前言
对于逻辑解码,如果要发布 UPDATE 和 DELETE,复制标识 (replica identity) 必不可少,总共有 4 种策略:
默认模式 (default):非系统表采用的默认模式,如果有主键,则用主键列作为身份标识 索引模式 (index):将某一个符合条件的索引中的列,用作身份标识 完整模式 (full):将整行记录中的所有列作为复制标识 无身份模式 (nothing):不记录任何复制标识,这意味着update和delete操作无法复制到订阅者上
但是很多情况下,可能无法建立主键或者唯一索引 (比如就是有重复值),那么作为最后的兜底模式——FULL,官方建议不到万不得已,不要使用该模式。那么,是否 FULL 模式就真的一无是处呢?
危害
官网对于 FULL 模式的介绍是:
If the table does not have any suitable key, then it can be set to replica identity “full”, which means the entire row becomes the key. This, however, is very inefficient and should only be used as a fallback if no other solution is possible. If a replica identity other than “full” is set on the publisher side, a replica identity comprising the same or fewer columns must also be set on the subscriber side.
如果表没有任何合适的键,则可以将复制标识设置为"full",这意味着整行都成为键。然而,这是非常低效的,只有在没有其他解决方案可行的情况下才应用作后备方案。如果在发布端设置了除"FULL"之外的副本标识,那么还必须在订阅方设置包含相同或更少列的副本标识。
以 wal2json 为例,如果没有复制标识,是无法解析 oldkey 的,报错信息十分明显:WARNING: table "t1" without primary key or replica identity is nothing。主键和唯一索引就不讨论了,让我们看看 FULL 模式:
postgres=# create table t1(id int,info text,t_time timestamp);
CREATE TABLE
postgres=# alter table t1 replica identity full;
ALTER TABLE
postgres=# select pg_create_logical_replication_slot('myslot','wal2json');
pg_create_logical_replication_slot
------------------------------------
(myslot,8/D807C318)
(1 row)
postgres=# insert into t1 values(1,'hello',now());
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# update t1 set id = 99 where id = 1;
UPDATE 1
接收变更的方式有很多种,可以使用标准 SQL,也可以基于 walsender,甚至可以写一段代码,基于 replication 协议去获取。

此处使用自带的 pg_recvlogical 进行观察:
[postgres@mypg ~]$ pg_recvlogical -d postgres --slot myslot --start -o pretty-print=1 -o add-msg-prefixes=wal2json -f -
{
"change": [
{
"kind": "insert",
"schema": "public",
"table": "t1",
"columnnames": ["id", "info", "t_time"],
"columntypes": ["integer", "text", "timestamp without time zone"],
"columnvalues": [1, "hello", "2024-04-04 22:23:24.362073"]
}
]
}
{
"change": [
{
"kind": "update",
"schema": "public",
"table": "t1",
"columnnames": ["id", "info", "t_time"],
"columntypes": ["integer", "text", "timestamp without time zone"],
"columnvalues": [99, "hello", "2024-04-04 22:23:24.362073"],
"oldkeys": {
"keynames": ["id", "info", "t_time"],
"keytypes": ["integer", "text", "timestamp without time zone"],
"keyvalues": [1, "hello", "2024-04-04 22:23:24.362073"]
}
}
]
}
可以看到,对于更新,oldkeys 的解析,将所有列都解析了出来——id、info、t_time。
为了便于观察,让我们再使用主键模式看下:
postgres=# alter table t1 add primary key(id);
ALTER TABLE
postgres=# alter table t1 replica identity default ;
ALTER TABLE
postgres=# insert into t1 values(1,'hello',now());
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# update t1 set id = 98 where id = 1;
UPDATE 1
这一次差异就很明显了,oldkeys,只将标识列 id 给解析了出来,不过这完全是预期之内的。
{
"change": [
{
"kind": "insert",
"schema": "public",
"table": "t1",
"columnnames": ["id", "info", "t_time"],
"columntypes": ["integer", "text", "timestamp without time zone"],
"columnvalues": [1, "hello", "2024-04-04 22:26:22.183715"]
}
]
}
{
"change": [
{
"kind": "update",
"schema": "public",
"table": "t1",
"columnnames": ["id", "info", "t_time"],
"columntypes": ["integer", "text", "timestamp without time zone"],
"columnvalues": [98, "hello", "2024-04-04 22:26:22.183715"],
"oldkeys": {
"keynames": ["id"],
"keytypes": ["integer"],
"keyvalues": [1]
}
}
]
}
不难理解,通过主键就可以快速定位到某一行,订阅端借助身份列也可以快速定位到某一行 (索引扫描),提升效率。所以这也是为什么要求如果使用的是主键模式或索引模式,订阅端也必须存在相对应的主键和唯一索引,如果不存在,那么订阅端会直接报错:
logical replication target relation ""public.t1"" has neither REPLICA IDENTITY index nor PRIMARY KEY and published relation does not have REPLICA IDENTITY FULL.
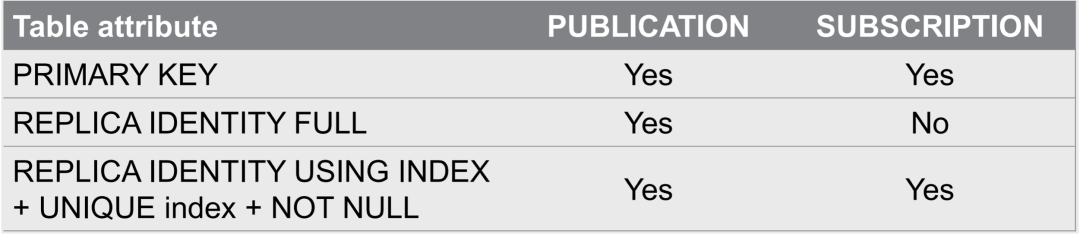
而如果你使用的是 FULL 模式,那么就没有这个要求——订阅端可以没有主键和索引,这个也算是 FULL 模式为数不多的"优势"了。但是其危害不言而喻,每一行都需要在订阅端全表扫描,很容易就将订阅端拖垮!
TOAST
现在,让我们再考虑一个微妙的问题——TOAST,那如果表中有 TOASTed 值怎么办?让我们验证一下:
postgres=# create table toast_demo(id int primary key, content text);
CREATE TABLE
postgres=# with dummy_string as
( select string_agg (md5(random()::text),'') as dummy
from generate_series(1,5000) )
insert into toast_demo
select 1
, dummy_string.dummy
from dummy_string;
INSERT 0 1
插入动作会触发 TOAST,现在让我们更新一下 (不更新 content 字段):
postgres=# update toast_demo set id = 99 where id = 1;
UPDATE 1
可以看到,这种情况下,解析出来的列 columnnames 是压根没有 content 列的
{
"change": [
{
"kind": "update",
"schema": "public",
"table": "toast_demo",
"columnnames": ["id"],
"columntypes": ["integer"],
"columnvalues": [99],
"oldkeys": {
"keynames": ["id"],
"keytypes": ["integer"],
"keyvalues": [1]
}
}
]
}
现在,让我们使用 FULL 模式再试一下:
postgres=# alter table toast_demo replica identity full ;
ALTER TABLE
postgres=# update toast_demo set id = 100 where id = 99;
UPDATE 1
这次,虽然 columnnames 依旧不包含 content,但是 oldkeys 是包括在内的,包括这个巨长无比的值
{
"change": [
{
"kind": "update",
"schema": "public",
"table": "toast_demo",
"columnnames": ["id"],
"columntypes": ["integer"],
"columnvalues": [100],
"oldkeys": {
"keynames": ["id", "content"],
"keytypes": ["integer", "text"],
"keyvalues": [99, "此处省略,特别特别长的值...."]
}
}
]
}
所以,如果你的表包括 TOAST,并且业务行为需要获取更改后的值 (newkeys) 以及更改前的值 (oldkeys),那么将复制标识设为 FULL 可以使 PostgreSQL 也将额外的 TOAST 列解析出来,即使没有操作 TOAST 列。至于为何会这样,当然和 TOAST 原理息息相关
UPDATE 一个普通表时,当该表的 TOAST 表存储的数据没有修改时,TOAST 表不需要更新,在此例中还可以看到,非 FULL 模式也压根没有解析出来。 由于 TOAST 在物理存储上和普通表分开,所以当 SELECT 时没有查询被 TOAST 的列数据时,不需要把这些 TOAST 的页面加载到内存,从而加快了检索速度并且节约了使用空间。 在排序时,由于 TOAST 和普通表存储分开,当针对非 TOAST 字段排序时大大提高了排序速度。
性能影响
但是前面也提了,FULL 模式会导致在订阅端每一行都是全表扫描,分分钟就将订阅端打垮。那有没有解决办法?当然有,在 16 版本中,关于逻辑复制,其实还引入了一个十分重要的特性
Improve performance for logical replication apply without a primary key (Onder Kalaci, Amit Kapila)
Specifically, REPLICA IDENTITY FULL can now use btree indexes rather than sequentially scanning the table to find matches.
也就是说,如果你使用的是 FULL 模式,还可以借助额外的 BTREE 索引,加速扫描,以找到匹配项。因此,在 16 版本的官网中,就有所不同了
If the table does not have any suitable key, then it can be set to replica identity FULL, which means the entire row becomes the key. When replica identity FULL is specified, indexes can be used on the subscriber side for searching the rows. Candidate indexes must be btree, non-partial, and the leftmost index field must be a column (not an expression) that references the published table column. These restrictions on the non-unique index properties adhere to some of the restrictions that are enforced for primary keys. If there are no such suitable indexes, the search on the subscriber side can be very inefficient, therefore replica identity FULL should only be used as a fallback if no other solution is possible.
如果表没有任何合适的键,则可将其设置为复制标识 FULL,这意味着整条记录都将成为键。指定复制标识 FULL 时,可以在用户端使用索引搜索行。候选索引必须是 BTREE、非部分索引,最左边的索引字段必须引用已发布表列的列 (而不是表达式)。这些对非唯一索引属性的限制与主键的一些限制相同。如果没有合适的索引,订阅端的搜索效率会非常低,因此只有在没有其他解决方案的情况下,才应将复制标识 FULL 作为备用方案使用。
让我们看下 16 的代码
/*
* Simple case, we already have a primary key or a replica identity index.
*/
idxoid = GetRelationIdentityOrPK(localrel);
if (OidIsValid(idxoid))
return idxoid;
if (remoterel->replident == REPLICA_IDENTITY_FULL)
{
/*
* We are looking for one more opportunity for using an index. If
* there are any indexes defined on the local relation, try to pick a
* suitable index.
*
* The index selection safely assumes that all the columns are going
* to be available for the index scan given that remote relation has
* replica identity full.
*
* Note that we are not using the planner to find the cheapest method
* to scan the relation as that would require us to either use lower
* level planner functions which would be a maintenance burden in the
* long run or use the full-fledged planner which could cause
* overhead.
*/
return FindUsableIndexForReplicaIdentityFull(localrel, attrMap);
}
如果是 REPLICA_IDENTITY_FULL,则进入到 IsIndexUsableForReplicaIdentityFull 函数中,通过遍历表中所有可用的索引,寻找第一个满足条件的索引。
/*
* Returns true if the index is usable for replica identity full.
*
* The index must be btree, non-partial, and the leftmost field must be a
* column (not an expression) that references the remote relation column.
* These limitations help to keep the index scan similar to PK/RI index
* scans.
*
* attrmap is a map of local attributes to remote ones. We can consult this
* map to check whether the local index attribute has a corresponding remote
* attribute.
*
* Note that the limitations of index scans for replica identity full only
* adheres to a subset of the limitations of PK/RI. For example, we support
* columns that are marked as [NULL] or we are not interested in the [NOT
* DEFERRABLE] aspect of constraints here. It works for us because we always
* compare the tuples for non-PK/RI index scans. See
* RelationFindReplTupleByIndex().
*
* XXX: There are no fundamental problems for supporting non-btree indexes.
* We mostly need to relax the limitations in RelationFindReplTupleByIndex().
* For partial indexes, the required changes are likely to be larger. If
* none of the tuples satisfy the expression for the index scan, we fall-back
* to sequential execution, which might not be a good idea in some cases.
*/
bool
IsIndexUsableForReplicaIdentityFull(IndexInfo *indexInfo, AttrMap *attrmap)
{
AttrNumber keycol;
/* The index must be a Btree index */
if (indexInfo->ii_Am != BTREE_AM_OID)
return false;
/* The index must not be a partial index */
if (indexInfo->ii_Predicate != NIL)
return false;
Assert(indexInfo->ii_NumIndexAttrs >= 1);
/* The leftmost index field must not be an expression */
keycol = indexInfo->ii_IndexAttrNumbers[0];
if (!AttributeNumberIsValid(keycol))
return false;
/*
* And the leftmost index field must reference the remote relation column.
* This is because if it doesn't, the sequential scan is favorable over
* index scan in most cases.
*/
if (attrmap->maplen <= AttrNumberGetAttrOffset(keycol) ||
attrmap->attnums[AttrNumberGetAttrOffset(keycol)] < 0)
return false;
return true;
}
那么怎样的索引算是满足条件?注释也很明显,必须是 BTREE,不能是唯一索引,并且最左边的字段必须是引用发布端表列的列 (不能是表达式),前两个限制不难理解,和索引模式类似,至于最后的"最左原则"则更加简单了,如果不这样做,在大多数情况下,顺序扫描比索引扫描更有利。
小结
所以,如果你的业务面临着这样的需求:
必须要获取更改前以及更改后的值,那么在 UPDATE 和 DELETE 操作中,Postgres 仅包含标识列更新前的值,这种情况下,你便需要设置为 FULL TOAST,如果 UPDATE 很少更新 TOAST 列,并且你也需要这一列,那么也需要设置为 FULL
在 16 之前的版本,就要格外小心了,因为每一行都会导致订阅端全表扫描。在 16 之后,这种情况有所缓解,可以借助索引加速扫描。
除了订阅端,发布端也会受到一定影响,因为需要解析所有的值,自然 WAL 里面需要存储更多的数据,进而导致需要向订阅端传输更多数据,导致 IO 带宽增加,CPU 使用率升高等。如果还包括 TOAST,还需要加载到内存中,先进行 detoast,才能写入到 WAL,内消耗存也会进一步加剧。
static HeapTuple
ExtractReplicaIdentity(Relation relation, HeapTuple tp, bool key_required,
bool *copy)
{
TupleDesc desc = RelationGetDescr(relation);
char replident = relation->rd_rel->relreplident;
Bitmapset *idattrs;
HeapTuple key_tuple;
bool nulls[MaxHeapAttributeNumber];
Datum values[MaxHeapAttributeNumber];
*copy = false;
if (!RelationIsLogicallyLogged(relation))
return NULL;
if (replident == REPLICA_IDENTITY_NOTHING)
return NULL;
if (replident == REPLICA_IDENTITY_FULL)
{
/*
* When logging the entire old tuple, it very well could contain
* toasted columns. If so, force them to be inlined.
*/
if (HeapTupleHasExternal(tp))
{
*copy = true;
tp = toast_flatten_tuple(tp, desc);
}
return tp;
}
参考
https://www.postgresql.fastware.com/blog/discussing-postgresql-what-changes-in-version-16
推荐阅读
Feel free to contact me
微信公众号:PostgreSQL学徒 Github:https://github.com/xiongcccc 微信:_xiongcc 知乎:xiongcc 墨天轮:https://www.modb.pro/u/3958






