10、JDBC(极其重点)
10.1、数据库驱动
程序需要通过数据库驱动和数据库交互
10.2、JDBC
SUN公司为了简化开发人员的(对数据库的统一)操作,提供了一个(Java操作数据库的)规范,称JDBC
规范的实现由具体数据库厂商去做
对开发人员开始,只需掌握JDBC接口的操作即可
JDBC所需包
java.sql
javax.sql
mysql-connector-java-xxx.jar
10.3、简单的JDBC程序
测试数据库
-- JDBC 测试数据库
CREATE DATABASE `jdbcStudy` CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci;
USE `jdbcStudy`;
CREATE TABLE `users`(
`id` INT PRIMARY KEY,
`NAME` VARCHAR(40),
`PASSWORD` VARCHAR(40),
`email` VARCHAR(60),
birthday DATE
);
1、idea中创建jdbc项目
2、在当前项目下新建lib目录,导入依赖mysql-connector-java-xxx.jar包
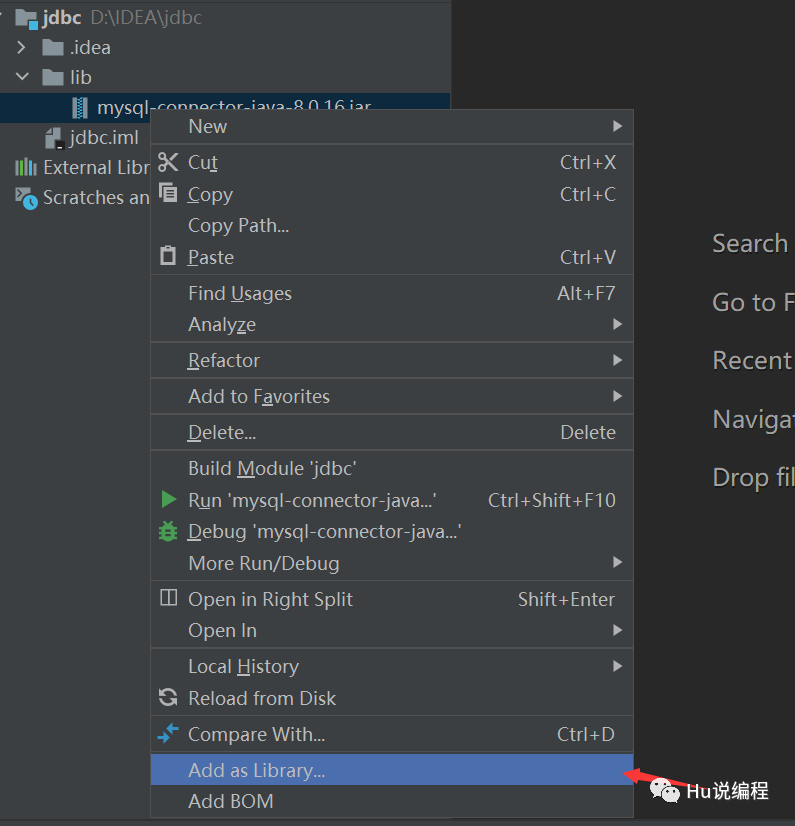
3、编写测试代码
/*
* Java中MySQL连接测试
* */
public class jdbc_First_Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
// 1 加载驱动
// MySQL8.0以上版本将 com.mysql.jdbc.Driver 更换为 com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); // 固定加载驱动的写法
// 2 用户信息和url
/*
* ?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
* 指定字符的编码、解码格式
mysql数据库用的是gbk编码,而你项目的mysql数据库需要的是utf-8编码,所以在url
后面添加?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8",表示
(1)数据库在存放项目数据的时候会先用UTF-8格式将数据解码成字节码,
然后再将解码后的字节码重新使用GBK编码存放到数据库中;
(2)从数据库中取数据的时候,数据库会先将数据库中的数据按GBK格式解码成字节码,
然后再将解码后的字节码重新按UTF-8格式编码数据,最后再将数据返回给客户端。
* MySQL 8.0 以上版本不需要建立 SSL 连接的,需要显示关闭。
* allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true 允许客户端从服务器获取公钥。
* serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai编译器上设置的时区属性会Asia/Shanghai,与国内时区保持一致
* */
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8" + "&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai";
String username = "root";
String password = "123456";
// 3 连接成功,数据库对象 connection表示数据库
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
// 4 执行SQL对象 statement表示执行SQL的对象
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
// 5 通过SQL对象 执行 SQL语句, 可能存在结果,查看返回结果
String sql = "SELECT * FROM users";
// 返回SQL语句执行后的结果集,结果集封装了全部的查询结果
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
while (resultSet.next()){
System.out.println("id: "+resultSet.getObject("id"));
System.out.println("name: "+resultSet.getObject("NAME"));
System.out.println("pwd: "+resultSet.getObject("PASSWORD"));
System.out.println("email: "+resultSet.getObject("email"));
System.out.println("birth: "+resultSet.getObject("birthday"));
System.out.println("---------------------");
}
// 6 释放连接
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
步骤:
1、加载MySQL驱动
2、连接数据库 DriverManager
3、获得SQL对象 statement
4、获得返回结果 resultSet
5、释放连接
DriverManager
// DriverManager.registerDriver(new com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver());
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); // 固定加载驱动的写法
// 源码
// Class.forName()利用反射获取对象时本质上是调用源码中静态代码块
// 这种方式会注册加载驱动,但不会创建Driver()对象
public class Driver extends NonRegisteringDriver implements java.sql.Driver {
public Driver() throws SQLException {
}
static {
try {
DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver());
} catch (SQLException var1) {
throw new RuntimeException("Can't register driver!");
}
}
}
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
// connection 代表数据库
// 数据库设置自动提交
// 事物提交
// 事物回滚
connection.rollback();
connection.commit();
connection.setAutoCommit(true);
URL
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8" + "&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai";
// mysql -- 3306(端口号)
// jdbc:mysql://主机地址:端口名/数据库名?参数1&参数2&参数3
// oracle -- 1521
// jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:sid
Statement 执行SQL对象 PrepareStatement 执行SQL对象String sql = "SELECT * FROM users"; // sql语句
statement.executeQuery(sql); // 查询操作返回结果集 ResultSet
statement.execute(sql); // 执行任意SQL语句
statement.executeUpdate(sql); // 更新、插入、删除都是这个语句,返回一个受影响的行数
ResultSet 查询的结果集:封装了所有的查询结果
获得指定数据类型
resultSet.getObject();
resultSet.getString();
resultSet.getInt();
resultSet.getFloat();
resultSet.getDate();
遍历(使用指针)
resultSet.beforeFirst(); // 移动到最前
resultSet.afterLast(); // 移动到最后
resultSet.next(); // 移动到下一个数据
resultSet.previous(); // 移动到前一行
resultSet.absolute(row); // 移动到指定行
释放资源
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close(); // 耗资源,用完关闭
10.4、statement对象
jdbc中的statement对象用于向数据库发送SQL语句,需要通过这个对象向数据库发送增删改查的语句来完成对数据库的增删改查。
Statement对象中的executeUpdate方法,用于向数据库发送增、删、改的SQL语句,执行完之后,返回一个整数(整数为增删改导致数据库中几行数据发生变化)
Statement.executeQuery方法用于向数据库发送查询语句,返回查询结果的ResultSet对象
CRUD-create
使用executeUpdate(String sql)方法完成数据添加操作,示例:
statement st = conn.createStatement();
String sql = "insert into users(...) values(...)";
int num = st.executeUpdate(sql);
if(num>0){
System.out.println("插入成功!");
}
CRUD-delete
使用executeUpdate(String sql)方法完成数据删除操作,示例:
statement st = conn.createStatement();
String sql = "delete from users where id = 1";
int num = st.executeUpdate(sql);
if(num>0){
System.out.println("删除成功!");
}
CRUD-update
使用executeUpdate(String sql)方法完成数据更新操作,示例:
statement st = conn.createStatement();
String sql = "update users set NAME='' where NAME = 1";
int num = st.executeUpdate(sql);
if(num>0){
System.out.println("删除成功!");
}
CRUD-read
使用executeQuery(String sql)方法完成数据更新操作,示例:
statement st = conn.createStatement();
String sql = "select * from users where id = 1";
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery(sql);
while(rs.next()){
// 根据结果集的列的数据类型,分别调用rs的相应方法映射到java对象中
}
代码实现
1、提取工具类
package com.second.utils;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JdbcUtils {
private static String driver = null;
private static String url = null;
private static String username = null;
private static String password = null;
static {
try {
// Class类封装一个对象和接口运行时的状态
// JDBCUtil.class是创建一个JDBCUtil的Class对象
// JDBCUtil.class.getClassLoader()是获得JDBCUtil类的类加载器
// JDBCUtil.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("db.properties")是返回一个读取指定资源的输入流
// 注意:db.properties配置文件应放在src目录下。不然加载不了
InputStream resourceAsStream = JdbcUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("db.properties");
// 创建一个Properties对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
// .load()是从输入流中读取属性列表
properties.load(resourceAsStream);
// 读取指定属性
driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
url = properties.getProperty("url");
username = properties.getProperty("username");
password = properties.getProperty("password");
// 驱动只加载一次
Class.forName(driver);
}catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 获取连接
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
}
// 释放连接资源
public static void release(Connection conn, Statement st, ResultSet rs){
if (rs!=null){
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (st!=null){
try {
st.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn!=null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
// db.properties配置文件,该文件放置于src目录下
driver = com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username = root
password = 123456
2、增删改方法executeUpdate
package com.second;
import com.second.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class _01_InsertTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); // 获取数据库连接
statement = connection.createStatement(); // 获取执行SQL的对象
String sql = "INSERT INTO users(id,`NAME`,`PASSWORD`,`email`,`birthday`) " +
"VALUES(4,'小明','123456','123456@qq.com','2021-05-26')";
int num = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
if (num>0){
System.out.println("插入成功!");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
// statement.close();
// connection.close();
JdbcUtils.release(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
}
}
package com.second;
import com.second.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class _02_DeleteTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); // 获取数据库连接
statement = connection.createStatement(); // 获取执行SQL的对象
String sql = "DELETE FROM users WHERE id=4";
int num = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
if (num>0){
System.out.println("删除成功!");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
}
}
package com.second;
import com.second.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class _03_UpdateTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); // 获取数据库连接
statement = connection.createStatement(); // 获取执行SQL的对象
String sql = "UPDATE users SET `NAME` = '小红' WHERE id = 1";
int num = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
if (num>0){
System.out.println("更新成功!");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
}
}
查询executeQuery
package com.second;
import com.second.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class _04_ReadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
statement = connection.createStatement();
// sql
String sql = "select * from users where id = 1";
resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql); // 查询返回结果集
while (resultSet.next()){
System.out.println(resultSet.getString("NAME"));
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtils.release(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
}
}
SQL注入问题
SQL存在漏洞,容易遭受攻击导致数据泄露。SQL语句被拼接(or)
/*
* SQL注入问题
* */
public class _05_SQLInjection {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// login("小红","123456");
login("'or'1=1","'or'1=1"); // 有对策的其他输入也能查询数据库
}
public static void login(String username,String password){
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
statement = connection.createStatement();
// sql
// SELECT * FROM users WHERE `NAME`='小红' AND `password`='123456'
// SELECT * FROM users WHERE `NAME`=''or'1=1' AND `password`=''or'1=1'
String sql = "select * from users where = `NAME` = '"+username+"' AND `password`='"+password+"'";
resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
while (resultSet.next()){
System.out.println(resultSet.getString("NAME"));
System.out.println(resultSet.getString("password"));
System.out.println("-----------------");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtils.release(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
}
}
10.5、PreparedStatement对象
1、插入
public class _1_InsertTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
// 区别,使用?占位符代替SQL参数,防止SQL注入导致的问题
String sql = "INSERT INTO users(id,`NAME`,`PASSWORD`,`email`,`birthday`) VALUES(?,?,?,?,?)";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 预编译SQL,先写SQL,不执行
// 手动给占位符赋值
statement.setInt(1,4);
statement.setString(2,"小明");
statement.setString(3,"123456");
statement.setString(4,"123456@qq.com");
statement.setString(5, "2021-05-27");
int num = statement.executeUpdate();
if (num>0){
System.out.println("插入成功!");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtils.release(connection,statement,null);
}
}
}
2、删除
public class _2_DeleteTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
// 区别,使用?占位符代替SQL参数,防止SQL注入导致的问题
String sql = "delete from users where id = ?";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 预编译SQL,先写SQL,不执行
// 手动给占位符赋值
statement.setInt(1,4);
int num = statement.executeUpdate();
if (num>0){
System.out.println("删除成功!");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtils.release(connection,statement,null);
}
}
}
3、更新
public class _3_UpdateTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
// 区别,使用?占位符代替SQL参数,防止SQL注入导致的问题
String sql = "update users set `NAME`=? where id = ?";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 预编译SQL,先写SQL,不执行
// 手动给占位符赋值
statement.setString(1,"小兰");
statement.setInt(2,1);
int num = statement.executeUpdate();
if (num>0){
System.out.println("更新成功!");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtils.release(connection,statement,null);
}
}
}
4、查询
public class _4_ReadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
// sql
String sql = "select * from users where id = ?";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 预编译
statement.setInt(1,1); // 传递参数
// 结果集
resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()){
System.out.println(resultSet.getString("NAME"));
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtils.release(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
}
}
5、防止SQL注入
public class _05_SQLInjection {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String username = "小兰";
String password = "123456";
login(username,password);
// login("'or'1=1","'or'1=1"); // 查询失败,有效避免数据泄露
}
public static void login(String username,String password){
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
// sql
// SELECT * FROM users WHERE `NAME`='小红' AND `password`='123456'
// SELECT * FROM users WHERE `NAME`=''or'1=1' AND `password`=''or'1=1'
// PreparedStatement中,把传递进来的参数当做字符
// 如果参数存在转义字符 比如 ' ,会被直接转义。防止SQL拼接
String sql = "select * from users where `NAME` = ? AND `password`=?";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1,username);
statement.setString(2,password);
resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()){
System.out.println(resultSet.getString("NAME"));
System.out.println(resultSet.getString("password"));
System.out.println("-----------------");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtils.release(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
}
}
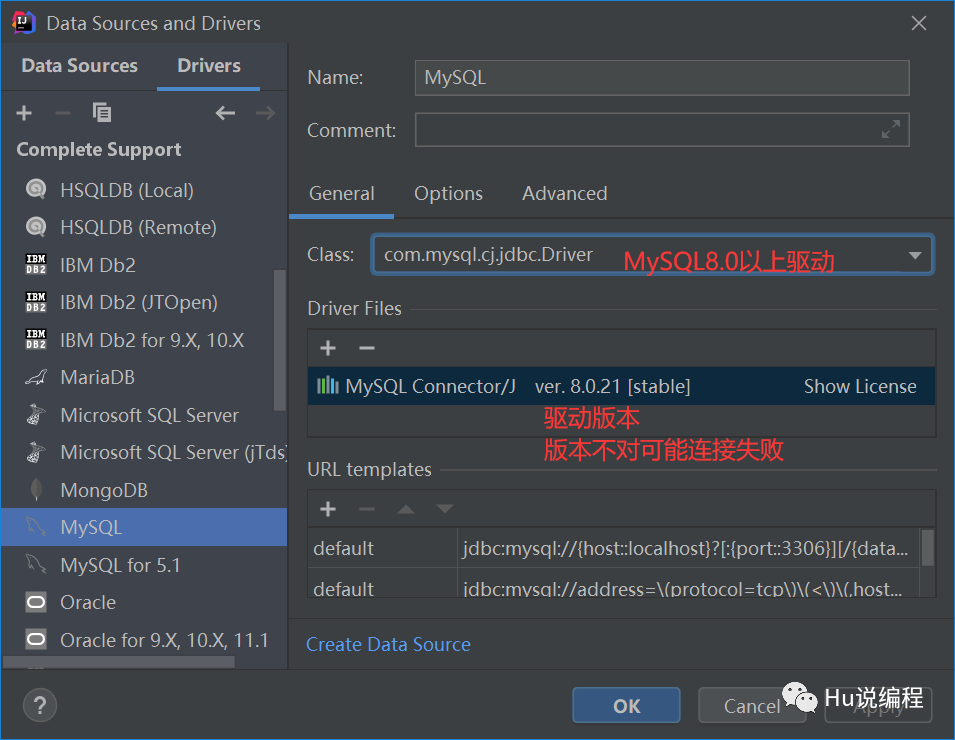
10.6、使用IDEA连接MySQL数据库
1、选择数据库
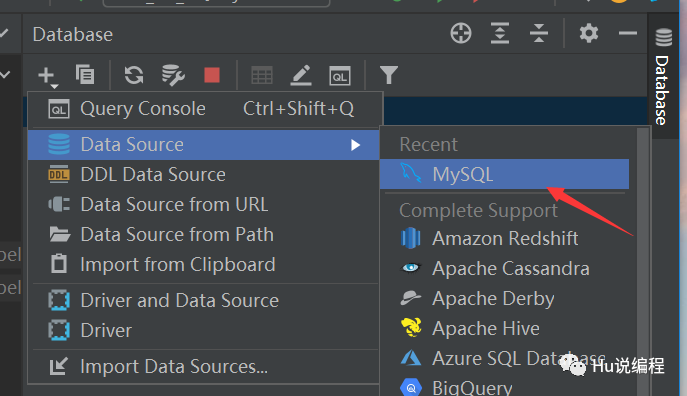
测试连接成功才算连接上。若出现设置时区如下,将时区设置为Asia/Shanghai即可
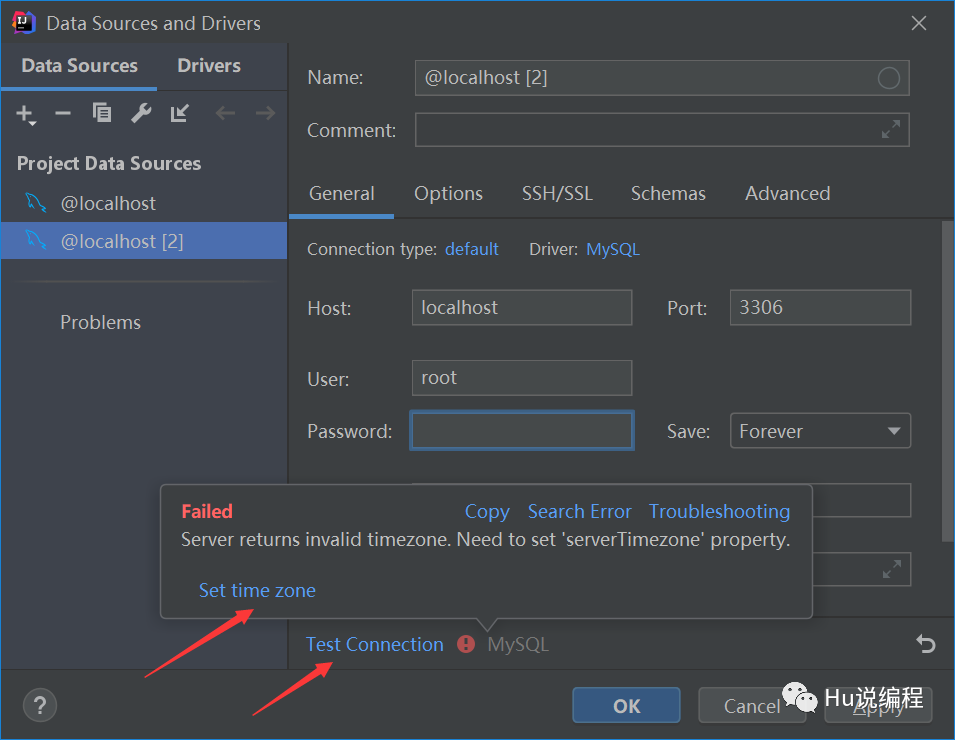
2、连接成功后选择数据库
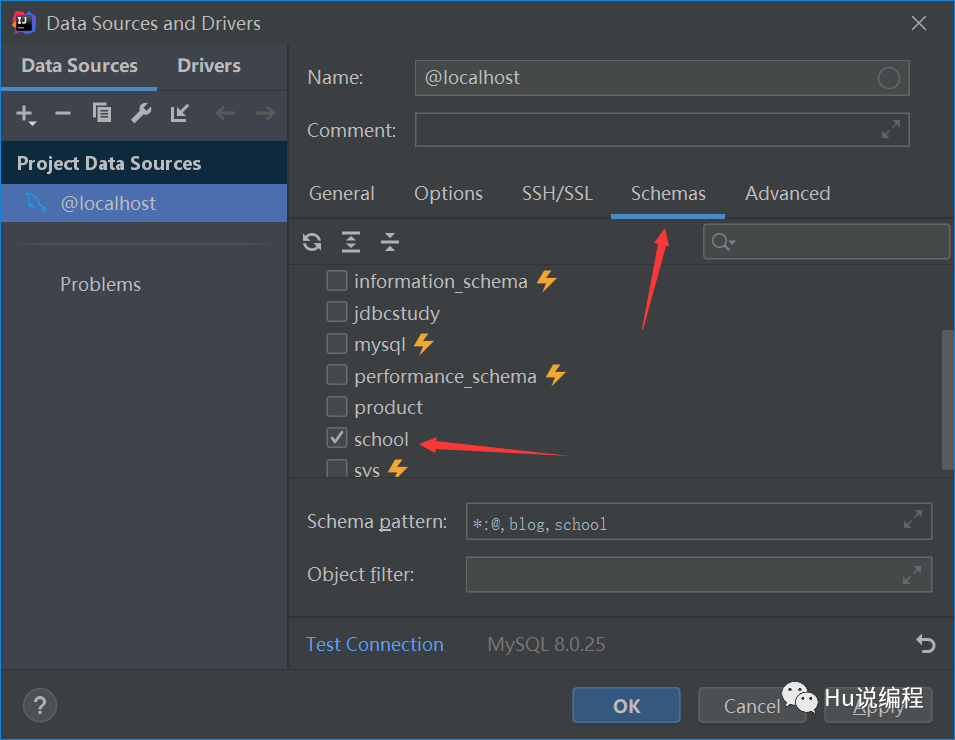
3、查看数据:直接双击数据库表
4、更新数据操作与可视化工具一致,更新完后需要手动提交才能更新成功
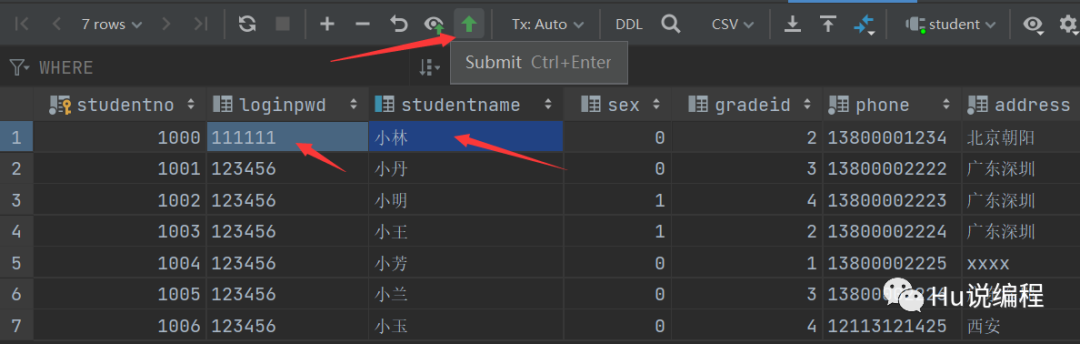
打开编写SQL代码的控制台
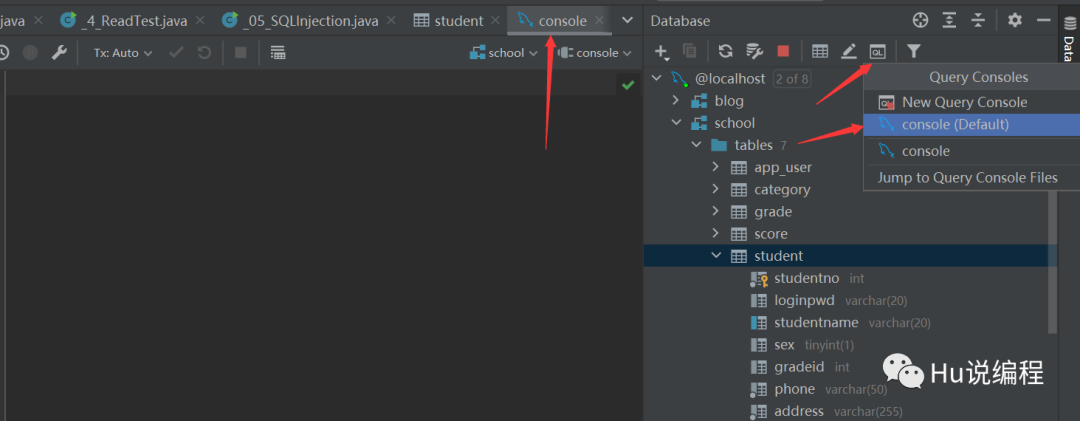
控制台创建表并插入数据
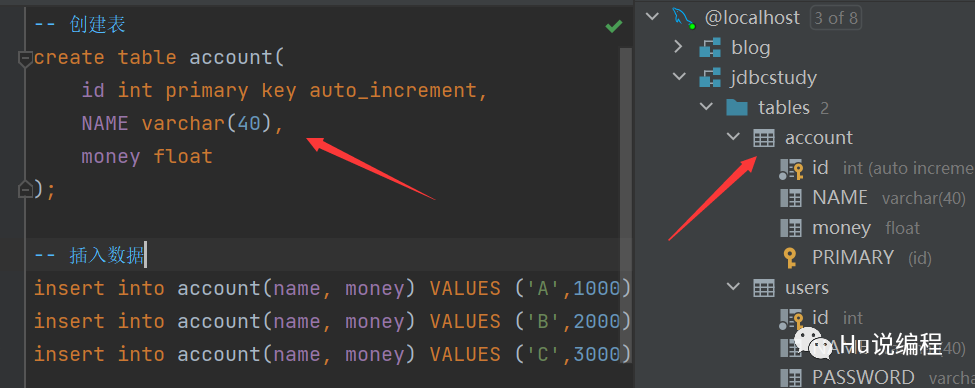
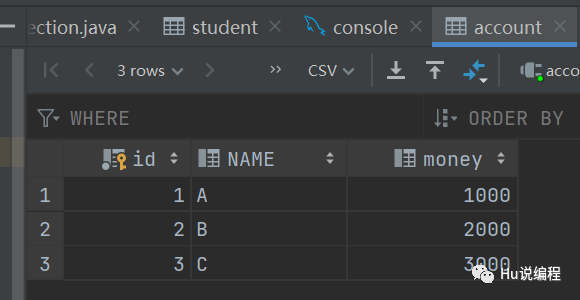
5、注意:
10.7、事物
要么都成功,要么都失败
原子性:要么都完成,要么都不完成
一致性:总数不变
隔离性:多个进程互不干扰
持久性:一旦提交互不可逆,持久化到数据库
隔离性问题:
脏读:一个事物读取另一个没有提交的事物数据
不可重复读:在同一个事物中,重复读取表中的数据,表数据发生改变
幻读:在一个事物内,读取了别的事物插入的数据,导致前后读出结果不一致
代码实现
1、开启事物
2、一组业务执行完毕,提交事物
3、可以在catch语句中显式定义回滚语句。不定义失败也会默认回滚事物
public class _02_TransactionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
// 关闭事物的自动提交,会自动开启事物
connection.setAutoCommit(false); // 开启事物
String sql1 = "update account set money = money-200 where name='A'";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql1);
statement.executeUpdate();
int x = 1/0; // 报错,业务执行失败(下面无法提交事物)
String sql2 = "update account set money = money+200 where name='B'";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql2);
statement.executeUpdate();
// 执行完毕,提交事物
connection.commit();
System.out.println("事物提交成功!");
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
// 如果失败,默认自动回滚事物
try { // 失败则回滚事物
connection.rollback();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
10.8、 数据库连接池
每次CRUD操作都要使用数据库的时候,都要创建一个数据库对象普通的JDBC数据库连接使用DriverManager来获取每次向数据库连接的时候都要将Connection加载到内容中然后再验证用户名和密码花费时间0.05s~1s左右每次CRUD操作就向数据库要一个连接,执行完成后再断开连接,
数据库连接 -- 执行完毕 -- 释放
每次使用数据库都要经历 连接 -- 释放 ,十分浪费系统资源。因此出现池化技术
池化技术:准备一些预先上的数据库资源,需要连接时直接使用预先准备好的
数据库连接池:保存数据库连接对象的容器
最小连接数:10
最大连接数:15
等待超时:100ms
编写连接池,实现一个接口 DataSource
开源数据源实现
DBCP
C3P0
Druid: 阿里
使用这些数据库连接池之后,在项目开发中就不需要编写连接数据库的代码
DBCP
需要的jar包:commons-dbcp-1.4.jar和commons-pool-1.6.jar
demo:
#配置文件
#连接设置
driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username=root
password=123456
#!-- 初始化连接 --
initialSize=10
#最大连接数量
maxActive=50
#!-- 最大空闲连接 --
maxIdle=20
#!-- 最小空闲连接 --
minIdle=5
#!-- 超时等待时间以毫秒为单位 6000毫秒/1000等于60秒 --
maxWait=60000
#JDBC驱动建立连接时附带的连接属性属性的格式必须为这样:【属性名=property;】
#注意:user 与 password 两个属性会被明确地传递,因此这里不需要包含他们。
connectionProperties=useUnicode=true;characterEncoding=UTF8
#指定由连接池所创建的连接的自动提交(auto-commit)状态。
defaultAutoCommit=true
#driver default 指定由连接池所创建的连接的只读(read-only)状态。
#如果没有设置该值,则“setReadOnly”方法将不被调用。(某些驱动并不支持只读模式,如:Informix)
defaultReadOnly=
#driver default 指定由连接池所创建的连接的事务级别(TransactionIsolation)。
#可用值为下列之一:(详情可见javadoc。)NONE,READ_UNCOMMITTED, READ_COMMITTED, REPEATABLE_READ, SERIALIZABLE
defaultTransactionIsolation=READ_UNCOMMITTED
// DBCP连接工具
package com.five.utils;
import com.second.utils.JdbcUtils;
import org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSourceFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JdbcUtils_DBCP {
private static DataSource dataSource = null;
static {
try {
InputStream resourceAsStream = JdbcUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("dbcpconfig.properties");
// 创建一个Properties对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
// .load()是从输入流中读取属性列表
properties.load(resourceAsStream);
// 创建数据源 工厂模式创建
dataSource = BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 获取连接
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return dataSource.getConnection(); // 从数据源中获取连接
}
// 释放连接资源
public static void release(Connection conn, Statement st, ResultSet rs){
if (rs!=null){
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (st!=null){
try {
st.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn!=null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
// DBCP连接池测试
package com.five.utils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class _02_C3P0_Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
// 更换C3P0数据源
connection = JdbcUtils_C3P0.getConnection();
// 区别,使用?占位符代替SQL参数,防止SQL注入导致的问题
String sql = "INSERT INTO users(id,`NAME`,`PASSWORD`,`email`,`birthday`) VALUES(?,?,?,?,?)";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 预编译SQL,先写SQL,不执行
// 手动给占位符赋值
statement.setInt(1,4);
statement.setString(2,"小明");
statement.setString(3,"123456");
statement.setString(4,"123456@qq.com");
statement.setString(5, "2021-05-27");
int num = statement.executeUpdate();
if (num>0){
System.out.println("插入成功!");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtils_C3P0.release(connection,statement,null);
}
}
}
C3P0
需要的jar包:c3p0-0.9.5.5.jar和mchange-commons-java-0.2.19.jar
demo:
<!--配置文件-->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<c3p0-config>
<!--
c3p0的缺省(默认)配置
如果在代码中ComboPooledDataSource ds=new ComboPooledDataSource();这样写就表示使用的是c3p0的缺省(默认)
-->
<default-config>
<property name="driverClass">com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="jdbcUrl">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai</property>
<property name="user">root</property>
<property name="password">123456</property>
<property name="acquiredIncrement">5</property>
<property name="initialPoolSize">10</property>
<property name="minPoolSize">5</property>
<property name="maxPoolSize">20</property>
</default-config>
<!--
c3p0的命名配置
如果在代码中ComboPooledDataSource ds=new ComboPooledDataSource(MySQL);这样写就表示使用的是mysql的缺省(默认)-->
<named-config name="MySQL">
<property name="driverClass">com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="jdbcUrl">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai</property>
<property name="user">root</property>
<property name="password">123456</property>
<property name="acquiredIncrement">5</property>
<property name="initialPoolSize">10</property>
<property name="minPoolSize">5</property>
<property name="maxPoolSize">20</property>
</named-config>
</c3p0-config>
// C3P0连接工具
package com.five.utils;
import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource;
import com.second.utils.JdbcUtils;
import org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSourceFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JdbcUtils_C3P0 {
private static ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = null; // 提高作用域
static {
try {
// 代码版配置
// dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
// dataSource.setDriverClass();
// dataSource.setUser();
// dataSource.setPassword();
// dataSource.setJdbcUrl();
//
// dataSource.setMaxPoolSize();
// dataSource.setMinPoolSize();
// 创建数据源
dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource("MySQL"); // 配置文件写法,不写参数是c3p0默认配置
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 获取连接
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return dataSource.getConnection(); // 从数据源中获取连接
}
// 释放连接资源
public static void release(Connection conn, Statement st, ResultSet rs){
if (rs!=null){
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (st!=null){
try {
st.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn!=null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
// C3P0连接测试
package com.five.utils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class _02_C3P0_Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
// 更换C3P0数据源
connection = JdbcUtils_C3P0.getConnection();
// 区别,使用?占位符代替SQL参数,防止SQL注入导致的问题
String sql = "INSERT INTO users(id,`NAME`,`PASSWORD`,`email`,`birthday`) VALUES(?,?,?,?,?)";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 预编译SQL,先写SQL,不执行
// 手动给占位符赋值
statement.setInt(1,4);
statement.setString(2,"小明");
statement.setString(3,"123456");
statement.setString(4,"123456@qq.com");
statement.setString(5, "2021-05-27");
int num = statement.executeUpdate();
if (num>0){
System.out.println("插入成功!");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtils_C3P0.release(connection,statement,null);
}
}
}
无论使用什么数据源,本质是一样的, DataSource接口不会变,方法一样。






