void *apc_mmap(char *file_mask, int size){void *shmaddr; /* the shared memory address *//* If no filename was provided, do an anonymous mmap */if (!file_mask || (file_mask && !strlen(file_mask))){shmaddr = (void *)mmap(NULL, size, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED | MAP_ANON, -1, 0);}else{int fd;/** If the filemask contains .shm we try to do a POSIX-compliant shared memory* backed mmap which should avoid synchs on some platforms. At least on* FreeBSD this implies MAP_NOSYNC and on Linux it is equivalent of mmap'ing* a file in a mounted shmfs. For this to work on Linux you need to make sure* you actually have shmfs mounted. Also on Linux, make sure the file_mask you* pass in has a leading and no other 's. eg. apc.shm.XXXXXX* On FreeBSD these are mapped onto the regular filesystem so you can put whatever* path you want here.*/if (strstr(file_mask, ".shm")){mktemp(file_mask);fd = shm_open(file_mask, O_CREAT | O_RDWR, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR);if (fd == -1){apc_eprint("apc_mmap: shm_open on %s failed:", file_mask);return (void *)-1;}if (ftruncate(fd, size) < 0){close(fd);shm_unlink(file_mask);apc_eprint("apc_mmap: ftruncate failed:");return (void *)-1;}shmaddr = (void *)mmap(NULL, size, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0);shm_unlink(file_mask);close(fd);}/** Support anonymous mmap through the dev/zero interface as well*/else if (!strcmp(file_mask, "/dev/zero")){fd = open("/dev/zero", O_RDWR, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR);if (fd == -1){apc_eprint("apc_mmap: open on dev/zero failed:");return (void *)-1;}shmaddr = (void *)mmap(NULL, size, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0);close(fd);}/** Otherwise we do a normal filesystem mmap*/else{fd = mkstemp(file_mask);if (fd == -1){apc_eprint("apc_mmap: mkstemp on %s failed:", file_mask);return (void *)-1;}if (ftruncate(fd, size) < 0){close(fd);unlink(file_mask);apc_eprint("apc_mmap: ftruncate failed:");}shmaddr = (void *)mmap(NULL, size, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED | MAP_NOSYNC, fd, 0);close(fd);unlink(file_mask);}}if ((int)shmaddr == -1){apc_eprint("apc_mmap: mmap failed:");}return shmaddr;}
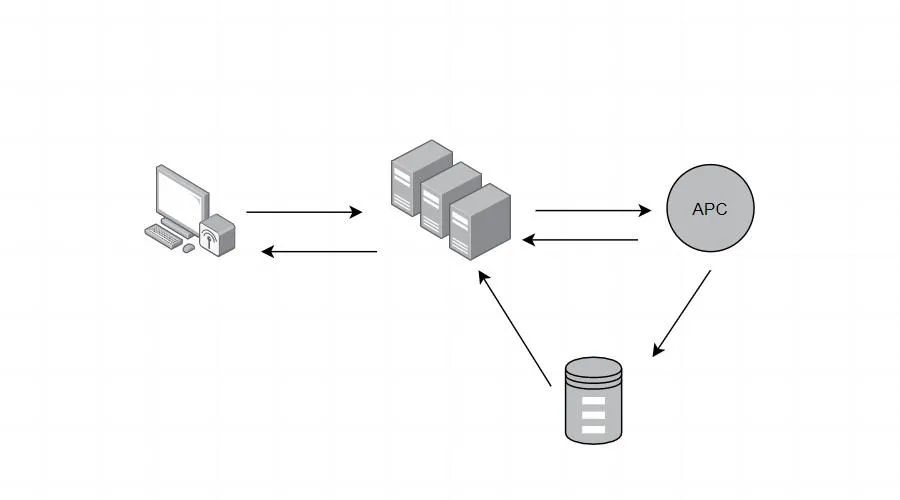
获取内存空间的函数是通过(apc_sma_init)进行调用的,这里会将得到的地址空间首地址赋值给(void **sma_shmaddrs)
#if APC_MMAPvoid apc_sma_init(int numseg, int segsize, char *mmap_file_mask)#elsevoid apc_sma_init(int numseg, int segsize)#endif{//......sma_segments = (int *)apc_emalloc(sma_numseg * sizeof(int));sma_shmaddrs = (void **)apc_emalloc(sma_numseg * sizeof(void *));sma_lock = apc_lck_create(NULL, 0, 1);for (i = 0; i < sma_numseg; i++){header_t *header;block_t *block;void *shmaddr;#if APC_MMAPsma_segments[i] = sma_segsize;sma_shmaddrs[i] = apc_mmap(mmap_file_mask, sma_segsize);#elsesma_segments[i] = apc_shm_create(NULL, i, sma_segsize);sma_shmaddrs[i] = apc_shm_attach(sma_segments[i]);#endifshmaddr = sma_shmaddrs[i];header = (header_t *)shmaddr;header->segsize = sma_segsize;header->avail = sma_segsize - sizeof(header_t) - sizeof(block_t) -alignword(sizeof(int));block = BLOCKAT(sizeof(header_t));block->size = 0;block->next = sizeof(header_t) + sizeof(block_t);block = BLOCKAT(block->next);block->size = header->avail;block->next = 0;}}
这里会初始化两个block块,可能会感觉很无用,但是确实是很有用的一段代码。主要原因是block的结构体。
typedef struct block_t block_t;struct block_t{int size; /* size of this block */int next; /* offset in segment of next free block */};
可以发现block的结构体只包含一个(size)。下面一张图可以看到经过上述两步,整个申请的空间被划分成的样子。
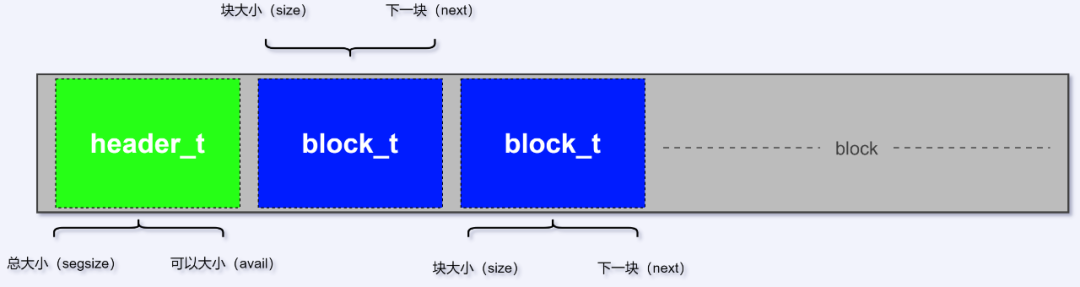
假设block的大小是100KB,当用掉10KB的时候size是90KB。但是在查找剩余空间的时候,并不知道block的实际初始大小。所以如果不初始化下一个next(块)的位置,那么是没有办法得到block的大小的。所以一开始会初始化两个(block_t)块。
int apc_module_init(){/* apc initialization */#if APC_MMAPapc_sma_init(APCG(shm_segments), APCG(shm_size)*1024*1024, APCG(mmap_file_mask));#elseapc_sma_init(APCG(shm_segments), APCG(shm_size)*1024*1024);#endifAPCG(cache) = apc_cache_create(APCG(num_files_hint), APCG(gc_ttl));APCG(cache_stack) = apc_stack_create(0);APCG(compiled_filters) = apc_regex_compile_array(APCG(filters));/* override compilation */old_compile_file = zend_compile_file;zend_compile_file = my_compile_file;/* override execution */old_execute = zend_execute;zend_execute = my_execute;apc_log(APC_NOTICE, "APC version %s -- startup complete", apc_version());APCG(initialized) = 1;return 0;}
当初始化内存完成以后,就涉及到了对cache结构体的初始化。使用的函数是(apc_cache_create)。这个函数会创建出一个apc_cache_t结构体指针。
struct apc_cache_t {void* shmaddr; /* process (local) address of shared cache */header_t* header; /* cache header (stored in SHM) */slot_t** slots; /* array of cache slots (stored in SHM) */int num_slots; /* number of slots in cache */int gc_ttl; /* maximum time on GC list for a slot */int lock; /* global semaphore lock */};
相当于所有插槽的一个信息吧。注意的是cache的空间并不是我们mmap申请的空间,而是malloc申请的空间,所以两个空间是互不关联的。
void* apc_emalloc(size_t n){void* p = malloc(n);if (p == NULL) {apc_eprint("apc_emalloc: malloc failed to allocate %u bytes:", n);}return p;}
创建cache的函数代码如下
apc_cache_t* apc_cache_create(int size_hint, int gc_ttl){apc_cache_t* cache;int cache_size;int num_slots;int i;num_slots = size_hint > 0 ? size_hint*2 : 1000;cache = (apc_cache_t*) apc_emalloc(sizeof(apc_cache_t));cache_size = sizeof(header_t) + num_slots*sizeof(slot_t*);cache->shmaddr = apc_sma_malloc(cache_size);memset(cache->shmaddr, 0, cache_size);cache->header = (header_t*) cache->shmaddr;cache->header->num_hits = 0;cache->header->num_misses = 0;cache->header->deleted_list = NULL;cache->slots = (slot_t**) (((char*) cache->shmaddr) + sizeof(header_t));cache->num_slots = num_slots;cache->gc_ttl = gc_ttl;cache->lock = CREATE_LOCK;for (i = 0; i < num_slots; i++) {cache->slots[i] = NULL;}return cache;}
其中的(apc_sma_malloc)函数可谓是重中之重,它主要是从我们用(mmap)申请的空间里或者可用空间。
void *apc_sma_malloc(size_t n){int off;int i;apc_lck_lock(sma_lock);assert(sma_initialized);off = sma_allocate(sma_shmaddrs[sma_lastseg], n);if (off != -1){void *p = sma_shmaddrs[sma_lastseg] + off;apc_lck_unlock(sma_lock);return p;}for (i = 0; i < sma_numseg; i++){if (i == sma_lastseg){continue;}off = sma_allocate(sma_shmaddrs[i], n);if (off != -1){void *p = sma_shmaddrs[i] + off;apc_lck_unlock(sma_lock);sma_lastseg = i;return p;}}apc_lck_unlock(sma_lock);return NULL;}
从函数来看重要的函数是:sma_allocate,函数代码如下。
static int sma_allocate(void *shmaddr, int size){header_t *header; /* header of shared memory segment */block_t *prv; /* block prior to working block */block_t *cur; /* working block in list */block_t *prvbestfit; /* block before best fit */int realsize; /* actual size of block needed, including header */int minsize; /* for finding best fit *//* Realsize must be aligned to a word boundary on some architectures. */realsize = alignword(max(size + alignword(sizeof(int)), sizeof(block_t)));/** Set realsize to the smallest power of 2 greater than or equal to* realsize. This increases the likelihood that neighboring blocks can be* coalesced, reducing memory fragmentation.*/if (POWER_OF_TWO_BLOCKSIZE){int p = 1;while (p < realsize){p <<= 1;}realsize = p;}/** First, insure that the segment contains at least realsize free bytes,* even if they are not contiguous.*/header = (header_t *)shmaddr;if (header->avail < realsize){return -1;}prvbestfit = 0; /* initially null (no fit) */minsize = INT_MAX; /* used to find best fit */prv = BLOCKAT(sizeof(header_t));while (prv->next != 0){cur = BLOCKAT(prv->next);if (cur->size == realsize){/* found a perfect fit, stop searching */prvbestfit = prv;break;}else if (cur->size > (sizeof(block_t) + realsize) &&cur->size < minsize){/* cur is acceptable and is the smallest so far */prvbestfit = prv;minsize = cur->size;}prv = cur;}if (prvbestfit == 0){return -1;}prv = prvbestfit;cur = BLOCKAT(prv->next);/* update the block header */header->avail -= realsize;if (cur->size == realsize){/* cur is a perfect fit for realsize; just unlink it */prv->next = cur->next;}else{block_t *nxt; /* the new block (chopped part of cur) */int nxtoffset; /* offset of the block currently after cur */int oldsize; /* size of cur before split *//* bestfit is too big; split it into two smaller blocks */nxtoffset = cur->next;oldsize = cur->size;prv->next += realsize;cur->size = realsize;nxt = BLOCKAT(prv->next);nxt->next = nxtoffset;nxt->size = oldsize - realsize;}return OFFSET(cur) + alignword(sizeof(int));}
这里会获取一个包含头结构的实际大小:realsize。然后会判断总的可用空间是否还够申请的空间。
header = (header_t *)shmaddr;if (header->avail < realsize){return -1;}
这里的header是最初的时候申请空间时赋值的header头结构。
minsize = INT_MAX; * used to find best fit */
上面这句话是INT类型的最大值,由于会溢出所以这里定义成了常量。
prv = BLOCKAT(sizeof(header_t));
这句话主要是获取第一个block结构。BLOCKAT是一个宏函数,源码如下。
#define BLOCKAT(offset) ((block_t *)((char *)shmaddr + offset))
shmaddr取的是当前代码空间的值。
while (prv->next != 0)
从上面这句while条件就可以知道,如果一开始不申请两个block空间的话,这里是没办法遍历的,因为不知道下一个块的位置。
while (prv->next != 0){cur = BLOCKAT(prv->next);if (cur->size == realsize){/* found a perfect fit, stop searching */prvbestfit = prv;break;}else if (cur->size > (sizeof(block_t) + realsize) &&cur->size < minsize){/* cur is acceptable and is the smallest so far */prvbestfit = prv;minsize = cur->size;}prv = cur;}
这里会取下一个block块,也就是第二个block,判断它的大小是否正好是我们要申请的空间大小。如果是的话则返回,按照第一次的逻辑是否,所以继续往下走。如果第二个块的大小大于要申请的,并且小于最大的int,则会将第一个的block块给到上一个块变量,然后进行赋值循环。
{block_t *nxt; /* the new block (chopped part of cur) */int nxtoffset; /* offset of the block currently after cur */int oldsize; /* size of cur before split *//* bestfit is too big; split it into two smaller blocks */nxtoffset = cur->next;oldsize = cur->size;prv->next += realsize;cur->size = realsize;nxt = BLOCKAT(prv->next);nxt->next = nxtoffset;nxt->size = oldsize - realsize;}
如果需要申请新块的话,也会将几个块的大小和位置重新计算一下。相当于每个块实际大小是不一样的。其中为了对齐系统字边界,也用到了一个函数。
/* {{{ alignword: returns x, aligned to the system's word boundary */static int alignword(int x){typedef union{void *p;int i;long l;double d;void (*f)();} word_t;return sizeof(word_t) * (1 + ((x - 1) / sizeof(word_t)));}
关于剩下的增删改查,按照APC更改了一份。
参照:https://gitee.com/iwonmo/iwonmo-php
其中的Key和Value结构进行了重改,符合我自己的扩展结构。







