PostgreSQL可通过pg_ctl start -D pgdata启动节点,我们看一下主节点启动流程。为了便于调试,我们以postgres -D pgdata命令启动数据库并进行调试分析。
启动主流程
我们分析一下启动的时候,需要做那些工作,数据库启动时,需要先判断版本是否兼容,pg_control文件是否存在,也就是说要判断一些启动的必要条件是否满足。然后启动日志,startup等进程。 在接受客户端连接之前,需要先启动startup进程,进行故障恢复,这是因为系统关闭的时候,不一定是正常关闭的,可能是因为故障而退出,退出的时候,内存中的脏页不一定被刷入磁盘中,这时候就需要启动startup进程,对WAL日志进行回放,回放完后,再进入ServerLoop,接受客户端的连接并处理SQL请求。
// main.c postgres进程主入口
main()
--> MemoryContextInit() // 初始化内存上下文: TopMemoryContext、ErrorContext
--> PostmasterMain(argc, argv); // Postmaster main entry point
--> pqsignal_pm(SIGCHLD, reaper); /* handle child termination */ // 注册信号处理函数
--> checkDataDir(); // 检查数据目录
--> ValidatePgVersion(DataDir); // 检查PG_VERSION文件,PG实例版本是否与程序兼容
--> checkControlFile(); // 检查pg_control文件
--> CreateDataDirLockFile(true); // 创建postmaster.pid文件
--> LocalProcessControlFile(false); // 读pg_control,到ControlFileData中
--> ReadControlFile();
--> process_shared_preload_libraries(); // 加载插件
--> load_libraries(shared_preload_libraries_string, "shared_preload_libraries", false);
--> load_file(filename, restricted);
--> internal_load_library(fullname);
--> SysLogger_Start(); // 启动日志进程 logger
--> RemovePgTempFiles();
--> pgstat_init();
--> autovac_init();
--> load_hba()
--> StartupDataBase(); // 启动startup进程 StartChildProcess
--> AuxiliaryProcessMain(ac, av);
--> StartupProcessMain()
--> StartupXLOG();
--> maybe_start_bgworkers();
--> ServerLoop();
for(;;)
{
// #define PG_SETMASK(mask) sigprocmask(SIG_SETMASK, mask, NULL)
// UnBlockSig is the set of signals to block when we don't want to block signals.
PG_SETMASK(&UnBlockSig); // 设置/解除阻塞信号, 触发reaper,创建checkpointer, bgwriter,walwriter进程
// 等待客户端连接
selres = select(nSockets, &rmask, NULL, NULL, &timeout);
ConnCreate(ListenSocket[i]);
BackendStartup(port);
--> canAcceptConnections(BACKEND_TYPE_NORMAL);
--> BackendRun(port);
--> PostgresMain(ac, av, port->database_name, port->user_name);
--> InitPostgres(dbname, InvalidOid, username, InvalidOid, NULL, false);
for (;;)
{
ReadCommand(&input_message);
// SQL 解析,优化,执行
// exec_simple_query(query_string);
}
}
startup进程
startup进程启动的几种情况:
- 数据库启动的时候,进行故障恢复
- 备机,不断的接收主节点的WAL日志并进行回放
- PITR,回放到指定时间点
可以说,启动阶段,非常重要的一个过程就是故障恢复,这是保障数据库正确性的一个非常关键的点。我们这里分析一下。
startup启动后,依据standby.signal和recovery.signal去判断进入何种状态,如果都不存在,则进行故障恢复,如果standby.signal存在,则表示当前为备机,如果recovery.signal文件存在,则代表当前数据库正在进行的是PITR操作,需根据recovery_target对日志进行回放。
下一个问题就是,从哪里进行回放?即:故障恢复的起点是最近的一次检查点,这个检查点保存在pg_control中,每次创建检查点时都会更新pg_control中的信息。 我们看下面的代码:
StartupProcessMain(void)
--> StartupXLOG();
--> ValidateXLOGDirectoryStructure(); // 检查pg_wal是否存在
--> readRecoverySignalFile(); // 依据standby.signal和recovery.signal是否存在,判断进入何种状态
--> validateRecoveryParameters();
if (read_backup_label(&checkPointLoc, &backupEndRequired, &backupFromStandby))
{
// 如果backup_label文件存在,则表示从备份文件中进行恢复(例如使用pg_basebackup进行备份)
// 此种情况,设置backup_label,而不是用pg_control,为啥呢?下面就是解释
/*
* If we see a backup_label during recovery, we assume that we are recovering
* from a backup dump file, and we therefore roll forward from the checkpoint
* identified by the label file, NOT what pg_control says. This avoids the
* problem that pg_control might have been archived one or more checkpoints
* later than the start of the dump, and so if we rely on it as the start
* point, we will fail to restore a consistent database state.
*/
}
else
{
/* Get the last valid checkpoint record. */
checkPointLoc = ControlFile->checkPoint; // 从pg_control中获取检查点信息
RedoStartLSN = ControlFile->checkPointCopy.redo;
record = ReadCheckpointRecord(xlogreader, checkPointLoc, 1, true);
--> XLogBeginRead(xlogreader, RecPtr); // Begin reading WAL at 'RecPtr'.
--> ReadRecord(xlogreader, LOG, true); // Attempt to read the next XLOG record.
for (;;)
{
XLogReadRecord(xlogreader, &errormsg); // Attempt to read an XLOG record.
}
}
--> RelationCacheInitFileRemove();
--> StartupReplicationSlots();
--> StartupReorderBuffer();
--> StartupReplicationOrigin();
if (InRecovery)
{
UpdateControlFile();
--> update_controlfile(DataDir, ControlFile, true);
/*
* Find the first record that logically follows the checkpoint --- it
* might physically precede it, though.
*/
if (checkPoint.redo < RecPtr)
{
/* back up to find the record */
XLogBeginRead(xlogreader, checkPoint.redo);
record = ReadRecord(xlogreader, PANIC, false);
}
else
{
/* just have to read next record after CheckPoint */
record = ReadRecord(xlogreader, LOG, false);
}
// main redo apply loop
do
{
/* Now apply the WAL record itself */
RmgrTable[record->xl_rmid].rm_redo(xlogreader); // 执行redo操作, 真正的恢复操作
/* Else, try to fetch the next WAL record */
record = ReadRecord(xlogreader, LOG, false);
} while (record != NULL);
/* Allow resource managers to do any required cleanup. */
for (rmid = 0; rmid <= RM_MAX_ID; rmid++)
{
if (RmgrTable[rmid].rm_cleanup != NULL)
RmgrTable[rmid].rm_cleanup();
}
}
startup进程主流程:
/* ----------------------------------
* Startup Process main entry point
* ----------------------------------
*/
void
StartupProcessMain(void)
{
/* Arrange to clean up at startup process exit */
on_shmem_exit(StartupProcExit, 0);
/*
* Properly accept or ignore signals the postmaster might send us.
*/
pqsignal(SIGHUP, StartupProcSigHupHandler); /* reload config file */
pqsignal(SIGINT, SIG_IGN); /* ignore query cancel */
pqsignal(SIGTERM, StartupProcShutdownHandler); /* request shutdown */
/* SIGQUIT handler was already set up by InitPostmasterChild */
InitializeTimeouts(); /* establishes SIGALRM handler */
pqsignal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN);
pqsignal(SIGUSR1, procsignal_sigusr1_handler);
pqsignal(SIGUSR2, StartupProcTriggerHandler);
/*
* Reset some signals that are accepted by postmaster but not here
*/
pqsignal(SIGCHLD, SIG_DFL);
/*
* Register timeouts needed for standby mode
*/
RegisterTimeout(STANDBY_DEADLOCK_TIMEOUT, StandbyDeadLockHandler);
RegisterTimeout(STANDBY_TIMEOUT, StandbyTimeoutHandler);
RegisterTimeout(STANDBY_LOCK_TIMEOUT, StandbyLockTimeoutHandler);
/*
* Unblock signals (they were blocked when the postmaster forked us)
*/
PG_SETMASK(&UnBlockSig);
/*
* Do what we came for.
*/
StartupXLOG();
/*
* Exit normally. Exit code 0 tells postmaster that we completed recovery
* successfully.
*/
proc_exit(0);
}
ServerLoop函数详解
这里,补充一下,为什么PG中,如果checkpointer,bgwriter等进程崩溃或杀掉后,PG自己就能将进程给重新拉起来,代码如下。可以看到,在ServerLoop循环中,不断检查checkpointer,bgwriter进程是否存在,如果不存在了,就立刻再启动该进程。
static int ServerLoop(void)
{
fd_set readmask;
int nSockets;
nSockets = initMasks(&readmask);
for (;;)
{
fd_set rmask;
int selres;
time_t now;
/*
* Wait for a connection request to arrive.
*
* We block all signals except while sleeping. That makes it safe for
* signal handlers, which again block all signals while executing, to
* do nontrivial work.
*
* If we are in PM_WAIT_DEAD_END state, then we don't want to accept
* any new connections, so we don't call select(), and just sleep.
*/
memcpy((char *) &rmask, (char *) &readmask, sizeof(fd_set));
if (pmState == PM_WAIT_DEAD_END)
{
PG_SETMASK(&UnBlockSig);
pg_usleep(100000L); /* 100 msec seems reasonable */
selres = 0;
PG_SETMASK(&BlockSig);
} else {
/* must set timeout each time; some OSes change it! */
struct timeval timeout;
/* Needs to run with blocked signals! */
DetermineSleepTime(&timeout);
PG_SETMASK(&UnBlockSig);
selres = select(nSockets, &rmask, NULL, NULL, &timeout);
PG_SETMASK(&BlockSig);
}
/* New connection pending on any of our sockets? If so, fork a child process to deal with it. */
if (selres > 0)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < MAXLISTEN; i++)
{
if (ListenSocket[i] == PGINVALID_SOCKET)
break;
if (FD_ISSET(ListenSocket[i], &rmask))
{
Port *port;
port = ConnCreate(ListenSocket[i]);
if (port)
{
BackendStartup(port);
/* We no longer need the open socket or port structure in this process */
StreamClose(port->sock);
ConnFree(port);
}
}
}
}
/* If we have lost the log collector, try to start a new one */
if (SysLoggerPID == 0 && Logging_collector)
SysLoggerPID = SysLogger_Start();
/* If no background writer process is running, and we are not in a
* state that prevents it, start one. It doesn't matter if this
* fails, we'll just try again later. Likewise for the checkpointer. */
if (pmState == PM_RUN || pmState == PM_RECOVERY || pmState == PM_HOT_STANDBY)
{
if (CheckpointerPID == 0)
CheckpointerPID = StartCheckpointer();
if (BgWriterPID == 0)
BgWriterPID = StartBackgroundWriter();
}
/*Likewise, if we have lost the walwriter process, try to start a new one.*/
if (WalWriterPID == 0 && pmState == PM_RUN)
WalWriterPID = StartWalWriter();
/* If we have lost the autovacuum launcher, try to start a new one. We
* don't want autovacuum to run in binary upgrade mode because
* autovacuum might update relfrozenxid for empty tables before the
* physical files are put in place. */
if (!IsBinaryUpgrade && AutoVacPID == 0 && (AutoVacuumingActive() || start_autovac_launcher) && pmState == PM_RUN)
{
AutoVacPID = StartAutoVacLauncher();
if (AutoVacPID != 0)
start_autovac_launcher = false; /* signal processed */
}
/* If we have lost the stats collector, try to start a new one */
if (PgStatPID == 0 &&
(pmState == PM_RUN || pmState == PM_HOT_STANDBY))
PgStatPID = pgstat_start();
/* If we have lost the archiver, try to start a new one. */
if (PgArchPID == 0 && PgArchStartupAllowed())
PgArchPID = StartArchiver();
/* If we need to signal the autovacuum launcher, do so now */
if (avlauncher_needs_signal)
{
avlauncher_needs_signal = false;
if (AutoVacPID != 0)
kill(AutoVacPID, SIGUSR2);
}
/* If we need to start a WAL receiver, try to do that now */
if (WalReceiverRequested)
MaybeStartWalReceiver();
/* Get other worker processes running, if needed */
if (StartWorkerNeeded || HaveCrashedWorker)
maybe_start_bgworkers();
// ...
}
}
其他
这里附一张阿里云分享的一张PPT,对PostgreSQL启动流程的梳理,详细文档参考PostgreSQL体系结构。
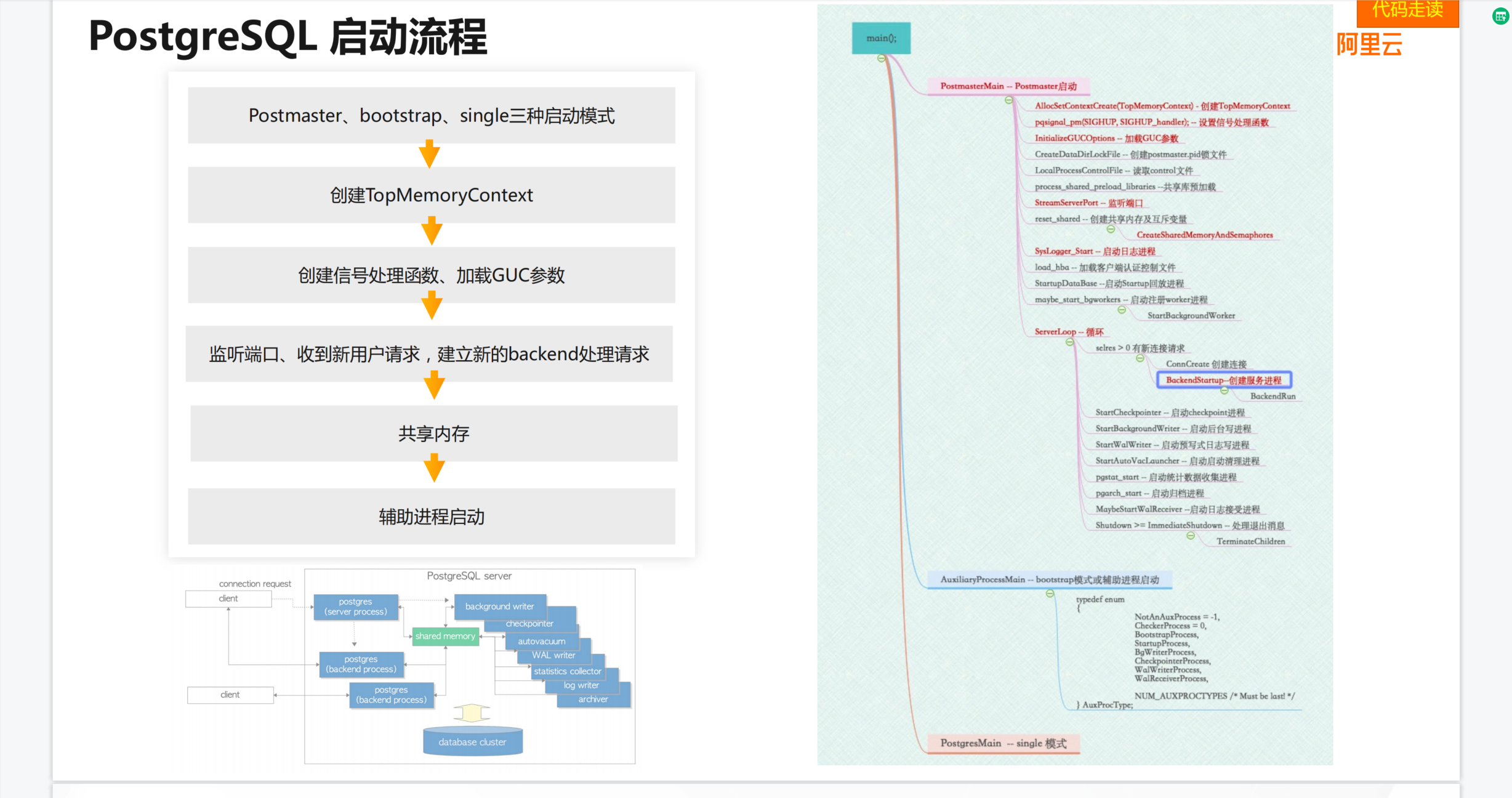
参考文档:
PostgreSQL 如何从崩溃状态恢复(上)
PostgreSQL的信号处理机制
Sigprocmask 函数|学习笔记






