本篇文章是 Flink 系列 的第七篇,这篇文章主要会讲述 Flink 中的 TaskManager 的一些内容,TaskManager 是 Flink 的 worker 节点,它负责 Flink 中本机 slot 资源的管理以及具体 task 的执行。TaskManager 上的基本资源单位是 slot,一个作业的 task 最终会部署在一个 TM 的 slot 上运行,TM 会负责维护本地的 slot 资源列表,并来与 Flink Master 和 JobManager 通信,预计将会通过两篇左右的文章来向大家揭秘 TaskManager 内部的实现原理。另外,本篇将采用先提出问题,然后再根据源码实现去解答这些问题的形式叙述,如果大家有其他建议,欢迎(博客/公众号)留言反馈。
对于 TaskManager 的内容,这里将会聚焦下面几个问题上,下面的文章将会逐个去分析这些问题(因为内容较多,会分为两篇文章讲述,本篇注重聚焦在前五个问题上):
1.TaskManager 启动流程?2.TaskManager 提供了哪些能力/功能?3.TaskManager 怎么发现 RM leader(在使用 ZK 做 HA 的情况下)?4.TM 如何维护 JobManager 的关系,如果 JobManager 挂掉,TM 会如何处理?5.TM Slot 资源是如何管理的?6.TM 如何处理提交过来的 Task;7.TM 如何处理 Task 之间 Shuffle 的需求?
TaskManager 启动流程
与 JobManager 类似,TaskManager 的启动类是 TaskManagerRunner
,大概的流程如下图所示:
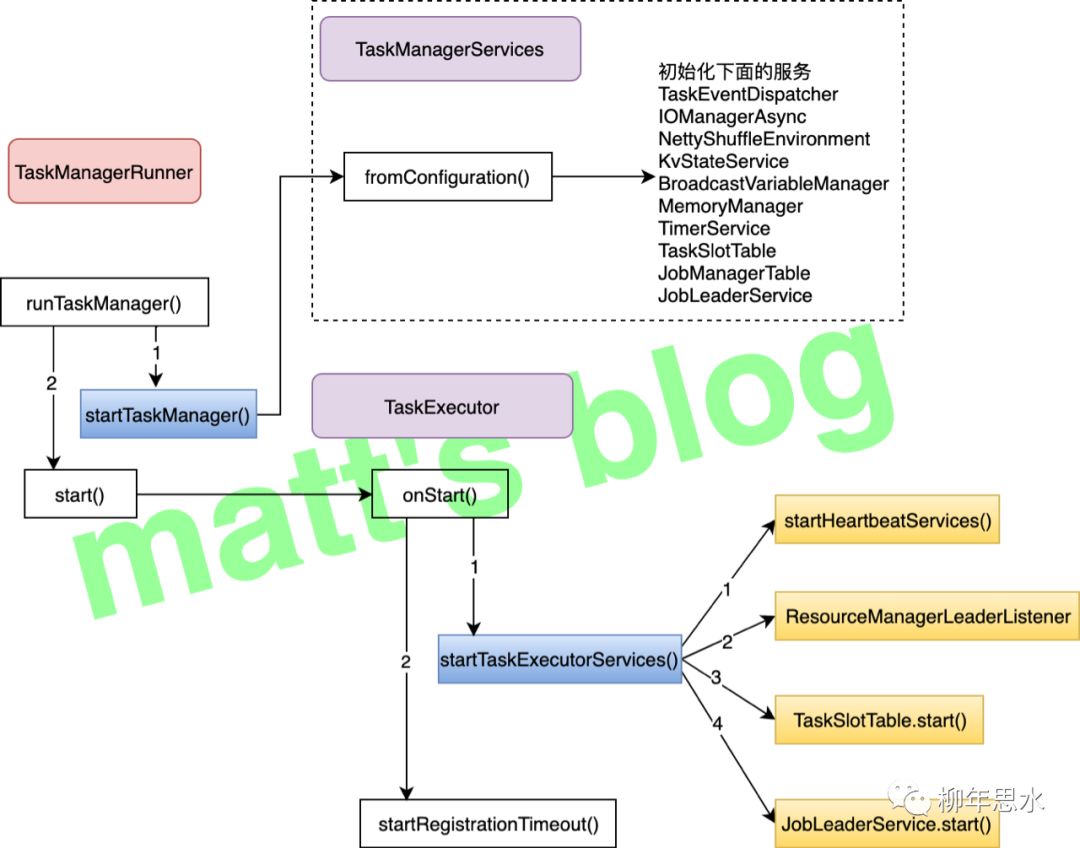
TaskManager 启动的入口方法是 runTaskManager()
,它会首先初始化 TaskManager 一些相关的服务,比如:初始化 RpcService、初始化 HighAvailabilityServices 等等,这些都是为 TaskManager 服务的启动做相应的准备工作。其实 TaskManager 初始化主要分为下面两大块:
1.TaskManager 相关 service 的初始化:比如:内存管理器、IO 管理器、TaskSlotTable(TaskSlot 的管理是在这里进行的)等,这里也包括 TaskExecutor 的初始化,注意这里对于一些需要启动的服务在这一步并没有启动;2.TaskExecutor 的启动:它会启动 TM 上相关的服务,Task 的提交和运行也是在 TaskExecutor 中处理的,上一步 TM 初始化的那些服务也是在 TaskExecutor 中使用的。
TM 的服务真正 Run 起来之后,核心流程还是在 TaskExecutor
中。
TaskManager 相关服务的初始化
这里,先从 TaskManager 的入口 runTaskManager()
来看 TaskManager 相关服务的初始化流程,总结来看流程如下:
// 1. 入口方法runTaskManager()// 2. 创建 TaskManagerRunner 对象TaskManagerRunner taskManagerRunner = new TaskManagerRunner(configuration, resourceId);// 3. 启动 TaskManager 服务startTaskManager()// 4. 初始化相关的服务TaskManagerServices.fromConfiguration()
首先看下具体的代码实现:
// TaskManagerRunner.java//note: 启动 TaskManagerRunnerpublic static void runTaskManager(Configuration configuration, ResourceID resourceId) throws Exception {final TaskManagerRunner taskManagerRunner = new TaskManagerRunner(configuration, resourceId);taskManagerRunner.start();}//note: 初始化 TaskManagerRunnerpublic TaskManagerRunner(Configuration configuration, ResourceID resourceId) throws Exception {this.configuration = checkNotNull(configuration);this.resourceId = checkNotNull(resourceId);//note: akka 超时设置timeout = AkkaUtils.getTimeoutAsTime(configuration);this.executor = java.util.concurrent.Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(Hardware.getNumberCPUCores(),new ExecutorThreadFactory("taskmanager-future"));//note: HA 的配置及服务初始化highAvailabilityServices = HighAvailabilityServicesUtils.createHighAvailabilityServices(configuration,executor,HighAvailabilityServicesUtils.AddressResolution.TRY_ADDRESS_RESOLUTION);//note: create rpc servicerpcService = createRpcService(configuration, highAvailabilityServices);//note: 初始化心跳服务HeartbeatServices heartbeatServices = HeartbeatServices.fromConfiguration(configuration);//note: metrics 服务metricRegistry = new MetricRegistryImpl(MetricRegistryConfiguration.fromConfiguration(configuration),ReporterSetup.fromConfiguration(configuration));//note: 启动相应的 metrics 服务final RpcService metricQueryServiceRpcService = MetricUtils.startMetricsRpcService(configuration, rpcService.getAddress());metricRegistry.startQueryService(metricQueryServiceRpcService, resourceId);//note: 初始化 blob 服务blobCacheService = new BlobCacheService(configuration, highAvailabilityServices.createBlobStore(), null);//note: 启动 TaskManager 服务及创建 TaskExecutor 对象taskManager = startTaskManager(this.configuration,this.resourceId,rpcService,highAvailabilityServices,heartbeatServices,metricRegistry,blobCacheService,false,this);this.terminationFuture = new CompletableFuture<>();this.shutdown = false;//note: 周期性地输出内存相关的日志信息,直到 terminationFuture completeMemoryLogger.startIfConfigured(LOG, configuration, terminationFuture);}
在上面的流程中,初始化了一些最基本的服务,比如:rpc 服务,在方法的最后调用了 startTaskManager()
启动 TaskManager,其代码实现如下:
// TaskManagerRunner.java//note: 创建并初始化 TaskExecutor 对象public static TaskExecutor startTaskManager(Configuration configuration,ResourceID resourceID,RpcService rpcService,HighAvailabilityServices highAvailabilityServices,HeartbeatServices heartbeatServices,MetricRegistry metricRegistry,BlobCacheService blobCacheService,boolean localCommunicationOnly,FatalErrorHandler fatalErrorHandler) throws Exception {checkNotNull(configuration);checkNotNull(resourceID);checkNotNull(rpcService);checkNotNull(highAvailabilityServices);LOG.info("Starting TaskManager with ResourceID: {}", resourceID);InetAddress remoteAddress = InetAddress.getByName(rpcService.getAddress());//note: TM 服务相关的配置都维护在这个对象中,这里会把使用的相关参数解析并维护起来TaskManagerServicesConfiguration taskManagerServicesConfiguration =TaskManagerServicesConfiguration.fromConfiguration(configuration,resourceID,remoteAddress,EnvironmentInformation.getSizeOfFreeHeapMemoryWithDefrag(),EnvironmentInformation.getMaxJvmHeapMemory(),localCommunicationOnly);//note: 初始化 TM 的 TaskManagerMetricGroup,并相应地初始化 TM 的基本状态(内存、CPU 等)监控Tuple2<TaskManagerMetricGroup, MetricGroup> taskManagerMetricGroup = MetricUtils.instantiateTaskManagerMetricGroup(metricRegistry,TaskManagerLocation.getHostName(remoteAddress),resourceID,taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getSystemResourceMetricsProbingInterval());//note: 初始化 TaskManagerServices(TM 相关服务的初始化都在这里)TaskManagerServices taskManagerServices = TaskManagerServices.fromConfiguration(taskManagerServicesConfiguration,taskManagerMetricGroup.f1,rpcService.getExecutor()); // TODO replace this later with some dedicated executor for io.//note: TaskManager 相关的配置,主要用于 TaskExecutor 的初始化TaskManagerConfiguration taskManagerConfiguration = TaskManagerConfiguration.fromConfiguration(configuration);String metricQueryServiceAddress = metricRegistry.getMetricQueryServiceGatewayRpcAddress();//note: 最后创建 TaskExecutor 对象return new TaskExecutor(rpcService,taskManagerConfiguration,highAvailabilityServices,taskManagerServices,heartbeatServices,taskManagerMetricGroup.f0,metricQueryServiceAddress,blobCacheService,fatalErrorHandler,new PartitionTable<>());}
这里,来着重看一下 TaskManagerServices.fromConfiguration()
这个方法,在这个方法初始了很多 TM 的服务,从下面的具体实现中也可以看出:
// TaskManagerServices.java/*** Creates and returns the task manager services.* note:根据创建 TM 服务** @param taskManagerServicesConfiguration task manager configuration* @param taskManagerMetricGroup metric group of the task manager* @param taskIOExecutor executor for async IO operations* @return task manager components* @throws Exception*/public static TaskManagerServices fromConfiguration(TaskManagerServicesConfiguration taskManagerServicesConfiguration,MetricGroup taskManagerMetricGroup,Executor taskIOExecutor) throws Exception {// pre-start checkscheckTempDirs(taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getTmpDirPaths());//note: 创建 taskEventDispatcherfinal TaskEventDispatcher taskEventDispatcher = new TaskEventDispatcher();// start the I/O manager, it will create some temp directories.//note: 创建 IO 管理器final IOManager ioManager = new IOManagerAsync(taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getTmpDirPaths());//note: 创建 ShuffleEnvironment 对象(默认是 NettyShuffleEnvironment)final ShuffleEnvironment<?, ?> shuffleEnvironment = createShuffleEnvironment(taskManagerServicesConfiguration,taskEventDispatcher,taskManagerMetricGroup);final int dataPort = shuffleEnvironment.start();//note: 创建 KvStateService 实例并启动final KvStateService kvStateService = KvStateService.fromConfiguration(taskManagerServicesConfiguration);kvStateService.start();//note: 初始化 taskManagerLocation,记录 connection 信息final TaskManagerLocation taskManagerLocation = new TaskManagerLocation(taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getResourceID(),taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getTaskManagerAddress(),dataPort);// this call has to happen strictly after the network stack has been initialized//note: 初始化 MemoryManagerfinal MemoryManager memoryManager = createMemoryManager(taskManagerServicesConfiguration);final long managedMemorySize = memoryManager.getMemorySize();//note: 初始化 BroadcastVariableManager 对象final BroadcastVariableManager broadcastVariableManager = new BroadcastVariableManager();//note: 当前 TM 拥有的 slot 及每个 slot 的资源信息final int numOfSlots = taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getNumberOfSlots();final List<ResourceProfile> resourceProfiles =Collections.nCopies(numOfSlots, computeSlotResourceProfile(numOfSlots, managedMemorySize));//note: 注册一个超时(AKKA 超时设置)服务(在 TaskSlotTable 用于监控 slot 分配是否超时)final TimerService<AllocationID> timerService = new TimerService<>(new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1),taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getTimerServiceShutdownTimeout());//note: 这里会维护 slot 相关列表final TaskSlotTable taskSlotTable = new TaskSlotTable(resourceProfiles, timerService);//note: 维护 jobId 与 JobManager connection 之间的关系final JobManagerTable jobManagerTable = new JobManagerTable();//note: 监控注册的 job 的 JobManger leader 信息final JobLeaderService jobLeaderService = new JobLeaderService(taskManagerLocation, taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getRetryingRegistrationConfiguration());final String[] stateRootDirectoryStrings = taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getLocalRecoveryStateRootDirectories();final File[] stateRootDirectoryFiles = new File[stateRootDirectoryStrings.length];for (int i = 0; i < stateRootDirectoryStrings.length; ++i) {stateRootDirectoryFiles[i] = new File(stateRootDirectoryStrings[i], LOCAL_STATE_SUB_DIRECTORY_ROOT);}//note: 创建 TaskExecutorLocalStateStoresManager 对象:维护状态信息final TaskExecutorLocalStateStoresManager taskStateManager = new TaskExecutorLocalStateStoresManager(taskManagerServicesConfiguration.isLocalRecoveryEnabled(),stateRootDirectoryFiles,taskIOExecutor);//note: 将上面初始化的这些服务,封装到一个 TaskManagerServices 对象中return new TaskManagerServices(taskManagerLocation,memoryManager,ioManager,shuffleEnvironment,kvStateService,broadcastVariableManager,taskSlotTable,jobManagerTable,jobLeaderService,taskStateManager,taskEventDispatcher);}
看到这里,是否有点懵圈了,是不是感觉 TaskManager 实现还挺复杂的,但与 TaskManager 要做的功能相比,上面的实现还不够,真正在 TaskManager 中处理复杂繁琐工作的组件是 TaskExecutor,这个才是 TaskManager 的核心。
TaskExecutor 的启动
回顾一下文章最开始的流程图,TaskManagerRunner 调用 run()
方法之后,真正要启动的是 TaskExecutor 服务,其 onStart()
具体实现如下:
//note: 启动服务@Overridepublic void onStart() throws Exception {try {//note: 启动 TM 的相关服务startTaskExecutorServices();} catch (Exception e) {final TaskManagerException exception = new TaskManagerException(String.format("Could not start the TaskExecutor %s", getAddress()), e);onFatalError(exception);throw exception;}//note: 注册超时检测,如果超时还未注册完成,就抛出错误,启动失败startRegistrationTimeout();}
这里,主要分为两个部分:
1.startTaskExecutorServices()
: 启动 TaskManager 相关的服务,结合流程图主要是四大块:•启动心跳服务;•向 Flink Master 的 ResourceManager 注册 TaskManager;•启动 TaskSlotTable 服务(TaskSlot 的维护主要在这个服务中);•启动 JobLeaderService 服务,它主要是监控各个作业 JobManager leader 的变化;2.startRegistrationTimeout()
: 启动注册超时的检测,默认是5 min,如果超过这个时间还没注册完成,就会抛出异常退出进程,启动失败。
TaskExecutor 启动的核心实现是在 startTaskExecutorServices()
中,其实现如下:
private void startTaskExecutorServices() throws Exception {try {//note: 启动心跳服务startHeartbeatServices();//note: 与集群的 ResourceManager 建立连接(并创建一个 listener)// start by connecting to the ResourceManagerresourceManagerLeaderRetriever.start(new ResourceManagerLeaderListener());// tell the task slot table who's responsible for the task slot actions//note: taskSlotTable 启动taskSlotTable.start(new SlotActionsImpl());// start the job leader service//note: 启动 job leader 服务jobLeaderService.start(getAddress(), getRpcService(), haServices, new JobLeaderListenerImpl());fileCache = new FileCache(taskManagerConfiguration.getTmpDirectories(), blobCacheService.getPermanentBlobService());} catch (Exception e) {handleStartTaskExecutorServicesException(e);}}
接下来,详细这块的实现。
1. 启动心跳服务
TaskExecutor 启动的第一个服务就是 HeartbeatManager,这里会启动两个:
1.jobManagerHeartbeatManager
: 用于与 JobManager(如果 Job 有 task 在这个 TM 上,这个 Job 的 JobManager 就与 TaskManager 有心跳通信)之间的心跳通信管理,如果 timeout,这里会重连;2.resourceManagerHeartbeatManager
:用于与 ResourceManager 之间的通信管理,如果 timeout,这里也会重连。
// TaskExecutor.java//note: 启动心跳服务private void startHeartbeatServices() {final ResourceID resourceId = taskExecutorServices.getTaskManagerLocation().getResourceID();//note: 创建一个与 JM 通信的心跳管理器jobManagerHeartbeatManager = heartbeatServices.createHeartbeatManager(resourceId,new JobManagerHeartbeatListener(),getMainThreadExecutor(),log);//note: 创建一个与 RM 通信的心跳管理器resourceManagerHeartbeatManager = heartbeatServices.createHeartbeatManager(resourceId,new ResourceManagerHeartbeatListener(),getMainThreadExecutor(),log);}
2. 向 RM 注册 TM
TaskManger 向 ResourceManager 注册是通过 ResourceManagerLeaderListener
来完成的,它会监控 ResourceManager 的 leader 变化,如果有新的 leader 被选举出来,将会调用 notifyLeaderAddress()
方法去触发与 ResourceManager 的重连,其实现如下:
// TaskExecutor.java/*** The listener for leader changes of the resource manager.* note:监控 ResourceManager leader 变化的 listener*/private final class ResourceManagerLeaderListener implements LeaderRetrievalListener {//note: 如果 leader 被选举处理(包括挂掉之后重新选举),将会调用这个方法通知 TM@Overridepublic void notifyLeaderAddress(final String leaderAddress, final UUID leaderSessionID) {runAsync(() -> notifyOfNewResourceManagerLeader(leaderAddress,ResourceManagerId.fromUuidOrNull(leaderSessionID)));}@Overridepublic void handleError(Exception exception) {onFatalError(exception);}}//note: 如果 RM 的 new leader 选举出来了,这里会新创建一个 ResourceManagerAddress 对象,并重新建立连接private void notifyOfNewResourceManagerLeader(String newLeaderAddress, ResourceManagerId newResourceManagerId) {resourceManagerAddress = createResourceManagerAddress(newLeaderAddress, newResourceManagerId);reconnectToResourceManager(new FlinkException(String.format("ResourceManager leader changed to new address %s", resourceManagerAddress)));}//note: 重新与 ResourceManager 连接(可能是 RM leader 切换)private void reconnectToResourceManager(Exception cause) {closeResourceManagerConnection(cause);//note: 注册超时检测,如果 timeout 还没注册成功,这里就会 failedstartRegistrationTimeout();//note: 与 RM 重新建立连接tryConnectToResourceManager();}//note: 建立与 ResourceManager 的连接private void tryConnectToResourceManager() {if (resourceManagerAddress != null) {connectToResourceManager();}}//note: 与 ResourceManager 建立连接private void connectToResourceManager() {assert(resourceManagerAddress != null);assert(establishedResourceManagerConnection == null);assert(resourceManagerConnection == null);log.info("Connecting to ResourceManager {}.", resourceManagerAddress);//note: 与 RM 建立连接resourceManagerConnection =new TaskExecutorToResourceManagerConnection(log,getRpcService(),getAddress(),getResourceID(),taskManagerConfiguration.getRetryingRegistrationConfiguration(),taskManagerLocation.dataPort(),hardwareDescription,resourceManagerAddress.getAddress(),resourceManagerAddress.getResourceManagerId(),getMainThreadExecutor(),new ResourceManagerRegistrationListener());resourceManagerConnection.start();}
在上面的最后一步,创建了 TaskExecutorToResourceManagerConnection
对象,它启动后,会向 ResourceManager 注册 TM,具体的方法实现如下:
// TaskExecutorToResourceManagerConnection.java@Overrideprotected CompletableFuture<RegistrationResponse> invokeRegistration(ResourceManagerGateway resourceManager, ResourceManagerId fencingToken, long timeoutMillis) throws Exception {Time timeout = Time.milliseconds(timeoutMillis);return resourceManager.registerTaskExecutor(taskExecutorAddress,resourceID,dataPort,hardwareDescription,timeout);}
ResourceManager 在收到这个请求,会做相应的处理,主要要做的事情就是:先从缓存里移除旧的 TM 注册信息(如果之前存在的话),然后再更新缓存,并增加心跳监控,只有这些工作完成之后,TM 的注册才会被认为是成功的。
3. 启动 TaskSlotTable 服务
TaskSlotTable 从名字也可以看出,它主要是为 TaskSlot 服务的,它主要的功能有以下三点:
1.维护这个 TM 上所有 TaskSlot 与 Task、及 Job 的关系;2.维护这个 TM 上所有 TaskSlot 的状态;3.TaskSlot 在进行 allocate/free 操作,通过 TimeService 做超时检测。
先看下 TaskSlotTable 是如何初始化的:
// TaskManagerServices.java//note: 当前 TM 拥有的 slot 及每个 slot 的资源信息//note: TM 的 slot 数由 taskmanager.numberOfTaskSlots 决定,默认是 1final int numOfSlots = taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getNumberOfSlots();final List<ResourceProfile> resourceProfiles =Collections.nCopies(numOfSlots, computeSlotResourceProfile(numOfSlots, managedMemorySize));//note: 注册一个超时(AKKA 超时设置)服务(在 TaskSlotTable 用于监控 slot 分配是否超时)//note: 超时参数由 akka.ask.timeout 控制,默认是 10sfinal TimerService<AllocationID> timerService = new TimerService<>(new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1),taskManagerServicesConfiguration.getTimerServiceShutdownTimeout());//note: 这里会维护 slot 相关列表final TaskSlotTable taskSlotTable = new TaskSlotTable(resourceProfiles, timerService);
TaskSlotTable 的初始化,只需要两个变量:
1.resourceProfiles
: TM 上每个 Slot 的资源信息;2.timerService
: 超时检测服务,来保证操作超时时做相应的处理。
TaskSlotTable 的启动流程如下:
// TaskExecutor.java// tell the task slot table who's responsible for the task slot actions//note: taskSlotTable 启动taskSlotTable.start(new SlotActionsImpl());//note: SlotActions 相关方法的实现private class SlotActionsImpl implements SlotActions {//note: 释放 slot 资源@Overridepublic void freeSlot(final AllocationID allocationId) {runAsync(() ->freeSlotInternal(allocationId,new FlinkException("TaskSlotTable requested freeing the TaskSlot " + allocationId + '.')));}//note: 如果 slot 相关的操作(分配/释放)失败,这里将会调用这个方法//note: 监控的手段是:操作前先注册一个 timeout 监控,操作完成后再取消这个监控,如果在这个期间 timeout 了,就会调用这个方法//note: TimeService 的 key 是 AllocationID@Overridepublic void timeoutSlot(final AllocationID allocationId, final UUID ticket) {runAsync(() -> TaskExecutor.this.timeoutSlot(allocationId, ticket));}}
4. 启动 JobLeaderService 服务
TaskExecutor 启动的最后一步是,启动 JobLeader 服务,这个服务通过 JobLeaderListenerImpl
监控 Job 的 JobManager leader 的变化,如果 leader 被选举出来之后,这里将会与新的 JobManager leader 建立通信连接。
// TaskExecutor.java// start the job leader service//note: 启动 job leader 服务jobLeaderService.start(getAddress(), getRpcService(), haServices, new JobLeaderListenerImpl());//note: JobLeaderListener 的实现private final class JobLeaderListenerImpl implements JobLeaderListener {@Overridepublic void jobManagerGainedLeadership(final JobID jobId,final JobMasterGateway jobManagerGateway,final JMTMRegistrationSuccess registrationMessage) {//note: 建立与 JobManager 的连接runAsync(() ->establishJobManagerConnection(jobId,jobManagerGateway,registrationMessage));}@Overridepublic void jobManagerLostLeadership(final JobID jobId, final JobMasterId jobMasterId) {log.info("JobManager for job {} with leader id {} lost leadership.", jobId, jobMasterId);runAsync(() ->closeJobManagerConnection(jobId,new Exception("Job leader for job id " + jobId + " lost leadership.")));}@Overridepublic void handleError(Throwable throwable) {onFatalError(throwable);}}
到这里,TaskManager 的启动流程就梳理完了,TaskManager 在实现上整体的复杂度还是比较高的,毕竟它要做的事情是非常多的,下面的几个问题,将会进一步分析 TaskManager 内部的实现机制。
TaskManager 提供了哪些能力/功能?
要想知道 TaskManager 提供了哪些能力,个人认为有一个最简单有效的方法就是查看其对外提供的 API 接口,它向上层暴露哪些 API,这些 API 背后都是 TaskManager 能力的体现,TaskManager 对外的包括的 API 列表如下:
1.requestSlot()
: RM 向 TM 请求一个 slot 资源;2.requestStackTraceSample()
: 请求某个 task 在执行过程中的一个 stack trace 抽样;3.submitTask()
: JobManager 向 TM 提交 task;4.updatePartitions()
: 更新这个 task 对应的 Partition 信息;5.releasePartitions()
: 释放这个 job 的所有中间结果,比如 close 的时候触发;6.triggerCheckpoint()
: Checkpoint Coordinator 触发 task 的 checkpoint;7.confirmCheckpoint()
: Checkpoint Coordinator 通知 task 这个 checkpoint 完成;8.cancelTask()
: task 取消;9.heartbeatFromJobManager()
: 接收来自 JobManager 的心跳请求;10.heartbeatFromResourceManager()
: 接收来自 ResourceManager 的心跳请求;11.disconnectJobManager()
;12.disconnectResourceManager()
;13.freeSlot()
: JobManager 释放 Slot;14.requestFileUpload()
: 一些文件(log 等)的上传请求;15.requestMetricQueryServiceAddress()
: 请求 TM 的 metric query service 地址;16.canBeReleased()
: 检查 TM 是否可以被 realease;
把上面的 API 列表分分类,大概有以下几块:
1.slot 的资源管理:slot 的分配/释放;2.task 运行:接收来自 JobManager 的 task 提交、也包括该 task 对应的 Partition(中间结果)信息;3.checkpoint 相关的处理;4.心跳监控、连接建立等。
通常,可以任务 TaskManager 提供的功能主要是前三点,如下图所示:

TaskManager 怎么发现 RM leader(在使用 ZK 做 HA 的情况下)?
这个是 Flink HA 内容,Flink HA 机制是有一套统一的框架,它跟这个问题(TM 如何维护 JobManager 的关系,如果 JobManager 挂掉,TM 会如何处理? )的原理是一样的,这里以 ResourceManager Leader 的发现为例简单介一下。
这里,我们以使用 Zookeeper 模式的情况来讲述,ZooKeeper 做 HA 是业内最常用的方案,Flink 在实现并没有使用 ZkClient
这个包,而是使用 curator
来做的(有兴趣可以看下这篇文章 跟着实例学习ZooKeeper的用法:缓存[1])。
关于 Flink HA 的使用,可以参考官方文档——JobManager High Availability (HA)[2]。这里 TaskExecutor 在注册完 ResourceManagerLeaderListener
后,如果 leader 被选举出来或者有节点有变化,就通过它的 notifyLeaderAddress()
方法来通知 TaskExecutor,核心还是利用了 ZK 的 watcher 机制。同理, JobManager leader 的处理也是一样。
TM Slot 资源是如何管理的?
TaskManager Slot 资源的管理主要是在 TaskSlotTable 中处理的,slot 资源的申请与释放都通过 它处理的,相关的流程如下图所示(图中只描述了主要逻辑,相关的异常处理没有展示在图中)
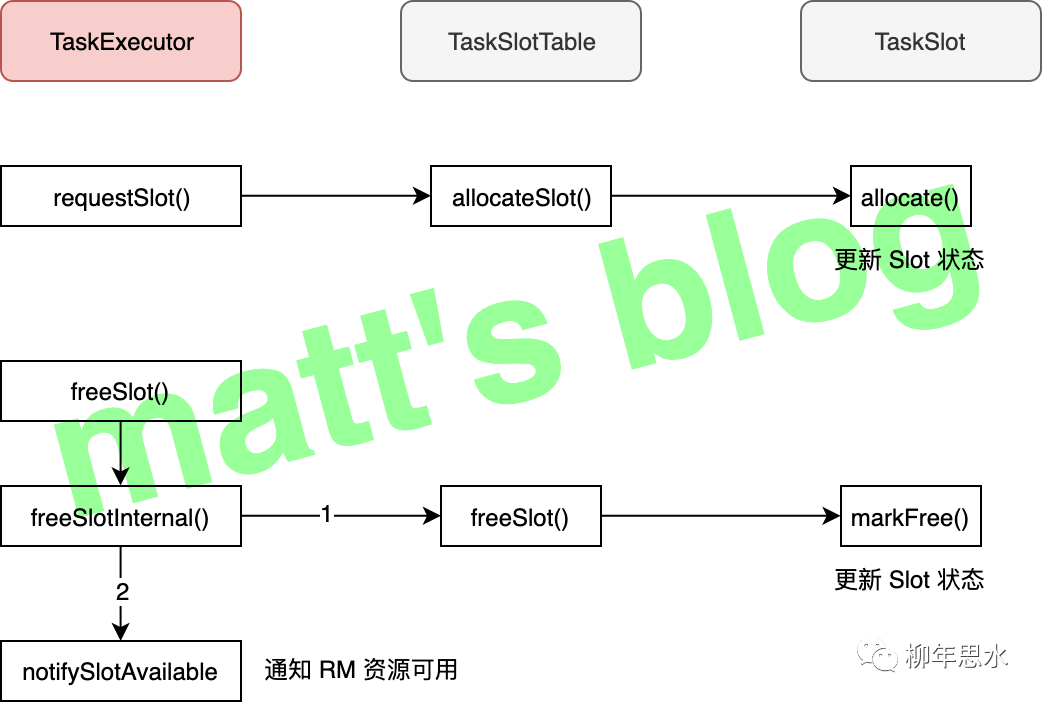
slot 的申请
这里先看下 slot 资源请求的处理,其实现如下:
// TaskExecutor.java//note: slot 请求@Overridepublic CompletableFuture<Acknowledge> requestSlot(final SlotID slotId,final JobID jobId,final AllocationID allocationId,final String targetAddress,final ResourceManagerId resourceManagerId,final Time timeout) {// TODO: Filter invalid requests from the resource manager by using the instance/registration Idlog.info("Receive slot request {} for job {} from resource manager with leader id {}.",allocationId, jobId, resourceManagerId);try {if (!isConnectedToResourceManager(resourceManagerId)) {//note: 如果 TM 并没有跟这个 RM 通信,就抛出异常final String message = String.format("TaskManager is not connected to the resource manager %s.", resourceManagerId);log.debug(message);throw new TaskManagerException(message);}if (taskSlotTable.isSlotFree(slotId.getSlotNumber())) {//note: Slot 状态是 free,还未分配出去if (taskSlotTable.allocateSlot(slotId.getSlotNumber(), jobId, allocationId, taskManagerConfiguration.getTimeout())) {log.info("Allocated slot for {}.", allocationId);//note: allcate 成功} else {log.info("Could not allocate slot for {}.", allocationId);throw new SlotAllocationException("Could not allocate slot.");}} else if (!taskSlotTable.isAllocated(slotId.getSlotNumber(), jobId, allocationId)) {//note: slot 已经分配出去,但分配的并不是当前这个作业final String message = "The slot " + slotId + " has already been allocated for a different job.";log.info(message);final AllocationID allocationID = taskSlotTable.getCurrentAllocation(slotId.getSlotNumber());throw new SlotOccupiedException(message, allocationID, taskSlotTable.getOwningJob(allocationID));}if (jobManagerTable.contains(jobId)) {//note: 如果 TM 已经有这个 JobManager 的 meta,这里会将这个 job 的 slot 分配再汇报给 JobManager 一次offerSlotsToJobManager(jobId);} else {try {//note: 监控这个作业 JobManager 的 leader 变化jobLeaderService.addJob(jobId, targetAddress);} catch (Exception e) {// free the allocated slottry {taskSlotTable.freeSlot(allocationId);} catch (SlotNotFoundException slotNotFoundException) {// slot no longer existent, this should actually never happen, because we've// just allocated the slot. So let's fail hard in this case!onFatalError(slotNotFoundException);}// release local state under the allocation id.localStateStoresManager.releaseLocalStateForAllocationId(allocationId);// sanity checkif (!taskSlotTable.isSlotFree(slotId.getSlotNumber())) {onFatalError(new Exception("Could not free slot " + slotId));}throw new SlotAllocationException("Could not add job to job leader service.", e);}}} catch (TaskManagerException taskManagerException) {return FutureUtils.completedExceptionally(taskManagerException);}return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(Acknowledge.get());}
相应的处理逻辑如下:
1.首先检测这个这个 RM 是否当前建立连接的 RM,如果不是,就抛出相应的异常,需要等到 TM 连接上 RM 之后才能处理 RM 上的 slot 请求;2.判断这个 slot 是否可以分配•如果 slot 是 FREE
状态,就进行分配(调用 TaskSlotTable 的 allocateSlot()
方法),如果分配失败,就抛出相应的异常;•如果 slot 已经分配,检查分配的是不是当前作业的 AllocationId,如果不是,也会抛出相应的异常,告诉 RM 这个 Slot 已经分配出去了;3.如果 TM 已经有了这个 JobManager 的 meta,这里会将这个 job 在这个 TM 上的 slot 分配再重新汇报给 JobManager 一次;
而 TaskSlotTable 在处理 slot 的分配时,主要是根据内部缓存的信息做相应的检查,其 allocateSlot()
的方法的实现如下:
// TaskSlotTable.javapublic boolean allocateSlot(int index, JobID jobId, AllocationID allocationId, Time slotTimeout) {checkInit();TaskSlot taskSlot = taskSlots.get(index);//note: 分配这个 TaskSlotboolean result = taskSlot.allocate(jobId, allocationId);if (result) {//note: 分配成功,记录到缓存中// update the allocation id to task slot mapallocationIDTaskSlotMap.put(allocationId, taskSlot);// register a timeout for this slot since it's in state allocatedtimerService.registerTimeout(allocationId, slotTimeout.getSize(), slotTimeout.getUnit());// add this slot to the set of job slotsSet<AllocationID> slots = slotsPerJob.get(jobId);if (slots == null) {slots = new HashSet<>(4);slotsPerJob.put(jobId, slots);}slots.add(allocationId);}return result;}
slot 的释放
这里再看下 Slot 的资源是如何释放的,代码实现如下:
// TaskExecutor.java//note: 释放这个 slot 资源@Overridepublic CompletableFuture<Acknowledge> freeSlot(AllocationID allocationId, Throwable cause, Time timeout) {freeSlotInternal(allocationId, cause);return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(Acknowledge.get());}//note: 将本地分配的 slot 释放掉(free the slot)private void freeSlotInternal(AllocationID allocationId, Throwable cause) {checkNotNull(allocationId);log.debug("Free slot with allocation id {} because: {}", allocationId, cause.getMessage());try {final JobID jobId = taskSlotTable.getOwningJob(allocationId);//note: 释放这个 slotfinal int slotIndex = taskSlotTable.freeSlot(allocationId, cause);if (slotIndex != -1) {//note: 成功释放掉的情况下if (isConnectedToResourceManager()) {//note: 通知 ResourceManager 这个 slot 因为被释放了,所以可以变可用了// the slot was freed. Tell the RM about itResourceManagerGateway resourceManagerGateway = establishedResourceManagerConnection.getResourceManagerGateway();resourceManagerGateway.notifySlotAvailable(establishedResourceManagerConnection.getTaskExecutorRegistrationId(),new SlotID(getResourceID(), slotIndex),allocationId);}if (jobId != null) {closeJobManagerConnectionIfNoAllocatedResources(jobId);}}} catch (SlotNotFoundException e) {log.debug("Could not free slot for allocation id {}.", allocationId, e);}//note: 释放这个 allocationId 的相应状态信息localStateStoresManager.releaseLocalStateForAllocationId(allocationId);}
总结一下,TaskExecutor 在处理 slot 释放请求的理逻辑如下:
1.先调用 TaskSlotTable 的 freeSlot()
方法,尝试释放这个 slot:•如果这个 slot 没有 task 在运行,那么 slot 是可以释放的(状态更新为 FREE
);•先将 slot 状态更新为 RELEASING
,然后再遍历这个 slot 上的 task,逐个将其标记为 failed;2.如果 slot 被成功释放(状态是 FREE
),这里将会通知 RM 这个 slot 现在又可用了;3.更新缓存信息。
总结
本篇文章主要把 TaskManager 的启动流程及资源管理做了相应的讲述,正如文章中所述,TaskManager 主要有三大功能:slot 资源管理、task 的提交与运行以及 checkpoint 处理,在下篇文章中将会着重在 Task 的提交与运行上,checkpoint 处理部分将会 checkpoint 的文章中一起介绍。
最后,说一些个人的感想吧,我个人在看开源项目的源码时,慢慢开始感受到阅读优秀的开源代码对个人技术能力的提升是非常有帮助的,它不但会增加你对这个项目的熟悉程度,还会让你看到一些设计或方案在代码里是如何落地或实现的,如果换做是你,你会怎么设计或实现,经常看看这些优秀代码,多多思考(如果能把其中的设计或实现应用到自己的工作上那就更好不过了),这对自己工程能力的提升是有帮助的。
参考:
1.Distributed Runtime Environment[3];2.Apache Flink 进阶(一):Runtime 核心机制剖析 ;
References
[1]
跟着实例学习ZooKeeper的用法:缓存: https://colobu.com/2014/12/15/zookeeper-recipes-by-example-5/[2]
JobManager High Availability (HA): https://ci.apache.org/projects/flink/flink-docs-stable/ops/jobmanager_high_availability.html[3]
Distributed Runtime Environment: https://ci.apache.org/projects/flink/flink-docs-release-1.9/concepts/runtime.html






