阅读源码首先要找准入口,所以我们先来看看mybatis的入口。我们平时使用mybatis是这样开始的:
/*** demo** @author eleven**/public class Test {private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;@Beforepublic void init() throws Exception{// 加载配置文件String resource = "SqlMapConfig.xml";InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);// sqlsessionFactory需要通过sqlsessionFactoryBuilder读取全局配置文件信息sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);}}
所以源码的入口也就是SqlSessionFactoryBuilder()类的build(inputStream)方法了:
public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder {...省略public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties) {try {XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties);return build(parser.parse());} catch (Exception e) {throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);} finally {ErrorContext.instance().reset();try {reader.close();} catch (IOException e) {// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.}}}...省略public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {try {// XMLConfigBuilder:用来解析XML配置文件// 使用构建者模式XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);// parser.parse():使用XPATH解析XML配置文件,将配置文件封装为Configuration对象// 返回DefaultSqlSessionFactory对象,该对象拥有Configuration对象(封装配置文件信息)return build(parser.parse());} catch (Exception e) {throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);} finally {ErrorContext.instance().reset();try {inputStream.close();} catch (IOException e) {// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.}}}public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {// 创建SqlSessionFactory接口的默认实现类return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);}}...省略
上面我们先找到了mybatis加载配置文件的入口,接下来我们从入口开始沿着主线一步步阅读即可,首先从整体出发把主线相关的类和方法按先后顺序列出来:
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder build() XMLConfigBuilder parse() parseConfiguration() environmentsElement() mapperElement() XMLMapperBuilder parse() configurationElement() buildStatementFromContext() XMLStatementBuilder parseStatementNode() getLanguageDriver() Configuration Configuration() MapperBuilderAssistant getLanguageDriver() Configuration getLanguageRegistry() getDefaultDriverClass() XMLLanguageDriver createSqlSource() XMLScriptBuilder parseScriptNode() MixedSqlNode DynamicSqlSource RawSqlSource builderAssistant()
调用流程示意图如下:
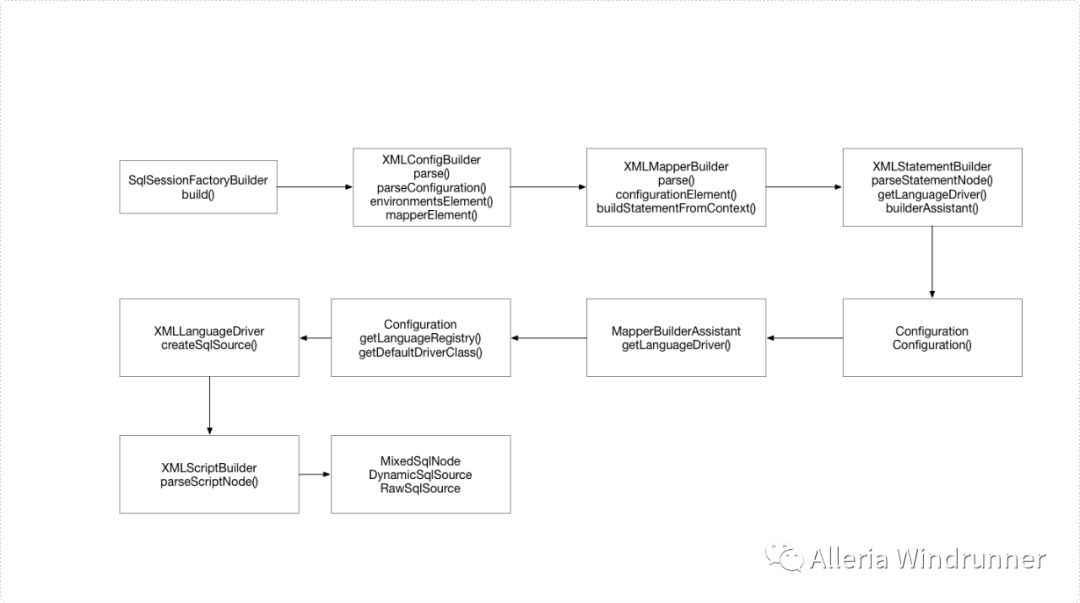
然后根据上面的顺序一个一个类的来看。SqlSessionFactoryBuilder#build():
public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder {...省略public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {try {// XMLConfigBuilder:用来解析XML配置文件// 使用构建者模式XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);// parser.parse():使用XPATH解析XML配置文件,将配置文件封装为Configuration对象// 返回DefaultSqlSessionFactory对象,该对象拥有Configuration对象(封装配置文件信息)return build(parser.parse());} catch (Exception e) {throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);} finally {ErrorContext.instance().reset();try {inputStream.close();} catch (IOException e) {// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.}}}...省略}
先创建XMLConfigBuilder然后调用parse()方法:
public class XMLConfigBuilder extends BaseBuilder {...省略/*** 解析XML配置文件* @return*/public Configuration parse() {if (parsed) {throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");}parsed = true;// parser.evalNode("/configuration"):通过XPATH解析器,解析configuration根节点// 从configuration根节点开始解析,最终将解析出的内容封装到Configuration对象中parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));return configuration;}private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {try {//issue #117 read properties first// 解析</properties>标签propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));// 解析</settings>标签Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));loadCustomVfs(settings);loadCustomLogImpl(settings);// 解析</typeAliases>标签typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));// 解析</plugins>标签pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));// 解析</objectFactory>标签objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));// 解析</objectWrapperFactory>标签objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));// 解析</reflectorFactory>标签reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));settingsElement(settings);// 解析</environments>标签environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));// 解析</databaseIdProvider>标签databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));// 解析</typeHandlers>标签typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));// 解析</mappers>标签mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));} catch (Exception e) {throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);}}/*** 解析environments标签* @param context* @throws Exception*/private void environmentsElement(XNode context) throws Exception {if (context != null) {if (environment == null) {environment = context.getStringAttribute("default");}for (XNode child : context.getChildren()) {String id = child.getStringAttribute("id");if (isSpecifiedEnvironment(id)) {TransactionFactory txFactory = transactionManagerElement(child.evalNode("transactionManager"));DataSourceFactory dsFactory = dataSourceElement(child.evalNode("dataSource"));DataSource dataSource = dsFactory.getDataSource();Environment.Builder environmentBuilder = new Environment.Builder(id).transactionFactory(txFactory).dataSource(dataSource);configuration.setEnvironment(environmentBuilder.build());}}}}/*** 解析<mappers>标签* @param parent mappers标签对应的XNode对象* @throws Exception*/private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {if (parent != null) {// 获取<mappers>标签的子标签for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {// <package>子标签if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {// 获取mapper接口和mapper映射文件对应的package包名String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");// 将包下所有的mapper接口以及它的代理对象存储到一个Map集合中,key为mapper接口类型,value为代理对象工厂configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);} else {// <mapper>子标签// 获取<mapper>子标签的resource属性String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");// 获取<mapper>子标签的url属性String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");// 获取<mapper>子标签的class属性String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");// 它们是互斥的if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);// 专门用来解析mapper映射文件XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());// 通过XMLMapperBuilder解析mapper映射文件mapperParser.parse();} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());// 通过XMLMapperBuilder解析mapper映射文件mapperParser.parse();} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);// 将指定mapper接口以及它的代理对象存储到一个Map集合中,key为mapper接口类型,value为代理对象工厂configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);} else {throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");}}}}}...省略}
XMLConfigBuilder解析了dtd中定义的所有标签,可以重点关注environmentsElement()解析数据源和mapperElement()解析sql映射文件。其中对于sql映射文件的解析调用了XMLMapperBuilder的parse()方法:
public class XMLMapperBuilder extends BaseBuilder {...省略public void parse() {// mapper映射文件是否已经加载过if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {// 从映射文件中的<mapper>根标签开始解析,直到完整的解析完毕configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));// 标记已经解析configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);bindMapperForNamespace();}parsePendingResultMaps();parsePendingCacheRefs();parsePendingStatements();}/*** 解析映射文件* @param context 映射文件根节点<mapper>对应的XNode*/private void configurationElement(XNode context) {try {// 获取<mapper>标签的namespace值,也就是命名空间String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");// 命名空间不能为空if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) {throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");}// 设置当前的命名空间为namespace的值builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);// 解析<cache-ref>子标签cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));// 解析<cache>子标签cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));// 解析<parameterMap>子标签parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));// 解析<resultMap>子标签resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));// 解析<sql>子标签,也就是SQL片段sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));// 解析<select>\<insert>\<update>\<delete>子标签buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));} catch (Exception e) {throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e);}}private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list) {if (configuration.getDatabaseId() != null) {buildStatementFromContext(list, configuration.getDatabaseId());}// 构建MappedStatementbuildStatementFromContext(list, null);}private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) {for (XNode context : list) {// MappedStatement解析器final XMLStatementBuilder statementParser = new XMLStatementBuilder(configuration, builderAssistant, context, requiredDatabaseId);try {// 解析select等4个标签,创建MappedStatement对象statementParser.parseStatementNode();} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {configuration.addIncompleteStatement(statementParser);}}}...省略}
对于映射文件的解析我们重点关注对于\<select>\<insert>\<update>\<delete>子标签的解析。myabtis框架使用了XMLStatementBuilder的parseStatementNode()方法执行:
public class XMLStatementBuilder extends BaseBuilder {...省略/*** 解析<select>\<insert>\<update>\<delete>子标签*/public void parseStatementNode() {// 获取statement的id属性(特别关键的值)String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) {return;}Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize");Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout");String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap");// 获取入参类型String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType");// 别名处理,获取入参对应的Java类型Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType);// 获取ResultMapString resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap");// 获取结果映射类型String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType");String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang");LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);// 别名处理,获取返回值对应的Java类型Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType);String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType");// 设置默认StatementType为Prepared,该参数指定了后面的JDBC处理时,采用哪种StatementStatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(context.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString()));ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = resolveResultSetType(resultSetType);String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName();// 解析SQL命令类型是什么?确定操作是CRUD中的哪一种SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));//是否查询语句boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect);boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect);boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered", false);// Include Fragments before parsing// <include>标签解析XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant);includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());// Parse selectKey after includes and remove them.// 解析<selectKey>标签processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver);// Parse the SQL (pre: <selectKey> and <include> were parsed and removed)// 创建SqlSource,解析SQL,封装SQL语句(未参数绑定)和入参信息SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets");String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty");String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn");KeyGenerator keyGenerator;String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX;keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true);if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) {keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId);} else {keyGenerator = context.getBooleanAttribute("useGeneratedKeys",configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType))? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;}// 通过构建者助手,创建MappedStatement对象builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);}private LanguageDriver getLanguageDriver(String lang) {Class<? extends LanguageDriver> langClass = null;if (lang != null) {langClass = resolveClass(lang);}return builderAssistant.getLanguageDriver(langClass);}...省略}
对于这些子标签框架最后会解析成对应的sql语句然后通过构建者助手,创建MappedStatement对象封装在configuration中的mappedStatements集合中供sql执行时获取。对于sql语句的解析默认使用XMLScriptBuilder进行解析,这里留了相关的口子进行扩展,如果你在mapper标签中设置了lang则需要提供对应的XXXScriptBuilder并实现createSqlSource()方法。我们直接看默认的实现:
public class XMLLanguageDriver implements LanguageDriver {...省略@Overridepublic SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, XNode script, Class<?> parameterType) {// 初始化了动态SQL标签处理器XMLScriptBuilder builder = new XMLScriptBuilder(configuration, script, parameterType);// 解析动态SQLreturn builder.parseScriptNode();}...省略}
源码看到这里我们会发现mybatis框架对于面向对象做的还是挺不错的,类的单一职责原则也遵守的很好,每一类文件的解析都是使用独立的Builder或者Parser。对于sql的解析又提供了一个XMLScriptBuilder来操作:
public class XMLScriptBuilder extends BaseBuilder {...省略public XMLScriptBuilder(Configuration configuration, XNode context) {this(configuration, context, null);}public XMLScriptBuilder(Configuration configuration, XNode context, Class<?> parameterType) {super(configuration);this.context = context;this.parameterType = parameterType;// 初始化动态SQL中的节点处理器集合initNodeHandlerMap();}private void initNodeHandlerMap() {nodeHandlerMap.put("trim", new TrimHandler());nodeHandlerMap.put("where", new WhereHandler());nodeHandlerMap.put("set", new SetHandler());nodeHandlerMap.put("foreach", new ForEachHandler());nodeHandlerMap.put("if", new IfHandler());nodeHandlerMap.put("choose", new ChooseHandler());nodeHandlerMap.put("when", new IfHandler());nodeHandlerMap.put("otherwise", new OtherwiseHandler());nodeHandlerMap.put("bind", new BindHandler());}public SqlSource parseScriptNode() {// 解析select\insert\ update\delete标签中的SQL语句,最终将解析到的SqlNode封装到MixedSqlNode中的List集合中// ****将带有${}号的SQL信息封装到TextSqlNode// ****将带有#{}号的SQL信息封装到StaticTextSqlNode// ****将动态SQL标签中的SQL信息分别封装到不同的SqlNode中MixedSqlNode rootSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(context);SqlSource sqlSource = null;// 如果SQL中包含${}和动态SQL语句,则将SqlNode封装到DynamicSqlSourceif (isDynamic) {sqlSource = new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode);} else {// 如果SQL中包含#{},则将SqlNode封装到RawSqlSource中,并指定parameterTypesqlSource = new RawSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode, parameterType);}return sqlSource;}protected MixedSqlNode parseDynamicTags(XNode node) {List<SqlNode> contents = new ArrayList<>();//获取<select>\<insert>等4个标签的子节点,子节点包括元素节点和文本节点NodeList children = node.getNode().getChildNodes();for (int i = 0; i < children.getLength(); i++) {XNode child = node.newXNode(children.item(i));// 处理文本节点if (child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.CDATA_SECTION_NODE|| child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.TEXT_NODE) {String data = child.getStringBody("");// 将文本内容封装到SqlNode中TextSqlNode textSqlNode = new TextSqlNode(data);// SQL语句中带有${}的话,就表示是dynamic的if (textSqlNode.isDynamic()) {contents.add(textSqlNode);isDynamic = true;} else {// SQL语句中(除了${}和下面的动态SQL标签),就表示是static的contents.add(new StaticTextSqlNode(data));}//处理元素节点} else if (child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) { // issue #628String nodeName = child.getNode().getNodeName();// 动态SQL标签处理器NodeHandler handler = nodeHandlerMap.get(nodeName);if (handler == null) {throw new BuilderException("Unknown element <" + nodeName + "> in SQL statement.");}handler.handleNode(child, contents);// 动态SQL标签是dynamic的isDynamic = true;}}return new MixedSqlNode(contents);}...省略}
sql解析分为两类:
动态的 静态的
对应的封装类型:DynamicSqlSource和RawSqlSource。动态的sql为包含${}和动态标签的sql语句,静态的是只包含#{}的sql语句。此处我们还需看一下SqlSource和SqlNode两个接口的设计:

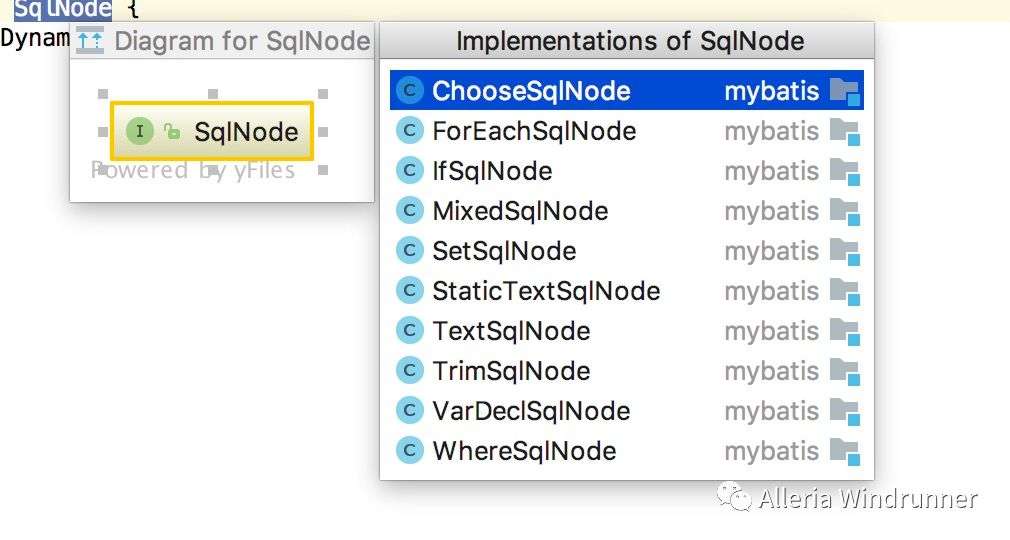
从SqlNode的示意图中可以看出其实现也是针对动态sql标签来的,ifSqlNode、ChooseSqlNode等都是我们开发中使用的滚瓜烂熟的标签。其实对于sql语句来说mybatis是这么识别的:
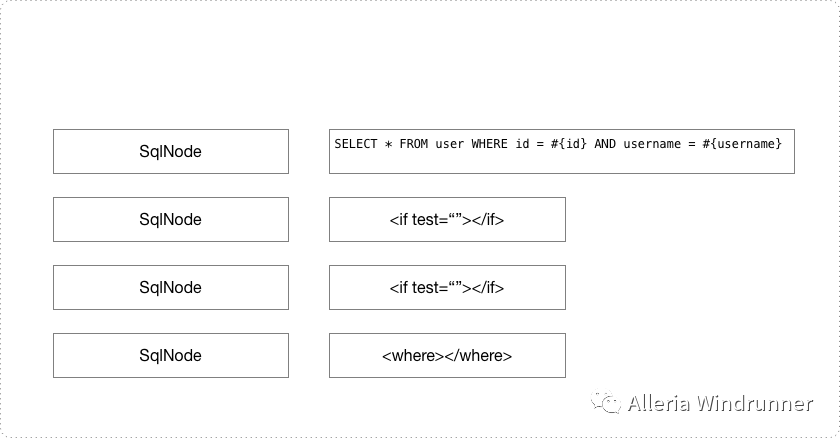
所有的这些SqlNode都封装在一个List集合里面,相当于把Sql的每一部分都分开对待。最后把解析好的SqlSource放在configuration中供执行sql的时候调用。
mybatis的整个配置文件的解析过程就是这样了,感兴趣的朋友可以根据我的思路阅读一下。






