前言
为什么集合写的好好的,突然要来写 Redis 呢 ?
一切的原因都要从今天的需求说起,今天接了一个需求,目标是做一个推广页的 UV (统计访客, 每天只记录同一个访客一次) 统计,因为前段时间刚刚看过老钱写的 《Redis深度历险》 HyperLogLog 篇依旧历历在目,一样是统计 UV 的场景,我就直接提出用 HyperLogLog 去处理这个问题,然后被领导问为什么要用 HyperLogLog 好在哪的时候卡壳了,emmm ... 本来想凭借我这广阔的技术海无形装逼,这特么不尴尬了。

于是我痛定思痛,决定对照着看过的本博客和书籍复习一波 HyperLogLog,连夜肝了一篇 HyperLogLog 也相当于读书笔记,准备明天分享给你们分享,有实战代码哦👍
HyperLogLog 与 基数统计
HyperLogLog 是最早由 Flajolet 及其同事在 2007 年提出的一种 估算基数的近似最优算法,具体定义可以参考维基百科:https://en.jinzhao.wiki/wiki/HyperLogLog
所谓基数统计可以理解为用来统计一个集合中不重复的元素,也就是我们今天要讲解 HyperLogLog 的原因
业务场景分析
领导的需求是:统计每个网页的访客数量, 每个用户只记录一次
我们来捋顺一下思路, 可能你会想出如下几种方案:
Plan A : 数据库里建张表,没有一个表解决不了的问题,如果有那么就建两张表 .
Plan B : 建立一个 Set 集合, 存储当天访问过此页面的所有用户 id .
Plan C : bitmap,类似用户签到的解决方案,依据年月做 key , 日期作为偏移量 .
我们来分析一下这几种方案,首先数据库解决是不可能了,甭说做每个月的 UV 统计分析了, 一天的访问量存起来空间就占了太多了; 那么为每个页面设置一个 Set 怎么样呢 ? 依旧是访问量的问题,如果访问量很高 Set 的集合会非常大,集合一大去重的时候就 ... 你懂的, 所以 Set 也不行; 那么 bitmap 呢 ? bitmap 的一个元素可以对应到 bit 数组中的一位,使用 bitmap 确实很节省内存,可是在大数据量的场景下,依旧需要很多内存,并不适用 。
三个计划全部拉闸,怎么办呢?哎,拉闸就对了,不拉闸怎么讲我们今天要说的 HyperLogLog 呢?
概率算法
HyperLogLog 采取概率算法,所谓概率算法就是通过一定的概率统计方法预估基数值,而概率算法并不直接存储数据集合本身,这种方法可以极大的节省内存,并保证误差在一定范围内,HyperLogLog 在标准误差(0.81%)的前提下能够统计 2^64 个数据!
Redis 中的 HyperLogLog 原理
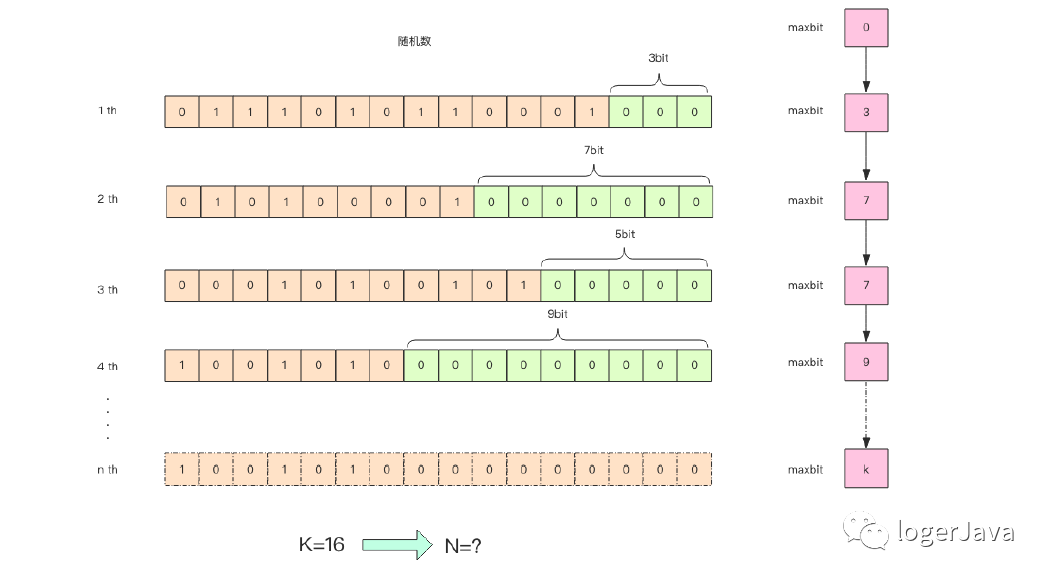
这张图的意思是,给定一系列的随机整数,我们记录下低位连续零位的最大长度K,这个参数就是图中的 maxbit,通过这个K值可以估算出随机数的数量 N,下面我们编写一段代码,观察 N 和 K 的关系
public class PfTest {static class BitKeeper {private int maxbits;public void random() {long value = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextLong(2L << 32);int bits = lowZeros(value);if (bits > this.maxbits) {this.maxbits = bits;}}private int lowZeros(long value) {int i = 1;for (; i < 32; i++) {if (value >> i << i != value) {break;}}return i - 1;}}static class Experiment {private int n;private BitKeeper bitKeeper;public Experiment(int n) {this.n = n;this.bitKeeper = new BitKeeper();}public void work() {for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {this.bitKeeper.random();}}public void debug() {System.out.printf("%d %.2f %d\n", this.n, Math.log(this.n) / Math.log(2), this.bitKeeper.maxbits);}}public static void main(String[] args) {for (int i = 1000; i < 100000; i += 100) {Experiment experiment = new Experiment(i);experiment.work();experiment.debug();}}}
输出结果很多,截取一部分,输出结果如下 :
1000 9.97 131100 10.10 151200 10.23 141300 10.34 111400 10.45 111500 10.55 121600 10.64 81700 10.73 101800 10.81 121900 10.89 102000 10.97 142100 11.04 92200 11.10 132300 11.17 112400 11.23 9
我们可以看到,K 和 N 的对数之间确实存在着线性相关性 :N ≈ 2K
如果 N 介于 2k 和 2k+1 之间,用这种方式估计的值都等于 2k,这明显是不合理的,所以我们可以使用多个 BitKeeper 进行加权估计,就可以得到一个比较准确的值了:
public class PfTest {static class BitKeeper {private int maxbits;public void random() {long value = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextLong(2L << 32);int bits = lowZeros(value);if (bits > this.maxbits) {this.maxbits = bits;}}private int lowZeros(long value) {int i = 1;for (; i < 32; i++) {if (value >> i << i != value) {break;}}return i - 1;}}static class Experiment {private int n;private int k;private BitKeeper[] keepers;public Experiment(int n) {this(n, 1024);}public Experiment(int n, int k) {this.n = n;this.k = k;this.keepers = new BitKeeper[k];for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {this.keepers[i] = new BitKeeper();}}public void work() {for (int i = 0; i < this.n; i++) {long m = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextLong(1L << 32);BitKeeper keeper = keepers[(int) (((m & 0xfff0000) >> 16) % keepers.length)];keeper.random();}}public double estimate() {double sumbitsInverse = 0.0;for (BitKeeper keeper : keepers) {sumbitsInverse += 1.0 / (float) keeper.maxbits;}double avgBits = (float) keepers.length / sumbitsInverse;return Math.pow(2, avgBits) * this.k;}}public static void main(String[] args) {for (int i = 100000; i < 1000000; i += 100000) {Experiment exp = new Experiment(i);exp.work();double est = exp.estimate();System.out.printf("%d %.2f %.2f\n", i, est, Math.abs(est - i) / i);}}}
我在搜寻网上博客解释时,有一个老哥的解释比较生动形象,我们这里也采用他的解释方法:
这个过程有点 类似于选秀节目里面的打分,一堆专业评委打分,但是有一些评委因为自己特别喜欢所以给高了,一些评委又打低了,所以一般都要 屏蔽最高分和最低分,然后 再计算平均值,这样得出来的分数就差不多是公平公正的了。
在计算平均值的时候,采用了 调和平均数,也就是倒数的平均值,它能有效地平滑离群值的影响
avg = (3 + 4 + 5 + 104) / 4 = 29avg = 4 / (1/3 + 1/4 + 1/5 + 1/104) = 5.044
我们观察输出结果,误差率百分比控制在个位数:
100000 93786.03 0.06200000 192010.26 0.04300000 295451.43 0.02400000 394595.83 0.01500000 502096.02 0.00600000 644347.82 0.07700000 752617.39 0.08800000 840280.38 0.05900000 898276.74 0.00
真实的 HyperLogLog 要比上面的示例代码更加复杂一些,也更加精确一些。上面这个算法在随机次数很少的情况下会出现除零错误,因为 maxbit = 0
是不可以求倒数的。
关于 HyperLogLog 大家也可以进入这个网站实际操作一下,理解的更快:http://content.research.neustar.biz/blog/hll.html
实战
我们先来看一下 RedisTemplate 操作 HyperLogLog 的方法 :
// 将指定的元素添加到HyperLogLog中,可以添加多个元素public void pfAdd(String key, String... value) {redisTemplate.opsForHyperLogLog().add(key, value);}// 返回给定HyperLogLog的基数估算值。当一次统计多个HyperLogLog时(通过key实现时间窗口统计user:web1:2020061600、user:web1:2020061601),需要对多个HyperLogLog结构进行比较,并将并集的结果放入一个临时的HyperLogLog,性能不高,谨慎使用public Long pfCount(String... key) {return redisTemplate.opsForHyperLogLog().size(key);}// 将多个HyperLogLog进行合并,将并集的结果放入一个指定的HyperLogLog中public void pfMerge(String destKey, String... sourceKey) {redisTemplate.opsForHyperLogLog().union(destKey, sourceKey);}
loger来写一段代码,看一下 HyperLogLog 到底怎么来统计 UV :
public class RedisTest {@Autowiredprivate RedisTemplate redisTemplate;public void addUV(String id, LocalDate localDate){String redisKey = String.format("single:%s", localDate);redisTemplate.opsForHyperLogLog().add(redisKey, id);}// 统计指定日期范围内的uvpublic long calculateUV(LocalDate start, LocalDate end) {// 整理该日期范围内的keyList<String> keyList = new ArrayList<>();while (!start.isAfter(end)) {String key = String.format("single:%s", start);keyList.add(key);start = start.plusDays(1);}// 合并这些日期内的数据String redisKey = String.format("interval:%s:%S", start, end);redisTemplate.opsForHyperLogLog().union(redisKey, keyList.toArray());// 返回统计后的结果return redisTemplate.opsForHyperLogLog().size(redisKey);}}
感兴趣的小伙伴建议自己写到 idea 里面试一下
参考资料
[HyperLogLog算法原文] HyperLogLog: the analysis of a near-optimal cardinality estimation algorithm
http://algo.inria.fr/flajolet/Publications/FlFuGaMe07.pdf
[Rdis作者博客] Redis new data structure: the HyperLogLog
http://antirez.com/news/75
[Reids—神奇的HyperLoglog解决统计问题] - 我没有三颗心脏、敖丙
《Redis深度历险-核心原理与实践应用》 - 钱文品/ 著
扫描二维码关注更多技术分享






