多个资源,所以,如果只是某一个资源存在问题,为了提升问题排查效率,可以使用有问题的资源名称过滤agent日志。
Agent crash会产程一个core文件
Grid_home/log/<hostname>/agent/{ohasd|crsd}/<agent名>_<用户名>
和对应的堆栈文件
Grid_home/log/<hostname>/agent/{ohasd|crsd}/<agent名>_<用户名>/<agent名>_<用户名>OUT.log






