关于Yolov8的安装在前一个环节忽略了,其实非常简单,只需要以下两个步骤:
1、安装pytorch
pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu118
2、安装ultralytics
pip install ultralytics
为什么把目录结构单独拿出来扯呢?这个和训练自己的数据集息息相关。
首先我们要知道YOLOv8这次发行中带的预训练模型,是是基于COCO val2017 数据集训练的结果。
Coco2017数据集是具有80个类别的大规模数据集,其数据分为三部分:训练、验证和测试,每部分分别包含 118287, 5000 和 40670张图片,总大小约25g。其中测试数据集没有标注信息,所以注释部分只有训练和验证的
我们看一下yolo进行模型训练的方法,一种是CLI方式,一种是Python方式
CLI方式:
# Build a new model from YAML and start training from scratch
yolo detect train data=coco128.yaml model=yolov8n.yaml epochs=100 imgsz=640
# Start training from a pretrained *.pt model
yolo detect train data=coco128.yaml model=yolov8n.pt epochs=100 imgsz=640
# Build a new model from YAML, transfer pretrained weights to it and start training
yolo detect train data=coco128.yaml model=yolov8n.yaml pretrained=yolov8n.pt epochs=100 imgsz=640
Python方式:
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load a model
model = YOLO('yolov8n.yaml') # build a new model from YAML
model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt') # load a pretrained model (recommended for training)
model = YOLO('yolov8n.yaml').load('yolov8n.pt') # build from YAML and transfer weights
# Train the model
results = model.train(data='coco128.yaml', epochs=100, imgsz=640)
我们以CLI方式为例
mode: 选择是训练、验证还是预测的任务蕾西 可选['train', 'val', 'predict']
model: 选择yolov8不同的预训练模型,可选yolov8s.pt、yolov8m.pt、yolov8l.pt、yolov8x.pt;或选择yolov8不同的模型配置文件,可选yolov8s.yaml、yolov8m.yaml、yolov8l.yaml、yolov8x.yaml
data: 选择生成的数据集配置文件
epochs:指的就是训练过程中整个数据集将被迭代多少次,显卡不行你就调小点。
batch:一次看完多少张图片才进行权重更新,梯度下降的mini-batch,显卡不行你就调小点
其中data和model要画重点,data是要自己训练的数据集配置文件。
model一般是预训练模型,通常用yolov8n.pt、yolov8s.pt、yolov8m.pt、yolov8l.pt、yolov8x.pt就可以了,但如果想自己指定训练配置文件呢?这个时候,model就使用yolov8n.yaml等网络配置文件, 增加参数pretrained使用yolov8n.pt了。
这些文件在哪儿呢?
到项目所在的venv\Lib\site-packages\ultralytics目录下,看两个重要的目录cfg/datasets和cfg/models/v8
<PycharmProjectsROOT>\<ProjectName>\venv\Lib\site-packages\ultralytics>
├─assets
├─cfg
│ ├─datasets
│ ├─models
│ │ ├─rt-detr
│ │ ├─v3
│ │ ├─v5
│ │ ├─v6
│ │ └─v8
yolov8内置了以下模型配置文件
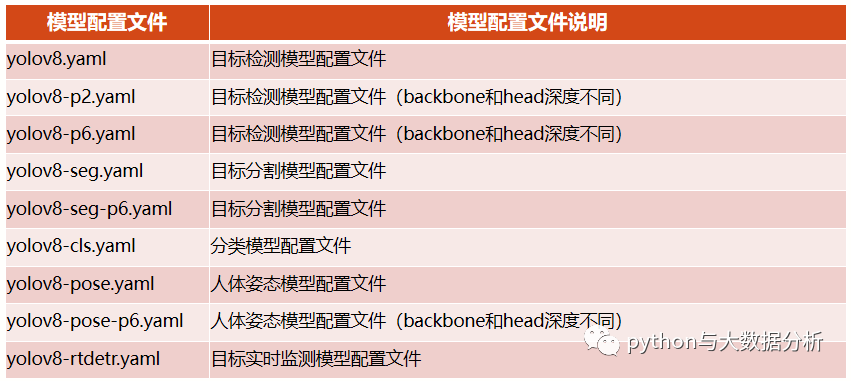
我们看一下yolov8.yaml文件,里面包含了标签总数,yolo几种不同训练模型的Layer数量、参数量、梯度量;骨干网的结构、Head的结构。
要做的事情很简单,基于yolov8.yaml另外复制一份基于训练集命名的文件,只需要修改nc后面的标签总数即可,在训练前可以认为标签总数是已知的。
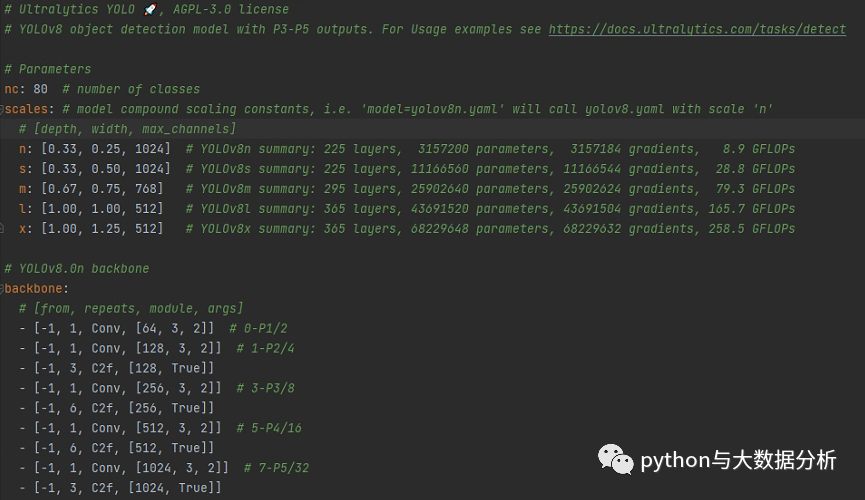
数据集配置文件还内置Argoverse.yaml、coco-pose.yaml、coco.yaml、coco128-seg.yaml、coco128.yaml、coco8-pose.yaml、coco8-seg.yaml、coco8.yaml、data.yaml、DOTAv2.yaml、GlobalWheat2020.yaml、ImageNet.yaml、Objects365.yaml、open-images-v7.yaml、SKU-110K.yaml、VisDrone.yaml、VOC.yaml、xView.yaml等模板。
我们看一下coco128.yaml文件,里面包含path(数据集根目录)、train(训练集图片路径))、val(验证集图片路径)、test(测试集图片路径);标签列表清单,按照序号:标签名的方式进行枚举,最后还包括了一个Download script/URL (optional)信息,即下载脚本和路径,这个是可选项 。
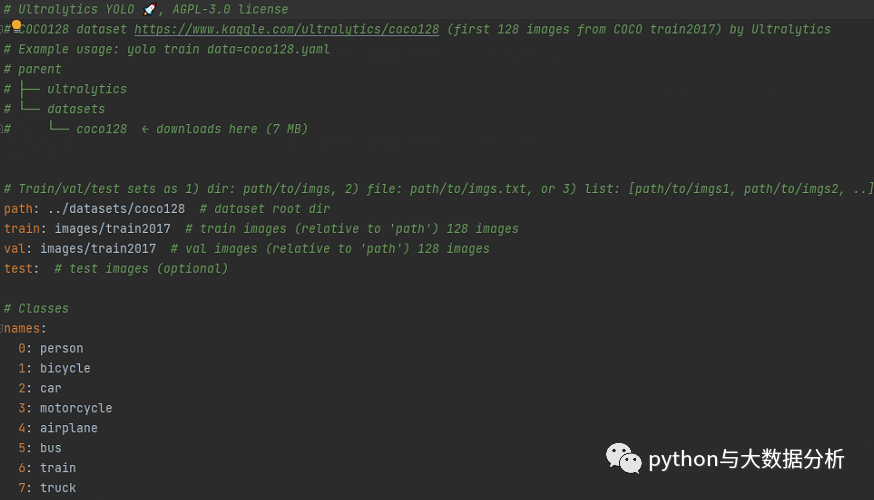
要做的事情很简单,基于coco128.yaml另外复制一份基于训练集命名VOC2012.yaml(我这里是VOC2012)的文件,只需要修改path、train、val、test路径即可;同时需要修改names下的标签列表,然后把多余的download脚本剔除掉,因为假设我们已经提前下载并标注了图片。
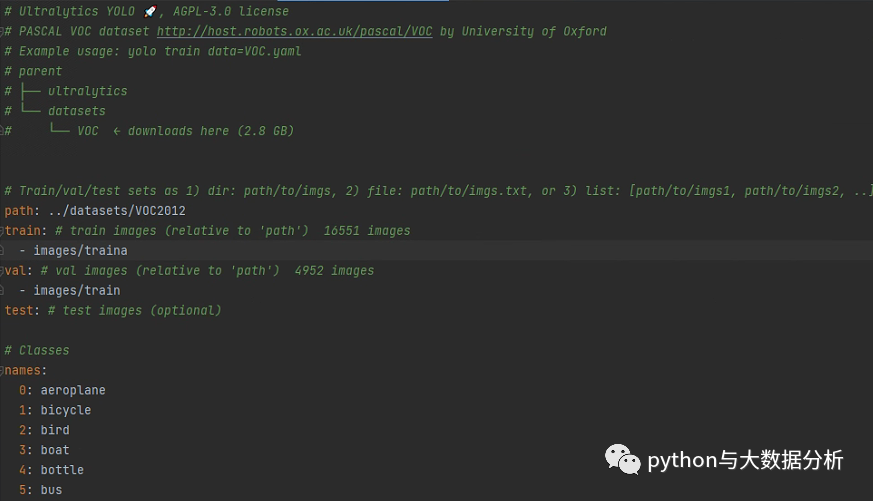
再回过头来看一下数据集的组织,在我们的项目根目录下增加一下datasets目录,然后每个目录一个文件夹,文件夹下包括images(图片文件夹)和label(标签文件夹),images放置train、val、test等图片目录,label下一般会放在train、val等标注信息。
└─datasets
├─coco128
│ ├─images
│ │ └─train2017
│ └─labels
│ └─train2017
└─VOC2012
├─images
│ └─train
└─labels
└─train
这个目录该怎么放数据呢?按照正常的做法是先下载VOC2012数据集
VOC2012数据集包括二十个对象类别:
Person :person
Animal :bird, cat, cow, dog, horse, sheep
Vehicle :aeroplane, bicycle, boat, bus, car, motorbike, train
Indoor :bottle, chair, dining table, potted plant, sofa, tv/monitor
VOC2012数据集的目录结构如下:
└─VOCdevkit
└─VOC2012
├─Annotations
├─ImageSets
│ ├─Action
│ ├─Layout
│ ├─Main
│ └─Segmentation
├─JPEGImages
├─SegmentationClass
└─SegmentationObject
其中Annotation是标注文件夹,JPEGImages是图片文件夹,基本用到这两个目录,正常情况下我们先会区分训练集、验证集和测试集,当然这次没这么做。不过可以看一下代码,后续做也可以。
import os
import random
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
#xml文件的地址,根据自己的数据进行修改 xml一般存放在Annotations下
parser.add_argument('--xml_path', default='VOCdevkit/VOC2012/Annotations', type=str, help='input xml label path')
#数据集的划分,地址选择自己数据下的ImageSets/Main
parser.add_argument('--txt_path', default='VOCdevkit/VOC2012/ImageSets/Main', type=str, help='output txt label path')
opt = parser.parse_args()
# Namespace(xml_path='VOCdevkit/VOC2012/Annotations', txt_path='VOCdevkit/VOC2012/ImageSets/Main')
# 训练+验证集一共所占的比例为0.8,剩下的0.2就是测试集
# (train+val)/(train+val+test)=80%
trainval_percent = 0.8
# (train)/(train+val)=80%
# 训练集在训练集和验证集总集合中占的比例
train_percent = 0.8
xmlfilepath = opt.xml_path
# VOCdevkit/VOC2012/Annotations
txtsavepath = opt.txt_path
# VOCdevkit/dataset/ImageSets/Main
# 获取标注文件数量
total_xml = os.listdir(xmlfilepath)
# 创建文件目录
if not os.path.exists(txtsavepath):
os.makedirs(txtsavepath)
# 随机打散文件序号,生成trainval和train两个随机数组
num = len(total_xml)
list_index = range(num)
tv = int(num * trainval_percent)
tr = int(tv * train_percent)
trainval = random.sample(list_index, tv)
train = random.sample(trainval, tr)
fileTrainVal = open(txtsavepath + '/trainval.txt', 'w')
fileTrain = open(txtsavepath + '/train.txt', 'w')
fileVal = open(txtsavepath + '/val.txt', 'w')
fileTest = open(txtsavepath + '/test.txt', 'w')
for i in list_index:
# 获取文件名
name = total_xml[i][:-4] + '\n'
# 根据trainval,train,val,test的顺序依次写入相关文件
if i in trainval:
fileTrainVal.write(name)
if i in train:
fileTrain.write(name)
else:
fileVal.write(name)
else:
fileTest.write(name)
fileTrainVal.close()
fileTrain.close()
fileVal.close()
fileTest.close()
再次是对VOC2012的标注文件XML转换为Yolo的Txt标注格式。
注这里的classes顺序要和上面的VOC2012.yaml中的name保持一致,否则会出现标签名称不对应的情况。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import os
sets = ['train', 'val', 'test']
classes = ["aeroplane", 'bicycle', 'bird', 'boat', 'bottle', 'bus', 'car', 'cat', 'chair', 'cow', 'diningtable', 'dog',
'horse', 'motorcycle', 'person', 'pottedplant', 'sheep', 'sofa', 'train', 'tvmonitor']
absPath = os.getcwd()
def convert(size, box):
'''
:param size: 图片size
:param box: 标注框坐标
:return:
VOC->YOLO转换算法
norm_x=(xmin + xmax)/2/width
norm_y=(ymin + ymax)/2/height
norm_w=(xmax - xmin)/width
norm_h=(ymax - ymin)/height
YOLO->VOC转换算法
xmin=width * (norm_x - 0.5 * norm_w)
ymin=height * (norm_y - 0.5 * norm_h)
xmax=width * (norm_x + 0.5 * norm_w)
ymax=height * (norm_y + 0.5 * norm_h)
'''
dw = 1. / (size[0])
dh = 1. / (size[1])
x = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0 - 1
y = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0 - 1
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[2]
x = x * dw
w = w * dw
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
return x, y, w, h
def ConvertAnnotation(image_id):
inputFile = open(absPath + '/VOCdevkit/VOC2012/Annotations/%s.xml' % (image_id), encoding='UTF-8')
outFile = open(absPath + '/VOCdevkit/VOC2012/YOLOLabels/%s.txt' % (image_id), 'w')
'''
VOC2012 标注格式
<annotation>
<folder>VOC2012</folder>
<filename>2008_007069.jpg</filename>
<source>
<database>The VOC2008 Database</database>
<annotation>PASCAL VOC2008</annotation>
<image>flickr</image>
</source>
<size>
<width>500</width>
<height>375</height>
<depth>3</depth>
</size>
<segmented>0</segmented>
<object>
<name>sheep</name>
<pose>Right</pose>
<truncated>0</truncated>
<occluded>0</occluded>
<bndbox>
<xmin>411</xmin>
<ymin>172</ymin>
<xmax>445</xmax>
<ymax>195</ymax>
</bndbox>
<difficult>0</difficult>
</object>
<object></object>
</annotation>
'''
'''
Yolo 标注文件格式
labelclass xCenter yCenter width height
每个标签有五个数据,依次代表:
所标注内容的类别,数字与类别一一对应
1、labelclass 标注框类别 labelclass
2、xCenter 归一化后标注框的中心点的x轴
3、yCenter 归一化后标注框的中心点的y轴
4、width 归一化后目标框的宽度
5、height 归一化后目标框的高度
'''
tree = ET.parse(inputFile)
root = tree.getroot()
# 获取标注图片的大小
size = root.find('size')
width = int(size.find('width').text)
height = int(size.find('height').text)
# 获取标注框信息
for obj in root.iter('object'):
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
# 获取标注类别名称
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in classes or int(difficult) == 1:
continue
# 将标注类别按照classes列表信息转换为索引ID
clsId = classes.index(cls)
# 获取标注框信息
xmlBox = obj.find('bndbox')
boundry = (float(xmlBox.find('xmin').text), float(xmlBox.find('xmax').text), float(xmlBox.find('ymin').text),
float(xmlBox.find('ymax').text))
xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax = boundry
# 标注越界修正
if xmax > width:
xmax = width
if ymax > height:
ymax = height
box = (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
transBox = convert((width, height), box)
outFile.write(str(clsId) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in transBox]) + '\n')
# 判断标注转换目录是否存在
if not os.path.exists(absPath + '/VOCdevkit/VOC2012/YOLOLabels/'):
os.makedirs(absPath + '/VOCdevkit/VOC2012/YOLOLabels/')
for imageSet in sets:
# 获取当前文件(train/val/test)的图片ID
imageIds = open(absPath + '/VOCdevkit/VOC2012/ImageSets/Main/%s.txt' % (imageSet)).read().strip().split()
listFile = open(absPath + '/VOCdevkit/VOC2012/%s.txt' % (imageSet), 'w')
for imageId in imageIds:
# 遍历文件名列表,分别将图片文件全路径写入新的文件中
listFile.write(absPath + '/VOCdevkit/VOC2012/JPEGImages/%s.jpg\n' % (imageId))
# 进行文件格式转换
ConvertAnnotation(imageId)
listFile.close()
关于Yolov8训练自己的数据集的前序准备工作已完成,后续讲一下怎么开展训练过程。
最后欢迎关注公众号:python与大数据分析







