
表格包含有价值的结构化信息,可供企业管理、共享和分析数据、做出明智的决策并提高效率。跨页表格很常见,尤其是在冗长或密集的文档中。Azure AI 文档智能 Layout 模型能够提取每个页面内的表格,若要有效解析一些跨页表格,需要将提取的表格整合为单个表格。当使用大型语言模型 (LLM) 进行自动化文档处理时,想要确保任务的高相关性或准确性是特别具有挑战性的。
本文提供了一种识别和合并表格的启发式方法,考虑了几种不同的跨页表格变体,包括垂直或水平跨页表格、具有重复表头或连续单元格的表格。然后可以将输出提供给 LLM ,通过优化上下文来得到更具有关联性和准确性的响应。在未来的更新中,Layout 模型将支持跨页表格。
01
示例说明由几个关键部分组成:
1.准备文档
首先准备您要分析的跨页表格的文档。可以是各种格式,例如 PDF、Word 文档、HTML 或图像。
2.返回表的基本信息
函数 get_table_page_numbers 返回给定文档中表格出现的页码列表。函数 get_table_span_offsets 计算表跨度的最小和最大偏移量。
3.查找候选的合并表
使用函数 get_merge_table_candidates_and_table_integral_span 查找候选合并表,并根据第2点中获得的列表计算每个表的积分跨度。
函数 check_paragraph_presence 检查指定范围内是否存在段落(即不属于页眉、页脚或页码的自然段落)。如果存在这样的段落,则该表不属于候选的合并表。
def check_paragraph_presence(paragraphs, start, end):"""Checks if there is a paragraph within the specified range that is not a page header, page footer, or page number. If this were the case, the table would not be a merge table candidate.Args:paragraphs (list): List of paragraphs to check.start (int): Start offset of the range.end (int): End offset of the range.Returns:bool: True if a paragraph is found within the range that meets the conditions, False otherwise."""for paragraph in paragraphs:for span in paragraph.spans:if span.offset > start and span.offset < end:# The logic role of a parapgaph is used to idenfiy if it's page header, page footer, page number, title, section heading, etc. Learn more: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/ai-services/document-intelligence/concept-layout?view=doc-intel-4.0.0#document-layout-analysisif not hasattr(paragraph, 'role'):return Trueelif hasattr(paragraph, 'role') and paragraph.role not in ["pageHeader", "pageFooter", "pageNumber"]:return Truereturn False
4.判断是否是跨页表格
垂直表格
如果连续页面中出现两个或多个表格,它们之间只有页眉、页脚或页码,并且这些表格具有相同的列数,则这些表格可以被视为一个垂直表格。这种判断方法适用于两个页面上都有表头的表格和仅在首页有表头的表格。
水平表格
连续页面中出现两个或多个表格,前一个表格的右侧紧邻当前页的右边缘,后一个表的左侧紧邻后一页的左边缘,并且这些表具有同样的行数,那么这些表可以被视为一个水平表格。check_tables_are_horizontal_distribution 函数识别两个连续的页是否水平分布。
5.合并跨页表
垂直表格
如果表格垂直分布为两页,那么根据分析结果将会有两个 Markdown 格式的表生成。要将它们合并到一张表中,必须使用函数 remove_header_from_markdown_table 先删除后一个 markdown 表格的表头格式字符串,然后函数 merge_vertical_tables 将两个连续的垂直 Markdown 表格合并为一个。当跨页表格的两页都有表头时,所有表头文本都会被输出,第一个表头将被作为合并表的表头。
def merge_vertical_tables(md_table_1, md_table_2) :"""Merge two consecutive vertical markdown tables into one markdown table.Args:md_table_1: markdown table 1md_table_2: markdown table 2Returns:string: merged markdown table"""table2_without_header = remove_header_from_markdown_table(md_table_2)rows1 = md_table_1.strip().splitlines()rows2 = table2_without_header.strip().splitlines()num_columns1 = len(rows1[0].split(BORDER_SYMBOL)) - 2num_columns2 = len(rows2[0].split(BORDER_SYMBOL)) - 2if num_columns1 != num_columns2:raise ValueError("Different count of columns")merged_rows = rows1 + rows2merged_table = '\n'.join(merged_rows)return merged_table
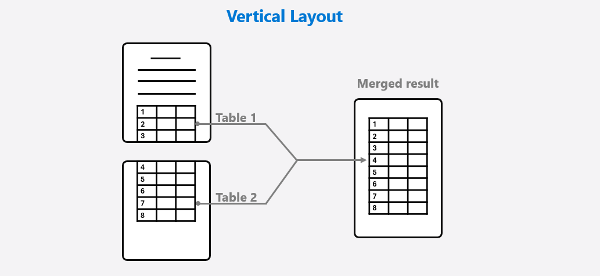
合并垂直跨页表格示意图
水平表格
如果表格水平分布为两页,那么根据分析结果将会有两个 Markdown 格式的表格生成。函数 merge_horizontal_tables 将两个连续的水平 Markdown 表格合并为一个。
def merge_horizontal_tables(md_table_1, md_table_2):"""Merge two consecutive horizontal markdown tables into one markdown table.Args:md_table_1: markdown table 1md_table_2: markdown table 2Returns:string: merged markdown table"""rows1 = md_table_1.strip().splitlines()rows2 = md_table_2.strip().splitlines()merged_rows = []for row1, row2 in zip(rows1, rows2):merged_row = ((row1[:-1] if row1.endswith(BORDER_SYMBOL) else row1)+ BORDER_SYMBOL+ (row2[1:] if row2.startswith(BORDER_SYMBOL) else row2))merged_rows.append(merged_row)merged_table = "\n".join(merged_rows)return merged_table
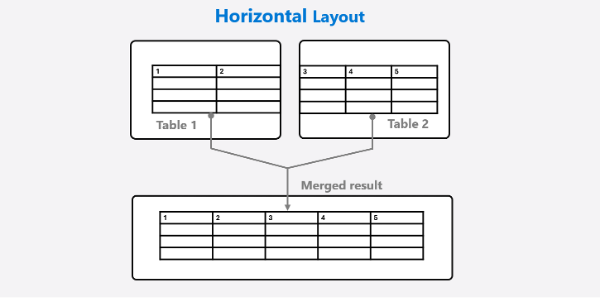
合并水平跨页表格示意图
6.合并多个连续页面
recognize_and_merge_cross_page_tables 是这个脚本的主要函数。 它将输入的文件路径作为参数,并使用 Azure 文档智能服务(涉及 Layout 模型)来分析文档并识别和合并跨多个页面的表格。该解决方案可以处理跨越3个或更多页面的表格。这个函数主要包括四个步骤:
创建 DocumentIntelligenceClient 实例,指定文件路径,然后使用 begin_analyze_document 方法分析文档。
获取候选的合并表和表积分跨度的列表。
对合并表进行判断,对表合并进行操作。
基于合并后的表格列表,生成优化后的内容。
02
该方案具有以下优势,让用户能够在多种场景下轻松处理跨页表:
1.保留表格原始语义:通过获取表的页码、跨度偏移等信息,采用各种复杂技术来确保合并后的表保留数据的原始语义和结构。
2.增强LLM表格理解:Markdown 格式提供了一种创建和格式化表格的简单方法,使LLM更易于阅读和理解表格中的数据。该解决方案以 Markdown 输出的形式合并了表格,进一步增强了 LLM 处理表格数据的能力。
3.简化数据分析处理:无论您需要处理大量文档还是对数据处理有很高的要求,通过该解决方案,分析和处理数据的过程都会被简化。
03
该方案为识别和合并跨页表格提供了灵活的解决方法。用户可以根据自己的具体情况定制规则,使其成为处理具有跨越多页的表格的文档的通用工具。
04
合并表格
这个示例说明演示了如何使用 Layout 模型的输出和一些判断规则来识别跨页表格。您也可以运行对应的 python 文件。一旦识别出来合并表,就会对其执行合并处理,同时保留表格的原本语义和结构。
应用于 RAG
可以将合并后的 Markdown 表格进一步集成到 LangChain 中。
第1步:将获得的合并后表格的 markdown 输出单独存储为 .md 格式的文件。
第2步:将代码复制到您的 IDE,将 LangChain 示例说明中 “Load a document and split it into semantic chunks” 代码片段替换为以下代码,并将 <path to your file> 替换为您在第1步存储的文件的路径。
# Initiate Azure AI Document Intelligence to load the document. You can either specify file_path or url_path to load the document.file_path = "<path to your file>"with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:markdown_text = file.read()# Split the document into chunks base on markdown headers.headers_to_split_on = [("#", "Header 1"),("##", "Header 2"),("###", "Header 3"),]text_splitter = MarkdownHeaderTextSplitter(headers_to_split_on=headers_to_split_on)docs_string = markdown_textsplits = text_splitter.split_text(docs_string)print("Length of splits: " + str(len(splits)))
当与 RAG 示例 结合使用时,Markdown 输出将成为一种更有效的工具,实现更准确、更明智的基于文档的问答交互。马上尝试一下,看它是如何改善您的数据处理体验的。
*所有发布内容均与微软全球产品和服务相关,各个国家或地区客户的产品可用性取决于当地情况







