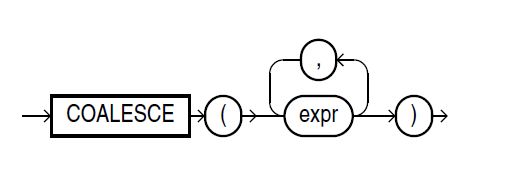
1.LAG函数
LAG is an analytic function. It provides access to more than one row of a table at the same time without a self join. Given a series of rows returned from a query and a position of the cursor, LAG provides access to a row at a given physical offset prior to that position.
For the optional offset argument, specify an integer that is greater than zero. If you do not specify offset, then its default is 1. The optional default value is returned if the offset goes beyond the scope of the window. If you do not specify default, then its
default is null.
{RESPECT | IGNORE} NULLS determines whether null values of value_expr are included in or eliminated from the calculation. The default is RESPECT NULLS.
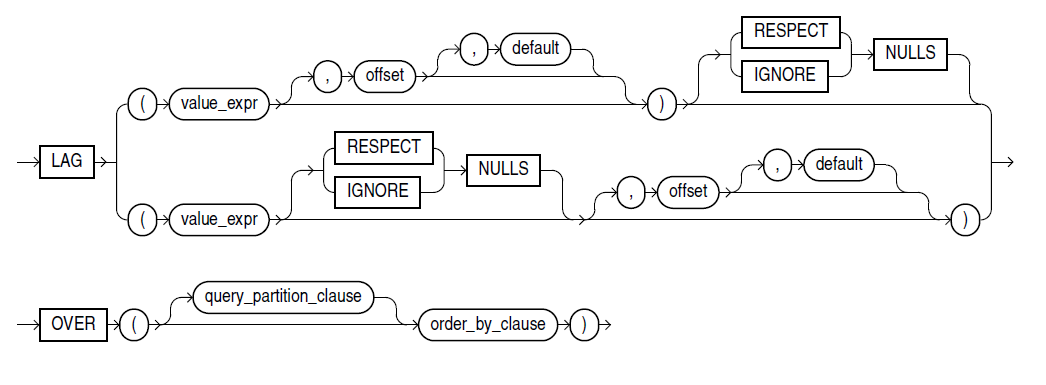
2.COALESCE函数
COALESCE returns the first non-null expr in the expression list. You must specify at least two expressions. If all occurrences of expr evaluate to null, then the function returns null.
Oracle Database uses short-circuit evaluation. The database evaluates each expr value and determines whether it is NULL, rather than evaluating all of the expr values before determining whether any of them is NULL.
If all occurrences of expr are numeric data type or any nonnumeric data type that can be implicitly converted to a numeric data type,then Oracle Database determines the argument with the highest numeric precedence, implicitly converts the remaining arguments to that data
type, and returns that data type.
This function is a generalization of the NVL function. You can also use COALESCE as a variety of the CASE expression. For example,
COALESCE(expr1, expr2)
is equivalent to:
CASE WHEN expr1 IS NOT NULL THEN expr1 ELSE expr2 END
Similarly,
COALESCE(expr1, expr2, …, exprn)
where n >= 3, is equivalent to:
CASE WHEN expr1 IS NOT NULL THEN expr1 ELSE COALESCE (expr2, …, exprn) END