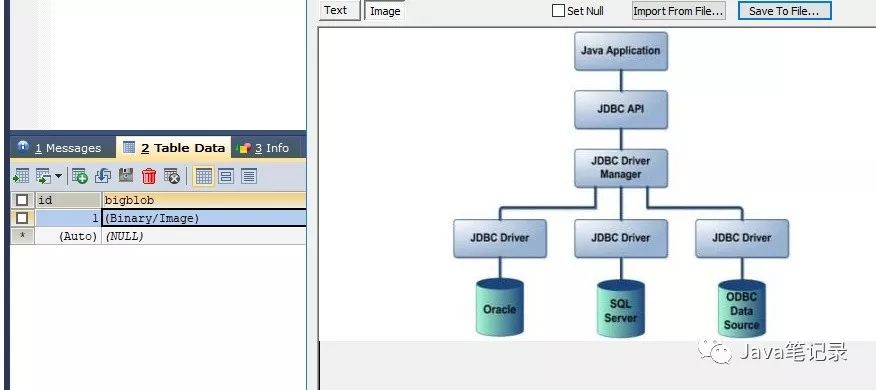
当需要向数据库中执行多条语句的时候,如果一条一条的发送显然会使效率很低,这时就要使用批处理了,使用
addBatch()方法将要执行的sql语句添加到批处理中,然后使用executeBatch()方法执行批处理,最后调用
clearBatch()方法清除,以防止数据太多时内存溢出。
实现批处理的时候当然也有两种方式,一种是使用
Statement类,另一种方法时使用PreparedStatement,使用Statement类要首先编译好sql语句,如果批处理的
sql语句规律性很强,则还是使用PreparedStatement比较好。
package com.demo.test;
import java.sql.*;
public class BatchTest1 {
private static final String USER = "root";
private static final String PASS = "ForMe=520";
private static final String URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test01";
private static final String DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
// batchTest();
batchTest1();
}
public static Connection getConn() throws SQLException {
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(URL,USER,PASS);
return connection;
}
public static void batchTest() throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Class.forName(DRIVER);
Connection connection = getConn();
String sql = "INSERT INTO THINGS(id,name) VALUES (?,?)";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for(int i = 0; i < 50; i++){
preparedStatement.setInt(1,i);
preparedStatement.setString(2,"username" + i);
preparedStatement.addBatch();
if(i%2 == 0) {
preparedStatement.executeBatch();//执行批处理
preparedStatement.clearBatch(); //清除处理,防止数量过多时内存溢出
}
}
preparedStatement.executeBatch();
preparedStatement.clearBatch();
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
public static void batchTest1(){
try {
Class.forName(DRIVER);
Connection connection = getConn();
String sql1 = "UPDATE THINGS SET name='UPDATED1' WHERE id=10 ";
String sql2 = "UPDATE THINGS SET name='UPDATED2' WHERE id=20";
String sql3 = "UPDATE THINGS SET name='UPDATED3' WHERE id=30";
String sql4 = "UPDATE THINGS SET name='UPDATED4' WHERE id=40";
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
statement.addBatch(sql1);
statement.addBatch(sql2);
statement.addBatch(sql3);
statement.addBatch(sql4);
statement.executeBatch();
statement.clearBatch();
statement.close();
connection.close();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
由上述例子可以看出,如果使用 Statement插入50条规律性很强的语句会有多么的麻烦。
使用PreparedStatement的缺点:只能应用在SQL语句相同,但参数不同的批处理中。因此此种形式的批处理经常用于在同一个表中批量插入数据,或批量更新表的数据。
首先先来了解一下主键是什么?
在数据表中每一行都应该有可以为以标识自己的一列(或一组列),例如订单有订单编号,学生有学生的学号等。如果没有主键,更新或者删除特定的行就会很困难,因为没有安全的保证只涉及相关的行。
定义主键的条件:
1、任意的两行都不具备相同的主键值
2、主键值不允许为空
何为自动主键?
也即是有自动增加约束(AUTO_INCREMENT)的主键,这样对行进行插入时会自动的增加主键,而无需在手动操作主键。
public static void auoPK(){
try {
Class.forName(DRIVER);
Connection connection = getConn();
ResultSet resultSet = null;
String sql = "INSERT INTO THINGS (name) VALUES (?)";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql,Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
preparedStatement.setString(1,"username");
int num = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
if(num > 0) {
resultSet = preparedStatement.getGeneratedKeys(); //获取到自动主键的值
if (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.println(resultSet.getInt(1));
}
}
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
大数据分为文本类型的和二进制类型的,文本类型的大数据mysql用Text代替,二进制类型的使用blob,其中的类型又可分为:
TINYTEXT、TEXT、MEDIUMTEXT和LONGTEXT
TINYBLOB、BLOB、MEDIUMBLOB和LONGBLOB
先来看文本类型存进数据库和从数据库中读取
存入数据库
public static void addBigText(){
try {
Connection connection = getConn();
Class.forName(DRIVER);
String sql = "INSERT INTO bigtest (bigdata) VALUES (?)";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
String path = BatchTest1.class.getClassLoader().getResource("data.txt").getPath();//获取文件路径
File file = new File(path);
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(file);
preparedStatement.setCharacterStream(1,fileReader,file.length()); //MySQL中存入Text类型
int num = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
if(num > 0)
System.out.println("插入大文本成功");
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
结果
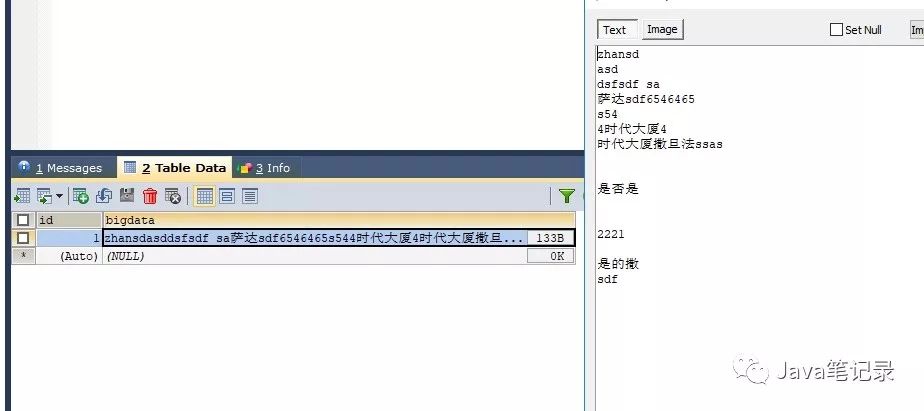
可以看到确实是存进了数据库
下面就把它读出来
public static void readBigText(){
try {
Connection connection = getConn();
String sql = "SELECT * FROM bigtest";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
if(resultSet.next()){
Reader reader = resultSet.getCharacterStream("bigdata"); //读取到数据库中的内容
FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter("F://big.txt");//下面的内容就相当于对文件的操作
char[] chars = new char[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = reader.read(chars)) != -1){
fileWriter.write(chars,0,len);
fileWriter.flush();
}
fileWriter.close();
reader.close();
}
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
把它存在F盘下的big.txt中,打开F盘发现确实读了出来,并且与原文本一致。
二进制类型的存取
二进制类型的存取和文本类型存取的原理是一样的,只不过是把字符流改成字节流,把读取文件改成setBinaryStream和getBinaryStream,其余的操作完全一致
存进数据库
public static void addBigBlob(){
try {
Connection connection = getConn();
Class.forName(DRIVER);
String sql = "INSERT INTO bigblob (bigblob) VALUES (?)";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
String path = BatchTest1.class.getClassLoader().getResource("jdbc.jpg").getPath();//获取文件路径
File file = new File(path);
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
preparedStatement.setBinaryStream(1,fileInputStream,file.length()); //MySQL中存入Text类型
int num = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
if(num > 0)
System.out.println("插入二进制类型成功");
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
从数据库中读取
public static void readBigBlob(){
try {
Connection connection = getConn();
String sql = "SELECT * FROM bigblob";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
if(resultSet.next()){
InputStream inputStream = resultSet.getBinaryStream("bigblob"); //读取到数据库中的内容
FileOutputStream fileWriter = new FileOutputStream("F://bigbolb.jpg");//下面的内容就相当于对文件的操作
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = inputStream.read(bytes)) != -1){
fileWriter.write(bytes,0,len);
fileWriter.flush();
}
fileWriter.close();
inputStream.close();
}
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
结果