一、背景
在之前的一篇业务规则引擎初试 文章中尝试了使用业务规则引擎来处理促销模块的功能实现,条件其实还相对单一,随着业务的迭代,会有复杂的组合条件的规则匹配,对这一块的功能通过DSL和前端拖拽的控件处理把我们赠品服务重构了一下,接下来就带大家分享下实践方案;
一段代码越容易看懂,就越容易发现错误,也就越容易对系统进行修改.
二、DSL 初识
在Martin Fowler的《Domain Specific Languages》书中。开篇就是以State Machine来作为引子介绍DSL的。有时间的话,强烈建议你去读读这本书。
DSL是一种工具,它的核心价值在于,它提供了一种手段,可以更加清晰地就系统某部分的意图进行沟通。
按照定义来说,DSL是针对某一特定领域,具有受限表达性的一种计算机程序设计语言。这一定义包含3个关键元素:
语言性(language nature):DSL是一种程序设计语言,因此它必须具备连贯的表达能力——不管是一个表达式还是多个表达式组合在一起。
受限的表达性(limited expressiveness):通用程序设计语言提供广泛的能力:支持各种数据、控制,以及抽象结构。这些能力很有用,但也会让语言难于学习和使用。DSL只支持特定领域所需要特性的最小集。使用DSL,无法构建一个完整的系统,相反,却可以解决系统某一方面的问题。
针对领域(domain focus):只有在一个明确的小领域下,这种能力有限的语言才会有用。这个领域才使得这种语言值得使用。
总结一下,DSL是什么?全称是Domain Specific Language,领域特定语言。举个例子SQL就是数据库领域的交互语言,它定义了一套标准语法,各大数据库厂商(如mysql、oracle)对其进行解析实现,任何人都可通过编写SQL实现与数据库的交互。类似还有正则表达式、HTML&CSS等均形成了自己的语法标准。
三、实践
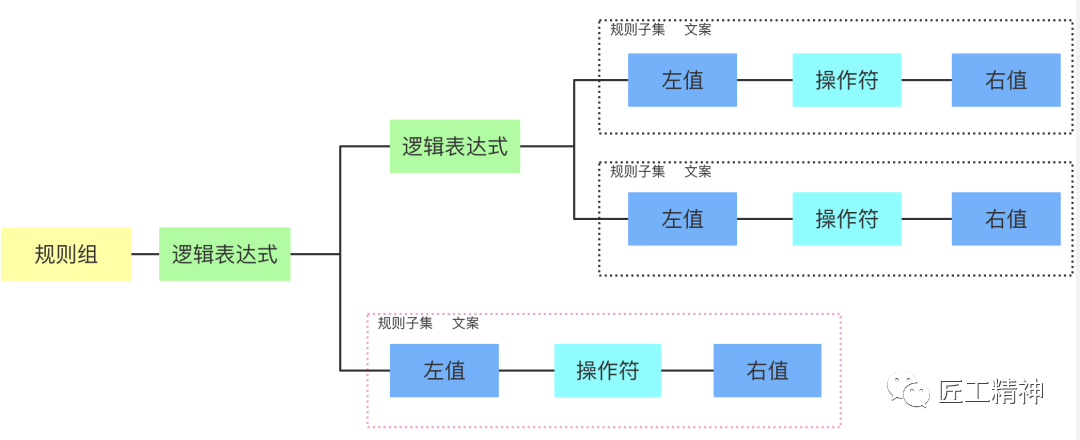
为了完成促销规则引擎,我们也实现一套自定义DSL语法,并对其解析,通过DSL语法实现与规则引擎的交互,一条规则的执行过程大致如下:先通过数据计算出特征(理解入参),然后带入条件表达式计算,并对多个表达式结果做逻辑运算,最终根据逻辑运算决定是否触发结果。实际的业务需求通常不会只有一组规则,会对不同的规则、规则集进行编排,还会出现分支流程,子流程,形成一个更复杂决策流程,我们叫决策流,决策流的解析就是实现一个流程引擎。
此处为了演示方便,使用yml文件定义规则:
workflow:
- node:
nodeName: start_test
category: start
nextNodeName: conditional_1
nextCategory: conditional
- node:
nodeName: conditional_1
category: conditional
nextNodeName: ""
nextCategory: ""
- node:
nodeName: ruleset_1
category: ruleset
nextNodeName: end_1
nextCategory: end
- node:
nodeName: ruleset_2
category: ruleset
nextNodeName: end_2
nextCategory: end
- node:
nodeName: end_1
category: end
nextNodeName: ""
nextCategory: ""
- node:
nodeName: end_2
category: end
nextNodeName: ""
nextCategory: ""
ruleSets:
- ruleset:
rulesetName: ruleset_1
rulesetCategory: internal
ruleExec: allrun
depends: [feature_1,feature_2,feature_3]
rules:
- rule:
ruleName: rule_1
conditions:
- condition:
feature: feature_1
operator: GT
value: 50
logic: ""
decision: reject
- rule:
ruleName: rule_2
conditions:
- condition:
feature: feature_2
operator: LT
value: 18
- condition:
feature: feature_3
operator: GT
value: 50
logic: OR
decision: reject
- ruleset:
rulesetName: ruleset_2
rulesetCategory: internal
ruleExec: allrun #rule execution strategy:allrun,rejectbreak
depends: [feature_1,feature_2]
rules:
- rule:
ruleName: rule_3
conditions:
- condition:
feature: feature_1
operator: GT
value: 50
logic: ""
decision: reject
- rule:
ruleName: rule_4
conditions:
- condition:
feature: feature_2
operator: LT
value: 18
- condition:
feature: feature_2
operator: GT
value: 50
logic: OR
decision: reject
conditionals:
- conditional:
conditionalName: conditional_1
depends: [feature_4]
branches:
- branch:
branchName: branch_1
conditions:
- condition:
feature: feature_4
operator: GT
value: 5
- condition:
feature: feature_4
operator: LE
value: 10
logic: AND
decision: ruleset_1
- branch:
branchName: branch_2
conditions:
- condition:
feature: feature_4
operator: GT
value: 10
logic: ""
decision: ruleset_2
对上面的结构做下说明,workflow部分,可以理解为一个业务处理的流程,ruleSets部分,一系列的规则集合,conditionals部分,理解为条件网关的实现。
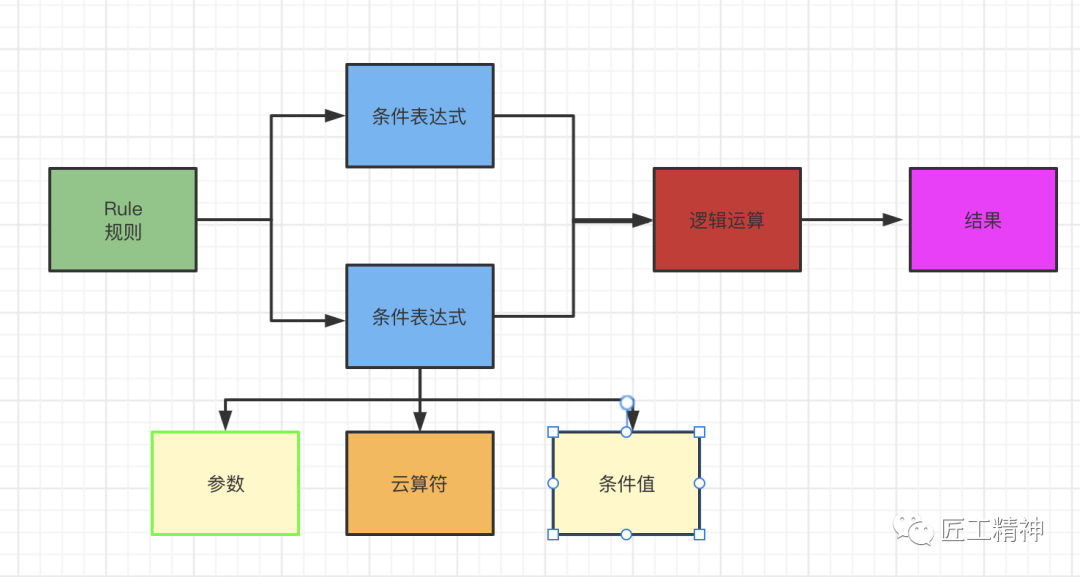
条件表达式计算完后会有一个结果,然后通过逻辑运算计算得到最终的结果:
这里会涉及到诸如 <=、>=、<、>等条件的判断处理及逻辑运算 AND、OR等组合的计算,系统引用的是groovyshell,在java里处理起来也很方便:
/**
* 条件表达式判断是否为true
* @param left
* @param right
* @param operator
* @return
*/
public static boolean evaluate(Object left,String operator,Object right) {
Binding binding = new Binding();
binding.setVariable("left", left);
binding.setVariable("right", right);
String expression = "left %s right";
String operation = OperatorMap.valueOf(operator).getCode();
expression = String.format(expression, operation);
GroovyShell groovyShell = new GroovyShell(binding);
String result = groovyShell.evaluate(expression).toString();
return Boolean.parseBoolean(result);
}
/**
* 逻辑表达式的计算
* @param results
* @param logic
* @return
*/
public static boolean logical(List<Boolean> results,String logic) {
if(!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(results)) {
if (results.size() == 1) {
return results.get(0);
}
String expression = "" ;
for(int i=0; i< results.size();i++) {
expression += results.get(i);
if (i != results.size()-1) {
expression += LogicMap.valueOf(logic).getCode();
}
}
GroovyShell groovyShell = new GroovyShell();
String result = groovyShell.evaluate(expression).toString();
return Boolean.parseBoolean(result);
}
return false;}
条件判断处理抽象:
/**
* @author villiam
* @date 2021-08-21
*
* 操作符号抽象
*/
public enum OperatorMap {
GT("GT",">"),
LT("LT","<"),
GE("GE",">="),
LE("LE","<="),
EQ("EQ","=="),
NEQ("NEQ","!=");
private String name;
private String code;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(String code) {
this.code = code;
}
OperatorMap(String name, String code){
this.code = code;
this.name = name;
}}
/**
* @author villiam
* @date 2021-08-21
*
* 逻辑运算符抽象处理
*/
public enum LogicMap {
AND("AND","&&"),
OR("OR","||");
private String name;
private String code;
LogicMap(String name,String code){
this.code = code;
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(String code) {
this.code = code;
}
}yml文件的解析用的是spring的 YamlMapFactoryBean:
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import com.yilimaizi.decision.dsl.Dsl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.YamlMapFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.ResourcePatternResolver;
import java.util.Map;
public class YmlRegister {
private static final String CLASSPATH_FLOW="*.yml";
public static Dsl init() {
try {
ResourcePatternResolver resolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
Resource[] resources = resolver.getResources(CLASSPATH_FLOW);
for(Resource resource: resources){
YamlMapFactoryBean yamlMapFactoryBean = new YamlMapFactoryBean();
yamlMapFactoryBean.setResources(resource);
yamlMapFactoryBean.afterPropertiesSet();
Map<String, Object> object = yamlMapFactoryBean.getObject();
System.out.println("parse result is =="+JSON.toJSONString(object));
Dsl flow = JSONObject.parseObject(JSON.toJSONString(object), Dsl.class);
return flow;
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}}
最后再附上domain的类:
/**
* @author villiam.li
* @date 2021-08-21
*
* workflow 节点
*/
@Data
public class Node {
private String nodeName;
private String category;
private String nextNodeName;
private String nextCategory;
}
/**
* @author villiam.li
* @date 2021-08-21
*
* 规则抽象
*/
@Data
public class Rule {
private List<Condition> conditions;
private String ruleName;
private String ruleGroup;
private String logic;
private DecisionMap decision;
private List<String> depends;
public boolean parse(Map<String, Feature> depends,Rule rule) {
List<Boolean> conditionResults = new ArrayList<>();
if (Objects.nonNull(rule)){
if(!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(rule.getConditions())) {
for(Condition condition: rule.getConditions()) {
if(depends.containsKey(condition.getFeature())) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(depends.get(condition.getFeature()).getName())) {
continue;
}
boolean result = GroovyExpressionUtil.evaluate(depends.get(condition.getFeature()).getValue(),condition.getOperator(),condition.getValue());
conditionResults.add(result);
}
}
}
return GroovyExpressionUtil.logical(conditionResults,rule.getLogic());
}
return false;
}
}
/**
* @author villiam.li
* @date 2021-08-21
*
* 规则集的抽象模型
*/
@Data
public class Ruleset {
private String ruleSetName;
private String ruleSetCategory;
private String ruleExec;
private List<Rule> rules;
private List<String> depends;
public Object parse(Ruleset ruleset, DslResult result, GlobalFeatures globalFeatures) {
NodeResult nodeResult = new NodeResult();
nodeResult.setNodeName(ruleset.getRuleSetName());
Map<String, Feature> depends = globalFeatures.get(ruleset.getDepends(),globalFeatures);
nodeResult.setFactor(depends);
List<Object> hits = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> ruleResult = new ArrayList<>();
for(Rule rule: ruleset.getRules()) {
boolean flag = rule.parse(depends,rule);
Integer ruleDecision = DecisionMap.REJECT.getCode();
if (flag) {
hits.add(rule.getRuleName());
nodeResult.setHits(hits);
ruleDecision = rule.getDecision().getCode();
}
ruleResult.add(ruleDecision);
}
if(!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(ruleResult)) {
nodeResult.setDecision(ruleResult.get(0));
result.getDetail().add(nodeResult);
return ruleResult.get(0);
}
return null;
}
}
/**
* @author villiam.li
* @date 2021-08-21
*
* dsl抽象
*/
@Data
public class Dsl {
private List<Node> workflow;
private List<Ruleset> ruleSets;
private List<Conditional> conditionals;
/**
* 获取第一个节点
* @param dsl
* @return
*/
public Node findStartNode(Dsl dsl){
if (Objects.nonNull(dsl)) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(dsl.getWorkflow())) {
for(Node node: dsl.getWorkflow()) {
if(Constants.START.equals(node.getCategory())) {
return node;
}
}
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 根据名称获取节点
* @param dsl
* @param nodeName
* @return
*/
public Node findNode(Dsl dsl,String nodeName){
if (Objects.nonNull(dsl)) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(dsl.getWorkflow())) {
for(Node node: dsl.getWorkflow()) {
if(nodeName.equals(node.getNodeName())) {
return node;
}
}
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 根据名称获取ruleset
* @param dsl
* @param name
* @return
*/
public Ruleset findRuleset(Dsl dsl,String name){
if (Objects.nonNull(dsl)) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(dsl.getWorkflow())) {
for(Ruleset ruleset: dsl.getRuleSets()) {
if(name.equals(ruleset.getRuleSetName())) {
return ruleset;
}
}
}
}
return null;
}
public Conditional findConditional(String name,Dsl dsl) {
for(Conditional conditional: dsl.getConditionals()){
if (conditional.getConditionalName().equals(name)) {
return conditional;
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 获取下一个node
* @param dsl
* @param nodeName
* @param category
* @param result
*/
public void gotoNextNode(Dsl dsl, String nodeName, String category, DslResult result, GlobalFeatures globalFeatures) {
Node node = dsl.findNode(dsl,nodeName);
List<String> trackList = new ArrayList<>();
if (Objects.nonNull(node)) {
trackList.add(nodeName);
result.setNextNodeName(node.getNextNodeName());
result.setNextCategory(node.getNextCategory());
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(result.getTrack())) {
result.setTrack(trackList);
}else {
result.getTrack().addAll(trackList);
}
switch (category) {
case Constants.START:
return;
case Constants.RULESET:
Ruleset ruleset = dsl.findRuleset(dsl,node.getNodeName());
Object decision = ruleset.parse(ruleset,result,globalFeatures);
if(Objects.nonNull(decision)) {
result.setDecision(decision);
}
return;
case Constants.CONDITIONAL:
Conditional conditional = findConditional(node.getNodeName(),dsl);
Object object = conditional.parse(conditional,result,globalFeatures);
if (Objects.nonNull(object)) {
result.setNextNodeName(object.toString());
result.setNextCategory(dsl.findNode(dsl,object.toString()).getCategory());
}
return;
case Constants.END:
result.setNextCategory(null);
result.setNextNodeName(null);
return;
default:
return;
}
}
}
public boolean isBreakDecision(Object decision){
if (Objects.isNull(decision)) {
return false;
}
return decision.toString().equals(DecisionMap.REJECT.getCode().toString());
}
}
/**
* @author villiam.li
* @date 2021-08-21
*
* 规则网关抽象
*/
@Data
public class Conditional {
private String conditionalName;
private List<String> depends;
private List<Branch> branches;
public Object parse(Conditional conditional, DslResult result, GlobalFeatures globalFeatures){
NodeResult nodeResult = new NodeResult();
nodeResult.setNodeName(conditional.getConditionalName());
Map<String, Feature> depends = globalFeatures.get(conditional.getDepends(),globalFeatures);
nodeResult.setFactor(depends);
for(Branch branch: conditional.getBranches()){
List<Boolean> conditionResults = new ArrayList<>();
for(Condition condition: branch.getConditions()) {
if(depends.containsKey(condition.getFeature())) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(depends.get(condition.getFeature()).getName())) {
continue;
}
boolean rs = GroovyExpressionUtil.evaluate(depends.get(condition.getFeature()).getValue(),condition.getOperator(),condition.getValue());
conditionResults.add(rs);
}
}
Boolean flag = GroovyExpressionUtil.logical(conditionResults,branch.getLogic());
if (flag) {
nodeResult.setDecision(branch.getDecision());
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(result.getDetail())) {
List<NodeResult> nodeResults = new ArrayList<>();
nodeResults.add(nodeResult);
result.setDetail(nodeResults);
}else {
result.getDetail().add(nodeResult);
}
return branch.getDecision();
}
}
return null;
}
}
/**
* @author villiam.li
* @date 2021-08-21
*
* 条件判断抽象
*/
@Data
public class Condition {
private String feature;
private String operator;
private String result;
private Object value;
}
/**
* @author villiam.li
* @date 2021-08-21
*
* 条件分支抽象
*/
@Data
public class Branch {
private String branchName;
private List<Condition> conditions;
private String logic;
private Double percent;
private Object decision;
}
请求request:
/**
* @author villiam.li
* @date 2021-08-21
*
* 请求request
*/
@Data
public class DslRunRequest {
private String flow;
private Map<String, Integer> features;
}
返回结果:
/**
* @author villiam.li
*/
@Data
public class DslResult {
private String nextNodeName;
private String nextCategory;
private Object decision;
private List<String> track;
private List<NodeResult> detail;
}最后进行测试:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1")
public class TestController {
@PostMapping(value = "/test")
public DslResult parse(@RequestBody DslRunRequest request) {
DslResult result = new DslResult();
GlobalFeatures globalFeatures = new GlobalFeatures();
Map<String, Feature> featureMap = new HashMap<>();
Map<String, Integer> features = request.getFeatures();
features.forEach((key,value)->{
Feature feature = new Feature();
feature.setName(key);
feature.setValue(value);
featureMap.put(key,feature);
globalFeatures.setFeatures(featureMap);
});
//1. 获取资源文件
Dsl dsl = YmlRegister.init();
if (Objects.nonNull(dsl)) {
if(! CollectionUtils.isEmpty(dsl.getWorkflow())) {
Node firstNode = dsl.findStartNode(dsl);
dsl.gotoNextNode(dsl,firstNode.getNodeName(),firstNode.getCategory(),result,globalFeatures);
while (!StringUtils.isEmpty(result.getNextNodeName()) && !dsl.isBreakDecision(result.getDecision())) {
dsl.gotoNextNode(dsl,result.getNextNodeName(), result.getNextCategory(), result,globalFeatures);
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
请求示例:
curl -XPOST -v http://localhost:8080/api/v1/test -H'Content-Type:application/json' -d'{"flow":"flow_conditional","features":{"feature_1":18,"feature_2":30,"feature_3":20,"feature_4":30}}';
四、总结
配置化的规则替代了硬编码的校验逻辑,减少了修改规则发布代码维护的成本,同时也让业务逻辑与代码分离。结合目前我们在做的低代码平台,通过前端页面的拖拽组件,配置好业务流程,让业务更快的迭代。






