原标题:Intrinsic dimension of datarepresentations in deep neural networks
作者:Alessio Ansuini Alessandro Laio Jakob H. Macke Davide Zoccolan
中文摘要:
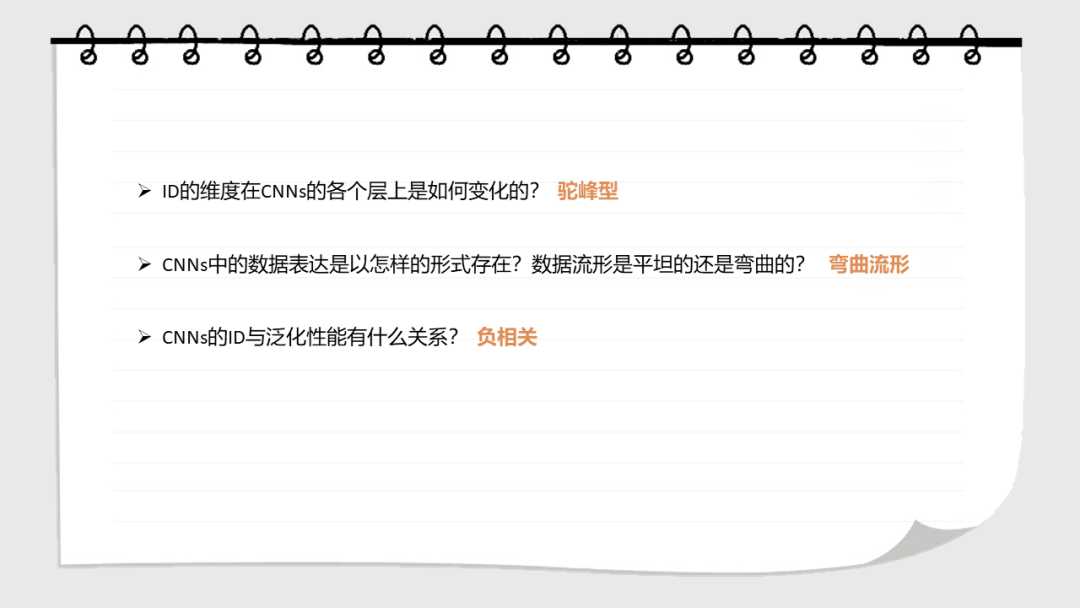
深层神经网络在多个处理层上逐步转换输入。这些网络学习到的表示的几何性质是什么?在这里,我们研究了数据表示的内在维度,即描述表示所需的参数的最小维度。我们发现,在一个训练有素的网络中,ID的数量级小于每层中的单位数。ID从第一层到最后一层的变化是ID先增大,然后逐渐减小。值得注意的是,最后一个隐藏层的ID维度的大小可以预测测试集上的分类精度。这些结果都不能通过线性维度估计(例如,通过主成分分析),或在被人为线性化的表达中发现。在未经训练的网络,以及通过随机标签训练的网络中也没有这种特征。这表明神经网络的泛化能力是那些将数据转换成低维的空间,但不一定是在平坦流形的子空间中。
英文摘要:
Deep neural networks progressively transformtheir inputs across multiple processing layers. What are the geometricalproperties of the representations learned by these networks? Here we study theintrinsic dimensionality (ID) of data-representations, i.e. the minimal number ofparameters needed to describe a representation. We find that, in a trainednetwork, the ID is orders of magnitude smaller than the number of units in eachlayer. Across layers, the ID first increases and then progressively decreasesin the final layers. Remarkably, the ID of the last hidden layer predictsclassification accuracy on the test set. These results can neither be found bylinear dimensionality estimates (e.g., with principal component analysis), nor inrepresentations that had been artificially linearized. They are neither foundin untrained networks, nor in networks that are trained on randomized labels.This suggests that neural networks that can generalize are those that transformthe data into low-dimensional, but not necessarily flat manifolds.
文献总结:




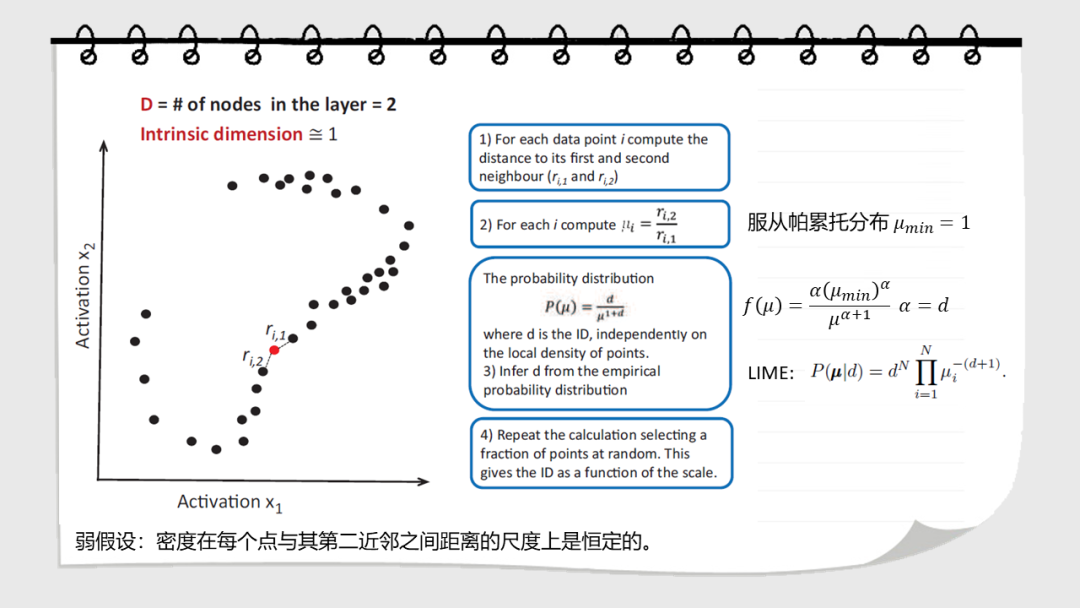


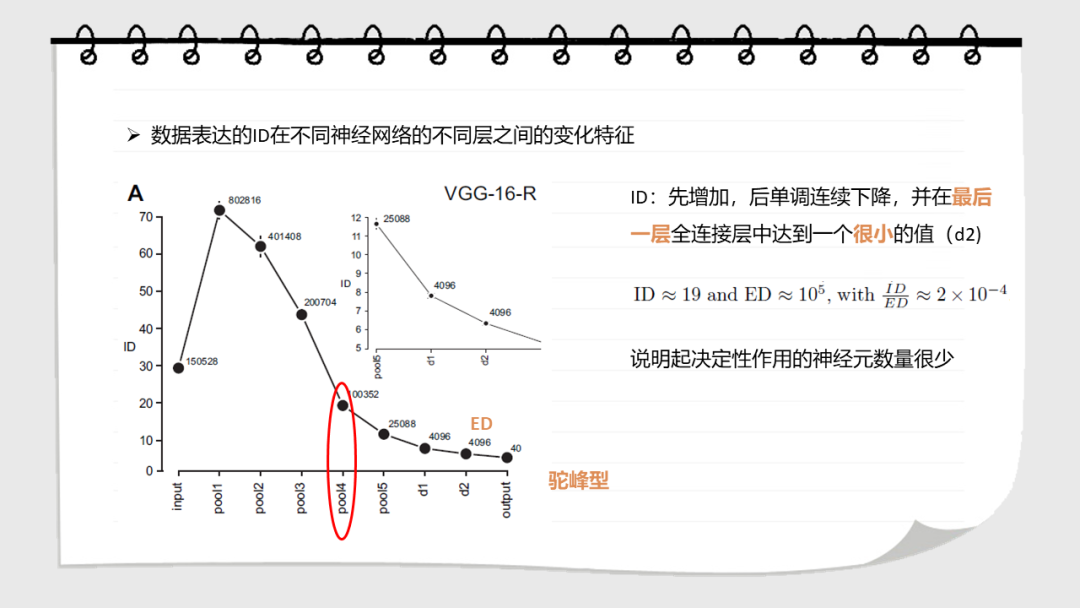
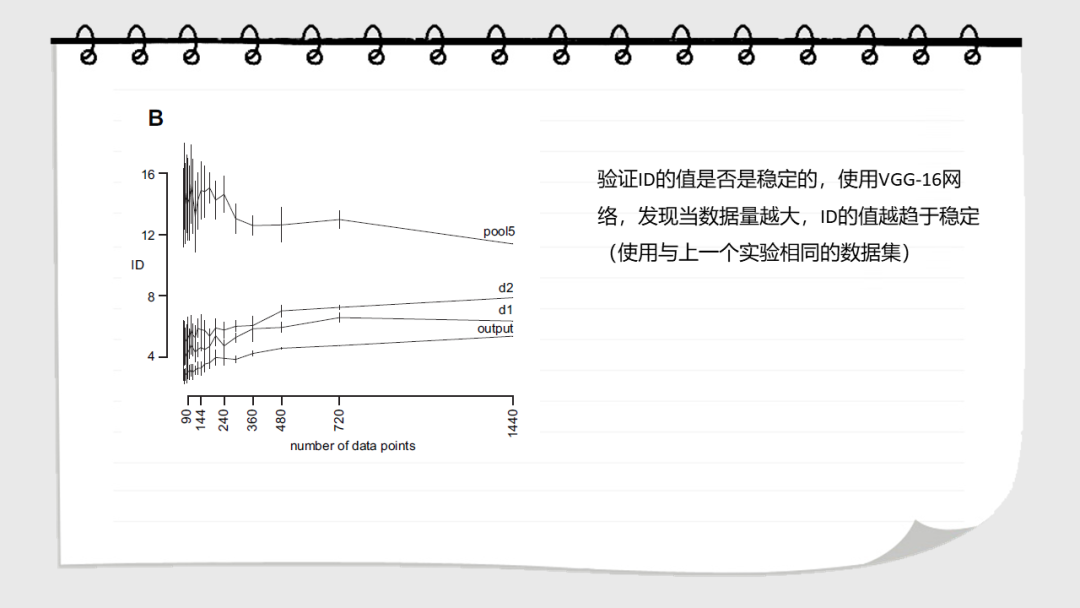

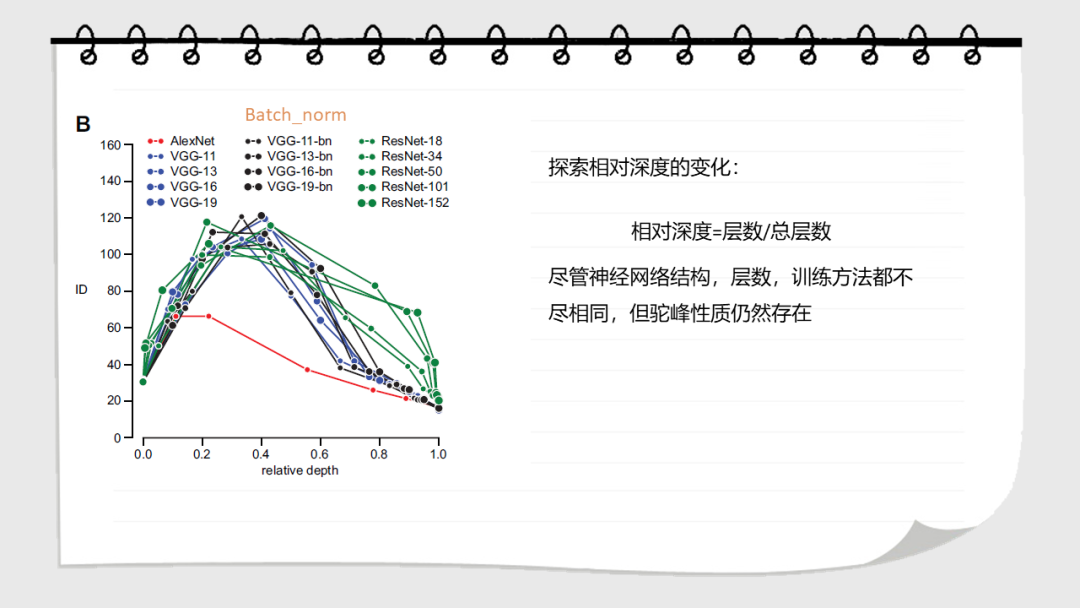
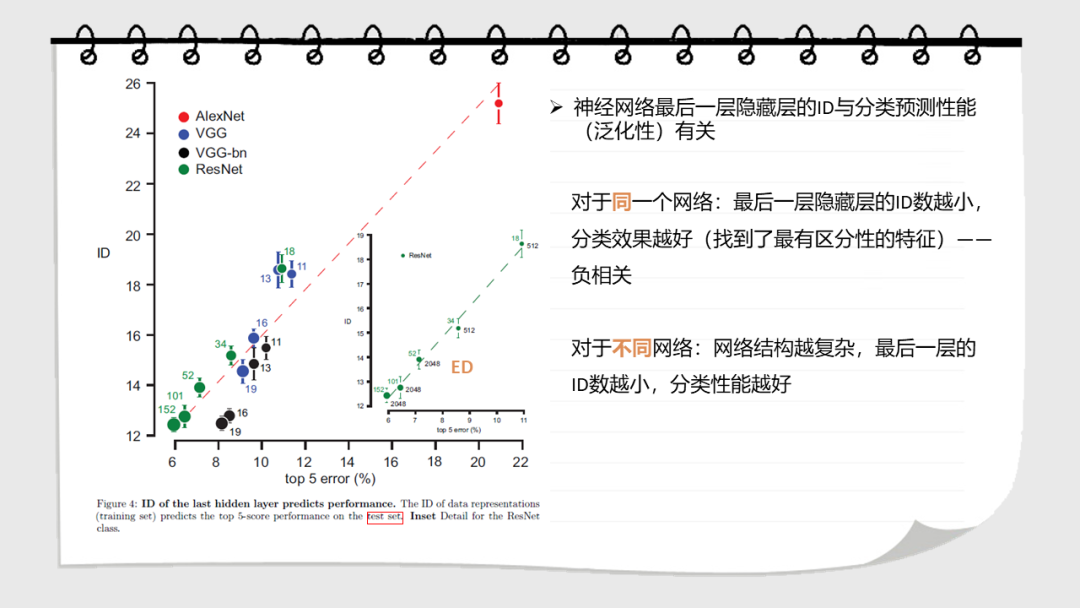
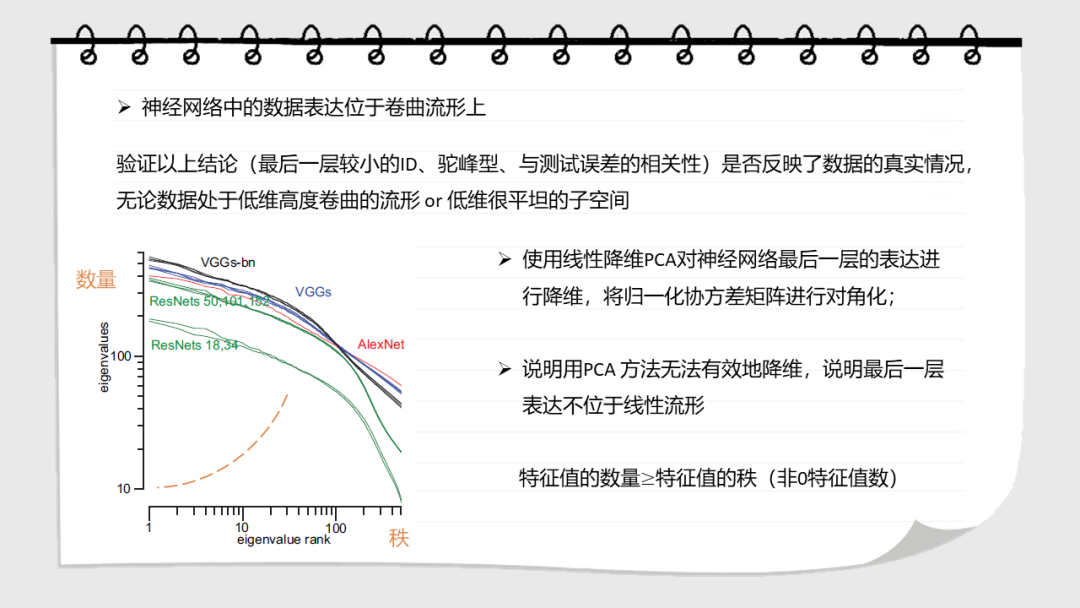
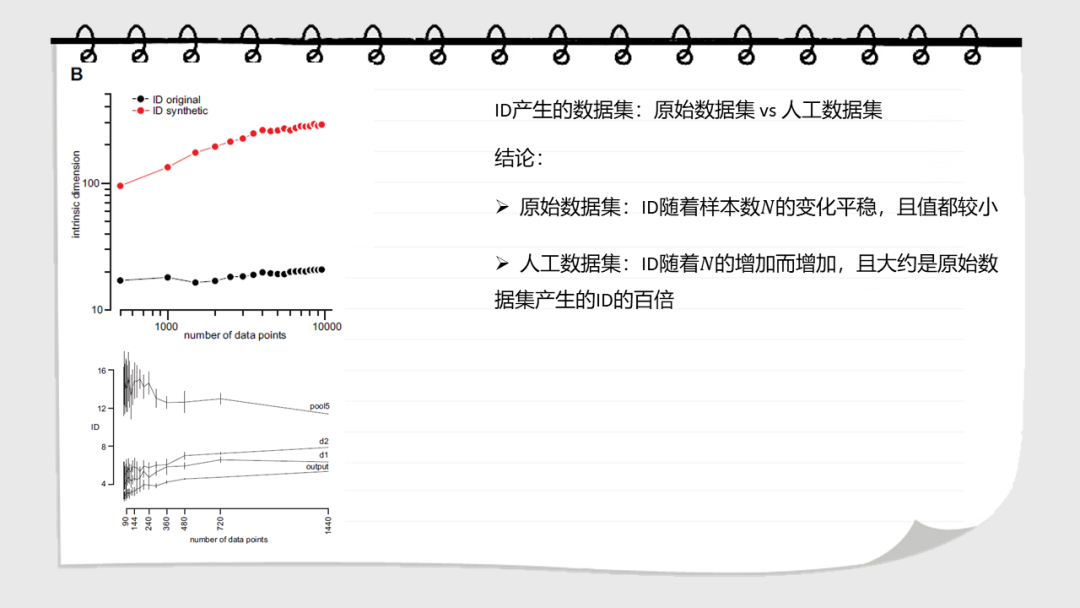
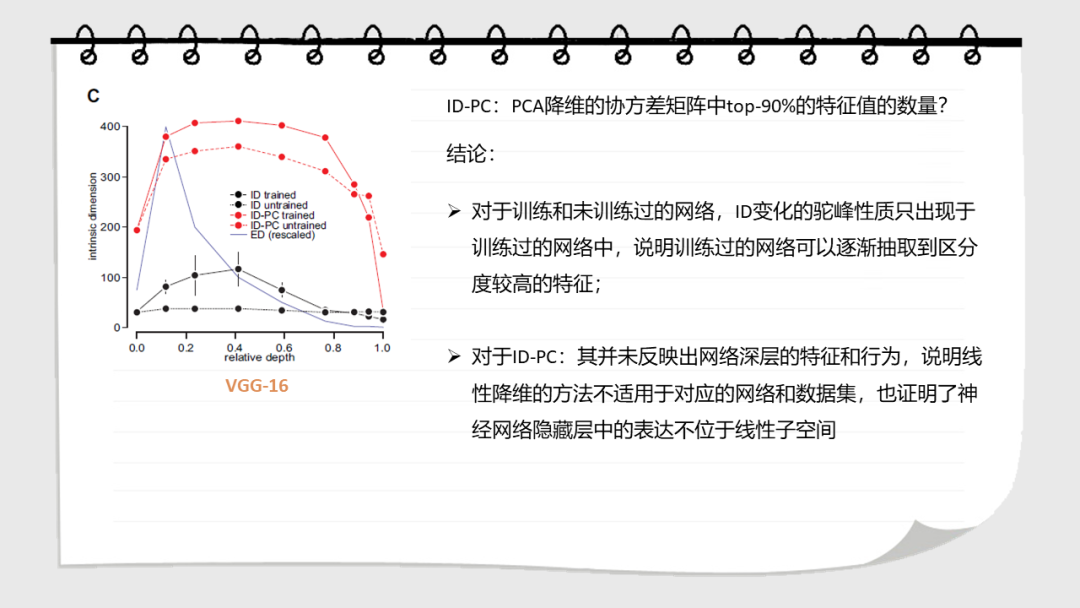


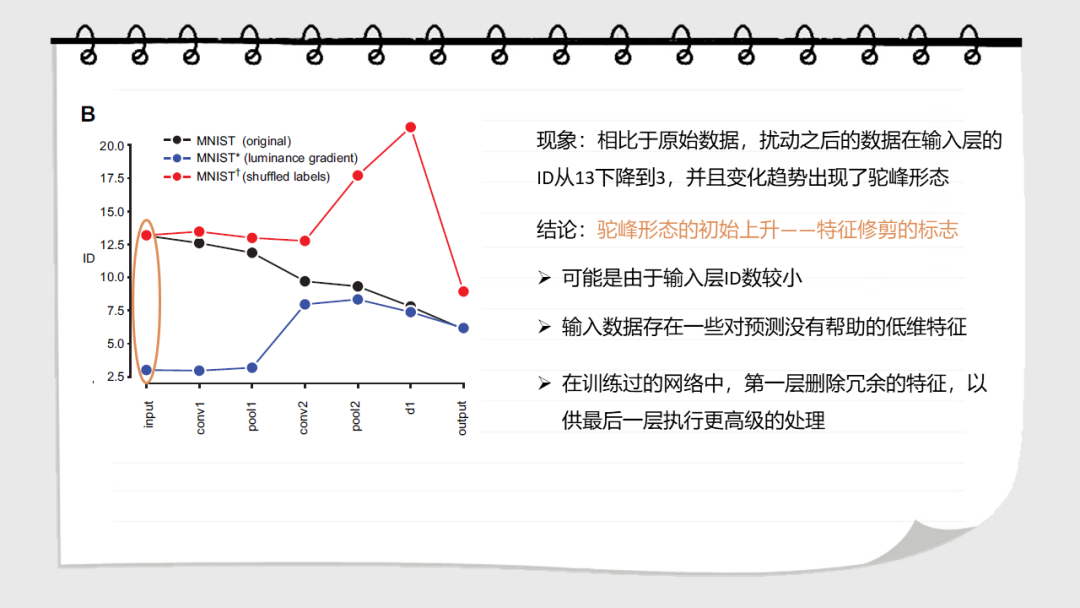
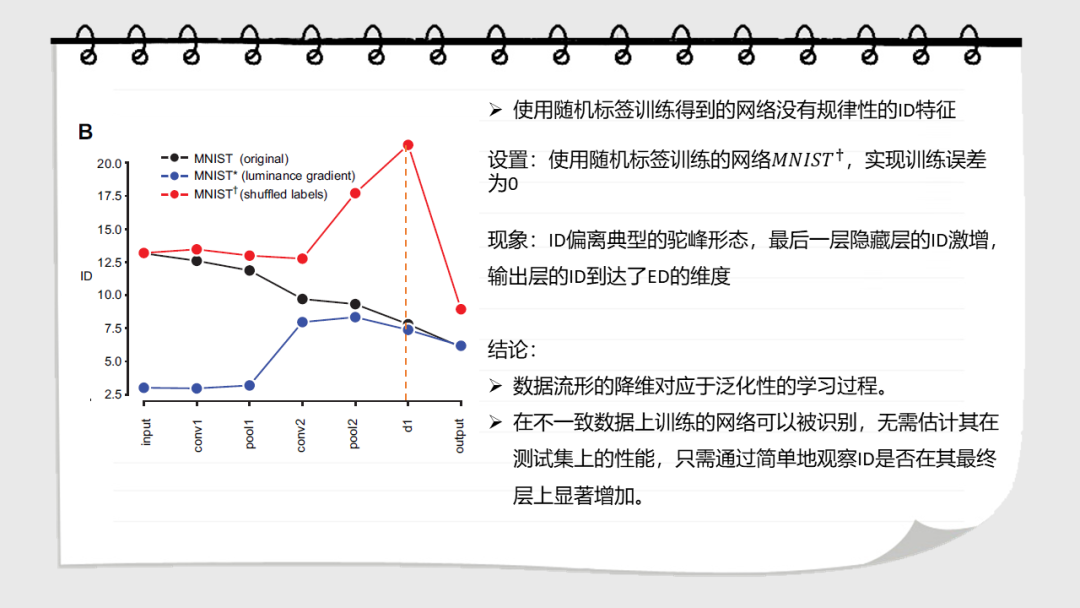

点击“阅读原文”,了解论文详情!






