今天我想着介绍一下关于生物学常见的数据格式,在电脑中我们的文件格式五花八门,比如:doc、ppt、excl、txt等等,其实在生物界也有好多数据格式,比如:fastq、sra、bed、vcf等等,它们都代表着不同的的信息。所以我们今天来学习一下生物学常见的数据格式。
生物信息学领域,常见的工作任务就是对某种数据进行处理和分析,从而解决一个生物学问题。
在知乎发现一个博主(梨酱)写了一篇关于生物学常见数据格式的文章,人家写的真的很棒,我知道我没有人家写到好,所以直接copy了过来。
特别声明:转载自知乎博主——梨酱
原文链接:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/67402565
在介绍之前,希望你先思考一个问题——“为什么要有通用的数据格式呢?”
用于呈现数据的最优信息学方法:以一种明确的方式对你的数据进行分类,有助于他人更容易理解并通过编程访问,也有利于数据在未来几年内的可用性。
使用通用的数据标准并注意数据在系统中的存储形式是成功管理数据的评判标准。
《生物信息学》T.Charlie Hodgman等人编著,陈铭等人译
不同的软件,针对某方向的某生物学问题,都会创建或使用一种或者多种格式标准。比如储存数据常用sra、比对数据常用bam,基因组注释信息常用bam或gff。
反过来,也可以思考为什么某个软件选取某格式标准而不用其他的格式,这可以加深我们对数据的理解。
理解数据格式的重要性和意义后,让我们先介绍下FASTA和FASTQ。
因为要便于存储生物序列信息,比如ACGT组成的DNA序列、蛋白质序列,生物信息学家们便基于 txt 文本格式定义了有一定规范的FASTA和FASTQ格式。
1.FASTA格式
FASTA文件格式,来自一款古老的名为“FASTA”的比对软件。
该软件1988年问世,发表于PNAS。
突然有一种翻出88年奇妙宝藏的感觉???

原版FASTA/Pearson格式定义出现在FASTA程序包的文档中。可随FASTA的任一免费版本下载(见fasta20.doc、fastaVN.doc或fastaVN.me,其中VN代表版本号)。
——维基百科
之后,生物学家们就沿用这个软件名作为后缀:.fasta,.fa,或其压缩格式.fasta.gz,.fa.gz。
所以,如果你以后开发出新兴领域的流行软件,也有可能被沿用为存储某类数据的格式名称哦~
以下为一个包含单个序列的FASTA文件示例:
>gi|31563518|ref|NP_852610.1| microtubule-associated proteins 1A/1B light chain 3A isoform b [Homo sapiens]
MKMRFFSSPCGKAAVDPADRCKEVQQIRDQHPSKIPVIIERYKGEKQLPVLDKTKFLVPDHVNMSELVKI
IRRRLQLNPTQAFFLLVNQHSMVSVSTPIADIYEQEKDEDGFLYMVYASQETFGFIRENE
第一行为“>”开头的标题行,包含序列的名称和/或唯一标识符等信息。
在标题行和注释之后,则是由一行或多行构成的蛋白质或核酸序列数据,其中每行的长度应短于80字符。
2.FASTQ格式
有了FASTA,为什么还要有FASTQ呢?
因为要把测序数据和其质量得分放在一个文件里储存,方便。
FASTQ格式是一种保存生物序列(通常为核酸序列)及其测序质量得分信息的文本格式。序列与质量得分皆由单个ASCII字符表示。
该格式最初由维尔康姆基金会桑格研究所开发,旨在将FASTA格式序列及其质量数据集成在一起。而当前,FASTQ格式已经成为了保存高通量测序结果的事实标准。
FASTQ格式_维基百科
质量得分,指一个碱基的错误概率的对数值。最早在Phred软件中被定义和使用,后来逐渐推广开来。
以下为一个包含单个序列的FASTQ文件示例:
@SRR001339.3 FC12160_04JAN08_s_3.tar:3:1:230:474 length=36
GTTAGTCGGGAACTAAGGCCTGTAGGCTCTTTCCAT
+SRR001339.3 FC12160_04JAN08_s_3.tar:3:1:230:474 length=36
IIIIBIII*II,III$I′I9IDI%II … 5′E%%(H
可以看到,在FASTQ文件中,一个序列通常由四行组成:
第一行以@开头,之后为序列的标识符以及描述信息(与FASTA格式的描述行类似)
第二行为序列信息
第三行以+开头,之后可以再次加上序列的标识及描述信息(可选)
第四行为质量得分信息,与第二行的序列相对应,长度必须与第二行相同
3. BED格式
BED (Browser Extensible Data)是一种灵活的储存数据的格式,主要用来储存基因组特征(genomic features)或注释信息。
补充说明下基因组特征:
This is a generic and general term to describe any genomic region with some annotated function. E.g. agene,CDS,mRNA,rRNA,tRNA,repeat sequence,inverted repeat,miRNA,siRNA,origin of replication.
A given genomic feature may be comprised of multiple specific genomic locations that together form the genomic feature. For example, a protein coding gene (CDS) is encoded by a gene that has multiple exons. Each exon is spliced together to form a maturemRNA. The CDS feature itself is therefore comprised of multiple genomic locations that neighbor one another.
参考:genomevolution.org/wiki
BED格式可用于UCSC的Genome Browser可视化工具中。
发现没,这两名称都很相似,Browser Extensible Data,Genome Browser。
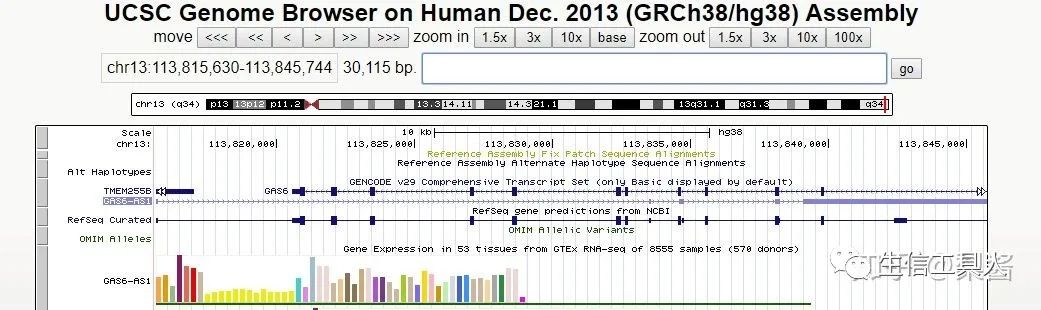
BED格式有3行信息必选:
1. chrom - 染色体名称 (e.g. chr3, chrY, chr2_random) 或 scaffold (e.g. scaffold10671).
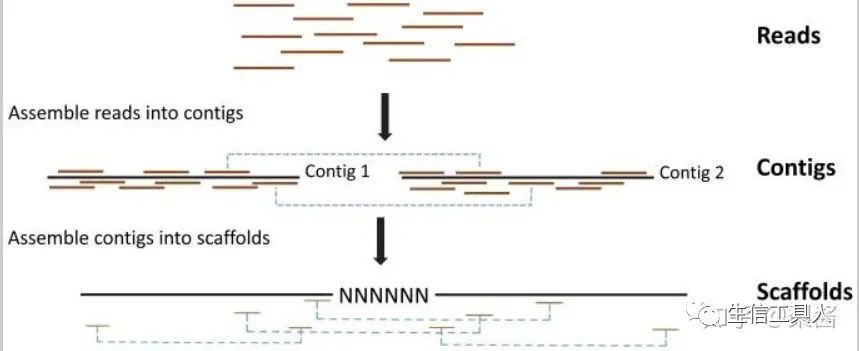
补充下什么是scaffold?
二代基因组测序的原始结果为reads,reads可以拼接为序列contig,contig进一步可以组装成更长的序列scaffold。
2. chromStart - 染色体或scaffold起始位点. 注意!是从0开始计数!是从0开始计数!是从0开始计数!
3. chromEnd - 染色体或scaffold终止位点. 注意!结束位点的碱基不包含在内。比如chromStart=0, chromEnd=100, 那么实际上表示为0-99.
以下为最简单的BED3文件示例:
(有几列就叫BED几,下面数据有3列,则是BED3)
chrom chromStart chromEnd
chr1 213941196 213942363
chr1 213942363 213943530
chr1 213943530 213944697
chr2 158364697 158365864
chr2 158365864 158367031
chr3 127477031 127478198
chr3 127478198 127479365
chr3 127479365 127480532
chr3 127480532 127481699
为什么说BED格式灵活呢?
因为我们可以根据需要,选择补充9行备选信息:
4. name - BED的名称.
5. score - 分数为0 到1000。颜色越深,分数越高。

6. strand - 链方向. "." (=no strand) 或"+" 或 "-".
7. thickStart - 绘制特征的起始位置(例如起始密码子)。当没有thick部分时,thickStart和thickEnd通常设置为chromStart位置。
8. thickEnd - 绘制特征的终止位置(例如终止密码子)。
9. itemRgb - RGB值 (e.g. 255,0,0). 如果track 行 itemRgb 参数设置为 "On", RBG值会决定BED文件中该行数据的颜色.
10. blockCount - blocks (exons)在BED line的数量.
11. blockSizes - 用逗号分隔的列表,用来表示block的的大小。列表中数字的数目应和blockCount 一致。
12. blockStarts - 用逗号分隔的列表,用来表示block的起始。所有blockStart 的位点应该和chromStart 相关。列表中数字的数目应和blockCount 一致。
在有block等相关列的BED文件中,blockStart 值必须是 0, 因此第一个block是从chromStart 开始。同样的,最后一个blockStart 位点加上最后一个blockSize 值应该和chromEnd相等。Blocks不能重叠.
以下为BED9文件示例:
track name="ItemRGBDemo" description="Item RGB demonstration" itemRgb="On"
chr7 127471196 127472363 Pos1 0 + 127471196 127472363 255,0,0
chr7 127472363 127473530 Pos2 0 + 127472363 127473530 255,0,0
chr7 127473530 127474697 Pos3 0 + 127473530 127474697 255,0,0
chr7 127474697 127475864 Pos4 0 + 127474697 127475864 255,0,0
chr7 127475864 127477031 Neg1 0 - 127475864 127477031 0,0,255
chr7 127477031 127478198 Neg2 0 - 127477031 127478198 0,0,255
chr7 127478198 127479365 Neg3 0 - 127478198 127479365 0,0,255
chr7 127479365 127480532 Pos5 0 + 127479365 127480532 255,0,0
chr7 127480532 127481699 Neg4 0 - 127480532 127481699 0,0,255
如何处理BED文件?
bedtools,可对储存了基因组特征信息的BED文件进行比较、注释、转化等操作。由美国犹他大学(University of Utah)的Quinlan laboratory开发。
在我刚开始学编程时,师兄曾强烈建议我写脚本模仿bedtools的各种功能来增强自己的代码能力。你也可以这样做来提高自己~
安装 bedtools
curl http://bedtools.googlecode.com/files/BEDTools.<version>.tar.gz > BEDTools.tar.gz
tar -zxvf BEDTools.tar.gz
cd BEDTools
make
sudo cp bin/* /usr/local/bin/
# 也可以使用conda
conda
2. bedtools常见用法
# 查看bedtools的说明文档
bedtools --help
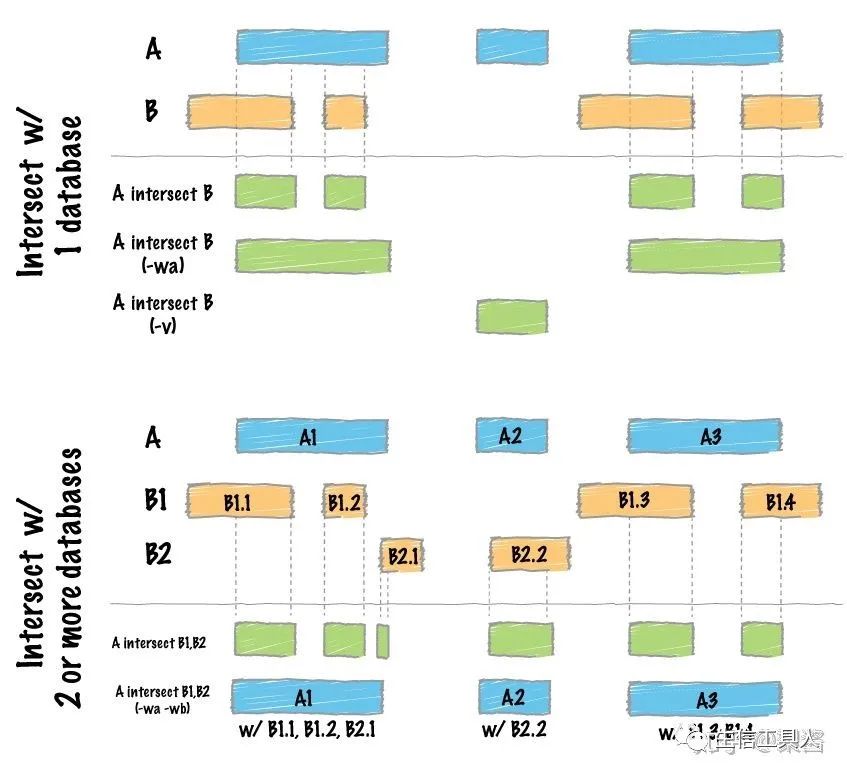
#从两个BED文件中得到genome feature的交集
bedtools intersect -a reads.bed/gff/bam/vcf -b genes.bed/gff/bam/vcf
#-wa参数可以报告出原始的在A文件中的feature
#-wb参数可以报告出原始的在B文件中的feature
#-c参数可以报告出两个文件中的overlap的feature的数量
#-wo 返回overlap碱基数
#-v 返回非overlap区间
#-s 相同链上的feature
这些参数不用记住,要用的时候直接在命令行查看参数即可。处理文件多了自然就会印在脑子里。别着急,慢慢来。
另外,可以阅读 http://quinlanlab.org/tutorials/bedtools/bedtools.html#reporting-the-original-feature-in-each-file 和 bedtools-Example usage 了解更多关于bedtools的妙用。
3. bedtools的背后故事:
The development of bedtools was motivated by a need for fast, flexible tools with which to compare large sets of genomic features. Answering fundamental research questions with existing tools was either too slow or required modifications to the way they reported or computed their results. We were aware of the utilities on the UCSC Genome Browser and Galaxy websites, as well as the elegant tools available as part of Jim Kent’s monolithic suite of tools (“Kent source”). However, we found that the web-based tools were too cumbersome when working with large datasets generated by current sequencing technologies. Similarly, we found that the Kent source command line tools often required a local installation of the UCSC Genome Browser. These limitations, combined with the fact that we often wanted an extra option here or there that wasn’t available with existing tools, led us to develop our own from scratch. The initial version of bedtools was publicly released in the spring of 2009.
这段话提到了Jim Kent开发的网站在线工具很难用,因此开发了bedtools。
Jim是谁?和 UCSC Genome Browser 有什么关系?

In 2000, Jim Kent wrote a program, GigAssembler, that allowed the publicly funded Human Genome Project to assemble and publish the first human genome sequence.
After GigAssembler, Kent went on to write BLAT (BLAST-like alignment tool) and the UCSC Genome Browser to help analyze important genome data. Kent continues to work at UCSC primarily on web tools to help understand the human genome. He helps maintain and upgrade the browser, and has worked on comparative genomics, Parasol, a job control management software for the UCSC kilocluster, and the Encode Project.
大佬!
Jim Kent 开发了GigAssembler使得Human Genome Project组装并发表了第一个人类基因组序列。在这之后,他开始写BLAT (BLAST-like alignment tool) 和 UCSC Genome Browser 来帮助分析数据。
厉害!
但是,如果你觉得大佬开发的东西不好用时,你会像bedtools的开发者们一样挑战权威进行创新吗?
4. SRA格式
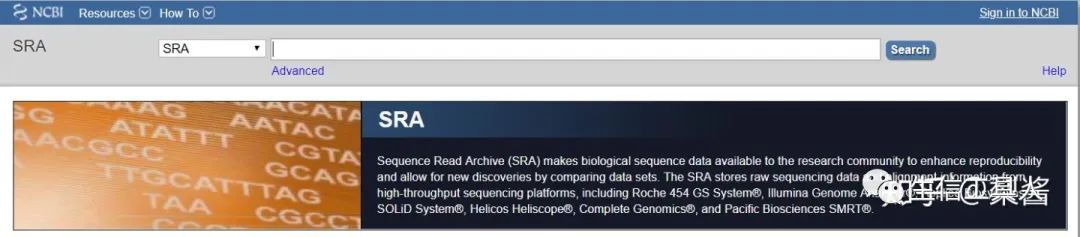
Sequence Read Archive (SRA) makes biological sequence data available to the research community to enhance reproducibility and allow for new discoveries by comparing data sets. The SRA stores raw sequencing data and alignment information from high-throughput sequencing platforms, including Roche 454 GS System®, Illumina Genome Analyzer®, Applied Biosystems SOLiD System®, Helicos Heliscope®, Complete Genomics®, and Pacific Biosciences SMRT®.
Sequence Read Archive (SRA) 数据库,用于储存来自不同高通量测序平台的原始序列数据和比对信息。
在提交测序数据到SRA数据库时,每一个样本会获得一个以SRR开头的数字编号:SRRxxx。
从SRA数据库下载公共的测试数据,原始格式即为 .sra 。
如何下载.sra数据?
可以用SRA数据库的SRA Toolkit下载sra数据。
怎么对.sra数据进行下一步分析?
可以用fasterq_dump将sra转换为fastq,进行下一步处理。
提醒一下,fasterq-dump不支持gzip!
# 单个数据解压
fasterq-dump --split-3 -e 20 SRRxxx.sra -O fastq/
# 批量解压
for i in *sra
do
echo $i
fastqer-dump --split-3 -e 20 $i
done
使用SRA数据库时,可以看到有不同的ID前缀,比如SRA、SRR,这是什么意思呢?
SRA数据库用6种不同的前缀区分不同的数据:
1. SRA是提交数据时得到的数据号,包含下列5种前缀所组成的数据集。
2. SRP表示 SRA Studies/projects;研究课题或项目的元数据;一个Study(SRP)可能包含多个experiments。
3. SRX 表示 Experiments;包含元数据及其建库方式、测序平台、处理方式。
4. SRR 表示 Runs;包含真实的测序数据;一个Experiment(SRX)可能有多个Run。
5. SRS 表示 Samples;描述进行测序的物理样本的元数据。
6. SRZ 表示 Analysis;包含序列数据分析的BAM文件和描述序列分析的元数据。
SRA中数据结构的层次关系为:Studies->Experiments->Samples->Runs。这样分类是以便更好的找到所需信息。
在公开发表的文章中,用SRA数据库中哪一种前缀的编号,目前没有统一标准。但是SRA数据库的开发人员建议使用SRP,因为可以让读者更好的了解数据的产生过程。
Currently, there is no requirement for authors to use a specific SRA accession in their publications. If there was, we would recommend that authors use the SRP (study) accession, which would provide the reader/user with a complete overview of the study and a set of links to all the data from that study.
可阅读 ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/ 了解更多关于SRA数据库的信息。
5. SAM格式
The Sequence Alignment/Map (SAM) format is a generic alignment format for storing read alignments against reference sequences, supporting short and long reads (up to 128 Mbp) produced by different sequencing platforms. It is flexible in style, compact in size, efficient in random access and is the format in which alignments from the 1000 Genomes Project are released. SAMtools implements various utilities for post-processing alignments in the SAM format, such as indexing, variant caller and alignment viewer, and thus provides universal tools for processing read alignments.
The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics. 2009 Aug 15; 25(16): 2078–2079
在挖掘生物数据信息时,我们会将未知的序列与已知的reference对比,从而找到未知序列中隐藏的信息。这就是序列比对。常见的序列比对的文件输出格式为sam和bam。
Sequence Alignment Mapping (SAM) 格式包括两部分:
1. 注释信息(header section)
2. 比对结果(alignment section)
1. 注释信息可有可无,都是以@开头,用不同的tag表示不同的信息:
@HD,说明符合标准的版本、对比序列的排列顺序;
@SQ,参考序列说明;
@RG,比对上的序列(read)说明;
@PG,使用的程序说明;
@CO,任意的说明信息。
2. 比对结果,必须通过11个tab间隔的字段来表示。注意,如果为空,则用*或0表示。
No. 名称 描述
1 QNAME Query NAME of the read or the read pair
2 FLAG Bitwise FLAG (pairing, strand, mate strand, etc.)
3 RNAME Reference sequence NAME
4 POS 1-Based leftmost POSition of clipped alignment
5 MAPQ MAPping Quality (Phred-scaled)
6 CIGAR Extended CIGAR string (operations: MIDNSHP)
7 MRNM Mate Reference NaMe (‘=’ if same as RNAME)
8 MPOS 1-Based leftmost Mate POSition
9 ISIZE Inferred Insert SIZE
10 SEQ Query SEQuence on the same strand as the reference
11 QUAL Query QUALity (ASCII-33=Phred base quality)
标准的CIGAR列描述的内容:
‘M’ for match/mismatch,
‘I’ for insertion compared with the reference
‘D’ for deletion.
阅读 samtools.github.io/hts- 了解更多。
为了更好的理解SAM格式,假设我们有下列原始数据:
Read r001/1 和 r001/2 组成一个 read pair;
r003 是 chimeric read;
r004 代表 split alignment.

将上图中序列转换为SAM格式为:
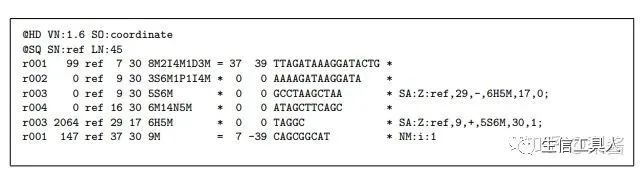
如何处理SAM格式的数据呢?
我们可以使用 SAMtools,顾名思义,就是用来处理SAM/BAM格式的数据:
SAMtools is a library and software package for parsing and manipulating alignments in the SAM/BAM format. It is able to convert from other alignment formats, sort and merge alignments, remove PCR duplicates, generate per-position information in the pileup format (Fig. 1c), call SNPs and short indel variants, and show alignments in a text-based viewer.
samtools.github

# 安装
conda install samtools
# 常见用法
samtools view [options] <输入bam文件> # 将sam文件与bam文件互换,详细参数查看samtool --help
samtools sort [options] <输入bam文件> <输出bam文件名> # 排序
samtools merge [options] <输出bam文件> <输入bam文件1> <输入bam文件> # 合并文件
samtools flagstat <输入bam文件> # 统计bam文件中的比对flag信息,并输出比对统计结果
samtools index <排序后的bam文件> # 建立索引,输出bai文件,用于快速随机处理。
samtools faidx <输入fasta文件> # 建立索引,输出fai文件,用于快速随机处理。
samtools tview [options] <aln.bam> [ref.fasta] # 显示reads比对基因组的情况,使用前要先建立index并sort
samtools mpileup # multi-way pileup,用于生成bcf文件,再使用samtool中附带的软件bcftools进行SNP和Indel的分析
6. BAM格式
Binary Alignment/Map (BAM)是SAM格式的二进制压缩格式,这两种格式是序列比对时软件常用的数据格式。
为什么有了SAM还要有BAM?
因为BAM占用的磁盘空间比SAM格式小,运算速度更快。
对BAM文件进行比对时,可以使用fastq_collapse将重复的序列放到一个数据集,从而提高比对效率:
测序数据存在大量重复序列,如果能够把重复的序列都放到一个数据集并计数,比对时只比对不重复的序列,就可提高效率。
这就是collapse的作用,合并重复序列以减少比对时间。
另外在去掉adaptor之后,可以把barcode相同的序列合并之后collapse,也可以提高效率。
补充说明下barcode:一个常见的测序片段为adaptor-barcode-insert-adaptor。barcode用于在多个样品进行测序时,标记不同的样品,也叫index,和商品条形码的作用一样。insert是要测序的序列。
怎么collapse?
使用fastx_collapser,用法是fastx_collapser [-h] [-v] [-i INFILE] [-o OUTFILE]。
注意!不是所有的数据都需要collapse。
7. GFF格式
The GFF format is described on the Sanger Institute’s website (sanger.ac.uk/resources/).
General Feature Format (GFF)格式,和BED格式一样,也可用于储存基因组或蛋白质特征。主要用来注释基因组。
目前主要用第三版GFF3,详细可查看 Generic Feature Format Version 3 (GFF3)。
9列分别为:seqid source type start end score strand strandattributes
为更好的理解GFF3,我们来看一个例子:
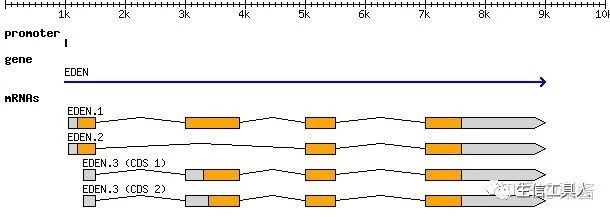
如果将上面这个基因用GFF3格式表示,则为:
0 ##gff-version 3.2.1
1 ##sequence-region ctg123 1 1497228
2 ctg123 . gene 1000 9000 . + . ID=gene00001;Name=EDEN
3 ctg123 . TF_binding_site 1000 1012 . + . ID=tfbs00001;Parent=gene00001
4 ctg123 . mRNA 1050 9000 . + . ID=mRNA00001;Parent=gene00001;Name=EDEN.1
5 ctg123 . mRNA 1050 9000 . + . ID=mRNA00002;Parent=gene00001;Name=EDEN.2
6 ctg123 . mRNA 1300 9000 . + . ID=mRNA00003;Parent=gene00001;Name=EDEN.3
7 ctg123 . exon 1300 1500 . + . ID=exon00001;Parent=mRNA00003
8 ctg123 . exon 1050 1500 . + . ID=exon00002;Parent=mRNA00001,mRNA00002
9 ctg123 . exon 3000 3902 . + . ID=exon00003;Parent=mRNA00001,mRNA00003
10 ctg123 . exon 5000 5500 . + . ID=exon00004;Parent=mRNA00001,mRNA00002,mRNA00003
11 ctg123 . exon 7000 9000 . + . ID=exon00005;Parent=mRNA00001,mRNA00002,mRNA00003
12 ctg123 . CDS 1201 1500 . + 0 ID=cds00001;Parent=mRNA00001;Name=edenprotein.1
13 ctg123 . CDS 3000 3902 . + 0 ID=cds00001;Parent=mRNA00001;Name=edenprotein.1
14 ctg123 . CDS 5000 5500 . + 0 ID=cds00001;Parent=mRNA00001;Name=edenprotein.1
15 ctg123 . CDS 7000 7600 . + 0 ID=cds00001;Parent=mRNA00001;Name=edenprotein.1
16 ctg123 . CDS 1201 1500 . + 0 ID=cds00002;Parent=mRNA00002;Name=edenprotein.2
17 ctg123 . CDS 5000 5500 . + 0 ID=cds00002;Parent=mRNA00002;Name=edenprotein.2
18 ctg123 . CDS 7000 7600 . + 0 ID=cds00002;Parent=mRNA00002;Name=edenprotein.2
19 ctg123 . CDS 3301 3902 . + 0 ID=cds00003;Parent=mRNA00003;Name=edenprotein.3
20 ctg123 . CDS 5000 5500 . + 1 ID=cds00003;Parent=mRNA00003;Name=edenprotein.3
21 ctg123 . CDS 7000 7600 . + 1 ID=cds00003;Parent=mRNA00003;Name=edenprotein.3
22 ctg123 . CDS 3391 3902 . + 0 ID=cds00004;Parent=mRNA00003;Name=edenprotein.4
23 ctg123 . CDS 5000 5500 . + 1 ID=cds00004;Parent=mRNA00003;Name=edenprotein.4
24 ctg123 . CDS 7000 7600 . + 1 ID=cds00004;Parent=mRNA00003;Name=edenprotein.4
8. GTF 格式
Gene Transfer Format (GTF),和GFF类似,都有9列数据并用tab键分隔。
但GTF格式主要是用来对基因进行注释,目前广泛使用的是第二版GTF2。
9列分别为:seqname source feature start end score strand frame attributes
GFF和GTF格式的区别:
1.第3列feature/type不同;GFF可以为任意名称,而GTF则必须注明
2. 第9列attribures不同;GFF名称和值是以等号=隔开,GTF则是以空格隔开
可以使用cufflinks中的gffread转换GFF和GTF:
#gff2gtf
gffread file1.gff3 -T -o file1.gtf
#gtf2gff
gffread file2.gtf -o file2.gff3
gffread工具由约翰·霍普金斯大学开发,他们开发了hisat2和stringtie。
9. VCF格式
The Variant Call Format (VCF) was conceived as part of the 1000 Genomes Project as a standardized means to report genetic variation calls from SNP, INDEL and structural variant detection programs (see 1000genomes.org/wiki/do for details).
VCF (Variant Call Format) version 4.0 是 1000 Genomes Project的标准数据格式之一,可用于储存SNP、INDEL和结构变异信息。
VCF is a text file format (most likely stored in a compressed manner). It contains meta-information lines, a header line, and then data lines each containing information about a position in the genome.
举例:
##fileformat=VCFv4.0
##fileDate=20090805
##source=myImputationProgramV3.1
##reference=1000GenomesPilot-NCBI36
##phasing=partial
##INFO=<ID=NS,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description="Number of Samples With Data">
##INFO=<ID=DP,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description="Total Depth">
##INFO=<ID=AF,Number=.,Type=Float,Description="Allele Frequency">
##INFO=<ID=AA,Number=1,Type=String,Description="Ancestral Allele">
##INFO=<ID=DB,Number=0,Type=Flag,Description="dbSNP membership, build 129">
##INFO=<ID=H2,Number=0,Type=Flag,Description="HapMap2 membership">
##FILTER=<ID=q10,Description="Quality below 10">
##FILTER=<ID=s50,Description="Less than 50% of samples have data">
##FORMAT=<ID=GT,Number=1,Type=String,Description="Genotype">
##FORMAT=<ID=GQ,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description="Genotype Quality">
##FORMAT=<ID=DP,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description="Read Depth">
##FORMAT=<ID=HQ,Number=2,Type=Integer,Description="Haplotype Quality">
#CHROM POS ID REF ALT QUAL FILTER INFO FORMAT NA00001 NA00002 NA00003
20 14370 rs6054257 G A 29 PASS NS=3;DP=14;AF=0.5;DB;H2 GT:GQ:DP:HQ 0|0:48:1:51,51 1|0:48:8:51,51 1/1:43:5:.,.
20 17330 . T A 3 q10 NS=3;DP=11;AF=0.017 GT:GQ:DP:HQ 0|0:49:3:58,50 0|1:3:5:65,3 0/0:41:3
20 1110696 rs6040355 A G,T 67 PASS NS=2;DP=10;AF=0.333,0.667;AA=T;DB GT:GQ:DP:HQ 1|2:21:6:23,27 2|1:2:0:18,2 2/2:35:4
20 1230237 . T . 47 PASS NS=3;DP=13;AA=T GT:GQ:DP:HQ 0|0:54:7:56,60 0|0:48:4:51,51 0/0:61:2
20 1234567 microsat1 GTCT G,GTACT 50 PASS NS=3;DP=9;AA=G GT:GQ:DP 0/1:35:4 0/2:17:2 1/1:40:3
可以查看bioinfo-scrounger.com/a 和 internationalgenome.org 了解更多。






