“ 用好装饰器,才是真正的Python工程师。”
14.1 概念
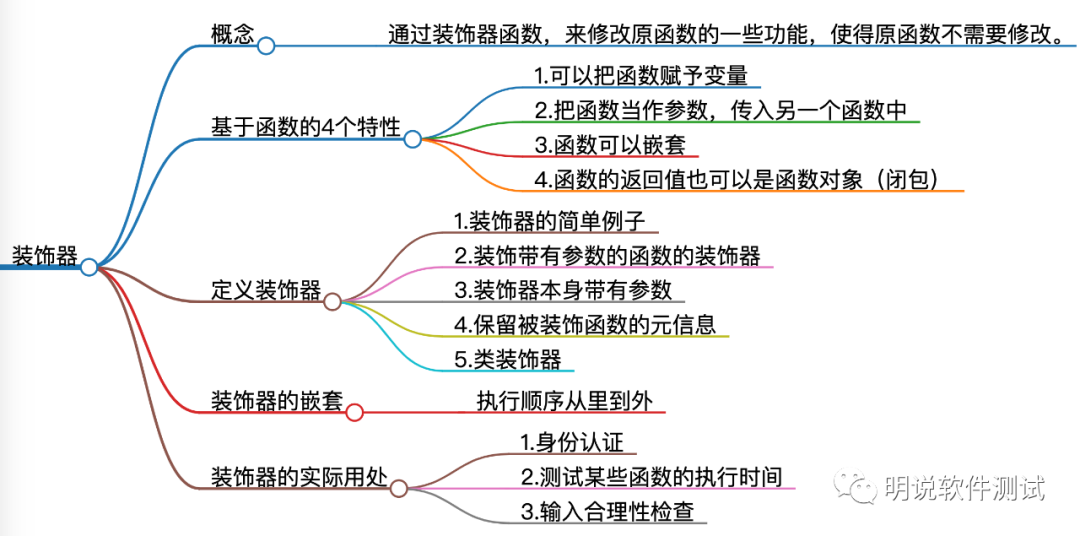
所谓的装饰器,其实就是通过装饰器函数,来修改原函数的一些功能,使得原函数不需要修改。装饰器依赖前面介绍的Python函数的五个特性:
函数也是对象
函数对象可以赋值给变量
函数对象可以作为参数传递给另外的函数
函数对象可以作为另外一个函数的返回值
函数可以嵌套定义
14.2 函数装饰器
14.2.1 装饰器的简单例子
my_decorator() 是一个装饰器,它把真正需要执行的函数 func() 包裹在其中,并且改变了它的行为,但是原函数 func不变。定义装饰器分三步走:
调用原函数前后做一通操作
调用原函数
返回内部函数对象
def my_decorator(func):def wrapper():print('wrapper of decorator') # ①这里做一通操作func() # ②调用原函数return wrapper # ③返回内部函数对象def greet():print('hello world')greet = my_decorator(greet) # 变量 greet 指向了内部函数 wrapper()greet() # 调用 greet() 相当于执行内部函数wrapper@my_decorator # @语法糖,相当于greet1 = my_decorator(greet1)def greet1():print('hello world')
14.2.2 装饰带有参数的函数
装饰器可以接受原函数任意类型和数量的参数,把*args和**kwargs,作为装饰器内部函数 wrapper() 的参数即可。
def my_decorator(func): # 这个func只是个参数,不一定是函数名。def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):print('wrapper of decorator') # 这里做一通操作func(*args, **kwargs) # 调用原函数return wrapper # 返回内部函数对象@my_decoratordef greet(message):print(message)@my_decoratordef celebrate(name, message):print(name+message)
14.2.3 装饰器本身带有参数
它还可以接受自己定义的参数。举个例子,比如我想要定义一个参数,来表示装饰器内部函数被执行的次数,那么就可以写成下面这种形式:在外边再套一层函数,并返回内层函数。参考:
def repeat(num):def my_decorator(func):def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):for i in range(num):print('wrapper of decorator')func(*args, **kwargs)return wrapperreturn my_decorator@repeat(4)def greet(message):print(message)
再看一个装饰器本身带参数的例子:
def type_decorator(**kwargs):"""检查实例属性类型的装饰器"""def decorate(cls): # 对instance进行装饰for key, value in kwargs.items():# 给cls的设置类属性,并给类属性设置描述符实例setattr(cls, key, TypedAssertion(key, value))return clsreturn decorate
TypedAssertion是一个描述符。这个装饰器的目标是给cls类添加kwargs中的key作为类属性,将TypedAssertion描述符作为类属性的值。举个例子:
@type_decorator(brand=str, shares=int, price=float)class Stock:def __init__(self, brand, shares, price):self.brand = brandself.shares = sharesself.price = price
效果就是对brand、shares和price属性做了类型校验。
14.2.4 保留被装饰函数的元信息
在内部函数上面用装饰器@functools.wraps(func)。
import functoolsdef my_decorator(func):@functools.wraps(func) # 为了保留被装饰函数的元信息def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):print('wrapper of decorator')func(*args, **kwargs)return wrapper@my_decoratordef greet(message):print(message)
14.3 类装饰器
这部分可以看完后面关于Python类的章节后再学习。类装饰器主要依赖于函数__call__
,每当你调用一个类的实例时,__call__
就会被执行。
这里,我们定义了类 Count,初始化时传入原函数 func(),而__call__
函数表示让变量 num_calls 自增 1,然后打印,并且调用原函数,并返回原函数。
因此,在我们第一次调用函数 example() 时,num_calls 的值是 1,而在第二次调用时,它的值变成了 2。
class Count:def __init__(self, func):self.func = funcself.num_calls = 0def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs):self.num_calls += 1 # 调用次数加1print('num of calls is: {}'.format(self.num_calls))return self.func(*args, **kwargs)@Count # Count类装饰example,会调用Count类的__call__函数def example():print("hello world")example()# 输出num of calls is: 1hello worldexample()# 输出num of calls is: 2hello world
14.4 装饰器的嵌套使用
函数可以被多个装饰器装饰,也就是下面这样:
@decorator1@decorator2@decorator3def func():...
装饰器的执行顺序是从里到外,等效于decorator1(decorator2(decorator3(func)))。
14.5 实际应用场景
1.身份认证
每次调用这个函数前,都会先检查用户是否处于登录状态,如果是登录状态,则允许这项操作;如果没有登录,则不允许。
import functoolsdef authenticate(func):@functools.wraps(func)def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):request = args[0]if check_user_logged_in(request): # 如果用户处于登录状态return func(*args, **kwargs) # 执行函数post_comment()else:raise Exception('Authentication failed')return wrapper@authenticatedef post_comment(request, ...)...
2.测试某些函数的执行时间
import timeimport functoolsdef log_execution_time(func):@functools.wraps(func)def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):start = time.perf_counter()res = func(*args, **kwargs)end = time.perf_counter()print('{} took {} ms'.format(func.__name__, (end - start) * 1000))return resreturn wrapper@log_execution_timedef calculate_similarity(items):...
3.输入合理性检查
import functoolsdef validation_check(input):@functools.wraps(func)def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):... # 检查输入是否合法@validation_checkdef neural_network_training(param1, param2, ...):...
参考资料:
https://foofish.net/python-decorator.html
https://python3-cookbook.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/latest/c09/p11_write_decorators_that_add_arguments_to_functions.html







