In the micro service, we always use RESTFul API as communication protocol which pass data using JSON format. So the mapping between JSON and Data Model is an essential work for every system.
In this blog, we will see how Scala use Circe library to do this type of work.
What is Circe?
Circe is a functional JSON library for Scala, its initial name is jfc which means JSON for cats. From this name, we can know it is based on the cats library.
In this Issue, the author talked about why he change the name to Circe.
The motivation of Circe is from Argonaut and make some important changes.
How to install?
The latest version is 0.12.3
, add the following code to build.sbt
libraryDependencies ++= Seq(
"io.circe" %% "circe-core" % "0.12.3",
"io.circe" %% "circe-generic" % "0.12.3",
"io.circe" %% "circe-parser" % "0.12.3"
)
circe-core
defines the core data type and type classes of Circecirce-generic
use Shapeless to auto-generate Decoder/Encoder for data model(case class).circe-parser
defines some implementation ofParser
type class to give an entry of decoding JSON.
What we can find in this library?
The workflow of Circe looks like this
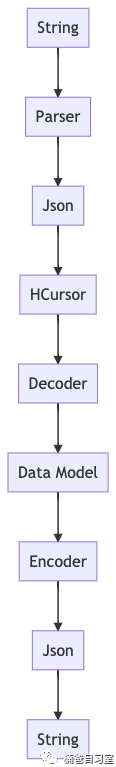
Let's give a high-level overview of this library.
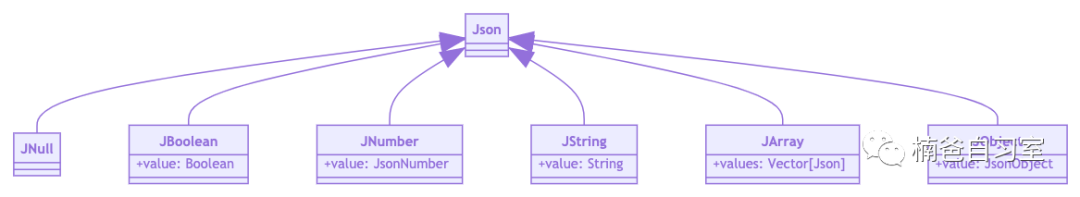
Data Type
To process JSON flexibly and easily, Circe defines a data type called Json
to describe any JSON string.
To convert the Json
to any other data model, Circe defines a data type Cursor
to get the value of given key.
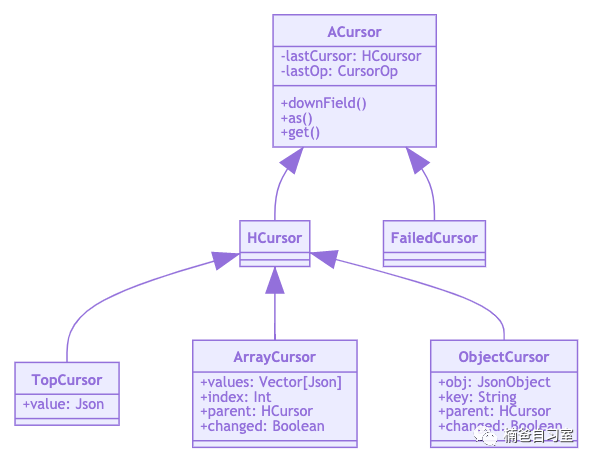
You may notice the Cursor
has two methods to get the expected type of value from given key or the current Json
final def as[A](implicit d: Decoder[A]): Decoder.Result[A] = d.tryDecode(this)
final def get[A](k: String)(implicit d: Decoder[A]): Decoder.Result[A] = downField(k).as[A]
These are the most popular methods we will use in Circe.
And there are lots of other methods which can move the current cursor(use new Json to construct a new cursor) to help us to do operation on expected Json
, such as downField
, downArray
.
Type Classes
Decoder
trait Decoder[A] {
def apply(c: HCursor): Decoder.Result[A]
}
By constructing a Decoder
instance, we can tell Cursor
how to convert the current Json
to given data model.
Parser
trait Parser {
def parse(input: String): Either[ParsingFailure, Json]
def decode[A: Decoder](input: String): Either[Error, A]
}
Parser
is used to convert String
to Json
and defined in circe-core
,
its implementation is defined in circe-parser
package which use jawn to do this work.
Encoder
trait Encoder[A] {
def apply(a: A): Json
}
implicit class EncoderOps[A](val wrappedEncodeable: A) {
def asJson(implicit encoder: Encoder[A]): Json = encoder(wrappedEncodeable)
def asJsonObject(implicit encoder: ObjectEncoder[A]): JsonObject =
encoder.encodeObject(wrappedEncodeable)
}
To implement Encoder
easily, Json
supply some methods such as Json.obj
, Json.arr
to help us.
For the type A
which already has an Encoder
instance, we can just use a.asJson
to convert it to Json
How to decode JSON to data model?
Say we have a raw JSON string like this
{
"id": "1100101010101",
"person": {
"name": "Job",
"age": 18
}
}
And we want to convert it to the model IdCard
case class Person(name: String, age: Int)
case class IdCard(id: String, person: Person)
How should we do it?
Define Decoder by ourself
To convert Json
to IdCard
, we need to define a Decoder
instance for IdCard
implicit val idCardDecoder: Decoder[IdCard] = new Decoder[IdCard] {
override def apply(c: HCursor): Decoder.Result[IdCard] = for {
id <- c.get[String]("id")
name <- c.downFeild("person").get[String]("name")
age <- c.downFeild("person").get[Int]("name")
} yield IdCard(id, Person(name, age))
}
You may notice
We use c.get[A]
to get the value of given key under current levelWe use c.downFeild(<key>)
to go to the next level with given key, and usec.get[A]
again to get the value at that level.
Then we can use the Decoder
instance like this
import io.circe.parser.decode
import io.circe.Error
val jsonStr: String = ???
val idCard:Either[Error, IdCard] = decode[IdCard](jsonStr)
Use the existing Decoder in another Decoder
You may notice, when we get the name
and age
, we need to do c.downFeild("person")
.
Actually we can remove this operation by define a separated Decoder
instance for Person
and then reuse it in the idCardDecoder
implicit val personDecoder: Decoder[Person] = new Decoder[Person] {
override def apply(c: HCursor): Decoder.Result[Person] = for {
name <- c.get[String]("name")
age <- c.get[Int]("age")
} yield Person(name, age)
}
implicit val idCardDecoder: Decoder[IdCard] = new Decoder[IdCard] {
override def apply(c: HCursor): Decoder.Result[IdCard] = for {
id <- c.get[String]("id")
person <- c.get[Person]("person")
} yield IdCard(id, person)
}
Use auto-generated Decoder
Actually the above definitions of Decoder
have lots of boilerplate, we can definitely generate it automatically, just like this
import io.circe.generic.auto._
import io.circe.parser.decode
import io.circe.Error
val jsonStr: String = ???
val idCard:Either[Error, IdCard] = decode[IdCard](jsonStr)
We just need to import io.circe.generic.auto._
, the macro in this package will help us to generate Decoder
.
But there is also restriction which requires the key of attribute in JSON have the same name with the attribute of data model.
Use Decoder generated from other Decoder
The Decoder
is a Monad
, so we can do map
, flatMap
on it.
Say we have another data model
case class UniqueIdentity(id: String)
And we want the id to be the join of IdCard.id
, Person.name
, Person.age
,
we can decode the JSON directly to this model like this
import io.circe.generic.auto._
import io.circe.parser.decode
import io.circe.Error
val jsonStr: String = ???
implicit val uniqIdentityDecoder: Decoder[UniqueIdentity] = Decoder[IdCard].map(x => s"${x.id}-${x.person.name}-${x.person.age}")
val uniqIdentity:Either[Error, UniqueIdentity] = decode[UniqueIdentity](jsonStr)
How to encode data model to JSON?
Now we want to do the reverse thing, convert the data model to JSON.
First we need to convert the data model to Json
, then Json
has some method to convert itself to String, such as noSpaces
, space2
, space4
.
So we will just focus on how to convert data model to Json
here.
Define Encoder by ourself
We can define Encoder
instance like this
implicit val idCardEncoder: Encoder[IdCard] = new Encoder[IdCard] {
override def apply(a: IdCard): Json = {
Json.obj(
"id" -> a.id.asJson
"person" -> Json.obj(
"name" -> a.person.name.asJson
"age" -> a.person.age.asJson
)
)
}
}
Then we can use it like this
import io.circe.syntax._
val idCard: IdCard = ???
val idCardJson:Json = idCard.asJson
Please note we are using Json.obj
to construct Json
.
Use the existing Encoder in another Encoder
Just like the Decoder
, we also can define an Encoder
instance for Person
to make the Encoder
instance of IdCard
simpler
implicit val personEncoder: Encoder[Person] = new Encoder[Person] {
override def apply(a: Person): Json = {
Json.obj(
"name" -> a.name.asJson
"age" -> a.age.asJson
)
}
}
implicit val idCardEncoder: Encoder[IdCard] = new Encoder[IdCard] {
override def apply(a: IdCard): Json = {
Json.obj(
"id" -> a.id.asJson
"person" -> a.person.asJson
)}
}
Use auto-generated Encoder
This is obvious, we can generate Encoder
automatically, it has the same restriction as Decoder
.
import io.circe.generic.auto._
import io.circe.syntax._
val idCard: IdCard = ???
val idCardJson:Json = idCard.asJson
Use Encoder generated from other Encoder
Encoder
has a contrmap
method which allows you to generate a new Encoder from the existing one.
import io.circe.generic.auto._
import io.circe.syntax._
val uniqIdentity: UniqueIdentity = ???
implicit val uniqIdentityEncoder: Encoder[UniqueIdentity] = Encoder[IdCard].contrmap(x: UniqueIdentity => {
val info = x.split("-")
IdCard(info(0), Person(info(1), info(2).toInt))
})
val uniqIdentityJson:Json = uniqIdentity.asJson






