陈旭,捷银消费金融有限公司DBA
既第一篇 实战PG vector构建DBA个人知识库之一:基础环境搭建以及大模型部署 之后,
今天分享的是本系列之二:向量数据库与 PG vector 介绍
目前随着大模型的普及,向量数据库如雨后春笋版出现,首先是一些传统的NOSQL 像mongo, redis, es 发布版本支持,
传统的老牌数据库干脆将23 C版本改名为 23 AI,MYSQL 甚至为了支持向量直接跳跃大版本发布了9.0. 市面上还有一些专门的向量数据库:FAISS、Milvus、Pinecone …

关于市面上向量数据库的比较可以参考: https://superlinked.com/vector-db-comparison
从这个榜单中,我们可以看到从不同的统计维度之间向量的数据库比较:
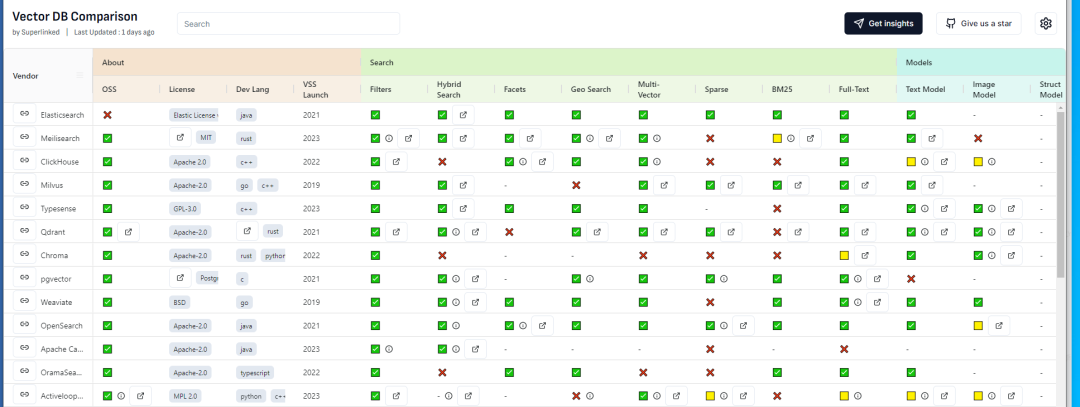
为什么要使用pg_vector做为我的向量数据库的方案呢?个人观点如下:
1.pg_vector 插件的方式支持向量,不需要单独安装一个全新的数据库,从而减少了机器,监控,运维,HA,灾备等等的一系列的成本。
2.不想NOSQL mongo. es 那样, 你可以使用SQL的方式进行向量数据库操作
3.pg_vector 在国外已经大面积使用,深受广大程序员的喜爱,而且视频问文字资料相对较多。
4.基于传统老牌RDBMS, 保证数据库ACID特性
5.如果你的公司存在PG的数据库或者有PG经验DB的话,直接开箱即用
我们先安装一下PG数据库16.3版本,为了插件安装便利,我们选择源码安装, 下载地址: https://www.postgresql.org/ftp/source/v16.3/
[postgres@VM-24-9-centos postgres]$ wget https://ftp.postgresql.org/pub/source/v16.3/postgresql-16.3.tar.gz
编译安装软件
[root@VM-24-9-centos postgres]# su - postgres
Last login: Wed Jul 24 14:39:07 CST 2024 on pts/4
[postgres@VM-24-9-centos ~]$ tar -xvf postgresql-16.3.tar.gz
[postgres@VM-24-9-centos ~]$ cd /opt/postgres/
[postgres@VM-24-9-centos postgres]$ tar -xvf postgresql-16.3.tar.gz
[postgres@VM-24-9-centos postgresql-16.3]$ ./configure --prefix=/opt/pgsql-16 -with-ssl=openssl --with-pgport=5432
[postgres@VM-24-9-centos postgresql-16.3]$ make world -j16
[postgres@VM-24-9-centos postgresql-16.3]$ make install-world -j16
设置环境变量
PG_HOME='/opt/pgsql-16'
PATH=$PATH:$HOME/.local/bin:$HOME/bin:$PG_HOME/bin
alias psql='/opt/pgsql-16/bin/psql'
export PATH
初始化数据库
[postgres@VM-24-9-centos ~]$ /opt/pgsql-16/bin/initdb -A trust --data-checksums -D /data/pg5432/ -U postgres -W
启动数据库
[postgres@VM-24-9-centos ~]$ /opt/pgsql-16/bin/pg_ctl -D /data/pg5432/ -l logfile start
waiting for server to start.... done
server started
[postgres@VM-24-9-centos ~]$ psql
psql (16.3)
Type "help" for help.
postgres=#
为了日后的程序地址IP的连接畅通性,我们需要小改2个参数
postgres=# alter system set listen_addresses = '*';
ALTER SYSTEM
postgres=# select pg_reload_conf();
pg_reload_conf
----------------
t
(1 row)
HBA文件修改:
host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5
以上我们完成了PG数据库的基本配置。
下面我们来看一下pgvector:
github上的下载地址: https://github.com/pgvector/pgvector
关于PG vector 的支持特性如下:
* exact and approximate nearest neighbor search
* single-precision, half-precision, binary, and sparse vectors
* L2 distance, inner product, cosine distance, L1 distance, Hamming distance, and Jaccard distance
* any language with a Postgres client
pgvector 下载
git clone --branch v0.7.3 https://github.com/pgvector/pgvector.git
pgvector的安装:
[postgres@VM-24-9-centos pgvector]$ make
[postgres@VM-24-9-centos pgvector]$ make install
创建vector 插件:我们可以看到关于插件的秒速 支持向量类型,以及 ivfflat and hnsw 2种索引的搜索方式
postgres=# create extension vector;
CREATE EXTENSION
postgres=# \dx
List of installed extensions
Name | Version | Schema | Description
---------+---------+------------+------------------------------------------------------
plpgsql | 1.0 | pg_catalog | PL/pgSQL procedural language
vector | 0.7.3 | public | vector data type and ivfflat and hnsw access methods
(2 rows)
我们来创建一张含有vector类型的商品表:
CREATE TABLE product (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
name VECTOR(8)
);
手动插入一些数据:大致分为2大类:水果和球类
postgres=# insert into product(name,vec) values ('苹果','[0.11, 0.12, 0.13,0.14, 0.15, 0.16,0.17,0.18]');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into product(name,vec) values ('香蕉','[0.10, 0.13, 0.15,0.15, 0.16, 0.17,0.18,0.19]');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into product(name,vec) values ('足球','[3.31, 3.32, 3.33,3.34, 3.35, 3.36,3.37,3.18]');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into product(name,vec) values ('篮球','[3.10, 3.13, 3.15,3.15, 3.16, 3.17,3.18,3.19]');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# select * from product;
id | name | vec
----+------+-------------------------------------------
1 | 苹果 | [0.11,0.12,0.13,0.14,0.15,0.16,0.17,0.18]
2 | 香蕉 | [0.1,0.13,0.15,0.15,0.16,0.17,0.18,0.19]
3 | 足球 | [3.31,3.32,3.33,3.34,3.35,3.36,3.37,3.18]
4 | 篮球 | [3.1,3.13,3.15,3.15,3.16,3.17,3.18,3.19]
(4 rows)
我们可以进行一个相似度的匹配: 我们采用大家初中数学学习的 cosine distance 计算距离。<=>:cosine distance
SELECT * FROM product
order by vec <=> '[0.11, 0.12, 0.13,0.14, 0.15, 0.11,0.19,0.28]' limit 2;
pgvector 支持的一些向量距离的运算符:
<-> - L2 distance
<#> - (negative) inner product
<=> - cosine distance
<+> - L1 distance (added in 0.7.0)
到这里你可能会好奇怎样把具体的文字抽象成具体的向量数值呢?下面介绍一下 embedding 的概念。
An embedding is a numerical representation of a piece of information, for example, text, documents, images, audio, etc
我们可以看到针对人脸识别和视频鉴别的embedding 模型。
针对文本的向量生成embedding 模型有 text2vec-large-chinese: https://github.com/shibing624/text2vec?tab=readme-ov-file
简介: text2vec, text to vector. 文本向量表征工具,把文本转化为向量矩阵,实现了Word2Vec、RankBM25、Sentence-BERT、CoSENT等文本表征、文本相似度计算模型,开箱即用。
我们可以在python 环境中直接安装包
pip3 install SentenceModel
pip3 install psycopg3
下载embedding model 模型文件:https://www.modelscope.cn/models/Jerry0/text2vec-base-chinese

我们下载到本地的电脑上:
Jason.ChenTJ@CN-L201098 MINGW64 /d/AI/MD课程大纲
$ git lfs install
Git LFS initialized.
Jason.ChenTJ@CN-L201098 MINGW64 /d/AI/MD课程大纲
$ git clone https://www.modelscope.cn/Jerry0/text2vec-base-chinese.git
测试文字生成向量数值:
from text2vec import SentenceModel
import json
sentences = ['苹果']
model = SentenceModel("D:\\AI\\text2vec-base-chinese")
embeddings = model.encode(sentences)
print(json.dumps(embeddings.tolist()[0]))
print('dimension size of vector is: {}'.format(len(json.dumps(embeddings.tolist()[0]))))
默认生成的维度是 768个(In general, each sentence is translated to a 768-dimensional vector.)
输出: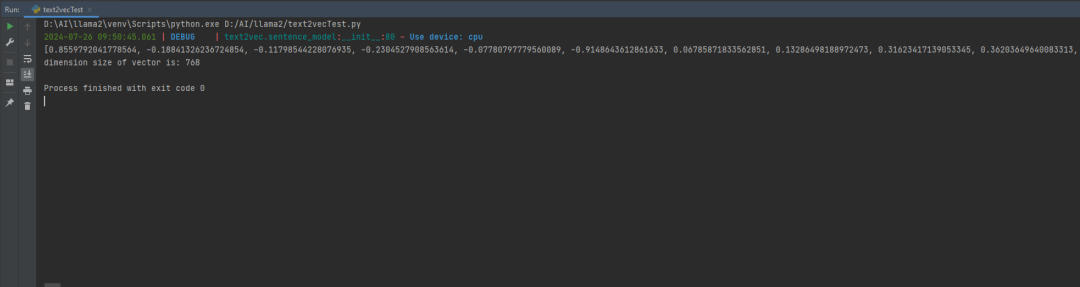
那我们现在试图写一个程序,把文本转换成向量写入到数据库pgvector中:
创建连接账户:
postgres=# create user app_vector password 'app_vector';
CREATE ROLE
postgres=# create schema app_vector authorization app_vector;
CREATE SCHEMA
postgres=# \c postgres app_vector
You are now connected to database "postgres" as user "app_vector".
创建表:
postgres=# \c postgres app_vector
You are now connected to database "postgres" as user "app_vector".
postgres=> create table product (id int , name text, embedding vector(768));
CREATE TABLE
写一段小程序load
from text2vec import SentenceModel
import psycopg2
import json
def connect2PG():
conn = psycopg2.connect(
user="app_vector",
password="app_vector",
host="XX.XX.XXX.XX",
port=5432, # The port you exposed in docker-compose.yml
database="postgres"
)
return conn
def execSQL(conn,sql):
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute(sql)
conn.commit()
cur.close()
conn.close()
def generatedEmbedding(text):
sentences = [text]
model = SentenceModel("D:\\AI\\text2vec-base-chinese")
embeddings = model.encode(sentences)
return json.dumps(embeddings.tolist()[0])
#print(json.dumps(embeddings.tolist()[0]))
#print('dimension size of vector is: {}'.format(len(json.dumps(embeddings.tolist()[0]).split(","))))
def loadVec2DB(id,text):
embeddings = generatedEmbedding(text)
print(embeddings)
sql = """ insert into product(id,name,embedding) values({},'{}','{}')""".format(id,text,embeddings)
print(sql)
conn = connect2PG()
execSQL(conn,sql)
if __name__ == '__main__':
loadVec2DB(1,'苹果')
loadVec2DB(2,'香蕉')
查看数据库: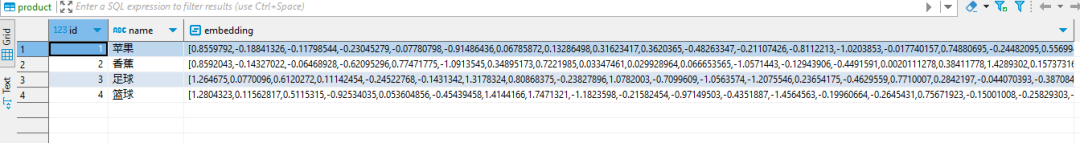
我们写一个相似度的查询SQL:
def querySimiliary(text):
embeddings = generatedEmbedding(text)
print(embeddings)
sql = """
SELECT id, name, 1 - (embedding <=> '{}') AS cosine_similarity
FROM product
ORDER BY cosine_similarity DESC LIMIT 2
""".format(embeddings)
conn = connect2PG()
return querySQL(conn,sql)
我们查询一下:querySimiliary(“一种水果糖分高,黄色表皮”)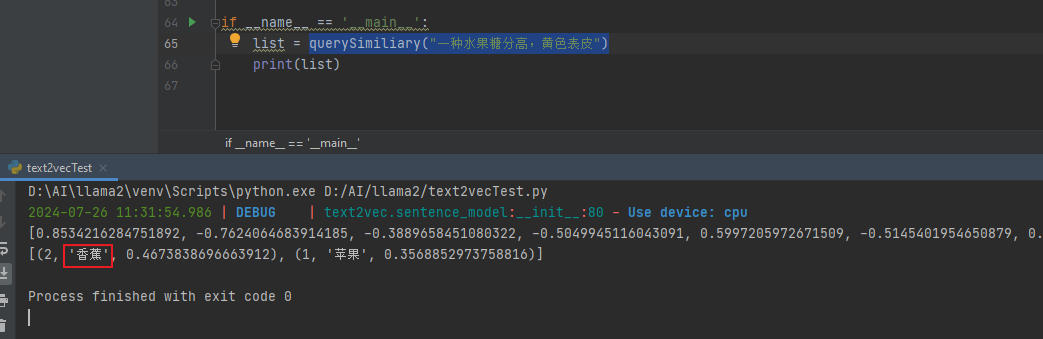
再次尝试:querySimiliary(“apple的中文是什么”)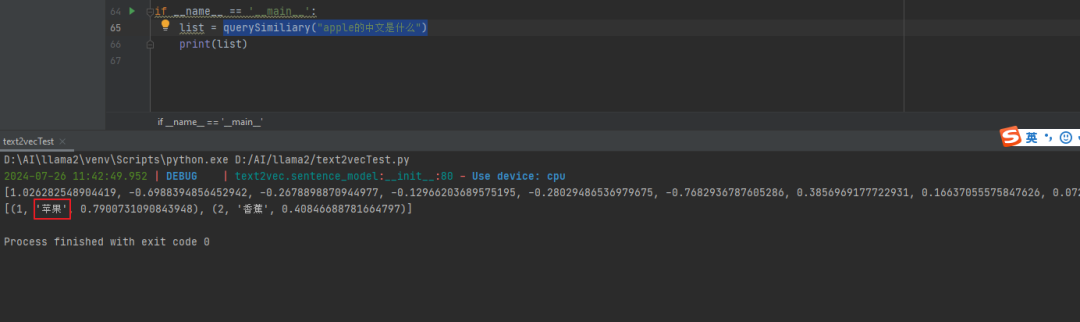
querySimiliary(“我要运动,有推荐的项目吗?”)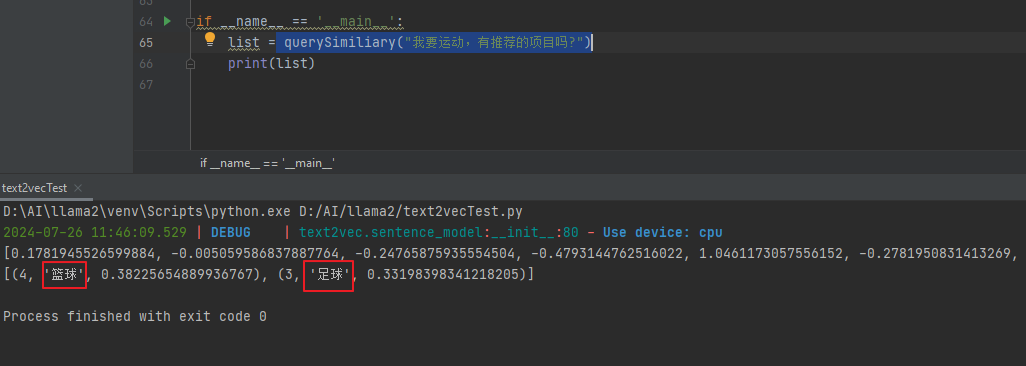
我们完成了python最数据库的基本操作后,下面我们看看vector 相关的索引:
hnsw类型索引:什么是HNSW呢?Hierarchical Navigable Small Word 网上基本上都翻译成:分层导航小世界
HNSW 是一种近似最近邻检索(ANN)索引。它基于图的性质旨在实现高效的搜索,尤其是在较大的数据规模下。HNSW 创建了一个多层次的图,每一层代表数据的一个子集,通过快速遍历这些层来找到近似最近邻。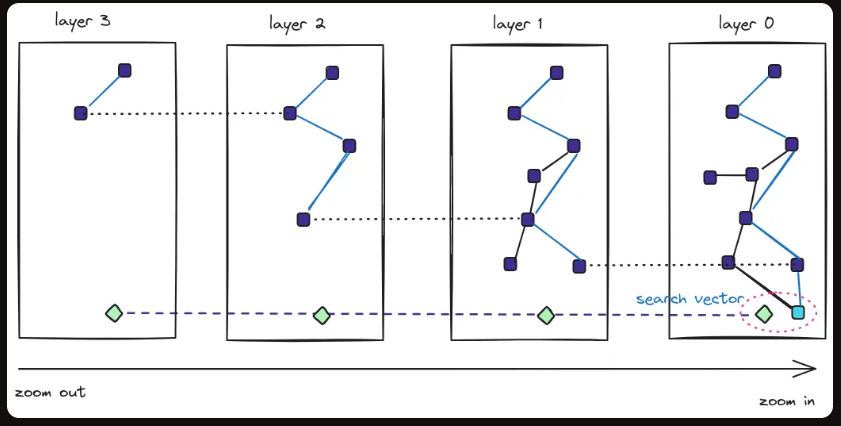
我们新建一张表,load进去一些数据,看一下执行查询语句的计划
postgres=> create table vector(id int, embeddings vector(3));
CREATE TABLE
postgres=> insert into vector select generate_series(1,10), STRING_TO_ARRAY(generate_series(1,10)||',1,2', ',')::int[];
INSERT 0 10
postgres=> select * from vector;
id | embeddings
----+------------
1 | [1,1,2]
2 | [2,1,2]
3 | [3,1,2]
4 | [4,1,2]
5 | [5,1,2]
6 | [6,1,2]
7 | [7,1,2]
8 | [8,1,2]
9 | [9,1,2]
10 | [10,1,2]
(10 rows)
相似度查询:我们看到计划是Seq Scan on vector
postgres=> explain analyze SELECT * FROM vector ORDER BY embeddings <-> '[3,1,2]' LIMIT 1;
QUERY PLAN
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Limit (cost=32.23..32.23 rows=1 width=44) (actual time=0.026..0.026 rows=1 loops=1)
-> Sort (cost=32.23..35.40 rows=1270 width=44) (actual time=0.025..0.025 rows=1 loops=1)
Sort Key: ((embeddings <-> '[3,1,2]'::public.vector))
Sort Method: top-N heapsort Memory: 25kB
-> Seq Scan on vector (cost=0.00..25.88 rows=1270 width=44) (actual time=0.011..0.014 rows=10 loops=1)
Planning Time: 0.055 ms
Execution Time: 0.044 ms
(7 rows)
我们在vector 这个列上 创建一个hnsw类型的索引:
postgres=> CREATE INDEX ON vector USING hnsw (embeddings vector_l2_ops);
CREATE INDEX
再次查看执行计划:我们看到触发了之前我们创建的索引
postgres=> explain analyze SELECT * FROM vector ORDER BY embeddings <-> '[3,1,2]' LIMIT 1;
QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Limit (cost=8.07..8.49 rows=1 width=44) (actual time=0.031..0.032 rows=1 loops=1)
-> Index Scan using vector_embeddings_idx on vector (cost=8.07..12.20 rows=10 width=44) (actual time=0.031..0.031 rows=1 loops=1)
Order By: (embeddings <-> '[3,1,2]'::public.vector)
Planning Time: 0.088 ms
Execution Time: 0.053 ms
(5 rows)
对于hnsw 索引的创建有如下几种距离的计算方式:
L2 distance:CREATE INDEX ON items USING hnsw (embedding vector_l2_ops);
Inner product:CREATE INDEX ON items USING hnsw (embedding vector_ip_ops);
Cosine distance:CREATE INDEX ON items USING hnsw (embedding vector_cosine_ops);
L1 distance:CREATE INDEX ON items USING hnsw (embedding vector_l1_ops);
Hamming distance :REATE INDEX ON items USING hnsw (embedding bit_hamming_ops);
Jaccard distance:CREATE INDEX ON items USING hnsw (embedding bit_jaccard_ops)
关于index 创建的参数选项:
m - the max number of connections per layer (16 by default)
m表示每一个图层layer中,点之间的相邻的最大个数 ,默认是16个,
增大M的值,意味着每个点有更多的邻居节点,从而加快了查询的速度,负面影响是创建的速度,磁盘和内存的开销
ef_construction - the size of the dynamic candidate list for constructing the graph (64 by default)
ef_construction 控制索引构建过程中使用的候选列表大小,默认是64个
理论上来说候选list 越大,index的质量越好,但是会增加索引构建的时间。
下面这幅图描述了hnsw 创建时间和参数ef_construction的关系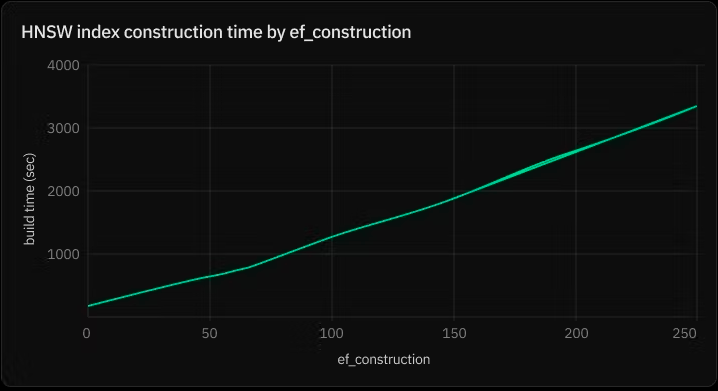
具体创建索引的语法参数是:
CREATE INDEX ON words USING hnsw (embedding vector_cosine_ops) WITH (m = 16, ef_construction = 64);
IVFFlat类型索引:Inverted File with Flat Indexing
IVFFlat结合了倒排文件和平坦索引的思想。它通过将数据集划分为多个list(或组),每个list维护一个倒排列表和一个平坦索引,用于快速搜索桶内的近邻。
It has faster build times and uses less memory than HNSW, but has lower query performance
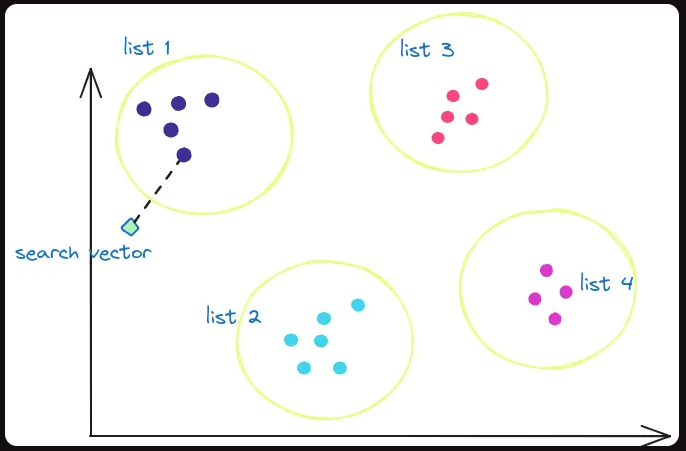
我们创建一张表 vector2 并创建 IVFFlat类型索引:
postgres=> create table vector2(id int, embedding vector(3));
CREATE TABLE
postgres=> insert into vector2 select generate_series(1,10000), STRING_TO_ARRAY(generate_series(1,10000)||',1,2', ',')::int[];
INSERT 0 10000
postgres=> select count(1) from vector2;
count
-------
10000
(1 row)
创建IVFFlat类型索引:
postgres=> CREATE INDEX ON vector2 USING ivfflat (embedding vector_l2_ops) WITH (lists = 10);
CREATE INDEX
查看查询执行计划:
postgres=> explain analyze SELECT * FROM vector2 ORDER BY embedding <-> '[3,1,2]' LIMIT 1;
QUERY PLAN
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Limit (cost=22.50..22.53 rows=1 width=29) (actual time=0.404..0.406 rows=1 loops=1)
-> Index Scan using vector2_embedding_idx2 on vector2 (cost=22.50..313.50 rows=10000 width=29) (actual time=0.402..0.404 rows=1 loops=1)
Order By: (embedding <-> '[3,1,2]'::vector)
Planning Time: 2.915 ms
Execution Time: 0.447 ms
(5 rows)
关于IVFFlat 索引创建的2个参数说明:
list : Choose an appropriate number of lists - a good place to start is rows 1000 for up to 1M rows and sqrt(rows) for over 1M rows
list 是创建索引的时候指定的参数从数值通常选取 表大小/1000 (1百万业内),(大于1百万的话) 采用sqrt(rows)
probes: When querying, specify an appropriate number of probes (higher is better for recall, lower is better for speed) - a good place to start is sqrt(lists)
probes:索引查询的时候设置的参数(数值小速度快,数值大recall好),最佳起始值为sqrt(rows)
postgres=> set ivfflat.probes =100;
SET
postgres=> explain analyze SELECT * FROM vector2 ORDER BY embedding <-> '[3,1,2]' LIMIT 1;
QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Limit (cost=205.00..205.04 rows=1 width=29) (actual time=9.330..9.334 rows=1 loops=1)
-> Index Scan using vector2_embedding_idx2 on vector2 (cost=205.00..586.00 rows=10000 width=29) (actual time=9.328..9.332 rows=1 loops=1)
Order By: (embedding <-> '[3,1,2]'::vector)
Planning Time: 0.146 ms
Execution Time: 9.546 ms
(5 rows)
这个参数默ivfflat.probes 认是1
postgres=> reset ivfflat.probes;
RESET
postgres=> show ivfflat.probes;
ivfflat.probes
----------------
1
(1 row)
postgres=> explain analyze SELECT * FROM vector2 ORDER BY embedding <-> '[3,1,2]' LIMIT 1;
QUERY PLAN
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Limit (cost=22.50..22.53 rows=1 width=29) (actual time=0.412..0.413 rows=1 loops=1)
-> Index Scan using vector2_embedding_idx2 on vector2 (cost=22.50..313.50 rows=10000 width=29) (actual time=0.411..0.411 rows=1 loops=1)
Order By: (embedding <-> '[3,1,2]'::vector)
Planning Time: 0.095 ms
Execution Time: 0.438 ms
(5 rows)
可以看出ivfflat.probes = 1 数值越小,执行查询的时间越快。Execution Time: 0.438 ms(ivfflat.probes = 1) vs Execution Time: 9.546 ms (ivfflat.probes =100)
最后我们横向的比较一下2种索引的构建时间和查询效率的比较:
数据量基数为1000万:max_parallel_maintenance_workers TO 4 和 set maintenance_work_mem=’8GB’ 条件下
hnsw: index 创建时间05:41.715 (4个并行和8GB的内存)
postgres=> create table vector_hnsw(id int, embedding vector(3));
CREATE TABLE
Time: 19.506 ms
postgres=> insert into vector_hnsw select generate_series(1,10000000), STRING_TO_ARRAY(generate_series(1,10000000)||',1,2', ',')::int[];
INSERT 0 10000000
Time: 22864.818 ms (00:22.865)
postgres=> SET max_parallel_maintenance_workers TO 4;
SET
Time: 0.269 ms
postgres=> set maintenance_work_mem='8GB';
SET
Time: 0.198 ms
postgres=> CREATE INDEX ON vector_hnsw USING hnsw (embedding vector_l2_ops);
CREATE INDEX
Time: 341715.259 ms (05:41.715)
表大小和hnsw 索引的大小:可以索引大小是表的6倍左右。3037 MB/498 M = 6
表大小:
postgres=> select pg_size_pretty(pg_relation_size('vector_hnsw'));
pg_size_pretty
----------------
498 MB
(1 row)
索引大小:
postgres=> select pg_size_pretty(pg_total_relation_size('vector_hnsw')-pg_relation_size('vector_hnsw'));
pg_size_pretty
----------------
3037 MB
(1 row)
Time: 0.909 ms
postgres=> select 3037/498;
?column?
----------
6
(1 row)
我们再来看一下 ivfflat: index 创建时间 04:34.026 (4个并行和8GB的内存)
postgres=> create table vector_ivfflat(id int, embedding vector(3));
CREATE TABLE
Time: 8.332 ms
postgres=> insert into vector_ivfflat select generate_series(1,10000000), STRING_TO_ARRAY(generate_series(1,10000000)||',1,2', ',')::int[];
INSERT 0 10000000
Time: 21212.166 ms (00:21.212)
postgres=> SET max_parallel_maintenance_workers TO 4;
SET
Time: 0.296 ms
postgres=> set maintenance_work_mem='8GB';
SET
Time: 0.211 ms
postgres=> select sqrt(10000000);
sqrt
--------------------
3162.2776601683795
(1 row)
Time: 1.175 ms
postgres=> CREATE INDEX ON vector_ivfflat USING ivfflat (embedding vector_l2_ops) WITH (lists = 3200);
CREATE INDEX
Time: 274025.837 ms (04:34.026)
表大小和ivfflat 索引的大小:索引(357 MB)比表(498 MB)略小
postgres=> select pg_size_pretty(pg_relation_size('vector_ivfflat'));
pg_size_pretty
----------------
498 MB
(1 row)
Time: 1.527 ms
postgres=> select pg_size_pretty(pg_total_relation_size('vector_ivfflat')-pg_relation_size('vector_ivfflat'));
pg_size_pretty
----------------
357 MB
(1 row)
Time: 0.989 ms
最后看一下单条SQL的查询效率:果然在查询性能上会精掉你的下巴:
Index Scan using vector_ivfflat_embedding_idx:Execution Time: 2879.538 ms
Index Scan using vector_hnsw_embedding_idx:Execution Time: 6.373 ms
至少在我的实验环境中 hnsw 类型的索引性能要远远好于vfflat 类型的索引
postgres=> explain analyze SELECT * FROM vector_ivfflat ORDER BY embedding <-> '[3,1,2]' LIMIT 1;
QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Limit (cost=45.94..45.94 rows=1 width=29) (actual time=2841.296..2841.300 rows=1 loops=1)
-> Index Scan using vector_ivfflat_embedding_idx on vector_ivfflat (cost=45.94..31179.19 rows=
10000000 width=29) (actual time=2841.292..2841.293 rows=1 loops=1)
Order By: (embedding <-> '[3,1,2]'::vector)
Planning Time: 0.097 ms
Execution Time: 2879.538 ms
(5 rows)
postgres=> explain analyze SELECT * FROM vector_hnsw ORDER BY embedding <-> '[3,1,2]' LIMIT 1;
QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------
Limit (cost=10.84..10.87 rows=1 width=29) (actual time=6.233..6.246 rows=1 loops=1)
-> Index Scan using vector_hnsw_embedding_idx on vector_hnsw (cost=10.84..252400.84 rows=10000
000 width=29) (actual time=6.230..6.231 rows=1 loops=1)
Order By: (embedding <-> '[3,1,2]'::vector)
Planning Time: 0.628 ms
Execution Time: 6.373 ms
(5 rows)
至此我们总结一下2种类型索引的对比:
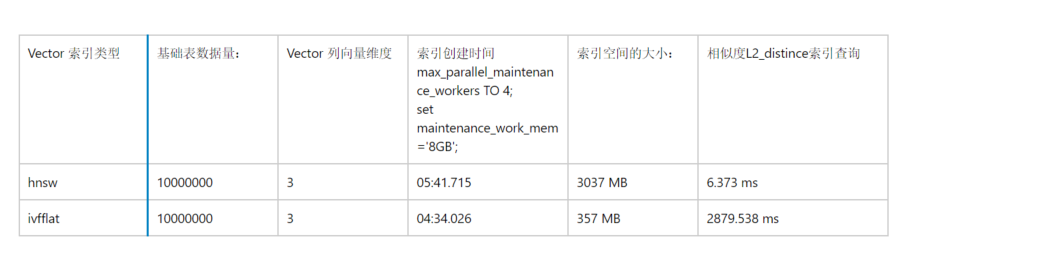
从上述对比的表格中,我们可以看出:
1.索引创建时间上,HNSW的构建时间要略长于ivfflat
2索引空间比上,由于hnsw是基于graph 多个layer 构建的,索引需要更大的空间,设置是表大小很多倍
3.单条查询效率上hnsw 远远好于ivfflat , hnsw 甚至适合于OLAP类型的查询,ivflat 适合OLAP类型的查询报表。
4.此外相对于传统btree索引, 向量索引在构建过程中对数据库内存,CPU资源要求更高。在索引创建过程中如果内存资源不足会产生提示:
postgres=> CREATE INDEX ON vector_hnsw USING hnsw (embedding vector_l2_ops);
NOTICE: hnsw graph no longer fits into maintenance_work_mem after 6146391 tuples
DETAIL: Building will take significantly more time.
HINT: Increase maintenance_work_mem to speed up builds.
最后我们总结一下:
1.市面上的向量数据库种类繁多, 可以参考一下向量数据库之间的比较,以及表达了DBA选择向量数据库的观点:按照实际的项目需求选择你熟悉的数据库
2.pgvector 的安装以及使用以及整合embedding model 进行向量数据的插入和相似度查询
3.关于vector 2种索引类型 hnsw 和 ivfflat 测试和比较:优先选择 hnsw 更适合业务系统, 相对于传统的btree索引,需要考虑到硬件资源加大投入的问题尤其是内存和磁盘空间。
Have a fun 🙂 !








