Trie
作者:王善文 @零熊
本文为 Leetcode 的 Trie 题分类与详解。代码均为Java。
208 Implement Trie
676 Implement Magic Dictionary
720 Longest Word in Dictionary (Trie + DFS)
692 Top K Frequent Words (HashMap + BucketSort + Trie + DFS)
421 Maximum XOR of Two Numbers in an Array (Trie + Bit Manipulation)
336 Palindrome Pairs
425 Word Squares (Trie + Backtracking)
208. Implement Trie (Prefix Tree)
Implement a trie with insert, search, and startsWith methods.
Example:
Trie trie = new Trie();trie.insert("apple");trie.search("apple"); // returns truetrie.search("app"); // returns falsetrie.startsWith("app"); // returns truetrie.insert("app"); trie.search("app"); // returns true
class Node {
public char val;
public boolean isWord = false;
public Node[] children = new Node[26];
public Node() {
}
public Node(char c) {
Node node = new Node();
node.val = c;
}
}
class Trie {
private Node root;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public Trie() {
root = new Node();
root.val = ' ';
}
/** Inserts a word into the trie. */
public void insert(String word) {
Node cur = root;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
char c = word.charAt(i);
if (cur.children[c - 'a'] == null)
cur.children[c - 'a'] = new Node(c);
cur = cur.children[c - 'a'];
}
cur.isWord = true;
}
/** Returns if the word is in the trie. */
public boolean search(String word) {
Node cur = root;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
if (cur.children[word.charAt(i) - 'a'] == null) return false;
cur = cur.children[word.charAt(i) - 'a'];
}
return cur.isWord;
}
/** Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. */
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
Node cur = root;
for (int i = 0; i < prefix.length(); i++) {
if (cur.children[prefix.charAt(i) - 'a'] == null) return false;
cur = cur.children[prefix.charAt(i) - 'a'];
}
return true;
}
}
/**
* Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Trie obj = new Trie();
* obj.insert(word);
* boolean param_2 = obj.search(word);
* boolean param_3 = obj.startsWith(prefix);
*/
总结:基本的Trie实现。接下来我们看它的一些应用。
676. Implement Magic Dictionary
Implement a magic directory with buildDict, and search methods.
For the method buildDict, you'll be given a list of non-repetitive words to build a dictionary.
For the method search, you'll be given a word, and judge whether if you modify exactly one character into another character in this word, the modified word is in the dictionary you just built.
Example 1:
Input: buildDict(["hello", "leetcode"]), Output: NullInput: search("hello"), Output: FalseInput: search("hhllo"), Output: TrueInput: search("hell"), Output: FalseInput: search("leetcoded"), Output: False
方法:将已有词典建Trie。把输入的单词一位位暴力修改,放入trie中验证修改后的单词是否存在。
class trieNode {
trieNode[] children;
boolean isword;
trieNode () {
children = new trieNode[26];
isword = false;
}
}
class MagicDictionary {
trieNode root;
public MagicDictionary() {
root = new trieNode();
}
/** Build a dictionary through a list of words */
public void buildDict(String[] dict) {
for (String str : dict) {
trieNode cur = root;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
char c = str.charAt(i);
if (cur.children[c - 'a'] == null) {
cur.children[c - 'a'] = new trieNode();
}
cur = cur.children[c - 'a'];
}
cur.isword = true;
}
}
/** Returns if there is any word in the trie that equals to the given word after modifying exactly one character */
public boolean search(String word) {
char[] arr = word.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
for (char c = 'a'; c <= 'z'; c++) {
if (c == arr[i]) continue;
char tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = c;
if (helper(new String(arr), root))
return true;
arr[i] = tmp;
}
}
return false;
}
boolean helper (String s, trieNode root) {
trieNode cur = root;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (cur.children[s.charAt(i) - 'a'] == null)
return false;
cur = cur.children[s.charAt(i) - 'a'];
}
return cur.isword;
}
}
/**
* Your MagicDictionary object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MagicDictionary obj = new MagicDictionary();
* obj.buildDict(dict);
* boolean param_2 = obj.search(word);
*/
总结:Trie用于验证某单词是否存在词典中。
720. Longest Word in Dictionary
Given a list of strings words representing an English Dictionary, find the longest word in words that can be built one character at a time by other words in words. If there is more than one possible answer, return the longest word with the smallest lexicographical order.
If there is no answer, return the empty string.
Example 1:
Input: words = ["w","wo","wor","worl", "world"]Output: "world"Explanation: The word "world" can be built one character at a time by "w", "wo", "wor", and "worl".
Example 2:
Input: words = ["a", "banana", "app", "appl", "ap", "apply", "apple"]Output: "apple"Explanation: Both "apply" and "apple" can be built from other words in the dictionary. However, "apple" is lexicographically smaller than "apply".
方法一:sort + set记录prefix
对单词从小到大排序,以保证: (1) 任意单词的前缀出现在该单词之前; (2)“apple”出现在“apply”之前。
沿着排序后单词数组找能形成的最长的单词。
class Solution_1 {
public String longestWord(String[] words) {
Arrays.sort(words);
Set<String> built = new HashSet<String>();
String res = "";
for (String w : words) {
if (w.length() == 1 || built.contains(w.substring(0, w.length() - 1))) {
res = w.length() > res.length() ? w : res;
built.add(w);
}
}
return res;
}
}
Build a trie in the normal way, then do a dfs to find the longest continuous downward path from the root. This is not a particularly hard question in the context of trie, the point of this solution is to present a generic way of trie building and inserting that can be easily adapted to similar questions
方法二:Trie + DFS
class Solution_2 {
public String longestWord(String[] words) {
if (words == null || words.length == 0) return "";
trieNode root = new trieNode();
root.val = " ";
for (String str : words) {
root.insert(str);
}
return dfs(root, "");
}
String dfs (trieNode node, String accum) {
if (node == null || node.val.length() == 0) return accum;
if (!node.val.equals(" ")) {
accum = node.val;
}
String res = "";
for (trieNode child : node.children) {
String tmp = dfs(child, accum);
if (tmp.length() > res.length() || (tmp.length() == res.length() && tmp.compareTo(res) < 0))
res = tmp;
}
return res;
}
}
class trieNode {
trieNode[] children = new trieNode[26];
String val = "";
trieNode() {}
void insert(String word) {
trieNode cur = this;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
char c = word.charAt(i);
if (cur.children[c - 'a'] == null) {
cur.children[c - 'a'] = new trieNode();
}
cur = cur.children[c - 'a'];
}
cur.val = word;
}
}
总结:DFS 按一定规则在Trie中找最长字符串。
692. Top K Frequent Words
Given a non-empty list of words, return the k most frequent elements.
Your answer should be sorted by frequency from highest to lowest. If two words have the same frequency, then the word with the lower alphabetical order comes first.
Example 1:
Input: ["i", "love", "leetcode", "i", "love", "coding"], k = 2Output: ["i", "love"]Explanation: "i" and "love" are the two most frequent words. Note that "i" comes before "love" due to a lower alphabetical order.
Example 2:
Input: ["the", "day", "is", "sunny", "the", "the", "the", "sunny", "is", "is"], k = 4Output: ["the", "is", "sunny", "day"]Explanation: "the", "is", "sunny" and "day" are the four most frequent words, with the number of occurrence being 4, 3, 2 and 1 respectively.
方法一:HashMap + PriorityQueue本题和Leetcode 347 Top K Frequent Elements比较像。
用一个map来统计每个词出现频率,用一个priorityQueue来按照词频排序,相同词频则按字母顺序从大到小排序。(想复习一下Heap的朋友可以看下这篇文章https://github.com/GingerBear/IS-Job-Hunting/issues/10, 对复杂度的分析比较清晰。)
class Solution {
public List<String> topKFrequent(String[] words, int k) {
Map<String, Integer> count = new HashMap();
for (String word: words) {
count.put(word, count.getOrDefault(word, 0) + 1);
}
PriorityQueue<String> heap = new PriorityQueue<String>(words.length, new Comparator<String>() {
public int compare(String a, String b) {
if (count.get(a).equals(count.get(b)))
return a.compareTo(b);
return count.get(b) - count.get(a);
}
});
for (String word: count.keySet()) {
heap.offer(word);
}
List<String> ans = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
ans.add(heap.poll());
return ans;
}
}
方法二:HashMap + BucketSort + Trie + DFS Leetcode 347. Top K Frequent Elements也有类似的解法https://leetcode.com/problems/top-k-frequent-elements/discuss/81602/java-on-solution-bucket-sort。用一个map统计词频。因为"1 <= 词频 <= 输入单词个数",所以可以用bucket存放单词,bucket为长度words.length + 1
的数据类型为trienode
的数组。Bucket的index是频率,存放的是以trieNode形式的所有单词。这样通过一个DFS可以将Trie中存放单词按字母顺序从低到高找出,从而省去bucket内排序的问题。时间复杂度为O(n * length of word).
public List<String> topKFrequent(String[] words, int k) {
// calculate frequency of each word
Map<String, Integer> freqMap = new HashMap<>();
for(String word : words) {
freqMap.put(word, freqMap.getOrDefault(word, 0) + 1);
}
// build the buckets
TrieNode[] bucket = new TrieNode[words.length + 1];
for(String word : freqMap.keySet()) {
int freq = freqMap.get(word);
if(bucket[freq] == null) {
bucket[freq] = new TrieNode();
}
addWord(bucket[freq], word);
}
// get k frequent words
List<String> list = new LinkedList<>();
for(int f = bucket.length - 1; f >= 1 && list.size() < k; f--) {
if(bucket[f] == null) continue;
getWords(bucket[f], list, k);
}
return list;
}
private void getWords(TrieNode node, List<String> list, int k) {
if(node == null) return;
if(list.size() == k) return;
if(node.word != null) {
list.add(node.word);
}
for(int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if(node.next[i] != null) {
getWords(node.next[i], list, k);
}
}
}
private boolean addWord(TrieNode root, String word) {
TrieNode curr = root;
for(char c : word.toCharArray()) {
if(curr.next[c - 'a'] == null) {
curr.next[c - 'a'] = new TrieNode();
}
curr = curr.next[c - 'a'];
}
curr.word = word;
return true;
}
class TrieNode {
TrieNode[] next;
String word;
TrieNode() {
this.next = new TrieNode[26];
this.word = null;
}
}
总结:本题是一个top K类问题。Trie用来存每个bucket里的所有单词。DFS遍历Trie可以保证Trie里的单词按字母顺序输出。
421. Maximum XOR of Two Numbers in an Array
Given a non-empty array of numbers, a0, a1, a2, … , an-1, where 0 ≤ ai < 231.
Find the maximum result of ai XOR aj, where 0 ≤ i, j < n.
Could you do this in O(n) runtime?
Example:
Input: [3, 10, 5, 25, 2, 8 Output: 28Explanation: The maximum result is 5 ^ 25 = 28.
本题涉及位运算。方法是把每个输入的数字转换成32位二进制数,存放在Trie里。接着将所有输入的数转32位二进制取反,一位一位在Trie中匹配。匹配到反的位则往反的位走,同时累加答案,匹配不到才走相同位。最后返回最大的答案。
class Solution {
public int findMaximumXOR(int[] nums) {
trieNode root = new trieNode();
for (int num : nums) {
trieNode cur = root;
for (int i = 31; i >= 0; i--) {
int bit = (num >>> i) & 1;
if (cur.children[bit] == null) {
cur.children[bit] = new trieNode();
}
cur = cur.children[bit];
}
}
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int num : nums) {
int res = 0;
trieNode cur = root;
for (int i = 31; i >= 0; i--) {
int bit = (num >> i) & 1;
int comp = bit ^ 1;
if (cur.children[comp] != null) {
res += 1 << i;
cur = cur.children[comp];
} else {
cur = cur.children[bit];
}
}
max = Math.max(max, res);
}
return max;
}
}
class trieNode {
trieNode[] children = new trieNode[2];
trieNode(){};
}
总结:本题是Trie与Bit Manipulation的一个结合。取反匹配Trie获得最大XOR结果。
336. Palindrome Pairs
Given a list of unique words, find all pairs of distinct indices (i, j) in the given list, so that the concatenation of the two words, i.e. words[i] + words[j] is a palindrome.
Example 1:
Input: ["abcd","dcba","lls","s","sssll"]Output: [[0,1],[1,0],[3,2],[2,4]] Explanation: The palindromes are ["dcbaabcd","abcddcba","slls","llssssll"]
Example 2:
Input: ["bat","tab","cat"]Output: [[0,1],[1,0]] Explanation: The palindromes are ["battab","tabbat"]
方法:对每个单词反向建Trie,例如sslll按照lllss, abcd按照bcda建trie。用每个单词去匹配这个反向建好的Trie。这样做的意义在于保证匹配结果的前后端能形成回文。例如lls sssll,形成回文llssssll。lls通过Trie可以匹配到sssll的后三个字母sll。最后检查中间ss有没有形成回文,返回答案。具体实现如下图。
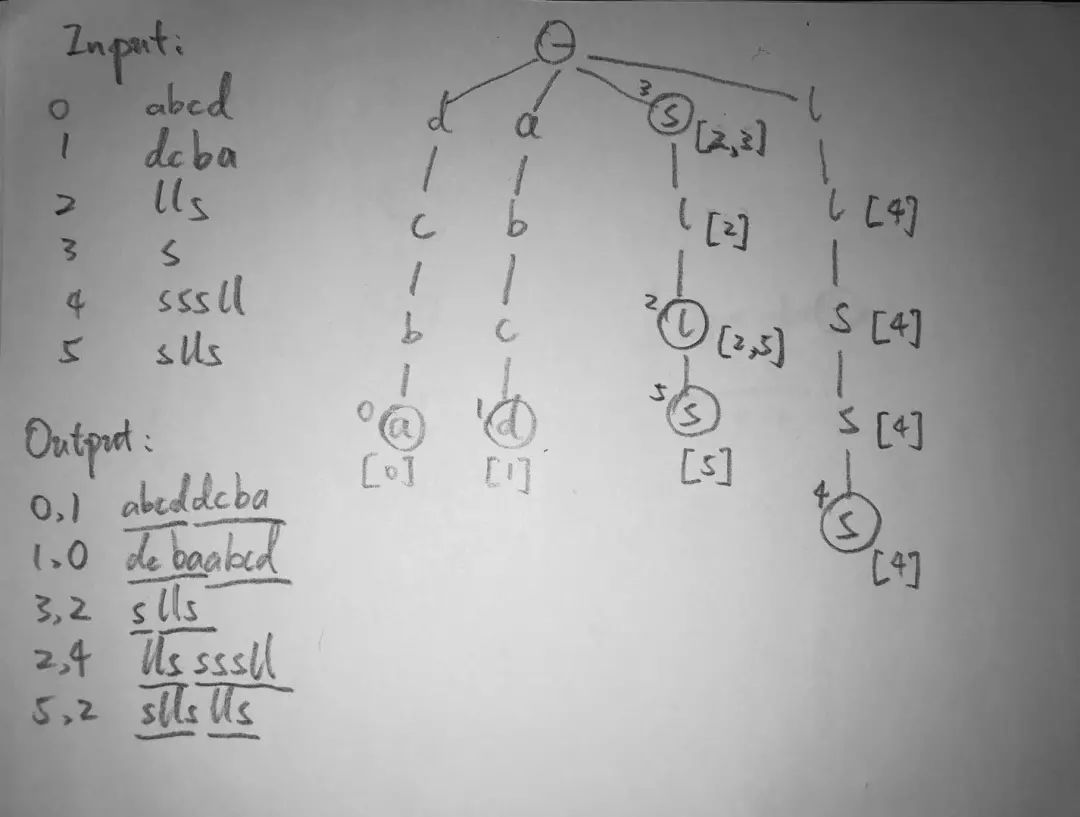
图中带圈的节点表示一个单词的结尾。圆圈左上标表示index,表示第几个单词。反向建trie过程中,每添加一个字母,同时检查该字母后面的substring是不是一个回文。如果是回文则将index存入list中。节点下方括号存list值。例如s下存[2,3],表示如果有单词正好匹配到s这里结束,那么对于单词2和单词3都能与其形成回文。因为单词2、3的后部分自己形成回文。
class TrieNode {
TrieNode[] next;
int index;
List<Integer> list;
TrieNode() {
next = new TrieNode[26];
index = -1;
list = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
private void addWord(TrieNode root, String word, int index) {
for (int i = word.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (root.next[word.charAt(i) - 'a'] == null) {
root.next[word.charAt(i) - 'a'] = new TrieNode();
}
if (isPalindrome(word, 0, i))
root.list.add(index);
root = root.next[word.charAt(i) - 'a'];
}
root.list.add(index);
root.index = index;
}
private void search(String[] words, int i, TrieNode root, List<List<Integer>> list) {
for (int j = 0; j < words[i].length(); j++) {
if (root.index >= 0 && root.index != i && isPalindrome(words[i], j, words[i].length() - 1))
list.add(Arrays.asList(i, root.index));
root = root.next[words[i].charAt(j) - 'a'];
if (root == null) return;
}
for (int j : root.list) {
if (i == j) continue;
list.add(Arrays.asList(i, j));
}
}
private boolean isPalindrome(String word, int i, int j) {
while (i < j)
if (word.charAt(i++) != word.charAt(j--)) return false;
return true;
}
public List<List<Integer>> palindromePairs(String[] words) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
TrieNode root = new TrieNode();
for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++)
addWord(root, words[i], i);
for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++)
search(words, i, root, ans);
return ans;
}
总结:Trie反向匹配用于找回文对。
425. Word Squares
Given a set of words (without duplicates), find all word squares you can build from them.
A sequence of words forms a valid word square if the kth row and column read the exact same string, where 0 ≤ k < max(numRows, numColumns).
For example, the word sequence ["ball","area","lead","lady"] forms a word square because each word reads the same both horizontally and vertically.
Example 1:
Input:["area","lead","wall","lady","ball"]Output:[[ "wall","area","lead","lady"],[ "ball","area","lead","lady"]]Explanation: The output consists of two word squares. The order of output does not matter (just the order of words in each word square matters).
Example 2:
Input:["abat","baba","atan","atal"]Output:[ [ "baba", "abat","baba","atan" ], [ "baba", "abat","baba","atal"]]Explanation: The output consists of two word squares. The order of output does not matter (just the order of words in each word square matters).
方法:建立square的时候同时检查合法性。Example: ["area","lead","wall","lady","ball"]
因为每个单词长度4,所以square由4个单词组成。每个单词都可以作为第一个单词,假如从"wall"开始,那么第二个单词必须以"a"开头,因为必须匹配"wall"的第二个字母。同理,第三个单词必须以"le"开头,最后一个单词必须以"lad"开头。
下图显示建square时如何匹配前缀。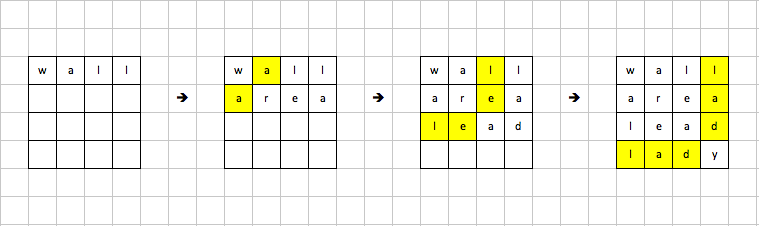 一般来说,有两种方法快速获得前缀:
一般来说,有两种方法快速获得前缀:
用一个hashtable, key是前缀, value是具有该前缀的单词的列表.
用Trie, 每个节点存放具有该前缀的单词的列表。
本题我们用Trie实现前缀匹配。
class TrieNode {
List<String> startWith = new ArrayList<>();
TrieNode[] children = new TrieNode[26];
TrieNode() {}
}
class Trie {
TrieNode root;
Trie(String[] words) {
root = new TrieNode();
for (String w : words) {
TrieNode cur = root;
for (char ch : w.toCharArray()) {
int idx = ch - 'a';
if (cur.children[idx] == null)
cur.children[idx] = new TrieNode();
cur.children[idx].startWith.add(w);
cur = cur.children[idx];
}
}
}
List<String> findByPrefix(String prefix) {
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<>();
TrieNode cur = root;
for (char ch : prefix.toCharArray()) {
int idx = ch - 'a';
if (cur.children[idx] == null)
return ans;
cur = cur.children[idx];
}
// 注意这里不要直接赋值例如 ans = cur.startWith;
ans.addAll(cur.startWith);
return ans;
}
}
private void search(int len, Trie trie, List<List<String>> ans, List<String> ansBuilder) {
if (ansBuilder.size() == len) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(ansBuilder));
return;
}
StringBuilder prefixBuilder = new StringBuilder();
int idx = ansBuilder.size();
for (String s : ansBuilder)
prefixBuilder.append(s.charAt(idx));
List<String> startWith = trie.findByPrefix(prefixBuilder.toString());
for (String sw : startWith) {
ansBuilder.add(sw);
search(len, trie, ans, ansBuilder);
ansBuilder.remove(sw);
}
}
public List<List<String>> wordSquares(String[] words) {
List<List<String>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (words == null || words.length == 0) return ans;
int len = words[0].length();
List<String> ansBuilder = new ArrayList<>();
Trie trie = new Trie(words);
for (String w : words) {
ansBuilder.add(w);
search(len, trie, ans, ansBuilder);
ansBuilder.remove(w);
}
return ans;
}
总结:很经典的Trie + BackTracking题。






