前 言
MOP 不用多说了,我这里指的就是 MySQL、Oracle、PostgreSQL 三种目前最主流的数据库,MOP 系列打算更新 MOP 三种数据库的索引知识、高可用架构及常用 SQL 语句等等,今天打算介绍一下这三种数据库的索引基础知识,但由于文章过长,前面已经分享了 Oracle 篇,MySQL 篇,今天分享 PG 篇。
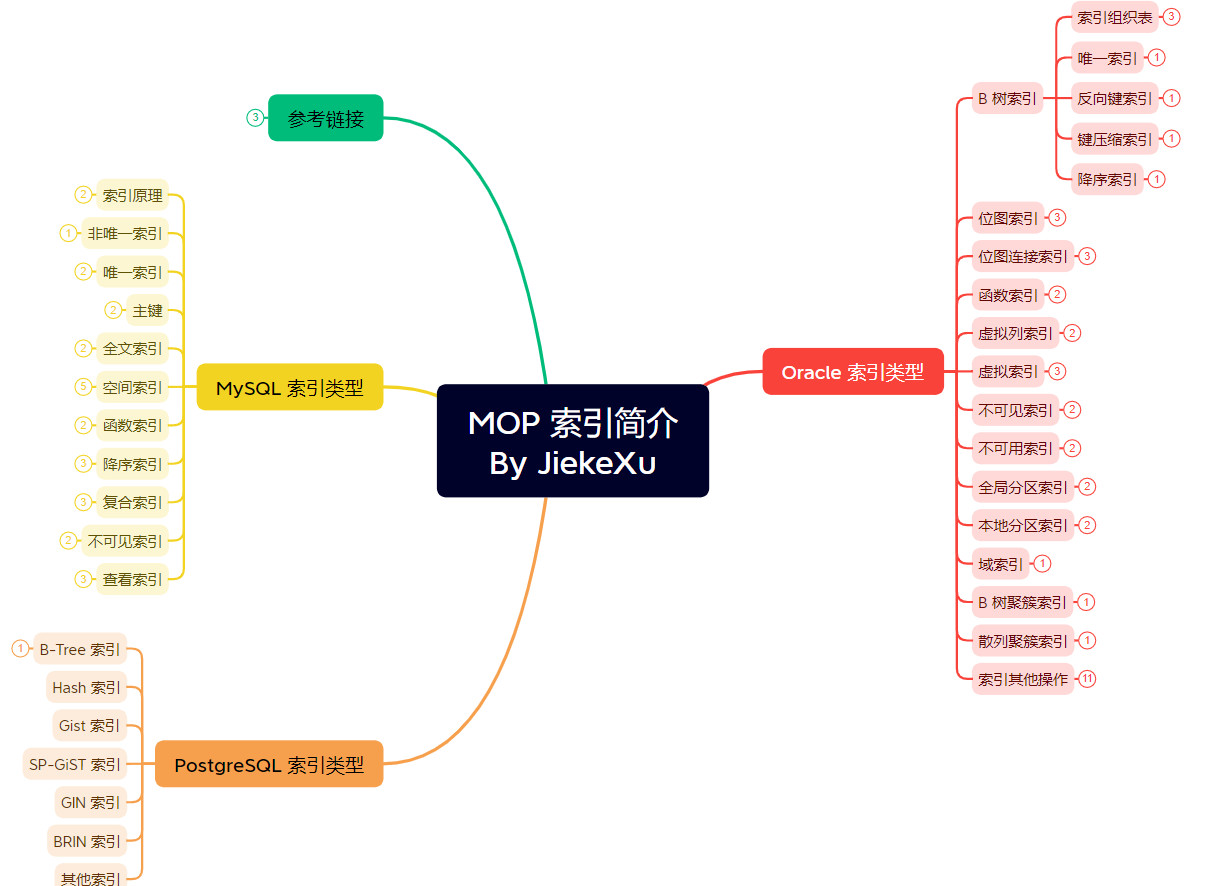
PostgreSQL 索引类型
PostgreSQL 提供了丰富的索引类型,除支持常规的数值类型、字符串类型数据的索引外,还支持时序、空间、JSON等类型数据的索引。PostgreSQL 提供了 B-tree、Hash、GiST、SP-GiST、GIN、BRIN 等多种索引类型,每种索引类型使用不同的算法来适应不同类型的查询。在默认情况下,创建的索引类型为 B-tree 索引。在索引类型名后面加上关键字 USING,可以选择其他的索引类型,例如,创建一个 HASH 索引:
CREATE INDEX name ON table USING HASH (column);
--创建索引的语法如下:
CREATE [ UNIQUE ] INDEX [ CONCURRENTLY ] [ name ] ON
table_name [ USING method ]
( { column_name | ( expression ) } [ COLLATE collation
] [ opclass ] [ ASC | DESC ] [ NULLS { FIRST | LAST } ]
[, ...] )
[ WITH ( storage_parameter = value [, ... ] ) ]
[ TABLESPACE tablespace_name ]
[ WHERE predicate ]
在创建索引的时候 PostgreSQL 会锁定表以防止写入,然后对表做全表扫描,从而完成创建索引的操作。在此过程中,
其他用户仍然可以读取表,但是插入、更新、删除等操作将一直被阻塞,直到索引创建完毕。如果这张表是更新较频繁且比较大的表,那么创建索引可能需要几十分钟,甚至数个小时,这段时间内都不能做任何插入、删除、更新操作,这在大多数的在线数据库中都是不可接受的。鉴于此,PostgreSQL 支持在不长时间阻塞更新的情况下建立创建索引,这是通过在 CREATE INDEX 中加 CONCURRENTLY 选项来实现的。当该选项被启用时,PostgreSQL 会执行表的两次扫描,因此该方法需要更长的时间来建索引。尽管如此,该选项也是很有用的。
修改索引的语法:
ALTER INDEX name RENAME TO new_name
ALTER INDEX name SET TABLESPACE tablespace_name
ALTER INDEX name SET ( storage_parameter = value [, ... ])
ALTER INDEX name RESET ( storage_parameter [, ... ] )
DROP INDEX [ IF EXISTS ] name [, ...] [ CASCADE |RESTRICT ]
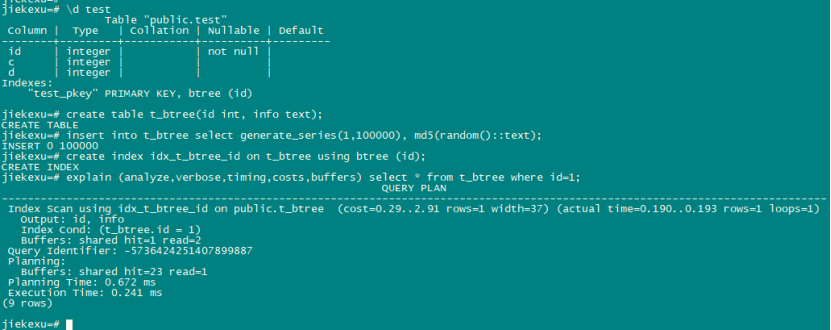
1、B-tree 索引
B-tree 索引使用 B-tree 数据结构来存储索引数据,可用于处理等值查询和范围查询,包括<、<=、=、>=、>等运算符,以及BETWEEN、IN、IS NULL、IS NOT NULL等条件。B-tree 还可以用于查询结果集排序,如 order by 排序。
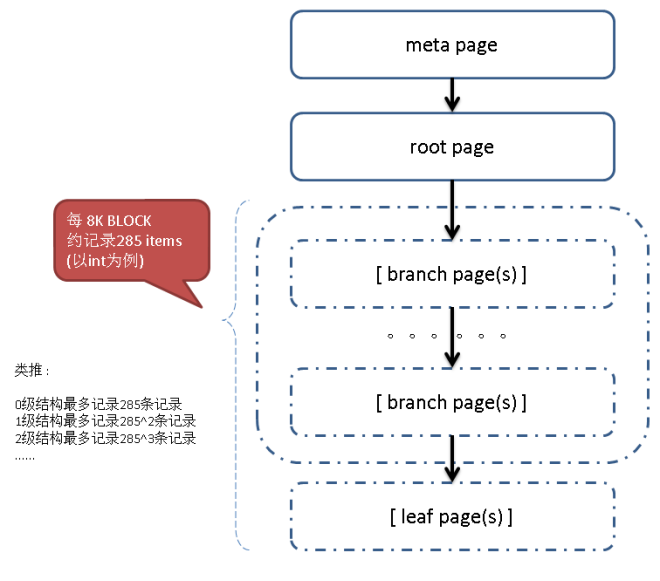
B-Tree 索引结构参考自德哥 https://github.com/digoal/blog/blob/master/201605/20160528_01.md
PostgreSQL 的 B-Tree索引页分为几种类别:
meta page
root page # btpo_flags=2
branch page # btpo_flags=0
leaf page # btpo_flags=1
如果即是 leaf 又是 root 则 btpo_flags=3。
其中 meta page 和 root page 是必须有的,meta page 需要一个页来存储,表示指向 root page 的 page id。随着记录数的增加,一个 root page 可能存不下所有的 heap item,就会有 leaf page,甚至 branch page,甚至多层的 branch page。
一共有几层 branch 和 leaf,就用 btree page 元数据的 level 来表示。
jiekexu=# create table t_btree(id int, info text);
CREATE TABLE
jiekexu=# insert into t_btree select generate_series(1,100000), md5(random()::text);
INSERT 0 100000
jiekexu=# create index idx_t_btree_id on t_btree using btree (id);
CREATE INDEX
jiekexu=# explain (analyze,verbose,timing,costs,buffers) select * from t_btree where id=1;
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Index Scan using idx_t_btree_id on public.t_btree (cost=0.29..2.91 rows=1 width=37) (actual time=0.190..0.193 rows=1 loops=1)
Output: id, info
Index Cond: (t_btree.id = 1)
Buffers: shared hit=1 read=2
Query Identifier: -5736424251407899887
Planning:
Buffers: shared hit=23 read=1
Planning Time: 0.672 ms
Execution Time: 0.241 ms
(9 rows)
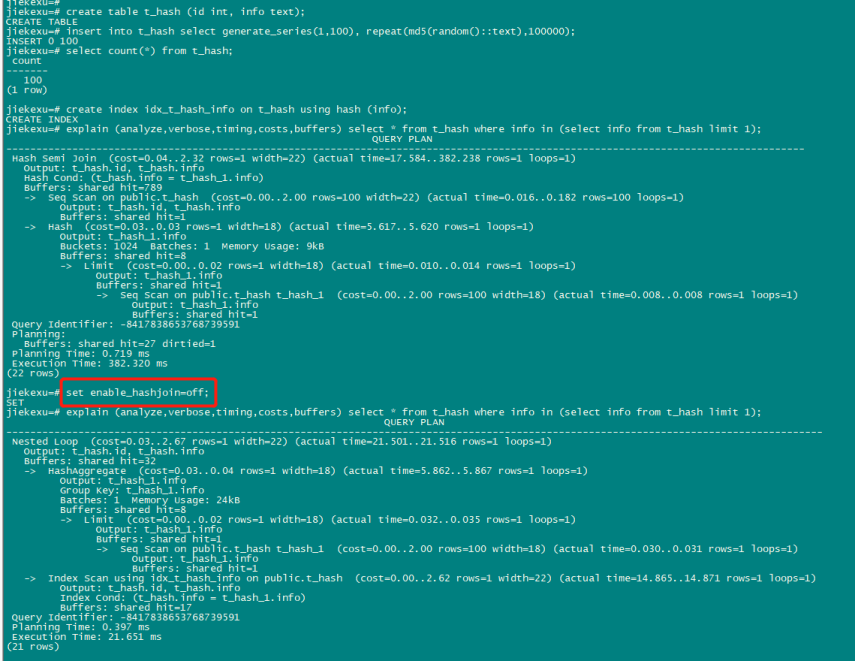
2、Hash 索引
HASH 索引存储一个由索引列计算出的 32 位的 hash code 值。因此,Hash 索引只能处理简单等值比较。每当索引列涉及到等值操作符的比较时,查询规划器将会使用 Hash 索引。
create table t_hash (id int, info text);
insert into t_hash select generate_series(1,100), repeat(md5(random()::text),100000);
create index idx_t_hash_info on t_hash using hash (info);
explain (analyze,verbose,timing,costs,buffers) select * from t_hash where info in (select info from t_hash limit 1);
3、GiST 索引
GiST 是 Generalized Search Trees 的缩写,意思是通用搜索树。它不是单独一种索引类型,而是一种架构,可以在这种架构上实现很多不同的索引策略。GiST 索引定义的特定操作符可以用于特定索引策略。PostgreSQL 的标准发布中包含了用于二维几何数据类型的 GiST操作符类,比如,一个图形包含另一个图形的操作符“@>”,一个图形在另一个图形的左边且没有重叠的操作符“<<”,等等。
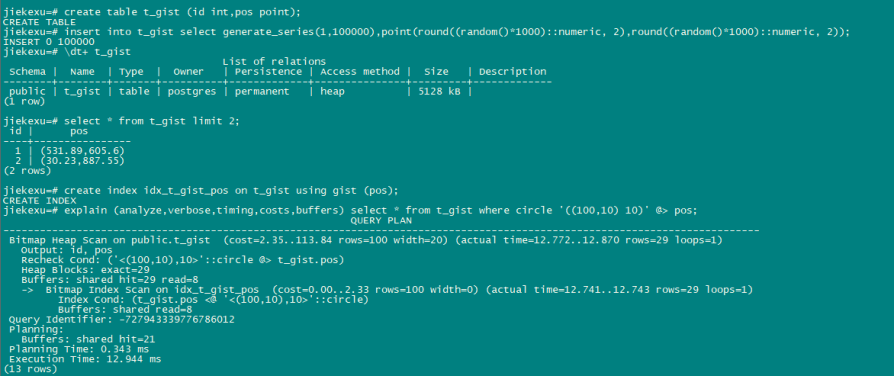
例如几何类型检索
create table t_gist (id int,pos point);
insert into t_gist select generate_series(1,100000),point(round((random()*1000)::numeric, 2),round((random()*1000)::numeric, 2));
create index idx_t_gist_pos on t_gist using gist (pos);
explain (analyze,verbose,timing,costs,buffers) select * from t_gist where circle '((100,10) 10)' @> pos;
4、SP-GiST 索引
SP-GiST 是 “Space-Partitioned GiST” 的缩写,即空间分区 GiST 索引。它是 从PostgreSQL9.2 版本开始提供的一种新索引类型,和 GiST 相似,SP-GiST 索引为支持多种搜索提供了一种基础结构。SP-GiST 允许实现众多不同的非平衡的基于磁盘的数据结构,例如四叉树、k-d 树和 radix 树。主要是通过一些新的索引算法来提高 GiST 索引在某种情况下的性能。
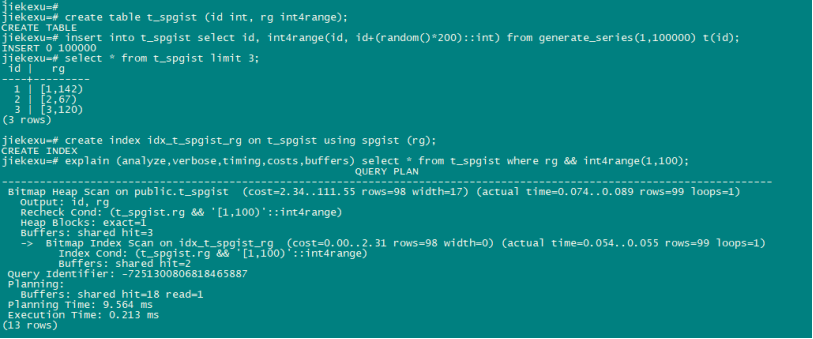
例如 范围类型搜索
create table t_spgist (id int, rg int4range);
insert into t_spgist select id, int4range(id, id+(random()*200)::int) from generate_series(1,100000) t(id);
create index idx_t_spgist_rg on t_spgist using spgist (rg);
explain (analyze,verbose,timing,costs,buffers) select * from t_spgist where rg && int4range(1,100);
5、GIN 索引
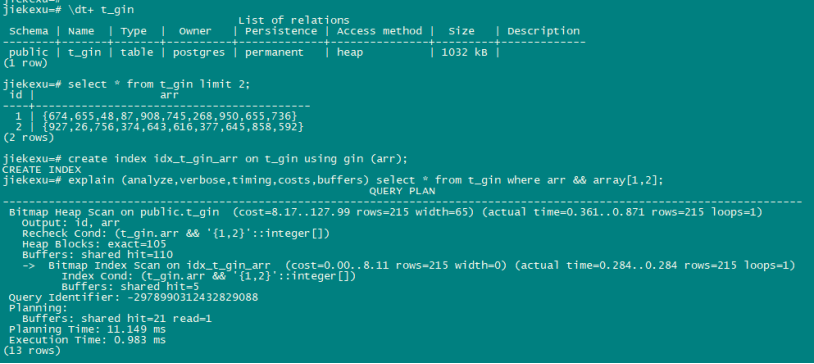
GIN 索引是“倒排索引”,它适合于包含多个组成值的数据值,例如数组。倒排索引中为每一个组成值都包含一个单独的项,它可以高效地处理测试指定组成值是否存在的查询。
create table t_gin (id int, arr int[]);
do language plpgsql $$
declare
begin
for i in 1..10000 loop
insert into t_gin select i, array(select random()*1000 from generate_series(1,10));
end loop;
end;
$$;
select * from t_gin limit 2;
id | arr
----+------------------------------------------
1 | {674,655,48,87,908,745,268,950,655,736}
2 | {927,26,756,374,643,616,377,645,858,592}
(2 rows)
create index idx_t_gin_arr on t_gin using gin (arr);
explain (analyze,verbose,timing,costs,buffers) select * from t_gin where arr && array[1,2];
6、BRIN 索引
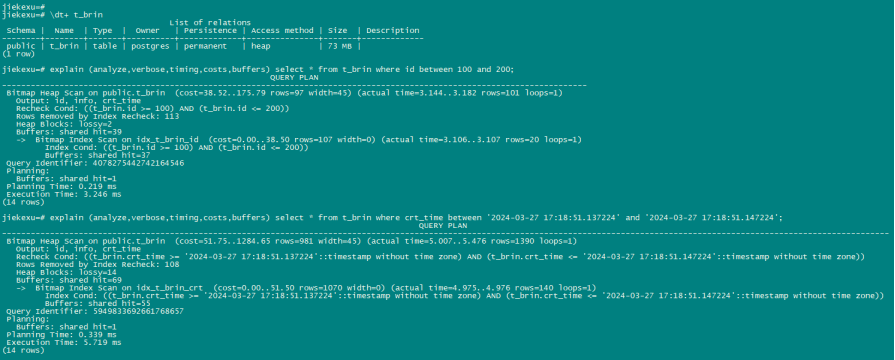
BRIN 索引(块范围索引的缩写)存储有关存放在一个表的连续物理块范围上的值摘要信息。因此,那些值和table中物理行存放顺序相关性更好的列更高效。与 GiST、SP-GiST 和 GIN 相似,BRIN 可以支持很多种不同的索引策略,并且可以与一个 BRIN 索引配合使用的特定操作符取决于索引策略。
BRIN索引是块级索引,它不同于B-tree等索引。BRIN索引在记录数据时,以数据块或每段连续的数据块为单位记录信息,而不是以行号为单位记录索引明细。如果块的边界范围很大,或者说块与块之间的重叠度很高,那么BRIN索引的过滤性就很差。因此,BRIN索引仅适合用于检索存储位置与取值线性相关性很强的字段。如时序数据,在时间或序列字段创建BRIN索引,进行等值、范围查询时效果很 Nice。
create table t_brin (id int,info text,crt_time timestamp);
insert into t_brin select generate_series(1,1000000), md5(random()::text), clock_timestamp();
select correlation from pg_stats where tablename='t_brin' and attname='id';
select correlation from pg_stats where tablename='t_brin' and attname='crt_time';
create index idx_t_brin_id on t_brin using brin (id) with (pages_per_range=1);
create index idx_t_brin_crt on t_brin using brin (crt_time) with (pages_per_range=1);
jiekexu=# \d t_brin
Table "public.t_brin"
Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default
----------+-----------------------------+-----------+----------+---------
id | integer | | |
info | text | | |
crt_time | timestamp without time zone | | |
Indexes:
"idx_t_brin_crt" brin (crt_time) WITH (pages_per_range='1')
"idx_t_brin_id" brin (id) WITH (pages_per_range='1')
explain (analyze,verbose,timing,costs,buffers) select * from t_brin where id between 100 and 200;
explain (analyze,verbose,timing,costs,buffers) select * from t_brin where crt_time between '2024-03-27 17:18:51.137224' and '2024-03-27 17:18:51.147224';
当然一个索引可以定义在表的多个列上,这样的索引称之为多列索引,CREATE INDEX idx_test_cc ON test2 (c1, c2);目前,只有 B-tree、GiST、GIN 和 BRIN 索引类型支持多列索引。是否可以有多个关键列与INCLUDE列是否可以被添加到索引中无关。索引最多可以有 32 列,包括 INCLUDE 列。Currently, only the B-tree, GiST, GIN, and BRIN index types support multiple-key-column indexes. Whether there can be multiple key columns is independent of whether INCLUDE columns can be added to the index. Indexes can have up to 32 columns, including INCLUDE columns. (This limit can be altered when building PostgreSQL; see the file pg_config_manual.h.)
7、表达式索引
一个索引列并不一定是底层表的一个列,也可以是从表的一列或多列计算而来的一个函数或
者标量表达式。和 Oracle 数据库一样,PostgreSQL 也支持函数索引。实际上,PostgreSQL 索引的键除了可以是一个函数外,还可以是从一个或多个字段计算出来的标量表达式。表达式上的索引并不是在索引查找时进行表达式的计算,而是在插入或更新数据行时进行计算,因此在插入或更新时,表达式上的索引会慢一些。
例子 如果我们经常进行如下的查询:
SELECT * FROM people WHERE (first_name || ' ' || last_name) = 'John Smith';
那么值得创建一个这样的索引:
CREATE INDEX people_names ON people ((first_name || ' ' || last_name));
如果我们经常进行如下的查询:
SELECT * FROM mytest WHERE lower(note) = 'hello world';
那么需要创建一个大小写转换的索引:
CREATE INDEX mytest_lower_note_idx ON mytest (lower(note));
8、部分索引
一个部分索引是建立在表的一个子集上,而该子集则由一个条件表达式(被称为部分索引
的谓词)定义。而索引中只包含那些符合该谓词的表行的项。部分索引是一种专门的特性,
但在很多种情况下它们也很有用。
create table test2(id int,info text,crt_time timestamp,active boolean);
create index idx_test2_id on test2(id) where active;
explain (analyze,verbose,timing,costs,buffers) select * from test where active and id=1;
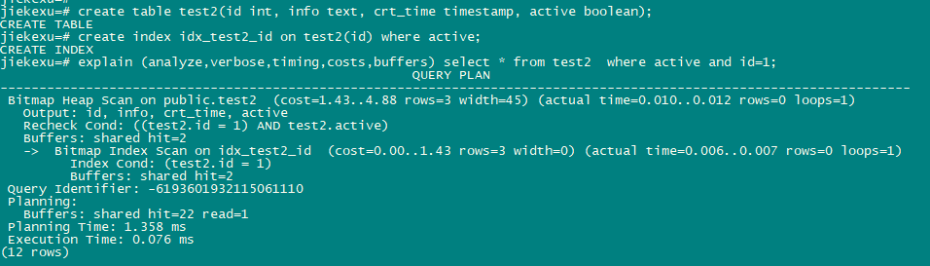
9、全文索引
PostgreSQL 内置了全文检索功能,但内置的功能只能检索英文。PostgreSQL 全文检索的搜索过程实际上使用一个 tsvector 和 tsquery 进行匹配,tsvector 代表了文档,而 tsquery 代表了检索条件,匹配的运算符是“@@”。
postgres=# select 'We Love PostgreSQL Database'::tsvector;
tsvector
-------------------------------------
'Database' 'Love' 'PostgreSQL' 'We'
(1 row)
当然还有 zhparser、rum 等索引插件可以用于全文检索,由于个人能力有限,这里就不介绍了,等以后有时间学习了再介绍。
参考链接
https://docs.oracle.com/en/database/oracle/oracle-database/23/cncpt/indexes-and-index-organized-tables.html#GUID-ACA0308E-5F01-4236-81D3-D0CDE5CB6695 https://docs.oracle.com/en/database/oracle/oracle-database/23/admin/managing-indexes.html#GUID-E637BC13-A2CA-454D-B680-07B95F7C4CE4
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/optimization-indexes.html
https://www.postgresql.org/files/documentation/pdf/16/postgresql-16-A4.pdf
全文完,希望可以帮到正在阅读的你,如果觉得有帮助,可以分享给你身边的朋友,同事,你关心谁就分享给谁,一起学习共同进步~~~
❤️ 欢迎关注我的公众号【JiekeXu DBA之路】,一起学习新知识!
————————————————————————————
公众号:JiekeXu DBA之路
墨天轮:https://www.modb.pro/u/4347
CSDN :https://blog.csdn.net/JiekeXu
ITPUB:https://blog.itpub.net/69968215
腾讯云:https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/user/5645107
————————————————————————————







