Mysql - 事务隔离级别和MVCC
1. 事务隔离级别
1.1 事务并发执行遇到的问题
- 脏写:一个事务修改了另一个未提交事务修改过的数据
- 脏读:一个事务读到了另一个未提交事务修改过的数据
- 不可重复读:一个事务只能读到另一个已经提交的事务修改过的数据,
并且其他事务每对该数据进行一次修改并提交后,该事务都能查询得到最新值 - 幻读:一个事务先根据某些条件查询出一些记录,之后另一个事务又向表中插入了符合这些条件的记录,
原先的事务再次按照该条件查询时,能把另一个事务插入的记录读出来
1.2 SQL标准中的四种隔离级别
| 隔离级别 | 脏读 | 不可重复读 | 幻读 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 未提交读 | 可能 | 可能 | 可能 |
| 已提交读 | 不可能 | 可能 | 可能 |
| 可重复读 | 不可能 | 不可能 | 可能 |
| 可串行化 | 不可能 | 不可能 | 不可能 |
1.3 MySQL中支持的四种隔离级别
| 隔离级别 | 脏读 | 不可重复读 | 幻读 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 未提交读 | 可能 | 可能 | 可能 |
| 已提交读 | 不可能 | 可能 | 可能 |
| 可重复读 | 不可能 | 不可能 | 不可能 |
| 可串行化 | 不可能 | 不可能 | 不可能 |
2. MVCC(多并发版本控制)
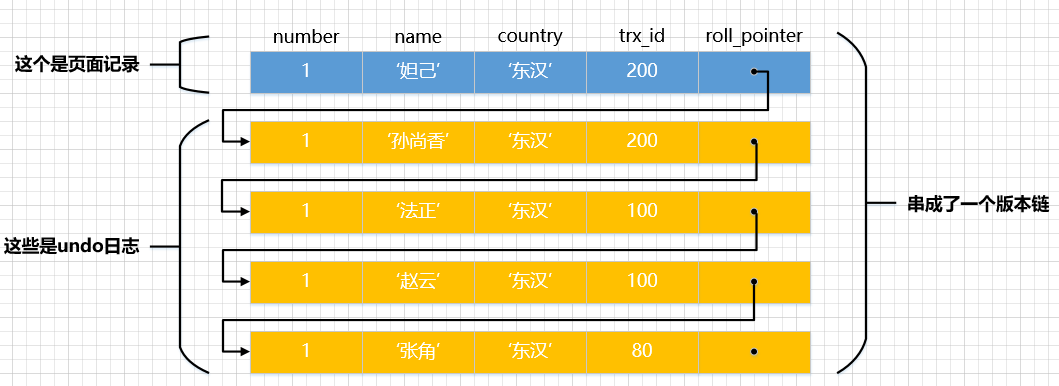
2.1 版本链
对该记录每次更新后,都会将旧值放到一条undo日志中,就算是该记录的一个旧版本,随着更新次数的增多,所有的版本都会被roll_pointer属性连接成一个链表,这个链表被称为版本链,版本链的头节点就是当前记录最新的值。
2.2 ReadView
未提交读:直接读取记录的最新版本
可串行化:使用加锁的方式访问记录
已提交读和可重复读:需要判断一下版本链中的哪个版本是当前事务可见的
ReadView中比较重要的4个内容:
m_ids: 表示在生成ReadView时当前系统中活跃的读写事物的事务id列表min_trx_id:表示在生成ReadView时当前系统中活跃的读写事务中最小的事务idmax_trx_id:表示生成ReadView时系统应该分配给下一个事务的id值creator_trx_id:表示生成ReadView的事务的事务id
按照下面的步骤判断记录的某个版本是否可见:
trx_id = creator_trx_id当前事务在访问它自己修改过的记录 该版本可以被当前事务访问trx_id < min_trx_id生成该版本的事务在当前事务生成ReadView前已经提交 该版本可以被当前事务访问trx_id >= max_trx_id生成该版本的的事务在当前事务生成ReadView后才开启 该版本不可以被当前事务访问min_trx_id <= trx_id < max_trx_id判断trx_id是否在m_ids中:在,则不能被访问;不在,则能被访问
使用已提交读隔离级别的事务在每次查询开始时都会生成一个独立的ReadView。
使用可重复读隔离级别的事务只会在第一次执行查询时生成一个ReadView,之后的查询不会重复生成。
2.3 MVCC小结
所谓的MVCC(Multi-Version Concurrency Control ,多版本并发控制)指的就是在使用READ COMMITTD、REPEATABLE READ这两种隔离级别的事务在执行普通的SELECT操作时访问记录的版本链的过程,这样子可以使不同事务的读-写、写-读操作并发执行,从而提升系统性能。
READ COMMITTD、REPEATABLE READ这两个隔离级别的一个很大不同就是:生成ReadView的时机不同,READ COMMITTD在每一次进行普通SELECT操作前都会生成一个ReadView,而REPEATABLE READ只在第一次进行普通SELECT操作前生成一个ReadView,之后的查询操作都重复使用这个ReadView就好了。
3、MVCC源码解析
3.1 ReadView数据结构
class Readview{
...
private:
/** The read should not see any transaction with trx id >= this
value. In other words, this is the "high water mark". */
trx_id_t m_low_limit_id;
/** The read should see all trx ids which are strictly
smaller (<) than this value. In other words, this is the
low water mark". */
trx_id_t m_up_limit_id;
/** trx id of creating transaction, set to TRX_ID_MAX for free
views. */
trx_id_t m_creator_trx_id;
/** Set of RW transactions that was active when this snapshot
was taken */
ids_t m_ids;
/** The view does not need to see the undo logs for transactions
whose transaction number is strictly smaller (<) than this value:
they can be removed in purge if not needed by other views */
trx_id_t m_low_limit_no;
/** AC-NL-RO transaction view that has been "closed". */
bool m_closed;
typedef UT_LIST_NODE_T(ReadView) node_t;
/** List of read views in trx_sys */
byte pad1[64 - sizeof(node_t)];
node_t m_view_list;
};
ReadView中的主要成员变量包括:
m_low_limit_id:即上文所述max_trx_id。若当前事务id >=m_low_limit_id,则当前事务不可见。m_up_limit_id:即上文所述min_trx_id。若当前事务id <m_up_limit_id,则当前事务不可见。m_creator_trx_id:创建该ReadView的事务IDm_ids:数组,包含了当前事务启动时所有活跃事务的ID。m_low_limit_no:表示ReadView不需要查看事务编号严格小于此值的事务的撤销日志:如果这些日志不被其他视图所需要,它们可以在清除过程中被删除。m_closed:AC-NL-RO事务试图是否被“关闭”。node_t:将ReadView链接在一个链表中。m_view_list:用于将当前ReadView链接到trx_sys(事务系统)中的其他ReadView。
3.2 判断数据行的版本对当前事务是否可见
lock_clust_rec_cons_read_sees 函数是 InnoDB 存储引擎中用于判断数据库表中的行数据在给定的一致性ReadView下是否可见的函数。
bool lock_clust_rec_cons_read_sees(
/*==========================*/
const rec_t *rec, /*!< in: user record which should be read or
passed over by a read cursor */
dict_index_t *index, /*!< in: clustered index */
const ulint *offsets, /*!< in: rec_get_offsets(rec, index) */
ReadView *view) /*!< in: consistent read view */
{
ut_ad(dict_index_is_clust(index));
ut_ad(page_rec_is_user_rec(rec));
ut_ad(rec_offs_validate(rec, index, offsets));
/* Temp-tables are not shared across connections and multiple
transactions from different connections cannot simultaneously
operate on same temp-table and so read of temp-table is
always consistent read. */
if ((srv_read_only_mode &&
(srv_in_role == SRV_AS_CE_PRIMARY || srv_in_role == SRV_AS_SE ||
(srv_in_role == SRV_AS_CE_REPLICA && opt_bootstrap))) ||
dict_table_is_temporary(index->table)) {
ut_ad(view == 0 || dict_table_is_temporary(index->table));
return (true);
}
ut_ad(view != NULL);
/* NOTE that we call this function while holding the search
system latch. */
trx_id_t trx_id = row_get_rec_trx_id(rec, index, offsets);
return (view->changes_visible(trx_id, index->table->name));
}
函数逻辑:
1、前提条件检查
ut_ad(dict_index_is_clust(index)):确保传入的索引是一个聚集索引
ut_ad(page_rec_is_user_rec(rec)):确保传入的记录是一个用户记录
ut_ad(rec_offs_validate(rec, index, offsets)):确保偏移量数组是有效的
2、特殊情况处理
- 如果数据库处于只读模式,或者操作的是临时表,则直接返回
true,表示读取总是一致的。
if ((srv_read_only_mode &&
(srv_in_role == SRV_AS_CE_PRIMARY || srv_in_role == SRV_AS_SE ||
(srv_in_role == SRV_AS_CE_REPLICA && opt_bootstrap))) ||
dict_table_is_temporary(index->table)) {
ut_ad(view == 0 || dict_table_is_temporary(index->table));
return (true);
}
- 确保
view不为NULL。
ut_ad(view != NULL);
3、一致性ReadView检查
- 通过调用
row_get_rec_trx_id函数获取记录所属事务的ID(trx_id)。 - 使用
view->changes_visible方法检查给定的事务ID在当前ReadView中是否可见。
核心依赖函数
bool changes_visible(
trx_id_t id,
const table_name_t& name) const
MY_ATTRIBUTE((warn_unused_result))
{
ut_ad(id > 0);
if (id < m_up_limit_id || id == m_creator_trx_id) {
return(true);
}
check_trx_id_sanity(id, name);
if (id >= m_low_limit_id) {
return(false);
} else if (m_ids.empty()) {
return(true);
}
const ids_t::value_type* p = m_ids.data();
return(!std::binary_search(p, p + m_ids.size(), id));
}
- 函数逻辑:
1、首先,断言(ut_ad(id > 0))确保传入的事务ID是正数。
2、如果事务ID小于上限(m_up_limit_id)或等于创建者的事务ID(m_creator_trx_id),则直接返回true,表示修改是可见的。
3、调用 check_trx_id_sanity 函数进行事务ID的有效性检查。
4、如果事务ID大于或等于下限(m_low_limit_id),则返回 false,表示修改不可见。
5、如果 m_ids 集合为空,返回 true,表示没有特定的事务ID集合限制,因此修改是可见的。
6、最后,使用二分查找(std::binary_search)在 m_ids 集合中查找给定的事务ID。如果找不到,表示该事务ID的修改是可见的;如果找到,则表示修改不可见。






