源码分析系列文章汇总在github,开源电子书地址如下:
github:
https://github.com/farmer-hutao/k8s-source-code-analysisgitbook:
https://farmer-hutao.github.io/k8s-source-code-analysis

IPtables-Mode Proxier
概述
Proxier 数据结构与类定义
Proxier对象生成与运行
Proxier 服务与端点更新 Tracker
syncProxyRule 同步配置与规则
UpdateServiceMap() SVC 服务的更新实现
UpdateEndpointsMap() 端点更新的实现
更新 service 和 endpoints ;返回更新结果
创建与联接 kube 链
创建 Iptables 基础数据
为每个 service 创建 rules
配置收尾规则数据
汇集与加载 iptables 配置规则数据
IPtables 底层的 runner 实现
iptables 执行器
iptables 执行器方法
1. 概述
kube-Proxy提供三种模式(userspace/iptables/ipvs)的proxier实现,userspace是早期的proxy模式,ipvs模式处于实验性阶段proxy模式,本文先从默认的内核级iptables proxier代码实现与逻辑分析开始,其它模式将用专文解析源码。
Iptables-mode Proxier的service配置和代码内都包含一些基础概念如clusterIP、nodeport、loadbalancer、Ingress、ClusterCIDR、onlyLocal、ExternalIP等,请在了解源码之前先熟悉其概念用途场景与类型区别,再看源码将对你理解proxy事半功倍。当然也需要对netfilter、iptables、connTrack等proxy基础依赖的工具熟悉。基础概念部分在本文将不深入介绍,有需求可自行查阅相关资料。
从kube-proxy组件整体框架层的代码来看,在ProxyServer.Run()最后走到了s.Proxier.SyncLoop()执行空间一直无限loop下去。而默认的ProxyServer配置的Proxier对象就是Iptables(if proxyMode == proxyModeIPTables),将调用iptabls-mode的Proxier.SyncLoop(),SyncLoop()时间定时循环执行syncProxyRules()完成services、endpoints与iptables规则的同步操作。
Iptables-mode proxier的负载均衡机制是通过底层netfliter/iptables规则来实现的,通过Informer机制watch服务与端点信息的变更事件触发对iptables的规则的同步更新,如下代码逻辑示意图:
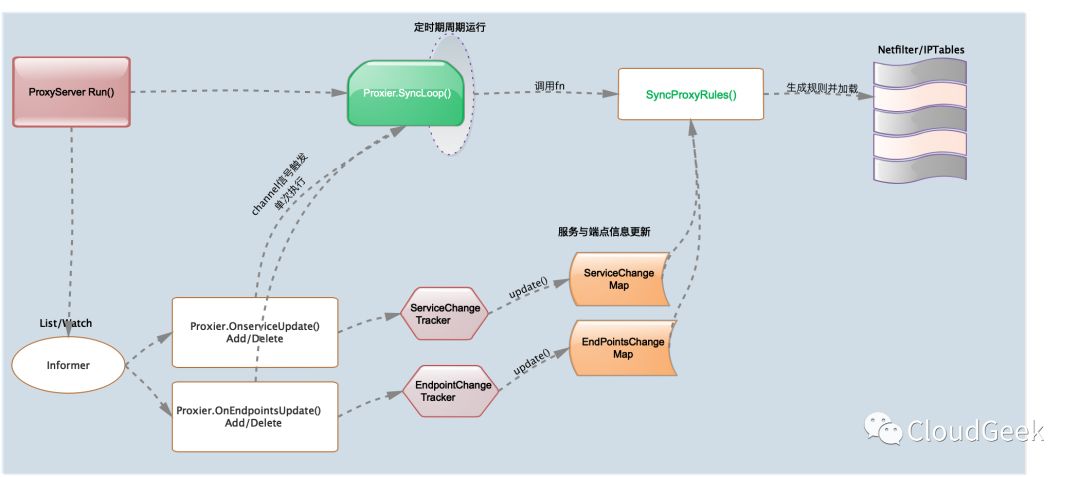
下面proxier源码分析,我们先从proxier的接口、实现类、实现类方法列表一窥究竟,从结构上看整体Proxier的框架。然后我们再详细分析proxier对象的产生时所定义的属性值、值类型和用途。有了前面的两项的了解后我们再来分析proxier类方法的实现,也就是proxier代理逻辑部分(关键逻辑部分在syncProxyRules()方法分析部分)。最后我们分析proxier底层内核iptables的runner实现,也就是proxy上层逻辑层最终会调用iptables命令去执行规则的操作部分。
2. Proxier 数据结构与类定义
ProxyProvider 代理提供者接口定义,需要实现两个proxy的关键方法Sync()和SyncLoop()
pkg/proxy/types.go:27
type ProxyProvider interface {
// Sync 即时同步Proxy提供者的当前状态至proxy规则
Sync()
// SyncLoop 周期性运行
// 作为一个线程或应用主loop运行,无返回.
SyncLoop()
}
Copy
Iptables-mode Proxier 为 ProxyProvider 接口实现类,proxier 类属性项比较多,我们先看一下注释用途与结构定义,在实例化proxier对象时我们再详看。
pkg/proxy/iptables/proxier.go:205
type Proxier struct {
endpointsChanges *proxy.EndpointChangeTracker // 端点更新信息跟踪器
serviceChanges *proxy.ServiceChangeTracker // 服务更新信息跟踪器
mu sync.Mutex // 保护同步锁
serviceMap proxy.ServiceMap // 存放服务列表信息 ①
endpointsMap proxy.EndpointsMap // 存放端点列表信息 ②
portsMap map[utilproxy.LocalPort]utilproxy.Closeable //端口关闭接口map
endpointsSynced bool // ep同步状态
servicesSynced bool // svc同步状态
initialized int32 // 初始化状态
syncRunner *async.BoundedFrequencyRunner // 指定频率运行器,此处用于管理对
// syncProxyRules的调用
iptables utiliptables.Interface // iptables命令执行接口
masqueradeAll bool
masqueradeMark string // SNAT地址伪装Mark
exec utilexec.Interface // exec命令执行工具接口
clusterCIDR string // 集群CIDR
hostname string // 主机名
nodeIP net.IP // 节点IP地址
portMapper utilproxy.PortOpener // TCP/UTP端口打开与监听
recorder record.EventRecorder // 事件记录器
healthChecker healthcheck.Server // healthcheck服务器对象
healthzServer healthcheck.HealthzUpdater // Healthz更新器
precomputedProbabilities []string //预计算可能性
//iptables规则与链数据(Filter/NAT)
iptablesData *bytes.Buffer
existingFilterChainsData *bytes.Buffer
filterChains *bytes.Buffer
filterRules *bytes.Buffer
natChains *bytes.Buffer
natRules *bytes.Buffer
endpointChainsNumber int
// Node节点IP与端口信息
nodePortAddresses []string
networkInterfacer utilproxy.NetworkInterfacer //网络接口
}
Copy
① ServiceMap和ServicePort定义
pkg/proxy/service.go:229
type ServiceMap map[ServicePortName]ServicePort
//String() => "NS/SvcName:PortName"
ServicePortName{NamespacedName: svcName, Port: servicePort.Name}
Copy
ServiceSpec service.spec定义,在用户前端可定义service的spec配置项。
vendor/k8s.io/api/core/v1/types.go:3606
type ServiceSpec struct {
Ports []ServicePort //服务端口列表
Selector map[string]string //选择器
ClusterIP string //VIP 、 portal
Type ServiceType //服务类型
ExternalIPs []string //外部IP列表,如外部负载均衡
SessionAffinity ServiceAffinity //会话保持
LoadBalancerIP string //service类型为"LoadBalancer"时配置LB ip
LoadBalancerSourceRanges []string //cloud-provider的限制client ip区间
ExternalName string
ExternalTrafficPolicy ServiceExternalTrafficPolicyType
HealthCheckNodePort int32
PublishNotReadyAddresses bool
SessionAffinityConfig *SessionAffinityConfig //会话保持配置信息
}
Copy
ServicePort类定义和ServicePort接口
vendor/k8s.io/api/core/v1/types.go:3563
type ServicePort struct {
Name string
Protocol Protocol
Port int32
TargetPort intstr.IntOrString
NodePort int32
}
//ServicePort接口
type ServicePort interface {
// 返回服务字串,格式如: `IP:Port/Protocol`.
String() string
// 返回集群IP字串
ClusterIPString() string
// 返回协议
GetProtocol() v1.Protocol
// 返回健康检测端口
GetHealthCheckNodePort() int
}
Copy
② EndpointsMap定义与Endpoint接口
pkg/proxy/endpoints.go:181
type EndpointsMap map[ServicePortName][]Endpoint
type Endpoint interface {
// 返回endpoint字串,格式 `IP:Port`.
String() string
// 是否本地
GetIsLocal() bool
// 返回IP
IP() string
// 返回端口
Port() (int, error)
// 检测两上endpoint是否相等
Equal(Endpoint) bool
}
Copy
Endpoints结构与相关定义
vendor/k8s.io/api/core/v1/types.go:3710
type Endpoints struct {
metav1.TypeMeta
metav1.ObjectMeta
Subsets []EndpointSubset
}
type EndpointSubset struct {
Addresses []EndpointAddress // EndpointAddress地址列表
NotReadyAddresses []EndpointAddress
Ports []EndpointPort // EndpointPort端口列表
}
type EndpointAddress struct {
IP string
Hostname string
NodeName *string
TargetRef *ObjectReference
}
type EndpointPort struct {
Name string
Port int32
Protocol Protocol
}
Copy
Iptables-mode Proxier提供的方法列表,先大概从名称上来了解一下方法用途,后面我在逻辑部分对主要使用的方法再深入分析。
func (proxier *Proxier) precomputeProbabilities(numberOfPrecomputed int) {/*...*/}
func (proxier *Proxier) probability(n int) string{/*...*/}
func (proxier *Proxier) Sync(){/*...*/}
func (proxier *Proxier) SyncLoop(){/*...*/}
func (proxier *Proxier) setInitialized(value bool){/*...*/}
func (proxier *Proxier) isInitialized() bool{/*...*/}
func (proxier *Proxier) OnServiceAdd(service *v1.Service){/*...*/}
func (proxier *Proxier) OnServiceUpdate(oldService, service *v1.Service){/*...*/}
func (proxier *Proxier) OnServiceDelete(service *v1.Service){/*...*/}
func (proxier *Proxier) OnServiceSynced(){/*...*/}
func (proxier *Proxier) OnEndpointsAdd(endpoints *v1.Endpoints){/*...*/}
func (proxier *Proxier) OnEndpointsUpdate(oldEndpoints, endpoints *v1.Endpoints){/*...*/}
func (proxier *Proxier) OnEndpointsDelete(endpoints *v1.Endpoints) {/*...*/}
func (proxier *Proxier) OnEndpointsSynced() {/*...*/}
func (proxier *Proxier) deleteEndpointConnections(connectionMap []proxy.ServiceEndpoint){/*...*/}
func (proxier *Proxier) appendServiceCommentLocked(args []string, svcName string){/*...*/}
func (proxier *Proxier) syncProxyRules(){/*...*/}
Copy
3. Proxier对象生成与运行
篇幅限制,本节参考 github
4. Proxier 服务与端点更新 Tracker
篇幅限制,本节参考 github
5. syncProxyRule 同步配置与规则
篇幅限制,本节参考 github
5.1. 更新 service 和 endpoints ;返回更新结果
pkg/proxy/iptables/proxier.go:652
//更新SVC/EP
serviceUpdateResult := proxy.UpdateServiceMap(proxier.serviceMap, proxier.serviceChanges)
endpointUpdateResult := proxy.UpdateEndpointsMap(proxier.endpointsMap, proxier.endpointsChanges)
staleServices := serviceUpdateResult.UDPStaleClusterIP
// 从EndpointsMap更新结果返回中合并UDP协议废弃服务信息
for _, svcPortName := range endpointUpdateResult.StaleServiceNames {
if svcInfo, ok := proxier.serviceMap[svcPortName]; ok && svcInfo != nil && svcInfo.GetProtocol() == v1.ProtocolUDP {
klog.V(2).Infof("Stale udp service %v -> %s", svcPortName, svcInfo.ClusterIPString())
staleServices.Insert(svcInfo.ClusterIPString())
}
}
Copy
5.1.1. UpdateServiceMap() SVC 服务的更新实现
篇幅限制,本节参考 github
5.1.2. UpdateEndpointsMap() 端点更新的实现
篇幅限制,本节参考 github
5.2. 创建与联接 kube 链
篇幅限制,本节参考 github
5.3. 创建 Iptables 基础数据
获取现存在的Filter/Nat表链数据
创建iptables-save/restore格式数据(表头、链)
创建SNAT地址伪装规则
pkg/proxy/iptables/proxier.go:688
//现存在的filter表链获取
existingFilterChains := make(map[utiliptables.Chain][]byte)
proxier.existingFilterChainsData.Reset()
err := proxier.iptables.SaveInto(utiliptables.TableFilter, proxier.existingFilterChainsData) //通过iptables-save方式来获取
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Failed to execute iptables-save, syncing all rules: %v", err)
} else {
existingFilterChains = utiliptables.GetChainLines(utiliptables.TableFilter, proxier.existingFilterChainsData.Bytes()) //输出结果
}
//同上,现存在的nat表链获取
existingNATChains := make(map[utiliptables.Chain][]byte)
proxier.iptablesData.Reset()
err = proxier.iptables.SaveInto(utiliptables.TableNAT, proxier.iptablesData)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Failed to execute iptables-save, syncing all rules: %v", err)
} else {
existingNATChains = utiliptables.GetChainLines(utiliptables.TableNAT, proxier.iptablesData.Bytes())
}
// Reset all buffers used later.
// This is to avoid memory reallocations and thus improve performance.
proxier.filterChains.Reset()
proxier.filterRules.Reset()
proxier.natChains.Reset()
proxier.natRules.Reset()
// 写表头
writeLine(proxier.filterChains, "*filter")
writeLine(proxier.natChains, "*nat")
Copy
写链数据
fileter: "KUBE-SERVICES" "KUBE-EXTERNAL-SERVICES"/ "KUBE-FORWARD"nat: "KUBE-SERVICES" "KUBE-NODEPORTS" "KUBE-POSTROUTING" "KUBE-MARK-MASQ"
pkg/proxy/iptables/proxier.go:720
// 写chain链数据,将filter和Nat相关链格式化存放buffer
for _, chainName := range []utiliptables.Chain{kubeServicesChain, kubeExternalServicesChain, kubeForwardChain} {
if chain, ok := existingFilterChains[chainName]; ok {
writeBytesLine(proxier.filterChains, chain)
} else {
// iptables-save/restore格式的链行":$chainName - [0:0]"
writeLine(proxier.filterChains, utiliptables.MakeChainLine(chainName))
}
}
for _, chainName := range []utiliptables.Chain{kubeServicesChain, kubeNodePortsChain, kubePostroutingChain, KubeMarkMasqChain} {
if chain, ok := existingNATChains[chainName]; ok {
writeBytesLine(proxier.natChains, chain)
} else {
writeLine(proxier.natChains, utiliptables.MakeChainLine(chainName))
}
}
Copy
写地址伪装规则,在POSTROUTING阶段对地址进行MASQUERADE(基于接口动态IP的SNAT)处理,原始请求源IP将被丢失,被请求POD的应用看到为NodeIP或CNI设备IP(bridge/vxlan设备)
pkg/proxy/iptables/proxier.go:738
// 写kubernets特有的SNAT地址伪装规则
// -A KUBE-POSTROUTING -m comment --comment "kubernetes service traffic requiring SNAT" -m mark --mark 0x4000/0x4000 -j MASQUERADE
writeLine(proxier.natRules, []string{
"-A", string(kubePostroutingChain),
"-m", "comment", "--comment", `"kubernetes service traffic requiring SNAT"`,
"-m", "mark", "--mark", proxier.masqueradeMark,
"-j", "MASQUERADE",
}...)
//-A KUBE-MARK-MASQ -j MARK --set-xmark 0x4000/0x4000
writeLine(proxier.natRules, []string{
"-A", string(KubeMarkMasqChain),
"-j", "MARK", "--set-xmark", proxier.masqueradeMark,
}...)
Copy
5.4. 为每个 service 创建 rules
先了解serviceInfo的完整定义说明
pkg/proxy/iptables/proxier.go:141
type serviceInfo struct {
*proxy.BaseServiceInfo
// The following fields are computed and stored for performance reasons.
serviceNameString string
servicePortChainName utiliptables.Chain // KUBE-SVC-XXXX16BitXXXX 服务链
serviceFirewallChainName utiliptables.Chain // KUBE-FW-XXXX16BitXXXX Firewall链
serviceLBChainName utiliptables.Chain // KUBE-XLB-XXXX16BitXXXX SLB链
}
type BaseServiceInfo struct {
ClusterIP net.IP //PortalIP(VIP)
Port int //portal端口
Protocol v1.Protocol //协议
NodePort int //node节点端口
LoadBalancerStatus v1.LoadBalancerStatus //LB Ingress
SessionAffinityType v1.ServiceAffinity //会话保持
StickyMaxAgeSeconds int //保持最大时长
ExternalIPs []string //ExternalIPs(指定的node上监听端口)
LoadBalancerSourceRanges []string //过滤源地址流量
HealthCheckNodePort int //HealthCheck检测端口
OnlyNodeLocalEndpoints bool
}
Copy
为每个服务创建服务"KUBE-SVC-XXX…"和外部负载均衡"KUBE-XLB-XXX…"链
pkg/proxy/iptables/proxier.go:791
svcChain := svcInfo.servicePortChainName //"KUBE-SVC-XXX..."
if hasEndpoints {
// Create the per-service chain, retaining counters if possible.
if chain, ok := existingNATChains[svcChain]; ok {
writeBytesLine(proxier.natChains, chain)
} else {
writeLine(proxier.natChains, utiliptables.MakeChainLine(svcChain))
}
activeNATChains[svcChain] = true
}
svcXlbChain := svcInfo.serviceLBChainName // "KUBE-XLB-XXX…"
if svcInfo.OnlyNodeLocalEndpoints {
// Only for services request OnlyLocal traffic
// create the per-service LB chain, retaining counters if possible.
if lbChain, ok := existingNATChains[svcXlbChain]; ok {
writeBytesLine(proxier.natChains, lbChain)
} else {
writeLine(proxier.natChains, utiliptables.MakeChainLine(svcXlbChain))
}
activeNATChains[svcXlbChain] = true
}
Copy
clusterIP流量的匹配,clusterIP为默认方式,仅资源集群内可访问。
pkg/proxy/iptables/proxier.go:815
//存在端点,写规则
if hasEndpoints {
args = append(args[:0],
"-A", string(kubeServicesChain),
"-m", "comment", "--comment", fmt.Sprintf(`"%s cluster IP"`, svcNameString),
"-m", protocol, "-p", protocol,
"-d", utilproxy.ToCIDR(svcInfo.ClusterIP),
"--dport", strconv.Itoa(svcInfo.Port),
)
// proxier配置masqueradeAll
// -A KUBE-SERVICES -m comment --comment "..." -m $prot -p $prot -d $clusterIP \
// --dport $port -j KUBE-MARK-MASQ
if proxier.masqueradeAll {
writeLine(proxier.natRules, append(args, "-j", string(KubeMarkMasqChain))...)
} else if len(proxier.clusterCIDR) > 0 {
// proxier配置clusterCIDR情况:
// -A KUBE-SERVICES ! -s $clusterCIDR -m comment --comment "..." -m $prot \
// -p $prot -d $clusterIP --dport $port -j KUBE-MARK-MASQ
writeLine(proxier.natRules, append(args, "! -s", proxier.clusterCIDR, "-j", string(KubeMarkMasqChain))...)
}
// -A KUBE-SERVICES -m comment --comment "..." -m $prot -p $prot -d $clusterIP \
// --dport $port -j KUBE-SVC-XXXX16bitXXXX
writeLine(proxier.natRules, append(args, "-j", string(svcChain))...)
} else {
// 无Endpoints的情况,则创建REJECT规则
// -A KUBE-SERVICES -m comment --comment $svcName -m $prot -p $prot -d $clusterIP \
// --dport $port -j REJECT
writeLine(proxier.filterRules,
"-A", string(kubeServicesChain),
"-m", "comment", "--comment", fmt.Sprintf(`"%s has no endpoints"`, svcNameString),
"-m", protocol, "-p", protocol,
"-d", utilproxy.ToCIDR(svcInfo.ClusterIP),
"--dport", strconv.Itoa(svcInfo.Port),
"-j", "REJECT",
)
}
Copy
服务是否启用ExternalIPs(指定的node上开启监听端口)
pkg/proxy/iptables/proxier.go:846
for _, externalIP := range svcInfo.ExternalIPs {
// 判断externalIP是否为本node的IP以及协议为SCTP,且端口是否已开启
// 如果未开启则在本地打开监听端口
if local, err := utilproxy.IsLocalIP(externalIP); err != nil {
klog.Errorf("can't determine if IP is local, assuming not: %v", err)
} else if local && (svcInfo.GetProtocol() != v1.ProtocolSCTP) {
lp := utilproxy.LocalPort{
Description: "externalIP for " + svcNameString,
IP: externalIP,
Port: svcInfo.Port,
Protocol: protocol,
}
if proxier.portsMap[lp] != nil {
klog.V(4).Infof("Port %s was open before and is still needed", lp.String())
replacementPortsMap[lp] = proxier.portsMap[lp]
} else {
//打开与监听本地端口
socket, err := proxier.portMapper.OpenLocalPort(&lp)
if err != nil {
msg := fmt.Sprintf("can't open %s, skipping this externalIP: %v", lp.String(), err)
proxier.recorder.Eventf(
&v1.ObjectReference{
Kind: "Node",
Name: proxier.hostname,
UID: types.UID(proxier.hostname),
Namespace: "",
}, v1.EventTypeWarning, err.Error(), msg)
klog.Error(msg)
continue
}
replacementPortsMap[lp] = socket
}
}
//存在端点,写规则
if hasEndpoints {
args = append(args[:0],
"-A", string(kubeServicesChain),
"-m", "comment", "--comment", fmt.Sprintf(`"%s external IP"`, svcNameString),
"-m", protocol, "-p", protocol,
"-d", utilproxy.ToCIDR(net.ParseIP(externalIP)),
"--dport", strconv.Itoa(svcInfo.Port),
)
// -A KUBE-EXTERNAL-SERVICES -m comment --comment "..." -m $prot -p $prot -d \
// $externalIP --dport $port -j KUBE-MARK-MASQ
writeLine(proxier.natRules, append(args, "-j", string(KubeMarkMasqChain))...)
// -A KUBE-EXTERNAL-SERVICES -m comment --comment "..." -m $prot -p $prot -d \
// $externalIP --dport $port -m physdev ! --physdev-is-in \
// -m addrtype ! --src-type Local -j KUBE-SVC-XXXX16bitXXXXX
externalTrafficOnlyArgs := append(args,
"-m", "physdev", "!", "--physdev-is-in",
"-m", "addrtype", "!", "--src-type", "LOCAL")
writeLine(proxier.natRules, append(externalTrafficOnlyArgs, "-j", string(svcChain))...)
dstLocalOnlyArgs := append(args, "-m", "addrtype", "--dst-type", "LOCAL")
// -A KUBE-EXTERNAL-SERVICES -m comment --comment "..." -m $prot -p $prot -d \
// $externalIP --dport $port -m addrtype --dst-type Local
// -j KUBE-SVC-XXXX16bitXXXXX
writeLine(proxier.natRules, append(dstLocalOnlyArgs, "-j", string(svcChain))...)
} else {
// 不存在端点信息则reject
// -A KUBE-EXTERNAL-SERVICES -m comment --comment "..." -m $prot -p $prot -d \
// $externalIP --dport $port -j REJECT
writeLine(proxier.filterRules,
"-A", string(kubeExternalServicesChain),
"-m", "comment", "--comment", fmt.Sprintf(`"%s has no endpoints"`, svcNameString),
"-m", protocol, "-p", protocol,
"-d", utilproxy.ToCIDR(net.ParseIP(externalIP)),
"--dport", strconv.Itoa(svcInfo.Port),
"-j", "REJECT",
)
}
}
Copy
服务是否启用了外部负载均衡服务load-balancer ingress
pkg/proxy/iptables/proxier.go:917
//存在端点,写规则
if hasEndpoints {
fwChain := svcInfo.serviceFirewallChainName //"KUBE-FW-XXXX16bitXXXXX"
for _, ingress := range svcInfo.LoadBalancerStatus.Ingress {
if ingress.IP != "" {
// 创建服务KUBE-FW-X链
if chain, ok := existingNATChains[fwChain]; ok {
writeBytesLine(proxier.natChains, chain)
} else { //原来不存在则新建
writeLine(proxier.natChains, utiliptables.MakeChainLine(fwChain))
}
activeNATChains[fwChain] = true
// The service firewall rules are created based on ServiceSpec.loadBalancerSourceRanges field.
// This currently works for loadbalancers that preserves source ips.
// For loadbalancers which direct traffic to service NodePort, the firewall rules will not apply.
args = append(args[:0],
"-A", string(kubeServicesChain),
"-m", "comment", "--comment", fmt.Sprintf(`"%s loadbalancer IP"`, svcNameString),
"-m", protocol, "-p", protocol,
"-d", utilproxy.ToCIDR(net.ParseIP(ingress.IP)),
"--dport", strconv.Itoa(svcInfo.Port),
)
// -A KUBE-SERVICES -m comment --comment "..." -m $prot -p $prot -d \
// $ingresIP --dport $port -j KUBE-FW-XXXX16bitXXXXX
writeLine(proxier.natRules, append(args, "-j", string(fwChain))...)
args = append(args[:0],
"-A", string(fwChain),
"-m", "comment", "--comment", fmt.Sprintf(`"%s loadbalancer IP"`, svcNameString),
)
// 在KUBE-FW链,每个源匹配规则可能跳转至一个SVC或XLB链
chosenChain := svcXlbChain
// If we are proxying globally, we need to masquerade in case we cross nodes.
// If we are proxying only locally, we can retain the source IP.
if !svcInfo.OnlyNodeLocalEndpoints {
// -j "KUBE-MARK-MASQ" 地址伪装实现跨主机访问
writeLine(proxier.natRules, append(args, "-j", string(KubeMarkMasqChain))...)
chosenChain = svcChain // 选择为SVC链
}
if len(svcInfo.LoadBalancerSourceRanges) == 0 {
// 允许所有源,直接跳转
writeLine(proxier.natRules, append(args, "-j", string(chosenChain))...)
} else {
// 基于source range配置过滤 "-s $srcRanges"
allowFromNode := false
for _, src := range svcInfo.LoadBalancerSourceRanges {
writeLine(proxier.natRules, append(args, "-s", src, "-j", string(chosenChain))...)
_, cidr, _ := net.ParseCIDR(src)
if cidr.Contains(proxier.nodeIP) {
allowFromNode = true //配置CIDR包含节点IP,则允许来自节点请求
}
}
// 添加 "-s $ingresIP" 来允许LB后端主机请求
if allowFromNode {
writeLine(proxier.natRules, append(args, "-s", utilproxy.ToCIDR(net.ParseIP(ingress.IP)), "-j", string(chosenChain))...)
}
}
// 条件ingress.IP为空"-j KUBE-MARK-DROP"
writeLine(proxier.natRules, append(args, "-j", string(KubeMarkDropChain))...)
}
}
}
Copy
服务是否启用了nodeport(在每个节点上都将开启一个nodeport端口)
pkg/proxy/iptables/proxier.go:989
if svcInfo.NodePort != 0 {
// 获取node addresses
addresses, err := utilproxy.GetNodeAddresses(proxier.nodePortAddresses, proxier.networkInterfacer)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Failed to get node ip address matching nodeport cidr: %v", err)
continue
}
lps := make([]utilproxy.LocalPort, 0)
for address := range addresses {
lp := utilproxy.LocalPort{
Description: "nodePort for " + svcNameString,
IP: address,
Port: svcInfo.NodePort,
Protocol: protocol,
}
if utilproxy.IsZeroCIDR(address) {
// Empty IP address means all
lp.IP = ""
lps = append(lps, lp)
// If we encounter a zero CIDR, then there is no point in processing the rest of the addresses.
break
}
lps = append(lps, lp) //IP列表
}
// 为node节点的ips打开端口并保存持有socket句柄
for _, lp := range lps {
if proxier.portsMap[lp] != nil {
klog.V(4).Infof("Port %s was open before and is still needed", lp.String())
replacementPortsMap[lp] = proxier.portsMap[lp]
} else if svcInfo.GetProtocol() != v1.ProtocolSCTP {
// 打开和监听端口
socket, err := proxier.portMapper.OpenLocalPort(&lp)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("can't open %s, skipping this nodePort: %v", lp.String(), err)
continue
}
if lp.Protocol == "udp" {
//清理udp conntrack记录
err := conntrack.ClearEntriesForPort(proxier.exec, lp.Port, isIPv6, v1.ProtocolUDP)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Failed to clear udp conntrack for port %d, error: %v", lp.Port, err)
}
}
replacementPortsMap[lp] = socket //socket保存
}
}
//存在端点,写规则
if hasEndpoints {
// -A KUBE-NODEPORTS -m comment --comment "..." -m $prot -p $prot --dport $nodePort
args = append(args[:0],
"-A", string(kubeNodePortsChain),
"-m", "comment", "--comment", svcNameString,
"-m", protocol, "-p", protocol,
"--dport", strconv.Itoa(svcInfo.NodePort),
)
if !svcInfo.OnlyNodeLocalEndpoints {
//非本地nodeports则需SNAT规则添加,
// -j KUBE-MARK-MASQ -j KUBE-XLB-XXXX16bitXXXX
writeLine(proxier.natRules, append(args, "-j", string(KubeMarkMasqChain))...)
// Jump to the service chain.
writeLine(proxier.natRules, append(args, "-j", string(svcChain))...)
} else {
loopback := "127.0.0.0/8"
if isIPv6 {
loopback = "::1/128"
}
// 本地nodeports则规则添加,
// -s $loopback -j KUBE-MARK-MASQ -j KUBE-XLB-XXXX16bitXXXX
writeLine(proxier.natRules, append(args, "-s", loopback, "-j", string(KubeMarkMasqChain))...)
writeLine(proxier.natRules, append(args, "-j", string(svcXlbChain))...)
}
} else {
// 无hasEndpoints,添加-j reject规则
// -A KUBE-EXTERNAL-SERVICES -m comment --comment "..." -m addrtype \
// --dst-type LOCAL -m $prot -p $prot --dport $nodePort -j REJECT
writeLine(proxier.filterRules,
"-A", string(kubeExternalServicesChain),
"-m", "comment", "--comment", fmt.Sprintf(`"%s has no endpoints"`, svcNameString),
"-m", "addrtype", "--dst-type", "LOCAL",
"-m", protocol, "-p", protocol,
"--dport", strconv.Itoa(svcInfo.NodePort),
"-j", "REJECT",
)
}
}
Copy
基于服务名和协议,生成每个端点链
pkg/proxy/iptables/proxier.go:1087
for _, ep := range proxier.endpointsMap[svcName] {
epInfo, ok := ep.(*endpointsInfo)
if !ok {
klog.Errorf("Failed to cast endpointsInfo %q", ep.String())
continue
}
endpoints = append(endpoints, epInfo)
//基于服务名和协议生成端点链名称 "KUBE-SEP-XXXX16bitXXXX"
endpointChain = epInfo.endpointChain(svcNameString, protocol)
endpointChains = append(endpointChains, endpointChain)
// 创建端点链
if chain, ok := existingNATChains[utiliptables.Chain(endpointChain)]; ok {
writeBytesLine(proxier.natChains, chain)
} else {
writeLine(proxier.natChains, utiliptables.MakeChainLine(endpointChain))
}
activeNATChains[endpointChain] = true
}
Copy
写SessionAffinity会话保持规则,实现在一段时间内保持session affinity,保持时间为180秒,通过添加“-m recent –rcheck –seconds 180 –reap”的iptables规则实现了会话保持。
pkg/proxy/iptables/proxier.go:1107
//SessionAffinityType设置为"ClientIP",则写session保持规则
// -A KUBE-SVC-XXXX16bitXXXX -m recent -m comment –comment "..." \
// --name KUBE-SEP-XXXX16bitXXXX --rcheck --seconds 180 --reap \
// -j KUBE-SEP-XXXX16bitXXXX
if svcInfo.SessionAffinityType == v1.ServiceAffinityClientIP {
for _, endpointChain := range endpointChains {
args = append(args[:0],
"-A", string(svcChain),
)
proxier.appendServiceCommentLocked(args, svcNameString)
args = append(args,
"-m", "recent", "--name", string(endpointChain),
"--rcheck", "--seconds", strconv.Itoa(svcInfo.StickyMaxAgeSeconds), "--reap",
"-j", string(endpointChain),
)
writeLine(proxier.natRules, args...)
}
}
Copy
写负载均衡和DNAT规则,使用“-m statistic –-mode random -–probability ” iptables规则将后端POD组成一个基于概率访问的组合,实现服务访问的负载均衡功能效果。
针对服务的每个端点在nat表内该service对应的自定义链“KUBE-SVC-XXXX16bitXXXX”中加入iptables规则。如果该服务对应的endpoints大于等于2,则添加负载均衡规则。
针对选择非本地Node上的POD,需进行DNAT,将请求的目标地址设置成后选的POD的IP后进行路由。KUBE-MARK-MASQ将重设(伪装)源地址
-A KUBE-SVC-XXXX16bitXXXX -m comment –comment "..." -m statistic --mode random --probability $prob -j KUBE-SEP-XXXX16bitXXXX
-A KUBE-SEP-XXXX16bitXXXX -m comment –comment "..." -s $epIp -j "KUBE-MARK-MASQ"
-A KUBE-SVC-XXXX16bitXXXX -m comment –comment "…" -m prot -p $prot -j DNAT --to-destination X.X.X.X:xxx
pkg/proxy/iptables/proxier.go:1123
// 写负载均衡和DNAT规则
n := len(endpointChains)
for i, endpointChain := range endpointChains {
epIP := endpoints[i].IP()
if epIP == "" {
// Error parsing this endpoint has been logged. Skip to next endpoint.
continue
}
// 每个服务生成的负载均衡规则,后端POD组成一个基于概率访问的组合
// -A KUBE-SVC-XXXX16bitXXXX -m comment –comment "..."
// -m statistic --mode random --probability $prob
// -j KUBE-SEP-XXXX16bitXXXX
args = append(args[:0], "-A", string(svcChain))
proxier.appendServiceCommentLocked(args, svcNameString)
if i < (n - 1) { // 当端点大于或等于2
args = append(args,
"-m", "statistic",
"--mode", "random",
"--probability", proxier.probability(n-i))
}
// The final (or only if n == 1) rule is a guaranteed match.
args = append(args, "-j", string(endpointChain))
writeLine(proxier.natRules, args...)
// 每个端点链规则
// -A KUBE-SEP-XXXX16bitXXXX -m comment –comment "..." -s $epIp -j "KUBE-MARK-MASQ"
args = append(args[:0], "-A", string(endpointChain))
proxier.appendServiceCommentLocked(args, svcNameString)
// Handle traffic that loops back to the originator with SNAT.
writeLine(proxier.natRules, append(args,
"-s", utilproxy.ToCIDR(net.ParseIP(epIP)),
"-j", string(KubeMarkMasqChain))...)
// 如配置session保持"ClientIP"
// -m recent --name KUBE-SEP-XXXX16bitXXXX --set
if svcInfo.SessionAffinityType == v1.ServiceAffinityClientIP {
args = append(args, "-m", "recent", "--name", string(endpointChain), "--set")
}
// DNAT至最终的端点服务上
// -A KUBE-SVC-XXXX16bitXXXX -m comment –comment "..."
// -m $prot -p $prot -j DNAT --to-destination X.X.X.X:xxx
args = append(args, "-m", protocol, "-p", protocol, "-j", "DNAT", "--to-destination", endpoints[i].Endpoint)
writeLine(proxier.natRules, args...)
}
// 服务请求仅本地流量
localEndpoints := make([]*endpointsInfo, 0)
localEndpointChains := make([]utiliptables.Chain, 0)
for i := range endpointChains {
if endpoints[i].IsLocal {
// These slices parallel each other; must be kept in sync
localEndpoints = append(localEndpoints, endpoints[i])
localEndpointChains = append(localEndpointChains, endpointChains[i])
}
}
Copy
启用clusterCIDR (Kube-proxy中的--cluster-dir
指定的是集群中pod使用的网段,而pod使用的网段和apiserver中指定的service的cluster ip或vip网段不是同一个网段)
pkg/proxy/iptables/proxier.go:1179
// pod -> external VIP流量导向服务VIP(服务链)
// -A KUBE-XLB-XXXX16bitXXXX -m comment --comment "..." -s $clusterCIDR
// -j KUBE-SVC-XXXX16bitXXXXX
if len(proxier.clusterCIDR) > 0 {
args = append(args[:0],
"-A", string(svcXlbChain),
"-m", "comment", "--comment",
`"Redirect pods trying to reach external loadbalancer VIP to clusterIP"`,
"-s", proxier.clusterCIDR,
"-j", string(svcChain),
)
writeLine(proxier.natRules, args...)
}
Copy
生成本地端点链规则,本地源IP保持(当只在本地选择POD服务请求时,则不存在SNAT规则,可保持源地址IP信息。在nodePort或XLB时,可定义"externalTrafficPolicy": "Local"
控制向属于这个service的本地的POD转发请求,如果本地没有POD能服务这个请求,请求将被DROP掉,客户端会发现请求超时没有响应。
pkg/proxy/iptables/proxier.go:1190
numLocalEndpoints := len(localEndpointChains)
if numLocalEndpoints == 0 {
// 无本地端点,将流量Drop(流量黑洞处理)
// -A KUBE-XLB-XXXX16bitXXXX -m comment --comment "..." -j KUBE-MARK-DROP
args = append(args[:0],
"-A", string(svcXlbChain),
"-m", "comment", "--comment",
fmt.Sprintf(`"%s has no local endpoints"`, svcNameString),
"-j",
string(KubeMarkDropChain),
)
writeLine(proxier.natRules, args...)
} else {
// 本地端点会话保持开启
// -A KUBE-XLB-XXXX16bitXXXX -m comment --comment "..." -m recent \
// --name KUBE-SEP-XXXX16bitXXXX \
// --rcheck --seconds $StickyMaxAge --reap -j KUBE-SEP-XXXX16bitXXXX
if svcInfo.SessionAffinityType == v1.ServiceAffinityClientIP {
for _, endpointChain := range localEndpointChains {
writeLine(proxier.natRules,
"-A", string(svcXlbChain),
"-m", "comment", "--comment", svcNameString,
"-m", "recent", "--name", string(endpointChain),
"--rcheck", "--seconds", strconv.Itoa(svcInfo.StickyMaxAgeSeconds), "--reap",
"-j", string(endpointChain))
}
}
// 本地端点负载均衡处理"-m statistic --mode random --probability"
// 后端POD组成一个基于概率访问的组合
for i, endpointChain := range localEndpointChains {
// Balancing rules in the per-service chain.
args = append(args[:0],
"-A", string(svcXlbChain),
"-m", "comment", "--comment",
fmt.Sprintf(`"Balancing rule %d for %s"`, i, svcNameString),
)
if i < (numLocalEndpoints - 1) {
// Each rule is a probabilistic match.
args = append(args,
"-m", "statistic",
"--mode", "random",
"--probability", proxier.probability(numLocalEndpoints-i))
}
args = append(args, "-j", string(endpointChain))
// -A KUBE-XLB-XXXX16bitXXXX -m comment --comment "..." -m recent \
// --name KUBE-SEP-XXXX16bitXXXX -m statistic --mode random \
// --probability 0.50000000000 -j KUBE-SEP-XXXX16bitXXXX
writeLine(proxier.natRules, args...)
}
}
Copy
5.5. 配置收尾规则数据
篇幅限制,本节参考 github
5.6. 汇集与加载 iptables 配置规则数据
pkg/proxy/iptables/proxier.go:1326
//汇集前面所处理的filter和nat表数据至iptablesData
proxier.iptablesData.Reset()
proxier.iptablesData.Write(proxier.filterChains.Bytes())
proxier.iptablesData.Write(proxier.filterRules.Bytes())
proxier.iptablesData.Write(proxier.natChains.Bytes())
proxier.iptablesData.Write(proxier.natRules.Bytes())
klog.V(5).Infof("Restoring iptables rules: %s", proxier.iptablesData.Bytes())
// iptables-restore加载新配置(iptablesData)
err = proxier.iptables.RestoreAll(proxier.iptablesData.Bytes(), utiliptables.NoFlushTables, utiliptables.RestoreCounters)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Failed to execute iptables-restore: %v", err)
// Revert new local ports.
klog.V(2).Infof("Closing local ports after iptables-restore failure")
utilproxy.RevertPorts(replacementPortsMap, proxier.portsMap)
return
}
Copy
6. IPtables 底层的 runner 实现
前面基本已看完整个proxy的执行流程,最后iptables proxier是如何使用系统层iptables命令进行底层的iptables规则CRUD操作(通俗的理解:iptables proxier实现都是在操作iptables命令生成相应的规则),下面我来看一下kuber-proxy组件底层iptables操作器的封装。
6.1. iptables 执行器
篇幅限制,本节参考 github
6.2. iptables 执行器方法
if ee, ok := err.(utilexec.ExitError); ok {
if ee.Exited() && ee.ExitStatus() == 1 {
return true, nil
}
}
return false, fmt.Errorf("error creating chain %q: %v: %s", chain, err, out)
}
return false, nil
}
Copy
runner.FlushChain() "-F" 清空指定链
pkg/util/iptables/iptables.go:242
func (runner *runner) FlushChain(table Table, chain Chain) error {
fullArgs := makeFullArgs(table, chain)
//...
//执行"iptables -t $tableName -F $chainName"
out, err := runner.run(opFlushChain, fullArgs)
//...
}
Copy
runner.DeleteChain() "-X" 删除指定的链
pkg/util/iptables/iptables.go:256
func (runner *runner) DeleteChain(table Table, chain Chain) error {
fullArgs := makeFullArgs(table, chain)
//...
//执行"iptables -t $tableName -X $chainName"
out, err := runner.run(opDeleteChain, fullArgs)
//...
}
Copy
runner.EnsureRule() 检测规则是否存在,不存在则指定的"表内链上", 指定position添加规则
pkg/util/iptables/iptables.go:271
func (runner *runner) EnsureRule(position RulePosition, table Table, chain Chain, args ...string) (bool, error) {
fullArgs := makeFullArgs(table, chain, args...)
runner.mu.Lock()
defer runner.mu.Unlock()
// 检测规则是否存在
exists, err := runner.checkRule(table, chain, args...)
if err != nil {
return false, err
}
if exists {
return true, nil
}
// RulePosition "-I" "-A"
// 指定链序插入规则,执行"iptables -I $chainName -t $tableName ... "
// 链末添加规则,执行"iptables -A $chainName -t $tableName ... "
out, err := runner.run(operation(position), fullArgs)
if err != nil {
return false, fmt.Errorf("error appending rule: %v: %s", err, out)
}
return false, nil
}
//checkRule()先判断iptables是否支持"-C"flag,调用不同版本的检测rule的方法
func (runner *runner) checkRule(table Table, chain Chain, args ...string) (bool, error) {
if runner.hasCheck {
return runner.checkRuleUsingCheck(makeFullArgs(table, chain, args...))
}
return runner.checkRuleWithoutCheck(table, chain, args...)
}
//支持"-C"flag
func (runner *runner) checkRuleUsingCheck(args []string) (bool, error) {
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 5*time.Minute)
defer cancel()
//...
//执行"iptables -wait -C $chainName -t $tableName ... "
out, err := runner.runContext(ctx, opCheckRule, args)
//...
}
//不支持"-C"flag,为了兼容iptables版本<1.4.11
func (runner *runner) checkRuleWithoutCheck(table Table, chain Chain, args ...string) (bool, error) {
// 'iptables-save -t $tableName'
iptablesSaveCmd := iptablesSaveCommand(runner.protocol)
klog.V(1).Infof("running %s -t %s", iptablesSaveCmd, string(table))
out, err := runner.exec.Command(iptablesSaveCmd, "-t", string(table)).CombinedOutput()
if err != nil {
return false, fmt.Errorf("error checking rule: %v", err)
}
//移除引号
var argsCopy []string
for i := range args {
tmpField := strings.Trim(args[i], "\"")
tmpField = trimhex(tmpField)
argsCopy = append(argsCopy, strings.Fields(tmpField)...)
}
argset := sets.NewString(argsCopy...)
for _, line := range strings.Split(string(out), "\n") {
var fields = strings.Fields(line)
//检测rule的链是否一致
if !strings.HasPrefix(line, fmt.Sprintf("-A %s", string(chain))) || len(fields) != len(argsCopy)+2 {
continue
}
// 移除所有引号
for i := range fields {
fields[i] = strings.Trim(fields[i], "\"")
fields[i] = trimhex(fields[i])
}
//字符集匹配查找是否存在
if sets.NewString(fields...).IsSuperset(argset) {
return true, nil
}
klog.V(5).Infof("DBG: fields is not a superset of args: fields=%v args=%v", fields, args)
}
return false, nil
}
Copy
runner.DeleteRule() "-D" 指定的"表中链上"删除规则
pkg/util/iptables/iptables.go:292
func (runner *runner) DeleteRule(table Table, chain Chain, args ...string) error {
fullArgs := makeFullArgs(table, chain, args...)
//...
//检测规则是否存在
exists, err := runner.checkRule(table, chain, args...)
//...
//执行"iptables -D $chainName -t $tableName ..."
out, err := runner.run(opDeleteRule, fullArgs)
//...
}
Copy
runner.SaveInto() 保存指定表的iptables规则集(buffer内)
pkg/util/iptables/iptables.go:317
func (runner *runner) SaveInto(table Table, buffer *bytes.Buffer) error {
//...
// 执行 "iptables-save -t $tableName"
iptablesSaveCmd := iptablesSaveCommand(runner.protocol)
args := []string{"-t", string(table)}
cmd := runner.exec.Command(iptablesSaveCmd, args...)
cmd.SetStdout(buffer)
cmd.SetStderr(buffer)
return cmd.Run()
}
Copy
runner.Restore() 装载指定表由iptables-save保存的规则集(从标准输入接收输入)
pkg/util/iptables/iptables.go:340
func (runner *runner) Restore(table Table, data []byte, flush FlushFlag, counters RestoreCountersFlag) error {
// "iptables-restore -T $tableName"
args := []string{"-T", string(table)}
return runner.restoreInternal(args, data, flush, counters) //call and return
}
// restoreInternal()参数组装和iptables-restore命令恢复规则集data
func (runner *runner) restoreInternal(args []string, data []byte, flush FlushFlag, counters RestoreCountersFlag) error {
runner.mu.Lock()
defer runner.mu.Unlock()
trace := utiltrace.New("iptables restore")
defer trace.LogIfLong(2 * time.Second)
//参数的组装 "--noflush" "--counters" "--wait"
if !flush {
args = append(args, "--noflush")
}
if counters {
args = append(args, "--counters")
}
if len(runner.restoreWaitFlag) == 0 {
locker, err := grabIptablesLocks(runner.lockfilePath)
if err != nil {
return err
}
trace.Step("Locks grabbed")
defer func(locker iptablesLocker) {
if err := locker.Close(); err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Failed to close iptables locks: %v", err)
}
}(locker)
}
fullArgs := append(runner.restoreWaitFlag, args...)
iptablesRestoreCmd := iptablesRestoreCommand(runner.protocol)
klog.V(4).Infof("running %s %v", iptablesRestoreCmd, fullArgs)
// "iptables-restore -T $tableName --wait --noflush --counters < data"
cmd := runner.exec.Command(iptablesRestoreCmd, fullArgs...)
//从标准输入接受输入规则集data
cmd.SetStdin(bytes.NewBuffer(data))
//command对象执行与输出反馈
b, err := cmd.CombinedOutput()
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("%v (%s)", err, b)
}
return nil
}
Copy
runner.RestoreAll() 如同上Restore(),调用命令iptables-restore装载所有备份规则集
pkg/util/iptables/iptables.go:347
func (runner *runner) RestoreAll(data []byte, flush FlushFlag, counters RestoreCountersFlag) error {
args := make([]string, 0)
//同上,无参数限制
return runner.restoreInternal(args, data, flush, counters)
}
Copy
runner.AddReloadFunc() 注册reload回调函数,实现iptables reload重新加载规则
pkg/util/iptables/iptables.go:679
func (runner *runner) AddReloadFunc(reloadFunc func()) {
runner.mu.Lock()
defer runner.mu.Unlock()
//是否已启动监听
if !runner.hasListener {
runner.connectToFirewallD() //启动D-bus监听
}
runner.reloadFuncs = append(runner.reloadFuncs, reloadFunc) //注册信号触发回调func
}
//通过Linux内核D-bus机制实现对FirewallD进程的信号监听与处理(实现reload iptables规则)
func (runner *runner) connectToFirewallD() {
bus, err := runner.dbus.SystemBus()
if err != nil {
klog.V(1).Infof("Could not connect to D-Bus system bus: %s", err)
return
}
runner.hasListener = true
//SystemBus对象添加匹配规则定义(firewalld)
rule := fmt.Sprintf("type='signal',sender='%s',path='%s',interface='%s',member='Reloaded'", firewalldName, firewalldPath, firewalldInterface)
bus.BusObject().Call("org.freedesktop.DBus.AddMatch", 0, rule)
rule = fmt.Sprintf("type='signal',interface='org.freedesktop.DBus',member='NameOwnerChanged',path='/org/freedesktop/DBus',sender='org.freedesktop.DBus',arg0='%s'", firewalldName)
bus.BusObject().Call("org.freedesktop.DBus.AddMatch", 0, rule)
runner.signal = make(chan *godbus.Signal, 10)
bus.Signal(runner.signal)
go runner.dbusSignalHandler(bus) //D-Bus信号监听处理Handler
}
//goroutine监听D-Bus信号,监听FirewallD发生变化和reload信号则reload规则集
func (runner *runner) dbusSignalHandler(bus utildbus.Connection) {
firewalld := bus.Object(firewalldName, firewalldPath)
for s := range runner.signal {
if s == nil {
// 反注册dbus
bus.Signal(runner.signal)
return
}
switch s.Name {
case "org.freedesktop.DBus.NameOwnerChanged": //信号:指定名称的拥有者发生了变化
name := s.Body[0].(string)
new_owner := s.Body[2].(string)
// 信号名称为"org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1"
if name != firewalldName || len(new_owner) == 0 {
continue
}
firewalld.Call(firewalldInterface+".getDefaultZone", 0)
runner.reload() //重新加载与同步规则(遍历调用runner.reloadFuncs())
case firewalldInterface + ".Reloaded":
runner.reload()
}
}
}
Copy
runner.Destroy() D-bus监听注消
pkg/util/iptables/iptables.go:218
func (runner *runner) Destroy() {
if runner.signal != nil {
runner.signal <- nil //D-Bug信号channel置为空实现反注册
}
}
Copy
上面为kube-proxy第三层的iptables Proxier代码分析所有内容,对于另外两种模式ipvs、userspace模式的proxier实现代码分析可查询userspace-mode proxier和ipvs-mode proxier文章内容。
~本文 END~