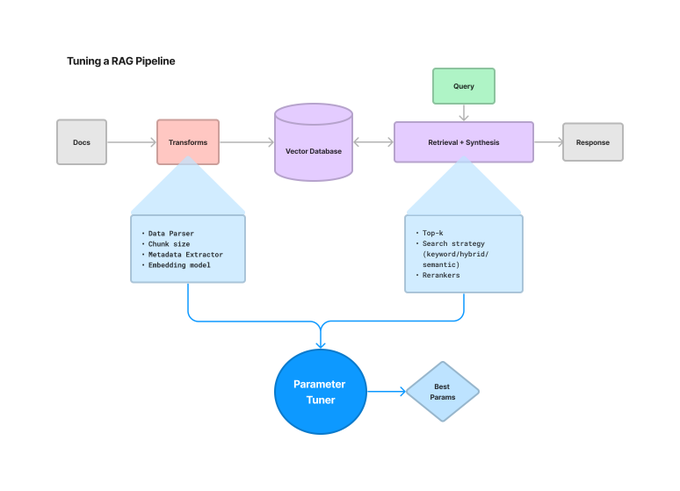
目前构建 LLM 应用程序存在一个巨大的问题,那就是需要调整大量的参数,而且远远超出了提示范围,例如分块、检索策略、元数据等。为了解决这些问题 LlamaIndex 推出了一个 ParamTuner 类,可以自动、高效地执行超参数调整。
ParamTuner 不仅可以定义我们想要的任何目标函数,例如带有评估的 RAG 管道;还能够以同步或者异步的方式进行网格搜索;并且 LlamaIndex 官方使用了 Ray Tune 将其提升到了一个新的水平。但是值得注意的是,该方法很有可能需要耗费很大的成本。
ParamTuner 有两种变体:
ParamTuner:一种通过遍历所有参数进行参数调优的简单方法。
RayTuneParamTuner:由 Ray tune 提供的超参数调优机制。
ParamTuner 可以接受任何输出值字典的函数。在这个设置中定义了一个函数,该函数从一组文档(Llama2 论文)构造一个基本的 RAG 摄取管道,选择最合适的评估数据集并运行它,最后为运行结果打分。
接下来将用一个完整的使用指南来展示如何对 RAG 进行超参数优化,主要针对块大小和 top-K 两个参数。
本文将会包括以下内容:
1.什么是超参数微调,以及为什么它很重要
2.超参数搜索的类型
3.ParamTuner 食用指南
01
什么是超参数调优,以及为什么它很重要
首先介绍超参数,超参数是模型不能从给定数据中估计的参数,是控制模型整体行为的变量。
超参数调优是一个过程,用于确定如何正确组合超参数以最大化模型性能。它涉及运行多个试验,每个试验都是训练程序的完整执行,采用不同的超参数设置值在指定范围内进行训练。一旦这一过程完成,将提供一组最适合模型的超参数值,以获得最佳结果。学习率就是一个很好的例子。当它太大时,学习不够灵敏,模型结果不稳定;但当它太小时,模型就会难以学习并且可能会卡住。
从上述介绍中不难看出,超参数调优是一个比较重要的步骤,因为它能够影响模型的最终的性能。
02
超参数搜索的类型
执行超参数搜索主要有以下三种方法:网格搜索、随机搜索和贝叶斯搜索。
网格搜索
网格搜索执行超参数调整的基本方法是尝试所有可能的参数组合。它在每一个可能的超参数组合上拟合模型并记录模型的性能。最后,它返回具有最佳超参数的最佳模型。这也是本文的方法用到的方式。
随机搜索
在随机搜索中,仅尝试部分参数值。采样的参数设置数量由 n_iter 给出。参数值是从给定列表或指定分布中采样的。当参数以列表形式呈现时(如网格搜索),将执行无替换采样。但如果参数以分布形式给出,一般使用放回抽样。
贝叶斯搜索
贝叶斯搜索与其他方法的主要区别在于,调整算法根据上一轮的得分来优化每轮的参数选择。因此,该算法不是随机选择下一组参数,而是优化选择,并且可能比前两种方法更快地达到最佳参数集。这意味着,此方法仅选择相关搜索空间并丢弃很可能无法提供最佳解决方案的范围。因此,该方法比较适用于当我们拥有大量数据、学习速度很慢并且希望最大限度地减少调整时间的情况。
03
ParamTuner 食用指南
首先我们来配置一下环境
pip install llama-indexmkdir data && wget --user-agent "Mozilla" "https://arxiv.org/pdf/2307.09288.pdf" -O "data/llama2.pdf"
import nest_asyncionest_asyncio.apply()
from pathlib import Pathfrom llama_hub.file.pdf.base import PDFReaderfrom llama_hub.file.unstructured.base import UnstructuredReaderfrom llama_hub.file.pymu_pdf.base import PyMuPDFReader
loader = PDFReader()docs0 = loader.load_data(file=Path("./data/llama2.pdf"))
from llama_index import Documentdoc_text = "\n\n".join([d.get_content() for d in docs0])docs = [Document(text=doc_text)]
from llama_index.node_parser import SimpleNodeParserfrom llama_index.schema import IndexNode
加载合适的评估数据集
在这里,我们为 llama2 论文建立了一个“黄金”评价数据集。
需要注意的是,数据集从 Dropbox 中提取。有关如何生成数据集的详细信息,可以参阅 LlamaIndex GitHub主页的 DatasetGenerator 模块。
wget "https://www.dropbox.com/scl/fi/fh9vsmmm8vu0j50l3ss38/llama2_eval_qr_dataset.json?rlkey=kkoaez7aqeb4z25gzc06ak6kb&dl=1" -O data/llama2_eval_qr_dataset.json
from llama_index.evaluation import QueryResponseDataset
# optionaleval_dataset = QueryResponseDataset.from_json("data/llama2_eval_qr_dataset.json")
eval_qs = eval_dataset.questionsref_response_strs = [r for (_, r) in eval_dataset.qr_pairs]
定义目标函数和参数
这里我们定义函数来优化给定的参数。该函数具体执行以下操作:
1.从文档构建索引,
2.查询索引,并运行一些基本计算。
from llama_index import (VectorStoreIndex,load_index_from_storage,StorageContext,ServiceContext,)from llama_index.param_tuner.base import ParamTuner, TunedResult, RunResultfrom llama_index.evaluation.eval_utils import get_responses, aget_responsesfrom llama_index.evaluation import SemanticSimilarityEvaluator, BatchEvalRunnerfrom llama_index.llms import OpenAIimport osimport numpy as npfrom pathlib import Path
辅助函数
def _build_index(chunk_size, docs):index_out_path = f"./storage_{chunk_size}"if not os.path.exists(index_out_path):Path(index_out_path).mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)# parse docsnode_parser = SimpleNodeParser.from_defaults(chunk_size=chunk_size)base_nodes = node_parser.get_nodes_from_documents(docs)# build indexindex = VectorStoreIndex(base_nodes)# save index to diskindex.storage_context.persist(index_out_path)else:# rebuild storage contextstorage_context = StorageContext.from_defaults(persist_dir=index_out_path)# load indexindex = load_index_from_storage(storage_context,)return indexdef _get_eval_batch_runner():eval_service_context = ServiceContext.from_defaults(llm=OpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo"))evaluator_s = SemanticSimilarityEvaluator(service_context=eval_service_context)eval_batch_runner = BatchEvalRunner({"semantic_similarity": evaluator_s}, workers=2, show_progress=True)return eval_batch_runner
同步目标函数
def objective_function(params_dict):chunk_size = params_dict["chunk_size"]docs = params_dict["docs"]top_k = params_dict["top_k"]eval_qs = params_dict["eval_qs"]ref_response_strs = params_dict["ref_response_strs"]# build indexindex = _build_index(chunk_size, docs)# query enginequery_engine = index.as_query_engine(similarity_top_k=top_k)# get predicted responsespred_response_objs = get_responses(eval_qs, query_engine, show_progress=True)# run evaluator# NOTE: can uncomment other evaluatorseval_batch_runner = _get_eval_batch_runner()eval_results = eval_batch_runner.evaluate_responses(eval_qs, responses=pred_response_objs, reference=ref_response_strs)# get semantic similarity metricmean_score = np.array([r.score for r in eval_results["semantic_similarity"]]).mean()return RunResult(score=mean_score, params=params_dict)
异步目标函数
async def aobjective_function(params_dict):chunk_size = params_dict["chunk_size"]docs = params_dict["docs"]top_k = params_dict["top_k"]eval_qs = params_dict["eval_qs"]ref_response_strs = params_dict["ref_response_strs"]# build indexindex = _build_index(chunk_size, docs)# query enginequery_engine = index.as_query_engine(similarity_top_k=top_k)# get predicted responsespred_response_objs = await aget_responses(eval_qs, query_engine, show_progress=True)# run evaluator# NOTE: can uncomment other evaluatorseval_batch_runner = _get_eval_batch_runner()eval_results = await eval_batch_runner.aevaluate_responses(eval_qs, responses=pred_response_objs, reference=ref_response_strs)# get semantic similarity metricmean_score = np.array([r.score for r in eval_results["semantic_similarity"]]).mean()return RunResult(score=mean_score, params=params_dict)
参数定义
这部分定义了在 param_dict 上进行网格搜索的参数和固定参数 fixed_param_dict。
param_dict = {"chunk_size": [256, 512, 1024], "top_k": [1, 2, 5]}# param_dict = {# "chunk_size": [256],# "top_k": [1]# }fixed_param_dict = {"docs": docs,"eval_qs": eval_qs[:10],"ref_response_strs": ref_response_strs[:10],}
运行默认的ParamTuner
这里我们运行默认的参数调优器,它以同步或异步方式迭代所有超参数组合。
from llama_index.param_tuner import ParamTuner
param_tuner = ParamTuner(param_fn=objective_function,param_dict=param_dict,fixed_param_dict=fixed_param_dict,show_progress=True,)
results = param_tuner.tune()
best_result = results.best_run_resultbest_top_k = results.best_run_result.params["top_k"]best_chunk_size = results.best_run_result.params["chunk_size"]print(f"Score: {best_result.score}")print(f"Top-k: {best_top_k}")print(f"Chunk size: {best_chunk_size}")
# adjust test_idx for additional testingtest_idx = 6p = results.run_results[test_idx].params(results.run_results[test_idx].score, p["top_k"], p["chunk_size"])
运行异步ParamTuner
from llama_index.param_tuner import AsyncParamTuner
aparam_tuner = AsyncParamTuner(aparam_fn=aobjective_function,param_dict=param_dict,fixed_param_dict=fixed_param_dict,num_workers=2,show_progress=True,)
results = await aparam_tuner.atune()
best_result = results.best_run_resultbest_top_k = results.best_run_result.params["top_k"]best_chunk_size = results.best_run_result.params["chunk_size"]print(f"Score: {best_result.score}")print(f"Top-k: {best_top_k}")print(f"Chunk size: {best_chunk_size}")
用Ray Tune运行ParamTuner
在这里,我们运行由 Ray Tune 提供支持的调谐器,Ray Tune 是一个用于任意规模的实验执行和超参数调整的 Python 库,集成了各种额外的超参数优化工具,包括 Ax、BayesOpt、BOHB、Dragonfly、FLAML、Hyperopt、Nevergrad、Optuna 和 SigOpt。
本指南中,我们在本地运行它,但其实也可以在集群上运行它。
from llama_index.param_tuner.base import RayTuneParamTuner
param_tuner = RayTuneParamTuner(param_fn=objective_function,param_dict=param_dict,fixed_param_dict=fixed_param_dict,run_config_dict={"storage_path": "/tmp/custom/ray_tune", "name": "my_exp"},)
results = param_tuner.tune()
results.best_run_result.params.keys()
results.best_idx
best_result = results.best_run_resultbest_top_k = results.best_run_result.params["top_k"]best_chunk_size = results.best_run_result.params["chunk_size"]print(f"Score: {best_result.score}")print(f"Top-k: {best_top_k}")print(f"Chunk size: {best_chunk_size}"
— 参考资料 —
https://github.com/run-llama/llama_index/blob/main/docs/examples/param_optimizer/param_optimizer.ipynb
https://twitter.com/llama_index/status/1721209688703062234
https://towardsdatascience.com/bayesian-optimization-for-hyperparameter-tuning-how-and-why-655b0ee0b399
https://blog.csdn.net/Baihai_IDP/article/details/128283742
https://docs.ray.io/en/latest/tune/index.html
向量检索实验室
微信号:VectorSearch
扫码关注 了解更多







