SQL PATCH主要设计给DBA、运维人员及其他需要对SQL进行调优的角色使用,用户通过其他运维视图或定位手段识别到业务语句存在计划不优导致的性能问题时,可以通过创建SQL PATCH对业务语句进行基于Hint的调优。目前支持行数、扫描方式、连接方式、连接顺序、PBE custom/generic计划选择、语句级参数设置、参数化路径的Hint。此外,对于部分由特定语句触发系统内部问题导致系统可服务性受损的语句,在不对业务语句变更的情况下,也可以通过创建用于单点规避的SQL PATCH,对问题场景提前报错处理,避免更大的损失。
特性约束
- 仅支持针对Unique SQL ID添加补丁,如果存在Unique SQL ID冲突,用于Hint调优的SQL PATCH可能影响性能,但不影响语义正确性。
- 仅支持不改变SQL语义的Hint作为PATCH,不支持SQL改写。
- 不支持逻辑备份、恢复。
- 不支持在DN上创建SQL PATCH。
- 仅初始用户、运维管理员、监控管理员、系统管理员用户有权限执行。
- 库之间不共享,创建SQL PATCH时需要连接目标库。如果创建SQL PATCH的CN被剔除并触发全量Build,则会继承全量Build的目标CN中的SQL PATCH,因此建议在各个CN上尽量都创建对应的SQL PATCH。
- CN之间由于Unique SQL ID不同,不共享SQL PATCH,需要用户手动在不同的CN上创建对应的SQL PATCH。
- 限制在存储过程内的SQL PATCH和全局的SQL PATCH不允许同时存在。
- SQL PATCH不建议在数据库中长期使用,只应该作为临时规避方法。遇到内核问题所导致的特定语句触发数据库服务不可用问题,以及使用Hint进行调优的场景,需要尽快修改业务或升级内核版本解决问题。并且升级后由于Unique SQL ID生成方法可能变化,可能导致规避方法失效。
- 当前,除DML语句之外,其他SQL语句(如CREATE TABLE等)的Unique SQL ID是对语句文本直接哈希生成的,所以对于此类语句,SQL PATCH对大小写、空格、换行等敏感,即不同的文本的语句,即使语义相同,仍然需要对应不同的SQL PATCH。对于DML,则同一个SQL PATCH可以对不同入参的语句生效,并且忽略大小写和空格。
示例
SQL PATCH的实现基于Unique SQL ID,所以需要打开相关的运维参数才可以生效(enable_resource_track = on,instr_unique_sql_count > 0),Unique SQL ID在WDR报告和慢SQL视图中都可以获取到,在创建SQL PATCH时需要指定Unique SQL ID,对于存储过程内的SQL则需要设置参数 instr_unique_sql_track_type = 'all' 后在dbe_perf.statement_history视图中查询Unique SQL ID。
下面给出简单的使用样例。
场景一:使用SQL PATCH对特定语句进行Hint调优。
gaussdb=# create table hint_t1(a int, b int, c int);
NOTICE: The 'DISTRIBUTE BY' clause is not specified. Using 'a' as the distribution column by default.
HINT: Please use 'DISTRIBUTE BY' clause to specify suitable data distribution column.
CREATE TABLE
gaussdb=# create index on hint_t1(a);
CREATE INDEX
gaussdb=# insert into hint_t1 values(1,1,1);
INSERT 0 1
gaussdb=# analyze hint_t1;
ANALYZE
gaussdb=# set track_stmt_stat_level = 'L1,L1'; --打开FullSQL统计信息
SET
gaussdb=# set enable_fast_query_shipping = off; --关闭语句下推,使得计划在CN上生成
SET
gaussdb=# set explain_perf_mode = normal; --调整计划显示格式
SET
gaussdb=# select * from hint_t1 where hint_t1.a = 1; --执行SQL语句
a | b | c
---+---+---
1 | 1 | 1
(1 row)
gaussdb=# \x --切换扩展显示模式,便于观察计划
Expanded display is on.
gaussdb=# select unique_query_id, query, query_plan from dbe_perf.statement_history where query like '%hint_t1%';--获取查询计划和Unique SQL ID,该语句需要在postgres库查询慢SQL视图dbe_perf.statement_history。
-[ RECORD 1 ]---+-------------------------------------------------------------
unique_query_id | 3929365485
query | select * from hint_t1 where hint_t1.a = ?;
query_plan | Coordinator Name: coordinator1
| Streaming (type: GATHER) (cost=0.06..1.11 rows=1 width=12)
| Node/s: datanode1
| -> Seq Scan on hint_t1 (cost=0.00..1.01 rows=1 width=12)
| Filter: (a = '***')
|
|
gaussdb=# \x --关闭扩展显示模式
gaussdb=# select * from dbe_sql_util.create_hint_sql_patch('patch1', 3929365485, 'indexscan(hint_t1)');
create_hint_sql_patch
-----------------------
t
(1 row)
gaussdb=# set track_stmt_stat_level = 'L1,L1'; --切换后重新设置参数
SET
gaussdb=# set enable_fast_query_shipping = off;
SET
gaussdb=# explain select * from hint_t1 where hint_t1.a = 1;
NOTICE: Plan influenced by SQL hint patch
QUERY PLAN
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Streaming (type: GATHER) (cost=0.06..8.36 rows=1 width=12)
Node/s: datanode1
-> Index Scan using hint_t1_a_idx on hint_t1 (cost=0.00..8.27 rows=1 width=12)
Index Cond: (a = 1)
(4 rows)
gaussdb=# select * from hint_t1 where hint_t1.a = 1; -- 再次执行语句
a | b | c
---+---+---
1 | 1 | 1
(1 row)
gaussdb=# \x
Expanded display is on.
gaussdb=# select unique_query_id, query, query_plan from dbe_perf.statement_history where query like '%hint_t1%';-- 可以看到新的执行记录计划已改变
-[ RECORD 1 ]---+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
unique_query_id | 3929365485
query | select * from hint_t1 where hint_t1.a = ?;
query_plan | Coordinator Name: coordinator1
| Streaming (type: GATHER) (cost=0.06..1.11 rows=1 width=12)
| Node/s: datanode1
| -> Seq Scan on hint_t1 (cost=0.00..1.01 rows=1 width=12)
| Filter: (a = '***')
|
|
-[ RECORD 2 ]---+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
unique_query_id | 3929365485
query | select * from hint_t1 where hint_t1.a = ?;
query_plan | Coordinator Name: coordinator1
| Streaming (type: GATHER) (cost=0.06..8.36 rows=1 width=12)
| Node/s: datanode1
| -> Index Scan using hint_t1_a_idx on hint_t1 (cost=0.00..8.27 rows=1 width=12)
| Index Cond: (a = '***')
|
|
|
场景二:使用SQL PATCH对特定语句进行提前报错规避。
gaussdb=# select * from dbe_sql_util.drop_sql_patch('patch1'); -- 删去patch1
drop_sql_patch
----------------
t
(1 row)
gaussdb=# select * from dbe_sql_util.create_abort_sql_patch('patch2', 3929365485); --对该语句的Unique SQL ID创建Abort Patch
create_abort_sql_patch
------------------------
t
(1 row)
gaussdb=# select * from hint_t1 t1 where t1.a = 1; -- 再次执行语句会提前报错
ERROR: Statement 2578396627 canceled by abort patch patch2场景三:针对存储过程内的SQL语句创建SQL PATCH。
gaussdb=# create table test_proc_patch(a int,b int);
NOTICE: The 'DISTRIBUTE BY' clause is not specified. Using 'a' as the distribution column by default.
HINT: Please use 'DISTRIBUTE BY' clause to specify suitable data distribution column.
CREATE TABLE
gaussdb=# insert into test_proc_patch values(1,2);
INSERT 0 1
gaussdb=# create procedure mypro() as num int;
gaussdb$# begin
gaussdb$# select b into num from test_proc_patch where a = 1;
gaussdb$# end;
gaussdb$# /
CREATE PROCEDURE
gaussdb=# set track_stmt_stat_level = 'L0,L1';
SET
gaussdb=# select b from test_proc_patch where a = 1;
b
---
2
(1 row)
gaussdb=# call mypro();
mypro
-------
(1 row)
gaussdb=# select unique_query_id, query, query_plan, parent_unique_sql_id from dbe_perf.statement_history where query like '%call mypro();%' or query like '%test_proc_patch%';
unique_query_id | query | query_plan | parent_unique_sql_id
-----------------+--------------------------------------------+----------------------------------------------------------+----------------------
2859505004 | select b from test_proc_patch where a = ?; | | 0
2502737203 | call mypro(); | Coordinator Name: cn1 +| 0
| | Function Scan on mypro (cost=0.25..0.26 rows=1 width=4)+|
| | +|
| | |
2859505004 | select b from test_proc_patch where a = ?; | Coordinator Name: cn1 +| 2502737203
| | Data Node Scan (cost=0.00..0.00 rows=0 width=0) +|
| | Node/s: datanode1 +|
| | +|
| | |
(3 rows)
gaussdb=# select * from dbe_sql_util.create_abort_sql_patch('patch1',2859505004,2502737203); -- 限制该abortpatch只对存过内语句生效
create_abort_sql_patch
------------------------
t
(1 row)
gaussdb=# select patch_name,unique_sql_id,parent_unique_sql_id,enable,abort,hint_string from gs_sql_patch where patch_name = 'patch1'; --确认patch创建无误以及是否生效
patch_name | unique_sql_id | parent_unique_sql_id | enable | abort | hint_string
------------+---------------+----------------------+--------+-------+-------------
patch1 | 2859505004 | 2502737203 | t | t |
(1 row)
gaussdb=# select b from test_proc_patch where a = 1;
b
---
2
(1 row)
gaussdb=# call mypro();
ERROR: Statement 2859505004 canceled by abort patch patch1
CONTEXT: SQL statement "select b from test_proc_patch where a = 1"
PL/pgSQL function mypro() line 3 at SQL statement场景四:在各个CN上针对同一慢SQL打SQL PATCH。
--找到各个节点上的慢SQL以及计划(此函数需要monadmin权限执行) select node_name, unique_query_id, start_time, query, query_plan from dbe_perf.get_global_full_sql_by_timestamp(<start_time>, <end_time>); --通过观察分析返回的慢SQL以及计划,本地进行调优验证,得到合适的hint_str --在任意CN执行下面的语句创建SQL PATCH,其中node_name和unique_query_id从第一步操作中获得 select * from dbe_sql_util.create_remote_hint_sql_patch(<node_name>, <patch_name>, <unique_query_id>, <hint_str>);
相关链接
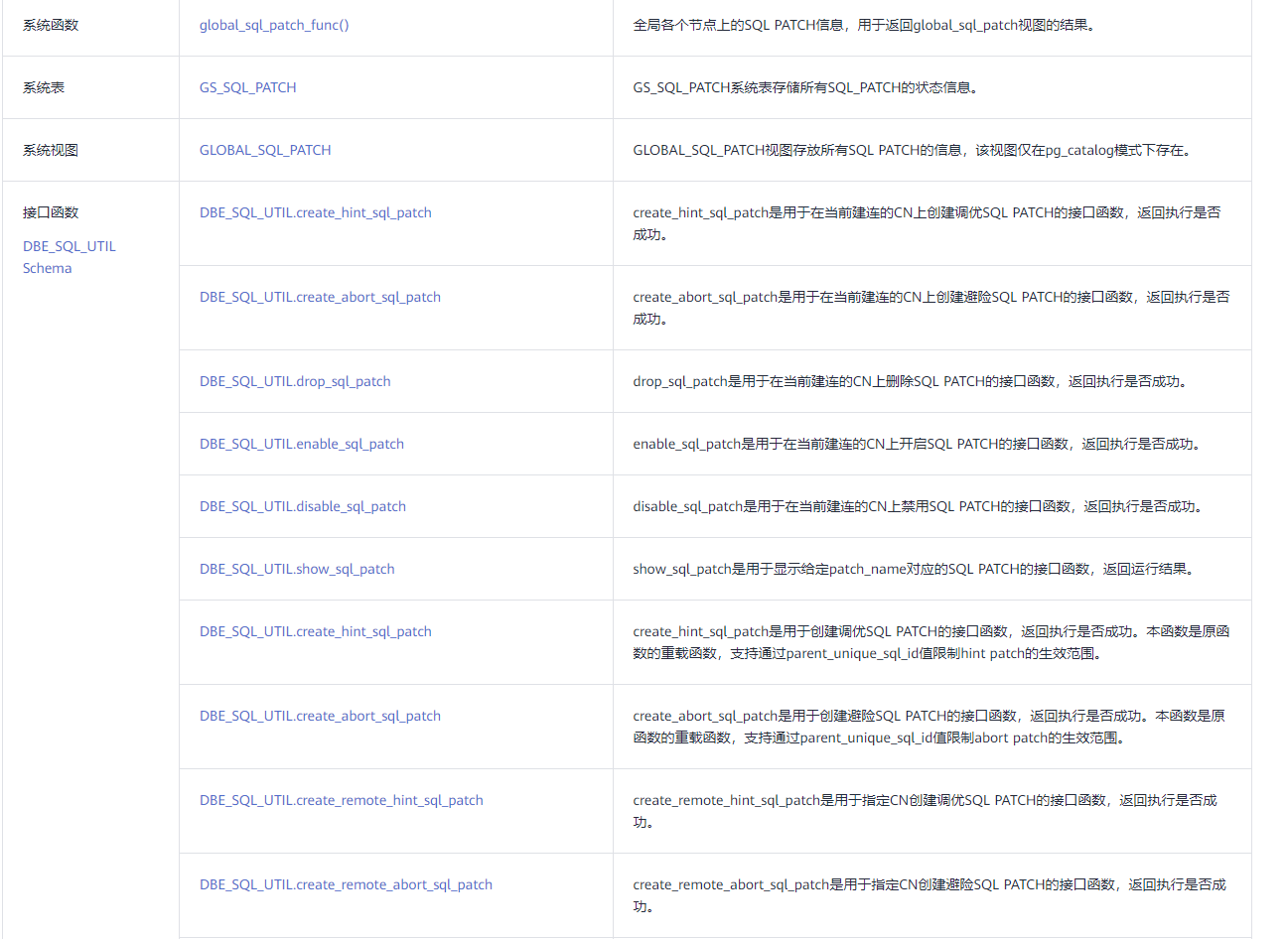
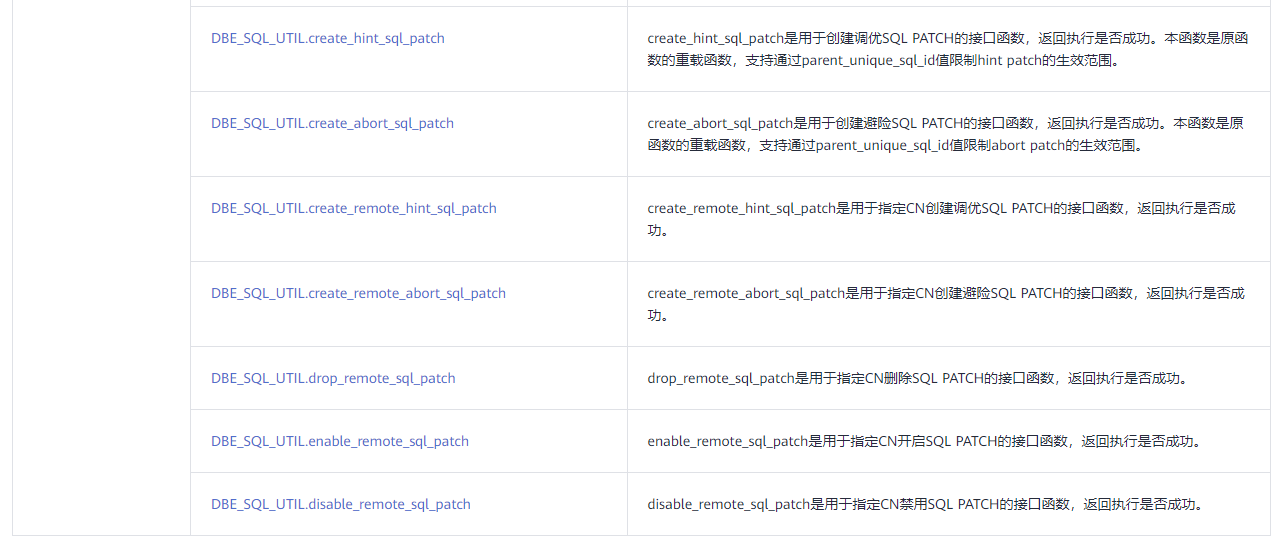
SQL PATCH相关系统函数、系统表、系统视图和接口函数见下表。
「喜欢这篇文章,您的关注和赞赏是给作者最好的鼓励」
关注作者
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文章的来源(墨天轮),文章链接,文章作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。






