本篇主要介绍SQL常用的必备语句。
数据准备
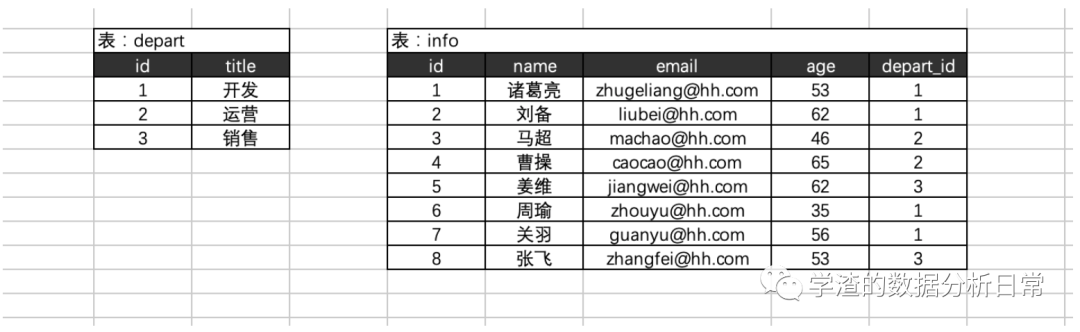

创建相应的数据库以及建表

# 创建数据库create database db2 default charset utf8 collate utf8_general_ci;# 创建部门表create table depart(id int not null auto_increment primary key,title varchar(16) not null)default charset=utf8;# 创建信息表create table info(id int not null auto_increment primary key,name varchar(16) not null,email varchar(32) not null,age int,depart_id int)default charset=utf8;

插入数据

# 向部门表插入数据insert into depart(title) values("开发"),("运营"),("销售");# 向信息表插入数据insert into info(name,email,age,depart_id) values("诸葛亮","zhugeliang@hh.com",53,1);insert into info(name,email,age,depart_id) values("刘备","liubei@hh.com",62,1);insert into info(name,email,age,depart_id) values("马超","machao@hh.com",46,2);insert into info(name,email,age,depart_id) values("曹操","caocao@hh.com",65,2);insert into info(name,email,age,depart_id) values("姜维","jiangwei@hh.com",62,3);insert into info(name,email,age,depart_id) values("周瑜","zhouyu@hh.com",35,1);insert into info(name,email,age,depart_id) values("关羽","guanyu@hh.com",56,1);insert into info(name,email,age,depart_id) values("张飞","zhangfei@hh.com",53,3);
装备工作完成之后,接下来就是介绍SQL常用的必备语句。
1、条件筛选:where
select * from info where id > 1;select * from info where id = 1;select * from info where id >= 1;select * from info where id != 1;select * from info where id between 2 and 4;select * from info where name = "诸葛亮" and age =53;select * from info where name = "马超" or age =53;select * from info where (name = "姜维" or email="liubei@hh.com") and age = 62;select * from info where id in (1,4,6);select * from info where id not in (1,4,6);select * from info where id in (select id from depart);select * from info where exists (select * from depart where id=5); -- e xists 判断是否存在,如果条件存在会执行,如果不存在则不执行。select * from info where not exists (select * from depart where id=5);select * from (select * from info where id > 5) as T where T.age > 10;
2、通配符:用于模糊搜索
# 一般用于模糊搜索# % 代表N个字符;# _ 代表单个字符。select * from info where name like "%葛%";select * from info where name like "%亮";select * from info where email like "%@hh.com";select * from info where name like "_葛亮";
3、映射:
# 想要获取的列。select * from info;select id,name as NN from info;select id,name as NN,123 from info;
4、 排序:order by
# desc:降序排序# asc:升序排序 (默认)select * from info order by age desc;select * from info order by age asc,id desc; -- 优秀按照age从小到大,如果age相同则按照id从大到小。
5、取部分数据:limit
# 一般要用于获取部分数据select * from info limit 5;select * from info order by id desc limit 3; -- 先排序,再获取前3条数据。select * from info limit 3 offset 2; -- 从位置2开始,向后获取3条数据。
6、分组:group by
select age, from info group by age;select age,max(id),min(id),count(id),sum(in) from info group by age;select age,count(id) from info group by age having count(id) > 2;
以上就是部分SQL常用语句,语句之间的执行顺序如下:
到目前为止SQL语句的执行顺序:wheregroup byhavingorder bylimit
示例:
select age,count(i) -- 查询age,以及计数from info -- 要查询的表infowhere id>2 -- 条件 id>2group by age -- 根据age分组having count(id)>1 -- 对分组后的数据再根据聚合条件过滤 count(id) >1order by age desc -- 根据age从大到小排序limit 1; -- 获取第1条
文章转载自学渣的数据分析日常,如果涉嫌侵权,请发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。






