原标题:Graph Few-shot Learning via Knowledge Transfer
作者:Huaxiu Yao , Chuxu Zhang , Ying Wei , Meng Jiang , Suhang Wang
中文摘要:
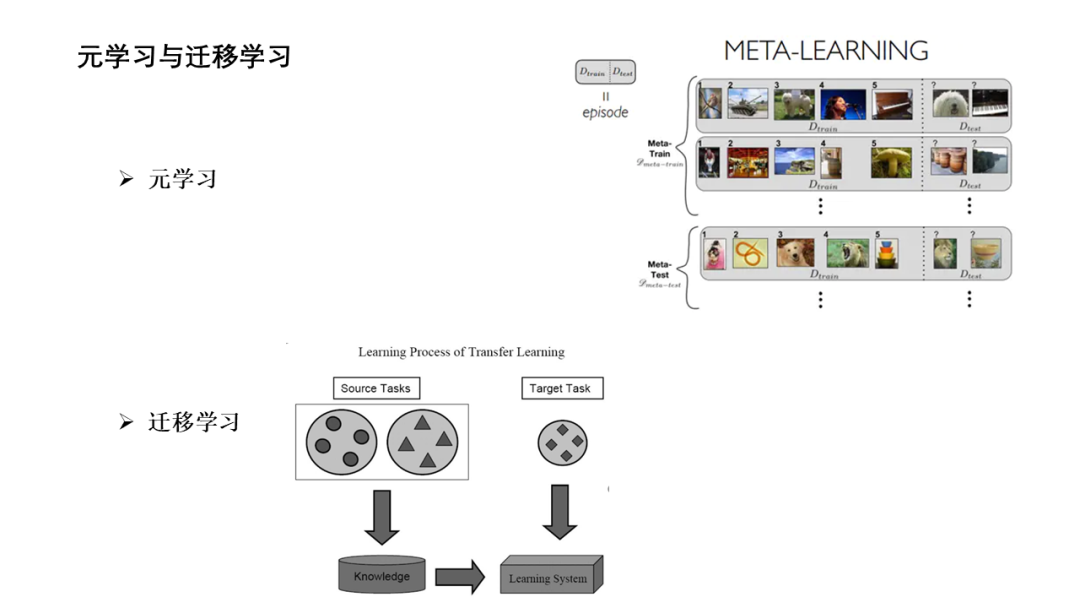
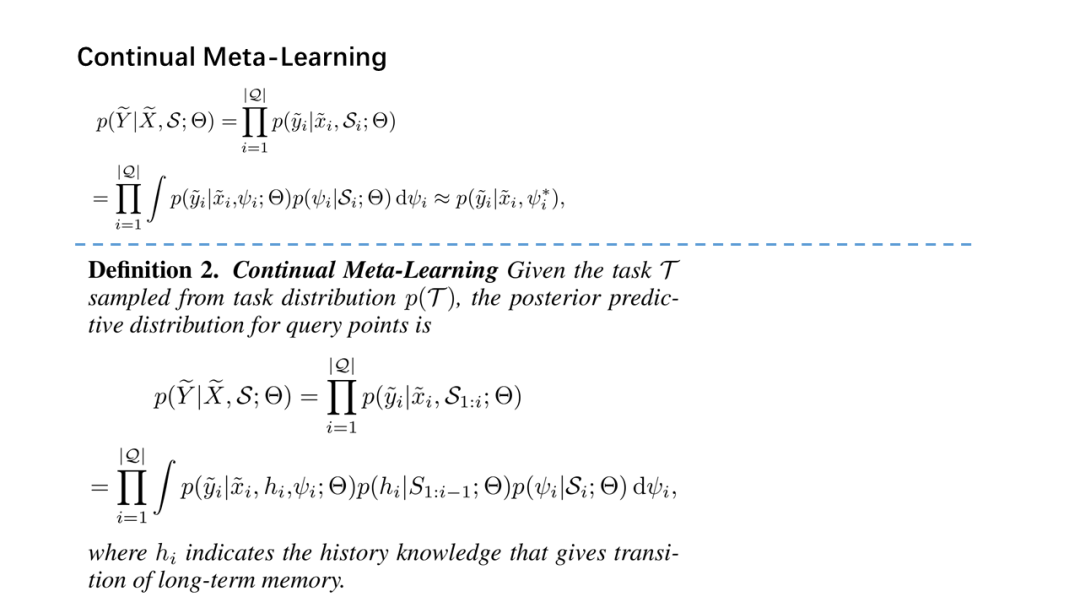
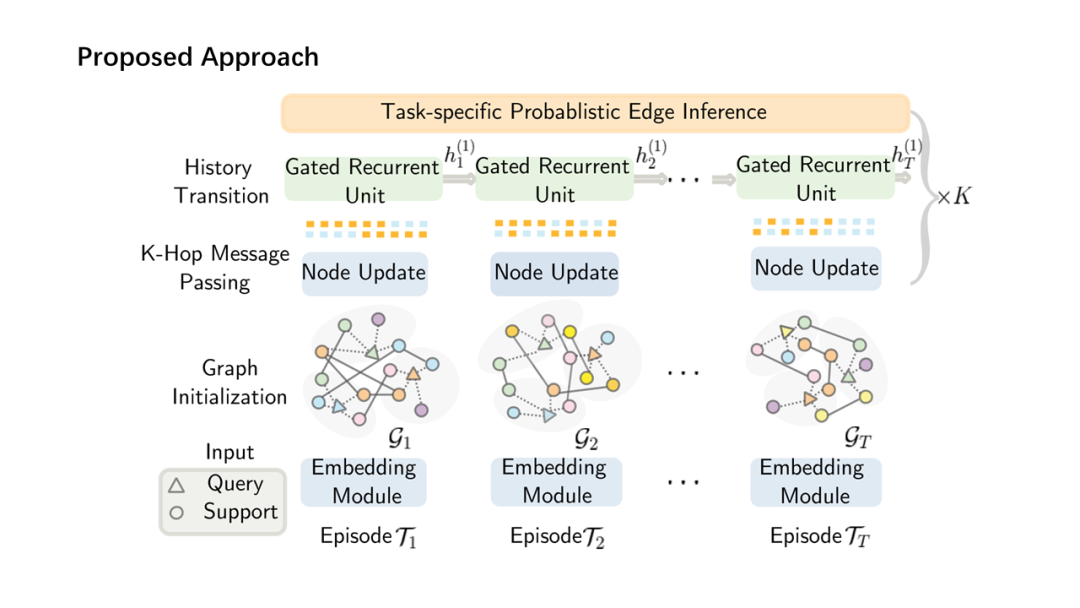
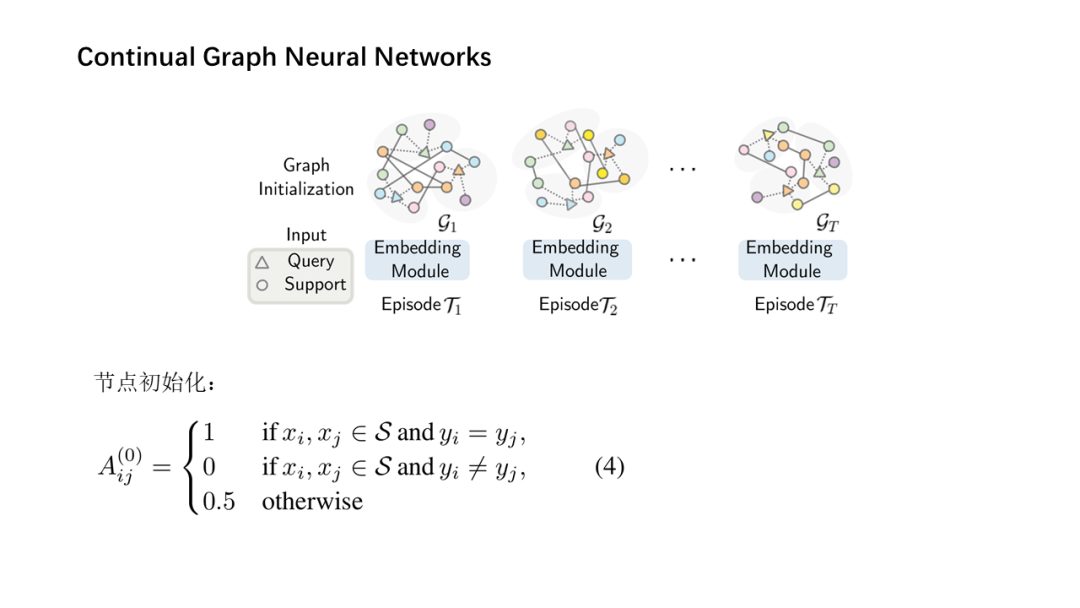
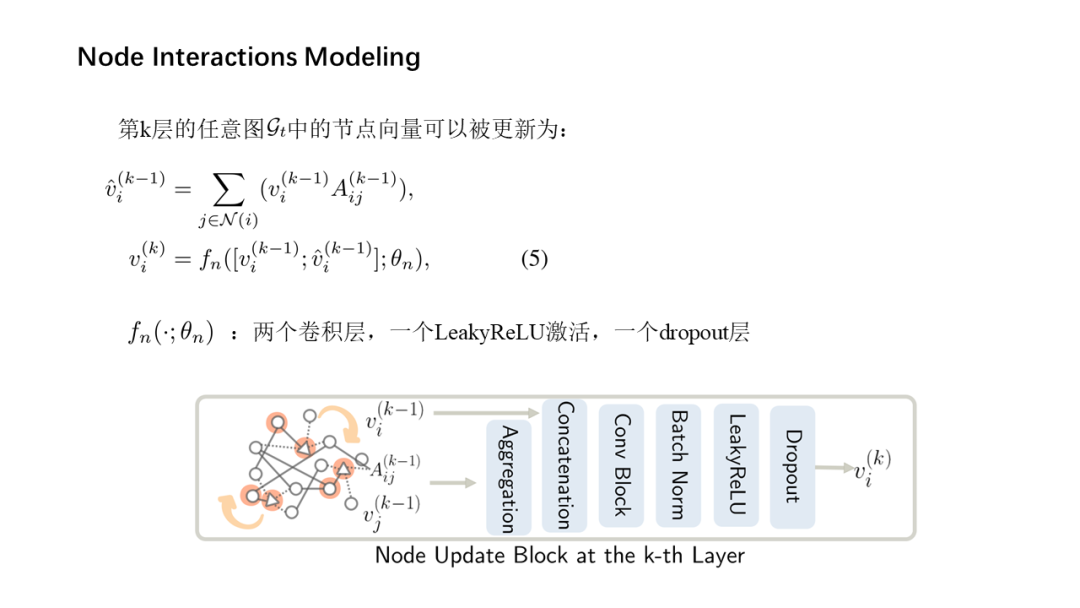
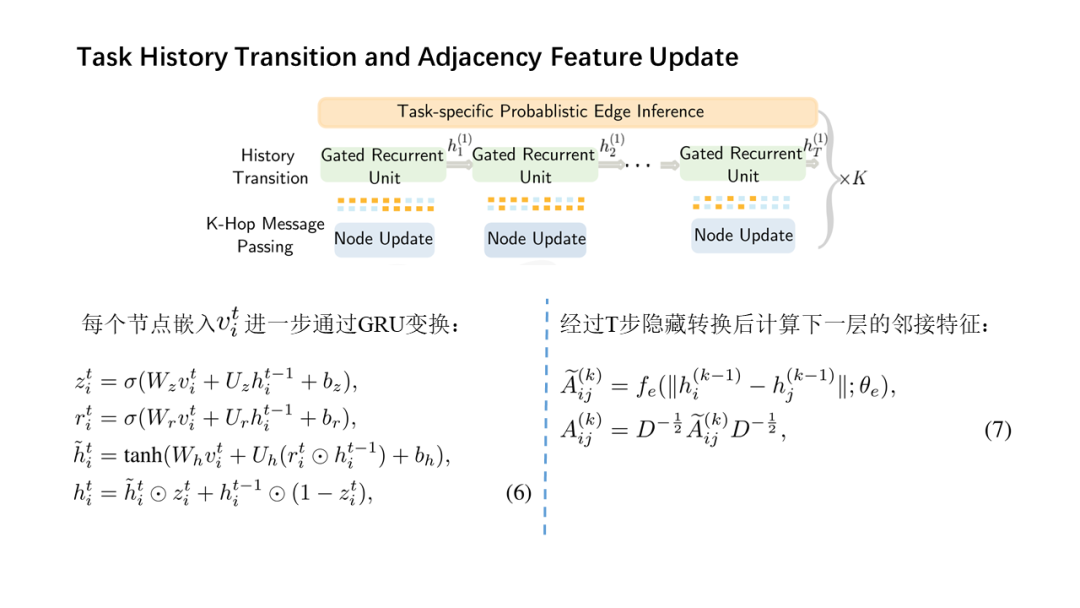
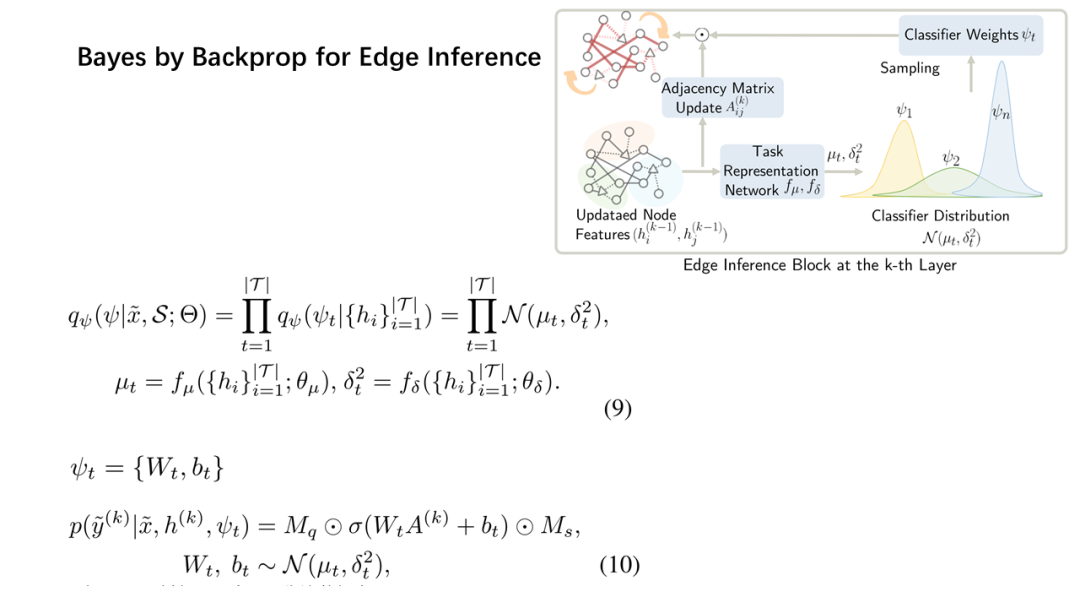
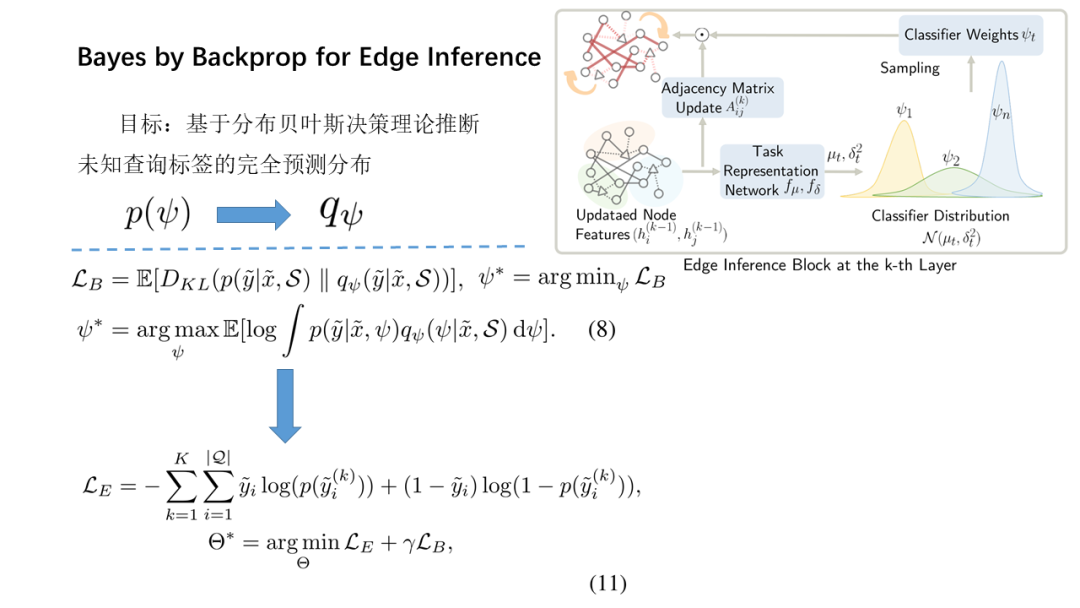
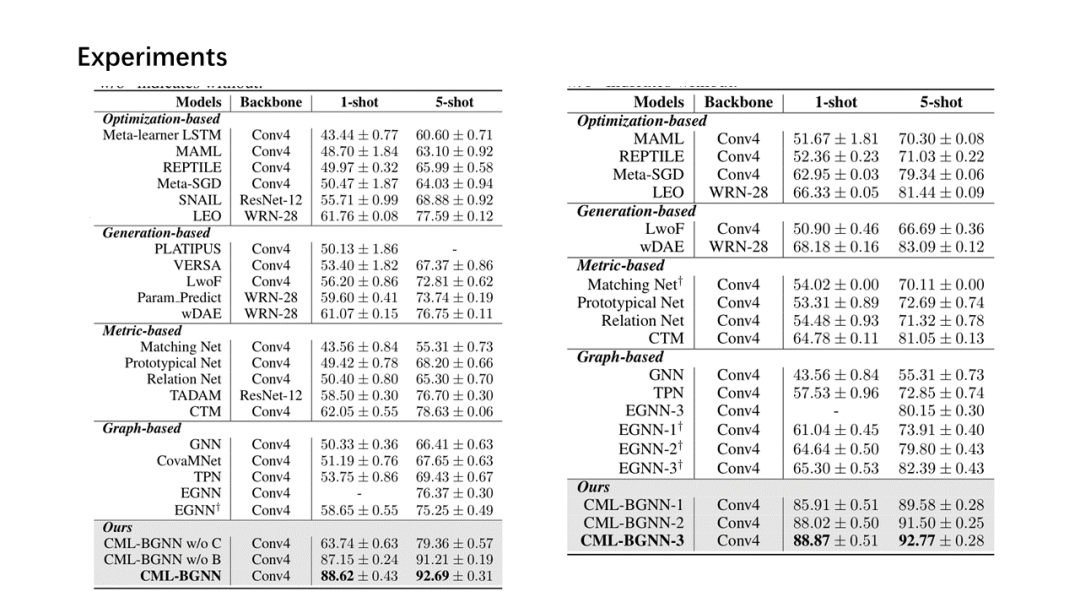
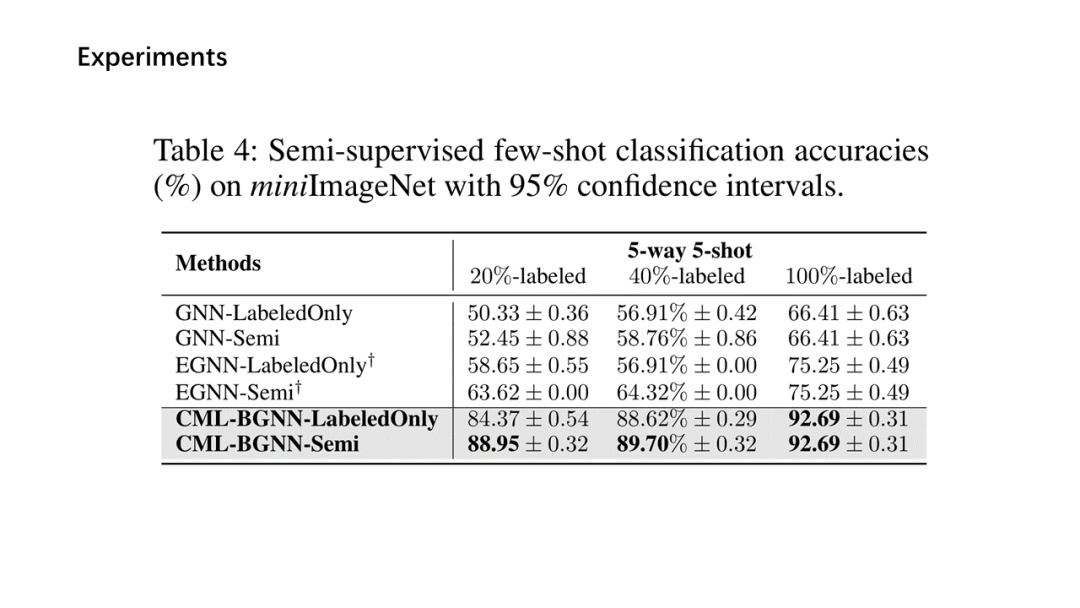
面向少量学习的元学习允许机器利用先前获得的知识作为先验知识,从而提高只需少量数据的新任务的性能。然而,大多数主流模型都存在灾难性遗忘和鲁棒性不足的问题,因此无法完全保留或利用长期知识,同时容易导致严重的错误积累。在这篇文章中,我们提出了一种新的基于贝叶斯图神经网络(CML-BGNN)的连续元学习方法,该方法在数学上把元学习表述为对一系列任务的连续学习。每个任务形成一个图形,任务内部和任务之间的相关性可以通过消息传递和历史转换很好地保存。为了弥补图初始化中的拓扑不确定性,我们利用贝叶斯反向传播策略,该策略利用摊销推理网络逼近任务特定参数的后验分布,该推理网络无缝集成到端到端边缘学习中。在miniImageNet和tieredImageNet数据集上进行的大量实验证明了该方法的有效性和效率,与现有的miniImageNet 5路单镜头分类任务相比,性能提高了42.8%。
英文摘要:
Meta-learning for few-shot learning allowsa machine to leverage previously acquired knowledge as a prior, thus improvingthe performance on novel tasks with only small amounts of data. However, mostmainstream models suffer from catastrophic forgetting and insufficientrobustness issues, thereby failing to fully retain or exploit long-term knowledgewhile being prone to cause severe error accumulation. In this paper, we proposea novel Continual Meta-Learning approach with Bayesian Graph Neural Networks (CML-BGNN)that mathematically formulates meta-learning as continual learning of asequence of tasks. With each task forming as a graph, the intra- and inter-taskcorrelations can be well preserved via message-passing and history transition. Toremedy topological uncertainty from graph initialization, we utilize Bayes byBackprop strategy that approximates the posterior distribution of task-specificparameters with amortized inference networks, which are seamlessly integrated intothe end-to-end edge learning. Extensive experiments conducted on theminiImageNet and tieredImageNet datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiencyof the proposed method, improving the performance by 42.8% compared withstate-of-the-art on the miniImageNet 5-way 1-shot classification task.
原文链接:
https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.04695
文献总结