4. 内存管理模型中的内存组织、管理模式
Spark是一个技术框架,数据以分区粒度进行处理,即每个分区对应一个处理的任务(Task),因此内存的组织与管理等可以通过与Task一一对应的TaskMemoryManager来理解。
下面首先给出TaskMemoryManager与MemoryManager间的关系图,如图3-6所示:
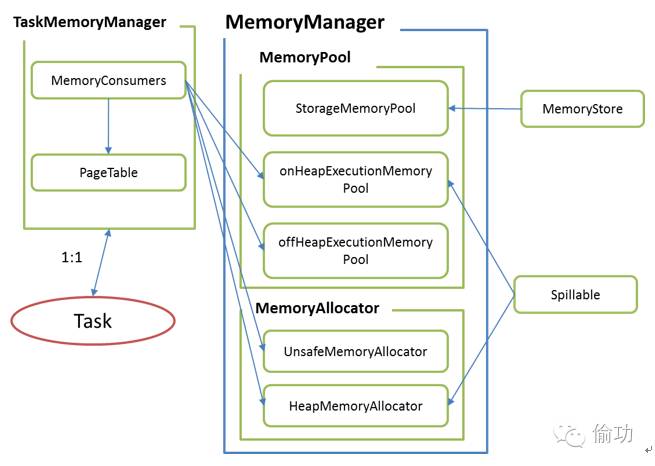
图3-6TaskMemoryManager与MemoryManager的关系图
在图3-6,各个MemoryConsumer是具体处理时需要使用(消耗)内存块的实体,MemoryConsumer通过TaskMemoryManager提供的接口向MemoryManager申请或释放内存资源,即申请或释放内存块,TaskMemoryManager类中会管理全部MemoryConsumer,并对这些内存消耗实体所申请的内存块进行组织与管理,具体是通过通过PageTable的方式来实现。
首先查看下类的注释信息,原注释信息比较多,在此仅给出简单的中文描述,其他相关信息可以在后续内容中补充,具体代码如下所示:
1. /** 2. * Manages the memory allocated by an individual task. 3. * …… 4. * 管理为单个 Task 所分配的内存。 5. * 内存地址在不同的内存模式下的表示: 6. * 1. off-heap :直接使用 64-bit 表示内存地址。 7. * 2. on-heap :通过 base object 和该对象中 64-bit 的偏移量来表示。 8. * 通过封装类 MemoryBlock 统一表示内存块信息: 9. * 1. off-heap :MemoryBlock 的 base object 为 null,偏移量对应 64-bit 的绝对地址。 10. * 2. on-heap :MemoryBlock 的 base object 保存对象的引用(该引用可以由 page 的索引从pageTable获取), 11. * 偏移量对应数据在该对象中的偏移量。 12. * 13. * 通过这两种内存模式对应的编码方式,最终对外提供的编码格式为 13bit-pageNumber + 51bit-offset 14. */ 15. public class TaskMemoryManager { |
下面从三个方面对TaskMemoryManager进行解析,包含内存地址的编码与解码、PageTable的组织与管理,以及内存的分配与释放。
首先解析内存地址的编码与解码部分。从TaskMemoryManager类的注释部分可以知道,off-heap与on-heap两种内存模式最终对外都是是采用一致的编码格式,即对应13bit的pageNumber(页码)和 51bit的offset(偏移量),可以通过图3-7来描述对应的编码方式:
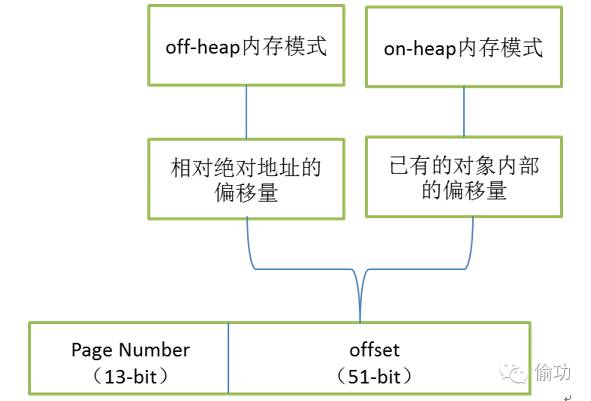
图3-7 Page的编码方式
下面分别对TaskMemoryManager类中与编码与解码相关的几个接口进行解析,编码接口主要有两个,其源码与解析如下所示:
1. /** 2. * Given a memory page and offset within that page, encode this address into a 64-bit long. 3. * This address will remain valid as long as the corresponding page has not been freed. 4. * 5. * @param page a data page allocated by {@link TaskMemoryManager#allocatePage}/ 6. * @param offsetInPage an offset in this page which incorporates the base offset. In other 7. * words, this should be the value that you would pass as the base offset into an 8. * UNSAFE call (e.g. page.baseOffset() + something). 9. * @return an encoded page address. 10. * 11. * 将针对某个 Page 的地址进行编码: 12. * on-heap :offsetInPage 是针对 base object 的偏移量。 13. * off-heap :此时, offsetInPage 是绝对地址,因此编码到 Page方式的地址时, 14. * 需要将绝对地址转换为相对于已有的Page(MemoryBlock)中的绝对 15. *地址 offset 的相对地址。最后将得到的两个偏移量和 Page Number 一起组装到 13 + 51 bits 的 64 bit 中。 16. */ 17. public long encodePageNumberAndOffset(MemoryBlock page, long offsetInPage) { 18. if (tungstenMemoryMode == MemoryMode.OFF_HEAP) { 19. // 如果是off-heap,则对应的offsetInPage为64bit的绝对地址,需要转换为Page 20. // 编码能容纳的51bit编码中,因此此时需要将其转换为Page内的相对地址, 21. // 即页内的偏移地址。 22. // In off-heap mode, an offset is an absolute address that may require a full 64 bits to 23. // encode. Due to our page size limitation, though, we can convert this into an offset that's 24. // relative to the page's base offset; this relative offset will fit in 51 bits. 25. offsetInPage -= page.getBaseOffset(); 26. } 27. return encodePageNumberAndOffset(page.pageNumber, offsetInPage); 28. } 29. 30. @VisibleForTesting 31. public static long encodePageNumberAndOffset(int pageNumber, long offsetInPage) { 32. assert (pageNumber != -1) : "encodePageNumberAndOffset called with invalid page"; 33. // 将13bit的页码与51bit的页内偏移量组装成64bit的编码地址。 34. return (((long) pageNumber) << OFFSET_BITS) | (offsetInPage & MASK_LONG_LOWER_51_BITS); 35. } |
通过pageNumber可以找到最终的Page,Page内部会根据off-heap或on-heap两种模式分别存储Page对应内存块的起始地址(或对象内偏移地址),因此编码后的地址可以通过查找到Page,最终解码出原始地址。对应的的解码的源码及其解析如下所示:
1. @VisibleForTesting 2. public static int decodePageNumber(long pagePlusOffsetAddress) { 3. // 通过13bit掩码解析出编码地址中的页码信息,即对应的高13bit内容 4. return (int) ((pagePlusOffsetAddress & MASK_LONG_UPPER_13_BITS) >>> OFFSET_BITS); 5. } 6. 7. private static long decodeOffset(long pagePlusOffsetAddress) { 8. // 通过51bit掩码解析出编码地址中的页码信息,即对应的低51bit内容 9. return (pagePlusOffsetAddress & MASK_LONG_LOWER_51_BITS); 10. } |
在TaskMemoryManager类中另外还提供了针对on-heap内存模式下,获取baseobject的接口,对应的源码及其解析如下所示:
1. /** 2. * Get the page associated with an address encoded by 3. *获取编码地址相关的base object 4. * {@link TaskMemoryManager#encodePageNumberAndOffset(MemoryBlock, long)} 5. */ 6. public Object getPage(long pagePlusOffsetAddress) { 7. if (tungstenMemoryMode == MemoryMode.ON_HEAP) { 8. // 首先从地址中解析出页码 9. final int pageNumber = decodePageNumber(pagePlusOffsetAddress); 10. assert (pageNumber >= 0 && pageNumber < PAGE_TABLE_SIZE); 11. // 根据页码从pageTable变量中获取对应的内存块 12. final MemoryBlock page = pageTable[pageNumber]; 13. assert (page != null); 14. assert (page.getBaseObject() != null); 15. // 获取内存块对应的 BaseObject 16. return page.getBaseObject(); 17. } else { 18. // off-heap内存模式下MemoryBlock只需要保存一个绝对地址,因此对应 19. // base object 为null 20. return null; 21. } 22. } |
下面开始解析PageTable的组织与管理方面的内容,在解析之前先给出以Page Table方式进行组织与管理的大致描述图,如图3-8所示:
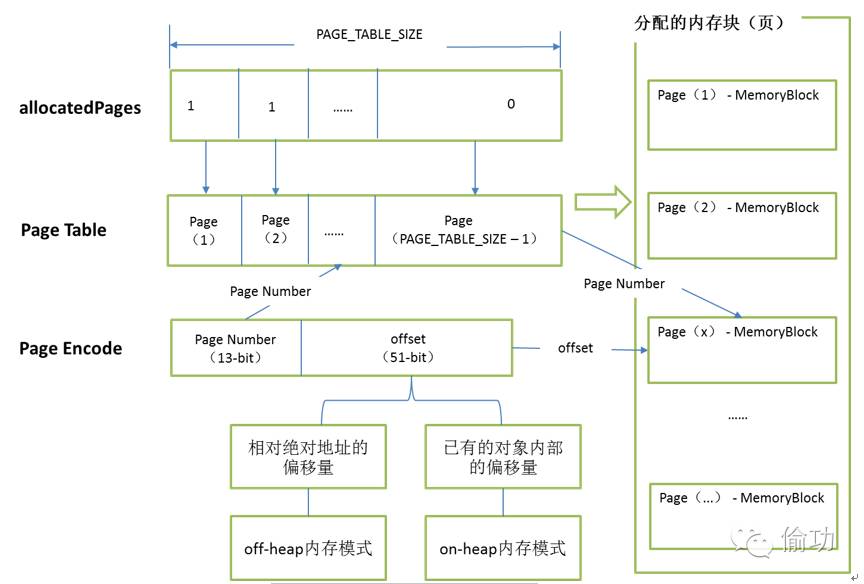
图3-8 PageTable组织与管理描述图
在图3-8中,右侧是分配的内存块,即当前需要管理的Page,在TaskMemoryManager中,通过Page Table来存放内存块,同时,通过变量allocatedPages中指定值为Page Number(页码)的下标(索引)对应的值是否为1来表示当前Page Number对应的Page Table中的Page是否已经存放了对应的内存块,即每当分配到一个内存块时,从allocatedPages获取一个值为0的位置(页码),并将该位置作为内存块放入到Page Table中的位置。
简单点描述的话,就是allocatedPages中各个位置上的值为1或0来表示在PageTable中相同位置是否已经放置了内存块(Page)。
而对应在PageTable中已经存放的内存块,实际上就是对应了右侧已经分配的内存块。
当针对一个PageEncode(页地址编码)时,首先从中获取Page Number,根据该值从Page Table中获取确定的内存块(MemoryBlock或Page),找到确定内存块之后,再通过页地址编码中的offset(具体两种内存模式下的概念如图3-8所示)确定的内存块中的相关偏移量,如果是off-heap,则该offset是相对于内存块(从前面分析可知,内存块本身的信息也与内存模式相关)中的绝对地址的相对地址,如果是on-heap,则该offset是相对于内存块的base object中的偏移量。
相关的源码主要涉及TaskMemoryManager类的两个成员变量,如下所示:
1. // 对应图3-8的Page Table 2. private final MemoryBlock[] pageTable = new MemoryBlock[PAGE_TABLE_SIZE]; 3. 4. // 对应图3-8的allocatedPages 5. private final BitSet allocatedPages = new BitSet(PAGE_TABLE_SIZE); |
PageTable的组织与管理中关于页码的偏移量已经在上一部分给出详细描述,而对应的具体的管理操作则与实际的内存分配与解析部分相关,通过图3-8对大致的管理有一定概念后,再继续通过内存分配与解析部分,来详细解析具体的管理细节。
下面开始分析TaskMemoryManager类提供的内存分配与解析部分。关于这部分内容,主要参考allocatePage与freePage两个方法,对应allocatePage内部如何申请内存,以及申请内存时采用的spill策略等细节,大家可以继续深入,比如查看acquireExecutionMemory的具体源码来加深理解。
allocatePage方法的源码及其解析如下所示:
1. /** 2. * Allocate a block of memory that will be tracked in the MemoryManager's page table; this 3. * is intended for allocating large blocks of Tungsten memory that will be shared between 4. * operators. 5. * Returns `null` if there was not enough memory to allocate the page. May return a page 6. * that contains fewer bytes than requested, so callers should verify the size of returned 7. * pages. 8. * 分配一块内存,并通过 MemoryManager(实际上是在 TaskMemoryManager 中)的 9. * Page Table 进行跟踪;分配的是 Execution 部分的内存。 10. * Project Tungsten 的内存包含 off-heap 和 on-heap 两种模式,由底层 11. * tungstenMemoryMode(在MemoryManager中设置)控制具体分配的 12. *MemoryAllocator 子类。 13. */ 14. public MemoryBlock allocatePage(long size, MemoryConsumer consumer) { 15. // 页大小的限制 16. if (size > MAXIMUM_PAGE_SIZE_BYTES) { 17. throw new IllegalArgumentException( 18. "Cannot allocate a page with more than " + MAXIMUM_PAGE_SIZE_BYTES + " bytes"); 19. } 20. 21. // 特定的内存消费者 consumer 以指定的内存模式 tungstenMemoryMode 22. // 申请一定的内存量 23. long acquired = acquireExecutionMemory(size, tungstenMemoryMode, consumer); 24. if (acquired <= 0) { 25. return null; 26. } 27. 28. final int pageNumber; 29. synchronized (this) { 30. // 获取当前未被占用的页码 31. pageNumber = allocatedPages.nextClearBit(0); 32. if (pageNumber >= PAGE_TABLE_SIZE) { 33. releaseExecutionMemory(acquired, tungstenMemoryMode, consumer); 34. throw new IllegalStateException( 35. "Have already allocated a maximum of " + PAGE_TABLE_SIZE + " pages"); 36. } 37. // 设置该页码已经被占用(即设置对应页码位置的值) 38. allocatedPages.set(pageNumber); 39. } 40. 41. // 开始通过 MemoryAllocator 真正分配内存 42. // 注意 : acquireExecutionMemory 中通过 ExecutionMemoryPool 进行分配时, 43. // 仅仅是内存使用大小上的控制,并没有真正分配内存。 44. // 有兴趣的话,可以查看对 acquireExecutionMemory 的调用点(其中 45. // 可以指定与tungstenMemoryMode不同的其他内存模式, 46. // 此时是不存在真正的内存分配的) 47. final MemoryBlock page = memoryManager.tungstenMemoryAllocator().allocate(acquired); 48. 49. // 分配得到内存块之后,会设置该内存块对应的 pageNumber, 50. // 即此时设置 MemoryBlock 在其管理的 Page Table 中的位置。 51. page.pageNumber = pageNumber; 52. pageTable[pageNumber] = page; 53. if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 54. logger.trace("Allocate page number {} ({} bytes)", pageNumber, acquired); 55. } 56. return page; 57. } |
其中,MAXIMUM_PAGE_SIZE_BYTES是页内数据量大小的现在,从之前MemoryBlock提供的从long型数组转换得到MemoryBlock接口,可以知道当前连续的内存块是通过long型数组来获取的,因此对应的内存块的大小也会受到数组的最大长度的现在。
至于对应在具体的处理过程中,对页内的数据量大小是否还有其他现在,可以参考具体的处理细节,下一章节会给出一个具体处理过程的源码解析,其中会包含这部分内容。
由于分配的细节比较多,这里给出主要的过程描述:
首先通过acquireExecutionMemory方法,向ExecutionMemoryPool申请内存(根据统一或静态两种具体实现给出):这一部分主要是判断当前可用内存是否满足申请需求,并根据申请结果修改当前内存池可用内存信息(实际是当前使用内存量信息)。
从当前Page Table中找出一个可用位置,用于存放所申请的内存块(MemoryBlock或Page)。
准备好前两步后,开始通过MemoryAllocator真正分区内存块。
将分配的内存块放入Page Table。
在整个过程中,allocatedPages与pageTable这两个成员变量的使用是体现PageTable组织与管理的关键所在。
下面解析freePage的源码,如下所示:
1. /** 2. * Free a block of memory allocated via {@link TaskMemoryManager#allocatePage}. 3. * 更新 Page Table 相关信息,通过 MemoryAllocator 释放 Page 的内存, 4. * 最后通过 MemoryManager 修改 ExecutorManagerPool 中内存使用量(即释放)。 5. */ 6. public void freePage(MemoryBlock page, MemoryConsumer consumer) { 7. // 首先确认当前释放的内存块是在 Page Table 的管理中的,即页码必须有效 8. assert (page.pageNumber != -1) : 9. "Called freePage() on memory that wasn't allocated with allocatePage()"; 10. assert(allocatedPages.get(page.pageNumber)); 11. pageTable[page.pageNumber] = null; 12. 13. // allocatedPages 是控制 pageTable 中对应位置是否可用的, 14. // 需要考虑释放与分配时的并发性,因此需同步处理 15. synchronized (this) { 16. allocatedPages.clear(page.pageNumber); 17. } 18. if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 19. logger.trace("Freed page number {} ({} bytes)", page.pageNumber, page.size()); 20. } 21. 22. // 通过当前内存模式对应的 MemoryAllocator 真正释放该内存块 23. long pageSize = page.size(); 24. memoryManager.tungstenMemoryAllocator().free(page); 25. 26. // 对应 ExecutionMemoryPool 部分的内存释放, 27. // 参考前面 acquireExecutionMemory 解析一起了解 28. releaseExecutionMemory(pageSize, tungstenMemoryMode, consumer); 29. } |
释放Page的逻辑实际上可以参考申请Page,大部分都是步骤相反而已。






