1.测试结论
1.全局索引是完全独立的,因此它也需要我们更多的维护操作,特别在添加分区和删除分区时要注意全局索引是否失效。
2.本地索引,其索引分区的维护自动进行,就是说你add/drop/split/truncate表的分区时,本地索引会自动维护其索引分区
3.查询的条件是需要跨分区查询内容的时候,LOCAL INDEX的效率比GLOBAL INDEX的效率要低,通过consistent gets和db block gets的对比可以看出来;
4.如果查询的条件是在单个分区里面查询的时候,那么LOCAL INDEX的效率比GLOBAL INDEX的效率要高
5.建议如果使用到本地索引,最好加分区字段,消除其它子分区性能更加高。
6.如果业务查询不会用到分区字段,建议使用全局索引,但是注意全局索引的可用状态。
2.创建分区表
采用自动分区功能,创建1000个分区表,id2创建local索引,id3创建全局索引
(partition p0 values less than (1000));
insert into part_table select rownum,rownum+1,rownum+2 from dual connect by rownum<=1000000;
create index idx_part_id2 on part_table(id2) local;
create index idx_part_id3 on part_table(id3);
3.查询分区表,表和两个索引对应段情况
分区表和本地索引分别有1001个段组成,全局索引只有1个段组成。
select segment_name,partition_name,segment_type from user_segments where segment_name='PART_TABLE';
select segment_name,partition_name,segment_type from user_segments where segment_name='IDX_PART_ID2';
select segment_name,partition_name,segment_type from user_segments where segment_name='IDX_PART_ID3';
本地索引每个分区索引对应blevel均为2,全局索引blevel为3
select index_name,blevel,leaf_blocks,num_rows,distinct_keys,clustering_factor from user_ind_partitions where index_name='IDX_PART_ID2';
select index_name,blevel,leaf_blocks,num_rows,distinct_keys,clustering_factor from user_ind_statistics where index_name='IDX_PART_ID3';
4.测试场景一
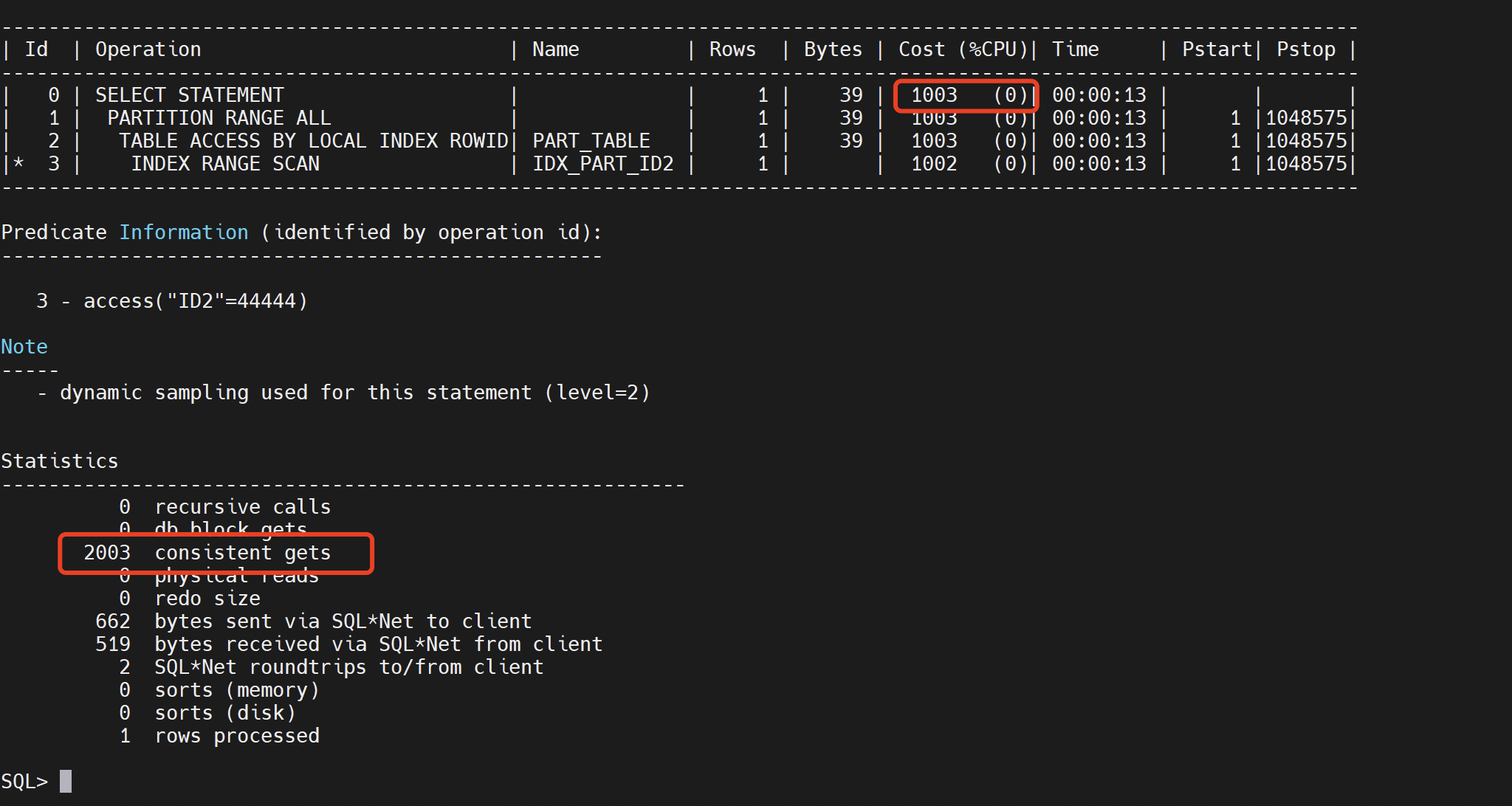
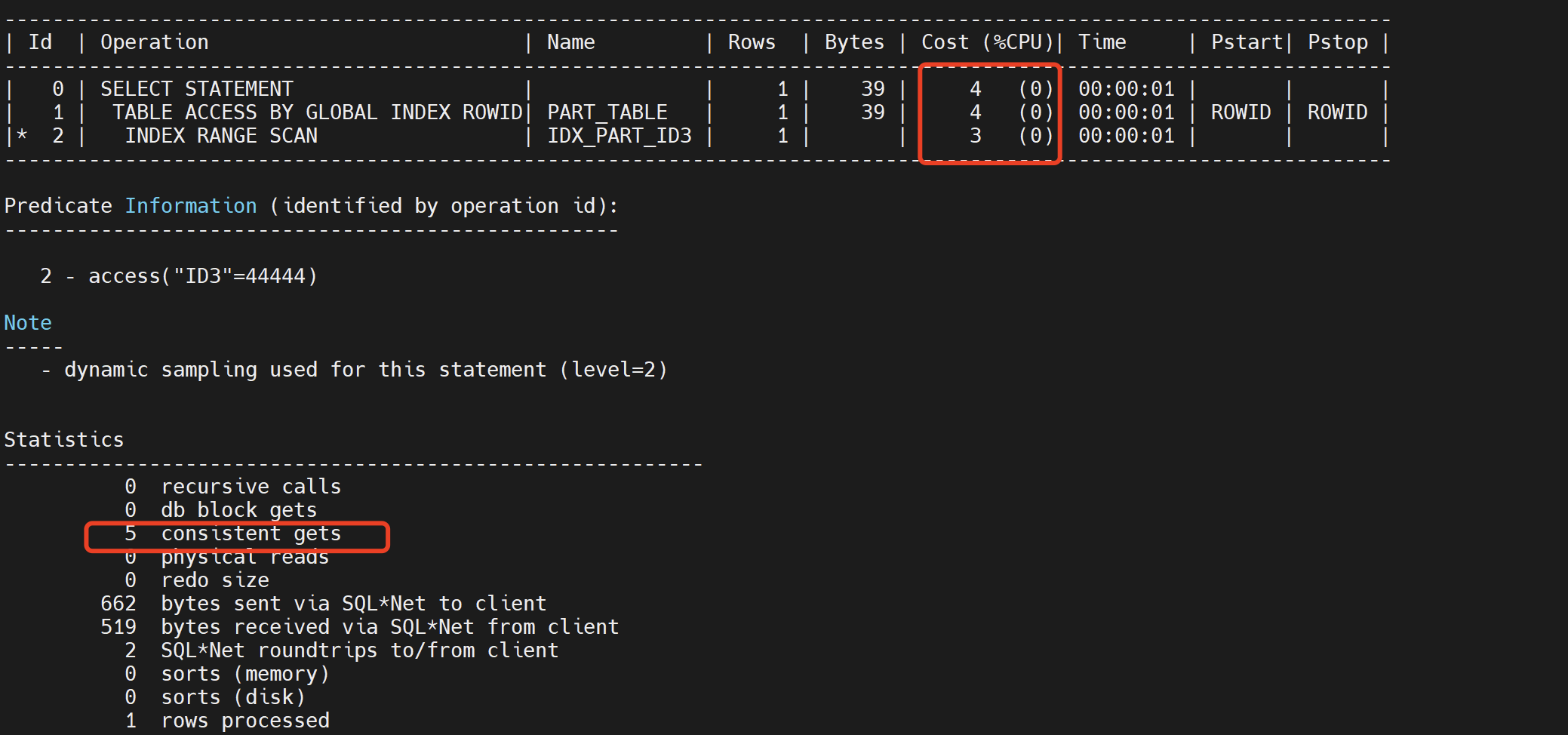
1、本地索引cost为1003,全局索引只有4. 本地索引需要扫描每个分区,每个分区索引都需要IO消耗,子分区越多效率越慢。
2、全局索引cost为4,因为只需要扫描一个索引,该索引blevel为3.
select * from part_table where id2=444444;
select * from part_table where id3=44444;
5. 测试场景二
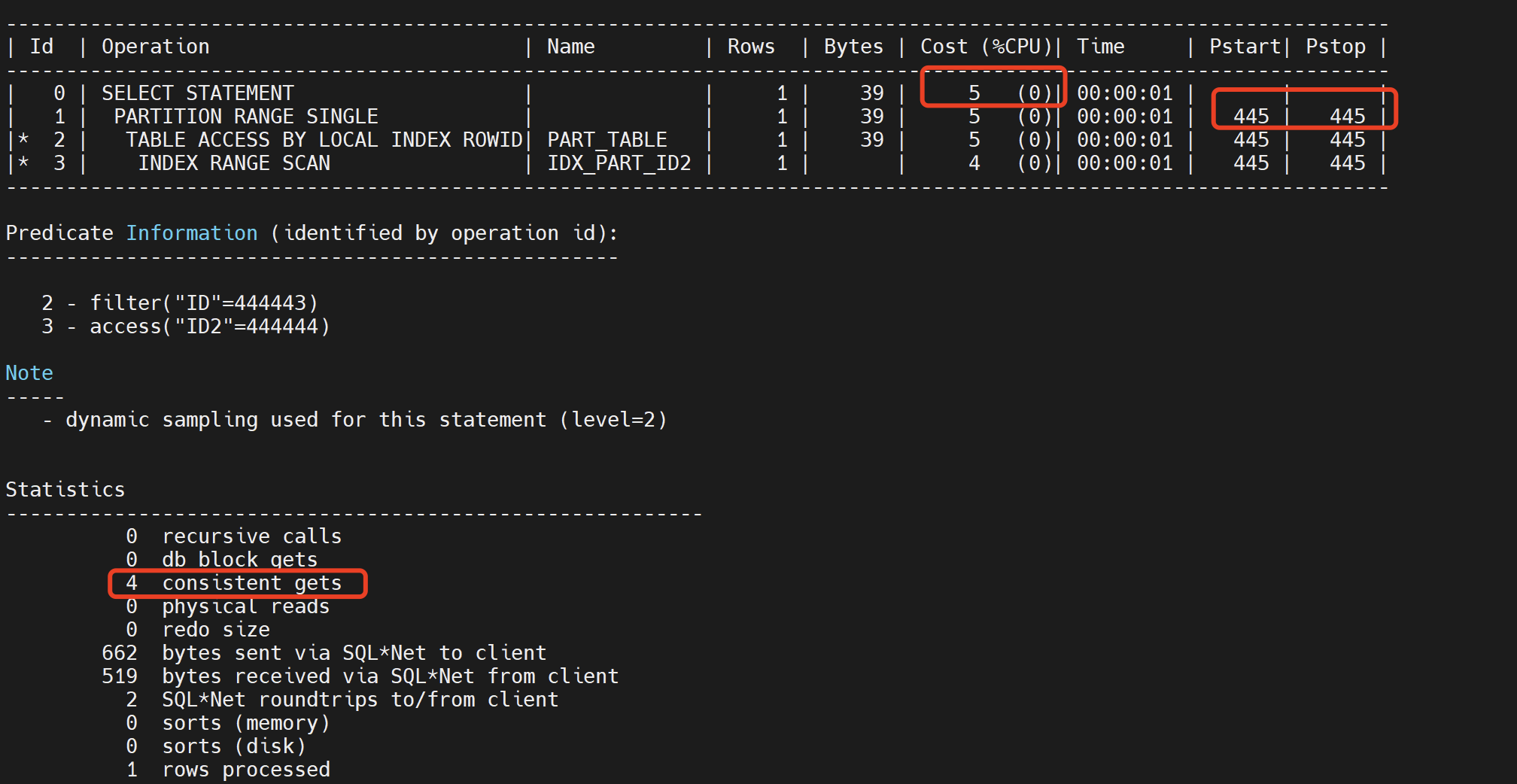
1、本地索引cost为5,加分区字段条件cost值明显下降很多,本次只扫描了某个分区表
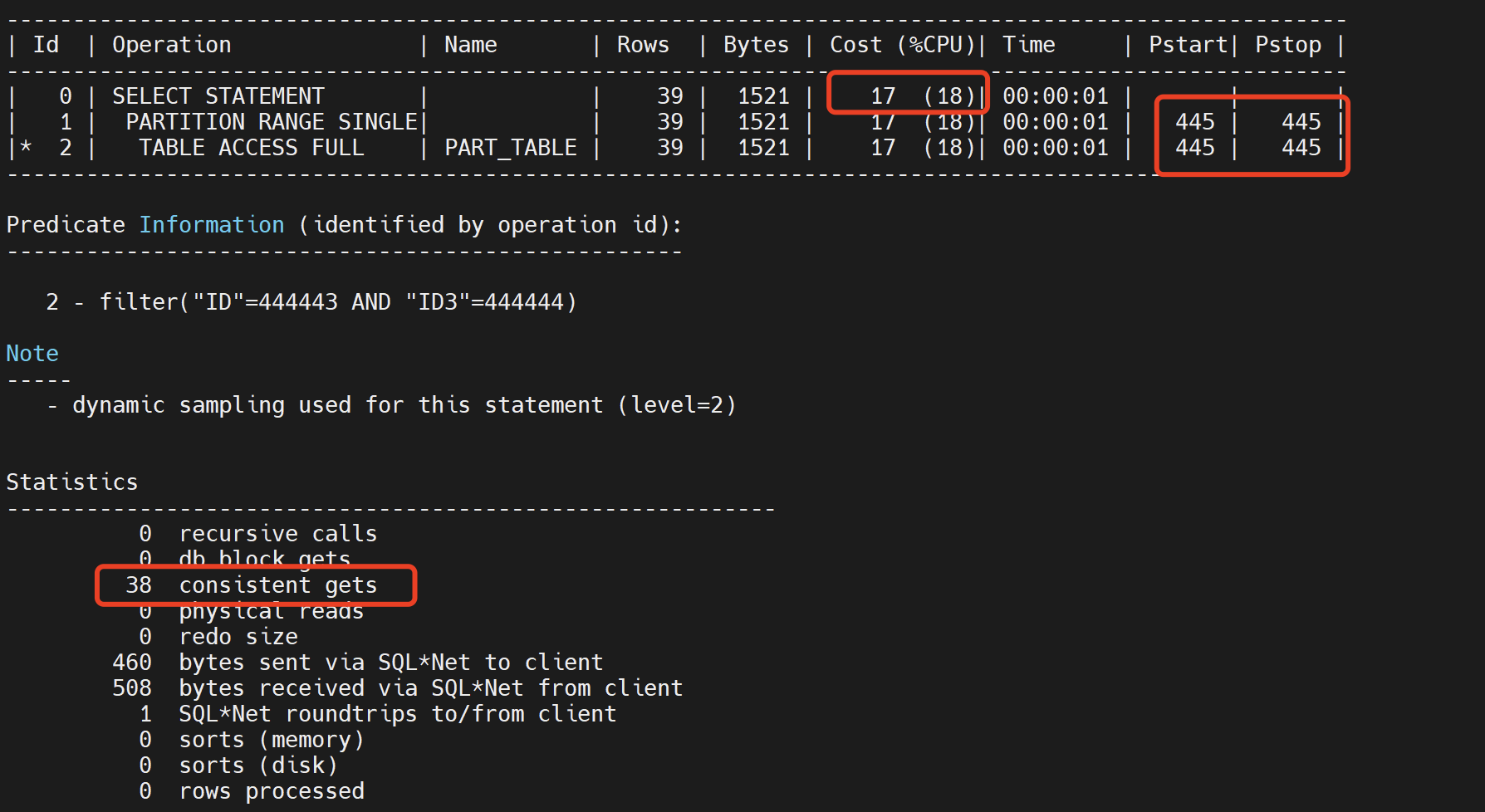
2、全局索引cost为17,走的是全表扫描,扫描整个445分区的所有数据。
select * from part_table where id=444443 and id2=444444;