2. MemoryManager的实现及其源码解析
MemoryManager目前实现了两种具体的内存管理模型,从Spark 1.6 版本开始,默认使用统一内存管理模型,对应的配置属性为"spark.memory.useLegacyMode",控制代码位于SparkEnv类中,代码如下所示:
1. // Spark 1.5 及之前的版本所使用的内存管理模型对应配置属性 2. // "spark.memory.useLegacyMode"为ture。当前默认为false。 3. val useLegacyMemoryManager = conf.getBoolean("spark.memory.useLegacyMode", false) 4. val memoryManager: MemoryManager = 5. if (useLegacyMemoryManager) { 6. // 使用静态内存管理模型 7. new StaticMemoryManager(conf, numUsableCores) 8. } else { 9. // 使用统一内存管理模型 10. UnifiedMemoryManager(conf, numUsableCores) 11. } |
以上是具体内存管理模型选择的代码,下面开始分析内存管理相关的源码,首先查看MemoryManager的注释,如下所示:
1. /** 2. * An abstract memory manager that enforces how memory is shared between execution and 3. * storage. 4. * In this context, execution memory refers to that used for computation in shuffles, joins, 5. * sorts and aggregations, while storage memory refers to that used for caching and 6. * propagating internal data across the cluster. There exists one MemoryManager per JVM. 7. * 8. * 内存管理的抽象接口,用于指定如何在 Execution 与 Storage 间共享内存。 9. * Execution Memory是指用计算的内容,包括Shuffles、joins、sorts以及aggregations。 10. * Storage Memory则是指用于缓存或内部数据传输过程中所使用的内存。 11. * MemoryManager与JVM进程的对应关系为1:1。即一个JVM进程中的内存由一个 12. *MemoryManager进行管理。 13. */ 14. private[spark] abstract class MemoryManager( 15. …… |
在MemoryManager类中提供的内存分配与释放的几个主要接口如下:
Storage部分内存的分配与释放接口:acquireStorageMemory、acquireUnrollMemory、releaseStorageMemory以及releaseUnrollMemory。
Execution部分内存的分配与释放接口:acquireExecutionMemory与releaseExecutionMemory。
具体分配与释放的实现由MemoryManager的具体子类提供。
两大实现子类的主要差别在于Storage与Execution内存之间的边界是静态的还是动态可变的,下面分别简单描述下两大子类的实现细节。
StaticMemoryManager类的注释如下所示:
1. /** 2. * A [[MemoryManager]] that statically partitions the heap space into disjoint regions. 3. * 4. * The sizes of the execution and storage regions are determined through 5. * `spark.shuffle.memoryFraction` and `spark.storage.memoryFraction` respectively. The two 6. * regions are cleanly separated such that neither usage can borrow memory from the other. 7. *静态划分Storage与Execution内存之间的边界的一种内存管理实现。 8. * Storage与Execution内存大小分别由配置属性`spark.shuffle.memoryFraction` 与 9. *`spark.storage.memoryFraction`各自指定,由于是静态划分边界,因此这两者之间不能 10. *互相借用多余的内存。 11. */ 12. private[spark] class StaticMemoryManager( |
静态内存管理模型中各部分内存的分配可以通过以下几个接口或成员变量查看:
maxUnrollMemory:unroll过程中可用的内存,占最大可用Storage内存的0.2。
getMaxStorageMemory:获取分配给Storage使用的最大内存大小。
getMaxExecutionMemory:获取分配给Execution使用的最大内存大小。
其中,getMaxStorageMemory对应用于Storage的最大内存,具体配置如下所示:
1. private def getMaxStorageMemory(conf: SparkConf): Long = { 2. val systemMaxMemory = conf.getLong("spark.testing.memory", Runtime.getRuntime.maxMemory) 3. val memoryFraction = conf.getDouble("spark.storage.memoryFraction", 0.6) 4. val safetyFraction = conf.getDouble("spark.storage.safetyFraction", 0.9) 5. (systemMaxMemory * memoryFraction * safetyFraction).toLong 6. } |
其中配置属性"spark.storage.memoryFraction"表示Storage内存占用全部内存(除预留给系统的内存外)的占比,"spark.storage.safetyFraction"对应为Storage内存的安全系数。
对应的getMaxExecutionMemory方法指明了用于Execution内存的相关配置属性,与Storage内存一样包含占总内存的占比(0.2)及对应的安全系数。
另外,除了Storage内存与Execution内存占用的0.6+0.2之外的剩余内存,作为系统预留内存。
通过StaticMemoryManager类简单分析静态内存管理模型后,继续查看统一内存管理模型,首先查看其类注释:
1. /** 2. * A [[MemoryManager]] that enforces a soft boundary between execution and storage such 3. * that either side can borrow memory from the other. 4. * 5. * The region shared between execution and storage is a fraction of (the total heap space - 6. * 300MB) configurable through `spark.memory.fraction` (default 0.75). The position of the 7. * boundary within this space is further determined by `spark.memory.storageFraction` 8. * (default 0.5).This means the size of the storage region is 0.75 * 0.5 = 0.375 of the heap 9. * space by default. 10. * Storage can borrow as much execution memory as is free until execution reclaims its space. 11. * When this happens, cached blocks will be evicted from memory until sufficient borrowed 12. * memory is released to satisfy the execution memory request. 13. * 14. * Similarly, execution can borrow as much storage memory as is free. However, execution 15. * memory is *never* evicted by storage due to the complexities involved in implementing 16. * T this.he implication is that attempts to cache blocks may fail if execution has already eaten 17. * up most of the storage space, in which case the new blocks will be evicted immediately 18. * according to their respective storage levels. 19. * 20. * @param storageRegionSize Size of the storage region, in bytes. 21. * This region is not statically reserved; execution can borrow 22. * from it if necessary. Cached blocks can be evicted only if 23. * actual storage memory usage exceeds this region. 24. * 25. * UnifiedMemoryManager :是 MemoryManager 的一个具体子类,实现 Storage 与 26. *Execution 间软边界(即动态边界)的内存管理模式。 27. * 动态边界意味着 Storage 与 Execution 的内存是可以相互借用的。 28. * Storage 与 Execution :共享的内存通过配置 `spark.memory.fraction` 进行设置。 29. * 两者间的内存分配通过配置 `spark.memory.storageFraction` 进行设置。 30. * 内存借用: 31. * 1) Storage 可以借用 Execution 中空闲的内存,但在 Execution 执行需要内存时 32. * 会被回收(回收缓存内存直到满足执行申请的内存)。 33. * 2)类似地,Execution 也可以借用 Storage 中空闲的内存。但是,出于实现的复 34. * 杂性考虑(具体可以参考前面给出的官方设计文档 35. *unified-memory-management-spark-10000.pdf), 36. * 借用的内存`永远`不会因为 Storage 需要而进行回收。 37. */ 38. private[spark] class UnifiedMemoryManager private[memory] ( 39. …… |
UnifiedMemoryManager与StaticMemoryManager一样实现了MemoryManager的几个内存分配、释放的接口,对应分配与释放接口的实现,在StaticMemoryManager相对比较简单,而在UnifiedMemoryManager中,由于考虑到动态借用的情况,实现相对比较复杂,具体细节可以参考官方提供的统一内存管理设计文档以及相关源码,比如针对各个Task如何保证其最小分配的内存(最少1/2N,其中N表示当前活动状态的Task个数,最大的Task个数可以从Executor分配的内核个数/每个Task占用的内核个数得到)等等。
下面简单分析下统一内存管理模型中,Storage内存与Execution内存等相关的配置。
查看方法,具体代码如下所示:
1. /** 2. * Return the total amount of memory shared between execution and storage, in bytes. 3. *返回Execution与Storage共享的最大内存。 4. */ 5. private def getMaxMemory(conf: SparkConf): Long = { 6. val systemMemory = conf.getLong("spark.testing.memory", Runtime.getRuntime.maxMemory) 7. // 系统预留的内存大小,默认为300M。 8. // 结合下面最小系统内存的限定条件(硬编码方式,因此修改需要重新编译), 9. // 可以人为修改该配置进行测试。 10. val reservedMemory = conf.getLong("spark.testing.reservedMemory", 11. if (conf.contains("spark.testing")) 0 else RESERVED_SYSTEM_MEMORY_BYTES) 12. // 当前最小的内存需要300 * 1.5,即450M,不满足该条件时会报错退出 13. val minSystemMemory = reservedMemory * 1.5 14. if (systemMemory < minSystemMemory) { 15. throw new IllegalArgumentException(s"System memory $systemMemory must " + 16. s"be at least $minSystemMemory. Please use a larger heap size.") 17. } 18. val usableMemory = systemMemory – reservedMemory 19. // 当前Execution与Storage共享的最大内存占比默认为0.75,即 20. // Execution与Storage内存为可用内存的0.75; 21. // 用户内存为可用内存的(1-0.75)= 0.25 22. // 由于前面提到的Alexey Grishchenko给出的博客上对统一内存管理模型给出了 23. // 非常详细、深入地解析,建议直接参考博客内容,同时结合此处源码进行理解。 24. val memoryFraction = conf.getDouble("spark.memory.fraction", 0.75) 25. (usableMemory * memoryFraction).toLong 26. } |
另外,虽然Execution与Storage之间共享内存,但仍然存在一个初始边界值,参考伴生对象UnifiedMemoryManager的apply工厂方法,具体代码如下所示:
1. def apply(conf: SparkConf, numCores: Int): UnifiedMemoryManager = { 2. val maxMemory = getMaxMemory(conf) 3. new UnifiedMemoryManager( 4. conf, 5. maxMemory = maxMemory, 6. // 通过配置属性"spark.memory.storageFraction",可以设置Execution与Storage 7. // 共享内存的初始边界值,即默认初始时,各占总的内存的一半。 8. storageRegionSize = 9. (maxMemory * conf.getDouble("spark.memory.storageFraction", 0.5)).toLong, 10. numCores = numCores) 11. } |
另外,需要注意的是,前面Execution内存指的是on-heap部分的内存,在ProjectTungsten中引入了off-heap(堆外)内存,这部分内存大小的设置在基类MemoryManager中,对应代码如下所示:
1. // 根据传入的内存大小或配置属性分别设置内存池管理的内存初始大小 2. // 1. Storage部分的内存池初始大小设置 3. storageMemoryPool.incrementPoolSize(storageMemory) 4. // 2. on-heap部分的Execution内存池初始大小设置 5. onHeapExecutionMemoryPool.incrementPoolSize(onHeapExecutionMemory) 6. // 3. 从配置属性中读取off-heap内存池的初始内存大小 7. offHeapExecutionMemoryPool.incrementPoolSize(conf.getSizeAsBytes("spark.memory.offHeap.size", 0)) |
当需要使用off-heap内存时,需要注意的是,除了需要修改off-heap内存池(offHeapExecutionMemoryPool)的内存初始值时(默认为0),还需要打开对应的控制开关,具体代码参考内存分配MemoryManager中内存模式的设置(该内存模式可以控制用于内存分配MemoryAllocator的具体子类。),对应代码如下所示:
1. final val tungstenMemoryMode: MemoryMode = { 2. // 当需要使用off-heap内存模式时,需要通过"spark.memory.offHeap.enabled" 3. // 配置属性打开开关,然后通过"spark.memory.offHeap.size"配置属性 4. // 指定off-heap的内存大小。 5. if (conf.getBoolean("spark.memory.offHeap.enabled", false)) { 6. require(conf.getSizeAsBytes("spark.memory.offHeap.size", 0) > 0, 7. "spark.memory.offHeap.size must be > 0 when spark.memory.offHeap.enabled == true") 8. MemoryMode.OFF_HEAP 9. } else { 10. MemoryMode.ON_HEAP 11. } 12. } |
从图3-4可以看出,Execution内存根据不同的内存模式(on-heap或off-heap)可以有两种内存池管理方式,对应可以查看下Execution内存分配的方法(方法注释中给出了为Task分配内存的实现细节,有兴趣可以查看源码注释),关键的代码如下所示:
1. override private[memory] def acquireExecutionMemory( 2. numBytes: Long, 3. taskAttemptId: Long, 4. memoryMode: MemoryMode): Long = synchronized { 5. assert(onHeapExecutionMemoryPool.poolSize + storageMemoryPool.poolSize == maxMemory) 6. assert(numBytes >= 0) 7. memoryMode match { 8. case MemoryMode.ON_HEAP => 9. …… 10. // 当内存模式为on-heap时,使用onHeapExecutionMemoryPool内存池来管理 11. onHeapExecutionMemoryPool.acquireMemory( 12. numBytes, taskAttemptId, maybeGrowExecutionPool, computeMaxExecutionPoolSize) 13. 14. case MemoryMode.OFF_HEAP => 15. //当内存模式为off-heap时,使用offHeapExecutionMemoryPool内存池来管理 16. offHeapExecutionMemoryPool.acquireMemory(numBytes, taskAttemptId) 17. } 18. } |
MemoryMode是二选一,因此在启动off-heap内存模式时,可以将Storage的内存占比(对应配置属性"spark.memory.storageFraction")设置高一点,虽然在具体分配过程中Storage也可以向on-heap这部分Execution借用内存。
关于内存池部分,下面给出主要类的类图,具体实现可以结合类图阅读源码来加深理解,主要类图如图3-5所示:
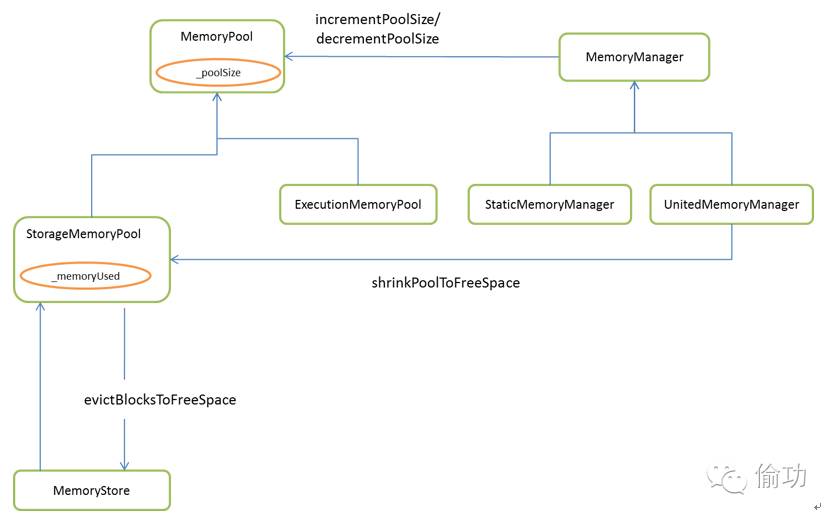
图3-5内存池相关类图
主要是通过内部池大小和使用的内存大小等进行控制,对应统一内存管理模型,需要考虑借用等具体实现(关键代码可以查看UnitedMemoryManager对StorageMemoryPool类的shrinkPoolToFreeSpace方法的调用)。
以上是对Tungsten的两种内存管理模型的简单解析,下面开始对内存管理模型的内部组织结构进行解析。






