什么是Worker-Thread模式

Worker-Thread模式实现
流水线工人:流水线工人主要用来对传送带上的产品进行加工。
流水线传送带:用于传送来自上游的产品。
产品组装说明书:用来说明该产品如何组装。
产品及组装说明书
//在流水线上需要被加工的产品,create 作为一个模板方法,提供了加工产品的说明书public abstract class InstructionBook{public final void create(){this.firstProcess();this.secondProcess();}protected abstract void firstProcess();protected abstract void secondProcess();}
public class Production extends InstructionBook{//产品编号private final int prodID;public Production(int prodID){this.prodID = prodID;}@Overrideprotected void firstProcess(){System.out.println("execute the " + prodID + " first process");}@Overrideprotected void secondProcess(){System.out.println("execute the " + prodID + " second process");}}
流水线传送带
//产品传送带,在传送带上除了负责产品加工的工人之外,还有在传送带上等待加工的产品public class ProductionChannel{//传送带上最多可以有多少个待加工的产品private final static int MAX_PROD = 100;//主要用来存放待加工的产品,也就是传送带private final Production[] productionQueue;//队列尾private int tail;//队列头private int head;//当前在流水线上有多少个待加工的产品private int total;//在流水线上工作的工人private final Worker[] workers;//创建 ProductionChannel 时应指定需要多少个流水线工人public ProductionChannel(int workerSize){this.workers = new Worker[workerSize];this.productionQueue = new Production[MAX_PROD];//实例化每一个工人(Worker 线程)并且启动for (int i = 0; i < workerSize; i++){workers[i] = new Worker("Worker-" + i, this);workers[i].start();}}//接受来自上游的半成品(待加工的产品)public void offerProduction(Production production){synchronized (this){//当传送带上待加工的产品超过了最大值时需要阻塞上游再次传送产品while (total >= productionQueue.length){try{this.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e){}}//将产品放到传送带,并且通知工人线程工作productionQueue[tail] = production;tail = (tail + 1) % productionQueue.length;total++;this.notifyAll();}}//工人线程(Worker)从传送带上获取产品,并且进行加工public Production takeProduction(){synchronized (this){//当传送带上没有产品时,工人等待着产品从上游输送到传送带上while (total <= 0){try{this.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e){}}//获取产品Production prod = productionQueue[head];head = (head + 1) % productionQueue.length;total--;this.notifyAll();return prod;}}}
流水线工人
public class Worker extends Thread{private final ProductionChannel channel;//主要用于获取一个随机值,模拟加工一个产品需要耗费一定的时间,当然每个工人操作时所花费的时间可也能不一样private final static Random random =new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());public Worker(String workerName, ProductionChannel channel){super(workerName);this.channel = channel;}@Overridepublic void run(){while (true){try{//从传送带上获取产品Production production = channel.takeProduction();System.out.println(getName() + " process the " + production);//对产品进行加工production.create();TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(random.nextInt(10));} catch (InterruptedException e){e.printStackTrace();}}}}
产品流水线测试
public class Test{public static void main(String[] args){//流水线上有5个工人final ProductionChannel channel = new ProductionChannel(5);AtomicInteger productionNo = new AtomicInteger();//流水线上有8个工作人员往传送带上不断地放置等待加工的半成品IntStream.range(1, 8).forEach(i ->new Thread(() ->{while (true){channel.offerProduction(new Production(productionNo.getAndIncrement()));try{TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(current().nextInt(10));} catch (InterruptedException e){e.printStackTrace();}}}).start());}}
...省略execute the 3 second processWorker-0 process the PROD:5execute the 5 first processexecute the 5 second processWorker-4 process the PROD:7Worker-0 process the PROD:6execute the 7 first processexecute the 6 first processexecute the 7 second processexecute the 6 second process...省略
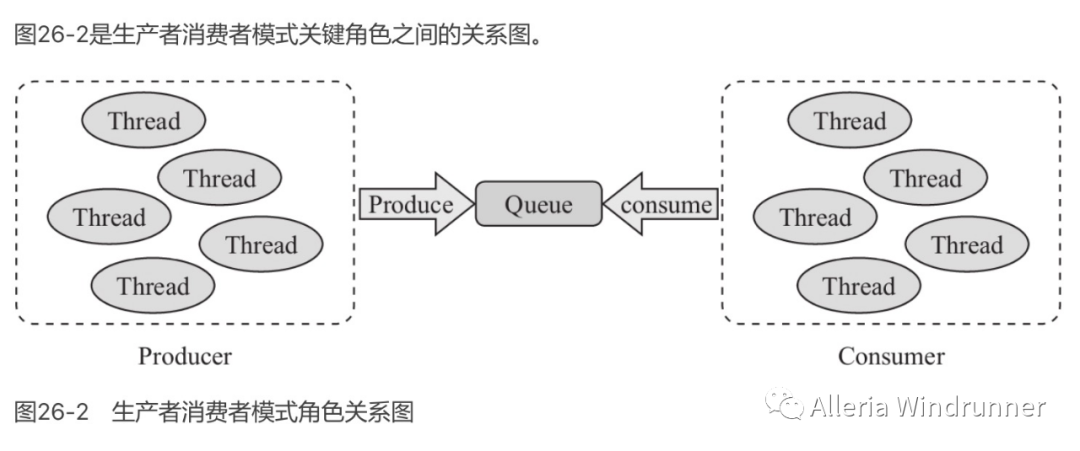
Worker-Thread 和 Producer-Consumer
Producer-Consumer 模式
Worker-Thread 模式

文章转载自Alleria Windrunner,如果涉嫌侵权,请发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。






