学习 探索 分享数据库知识和技术 共建数据库技术交流圈
书接上文GaussDB高智能--自治运维技术,从索引推荐、分布键推荐、参数调优等三方面介绍了GaussDB的自治运维技术,本篇将从机器学习算法的训练和推理方面对GaussDB的库内AI引擎进行详细解读。
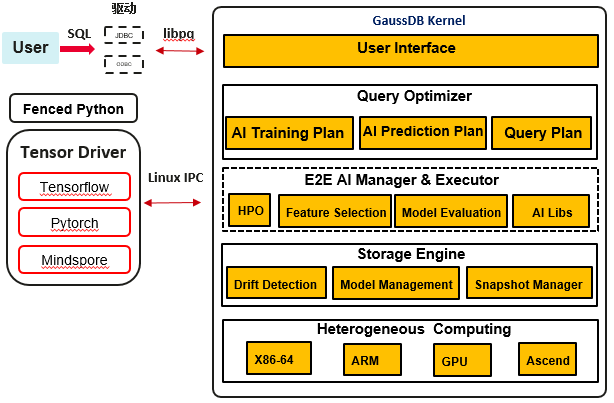
3 库内AI引擎
3.1 机器学习算法的训练和推理
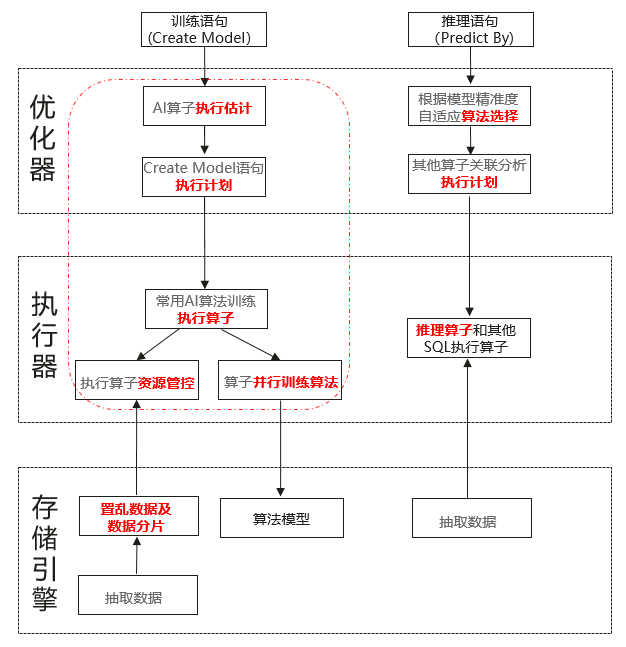
通过数据库并行训练算法,实现库内训练加速;
通过执行代价估计及资源管控,实现迭代轮次和模型参数最优化;
提供可视化执行计划,实现AI可查、可解释性。
Create Model price_model using logistic_regression Features size, lot Target price < 1000 from Houses;
基于数据集和查询特征进行模型归类;
优化器通过同类模型的精准度,自适应选择算法,实现最优化模型推理;
AI推理算子结合其他执行算子,实现关联分析。
Select address, Predict By price_model(Features size, lot), size from houses;
Binary logistic regression
Binary SVM linear classifier (Support Vector Machine)
Linear regression of continuous targets
typedef struct Matrix {size_t rows;size_t columns;bool transposed;size_t allocated;float* data; // consecutive rows, each as a sequence of values (one for each column)float cache[MATRIX_CACHE]; // default is 64 entries} Matrix;
构造函数:二维矩阵、一维向量、克隆和虚拟转置。 修饰符:用零填充,调整大小。 矩阵之间的运算:矩阵乘法、入口乘法(Hadamard积)、加法、减法、变换、点积、相关性。 标量系数运算:乘除 修改所有系数的操作:平方、平方根、sigmoid、log、log1p、取反、补、正、二值化。 聚集: 求和。
typedef struct SGD {Plan plan;AlgorithmML algorithm;int targetcol; // 0-index into the current projectionint max_seconds; // maximum execution time// hyperparametersint max_iterations; // maximum number of iterationsint batch_size;double learning_rate;double decay; // (0:1], learning rate decaydouble tolerance; // [0:1], 0 means to run all iterations// for SVMdouble lambda; // regularization strength} SGD;
typedef struct SGDState {ScanState ss; /* its first field is NodeTag */// tuple descriptionTupleDesc tupdesc;int n_features; // number of features// dependant var binary valuesint num_classes;Datum binary_classes[2];// training statebool done; // when finishedMatrix weights;double learning_rate;int n_iterations;int usecs; // execution timeint processed; // tuplesint discarded;float loss;Scores scores;} SGDState;
typedef void (*f_sgd_gradients)(const SGD* sgd_node, const Matrix* features, const Matrix* dep_var, Matrix* weights, Matrix* gradients);typedef double (*f_sgd_test)(const SGD* sgd_node, const Matrix* features, const Matrix* dep_var, const Matrix* weights, Scores* scores);typedef void (*f_sgd_predict)(const SGD* sgd_node, const Matrix* features, const Matrix* weights, Matrix* predictions);typedef struct SGDAlgorithm {const char* name;int flags;int metrics;// values for binary algorithms, .g. (0,1) for logistic regression or (-1,1) for svm classifierfloat min_class;float max_class;// callbacks for hooksf_sgd_gradients gradients_callback; // update gradientsf_sgd_test test_callback; // compute loss functionf_sgd_predict predict_callback; // predict targets} SGDAlgorithm;
迭代次数
总体执行时间
设计处理的元组数量
删除的元组数量 (含有NULL)
权重: 浮点数数组
类别: 二进制算法的不重复值数组
得分: 损失, 准确率, 精确率, 召回率, F1, MSE
sgd_predict:Extract weights and classesExtract tupleCompute prediction (through predict callback of the algorithm)If algorithm is not linear regression thenExtract classesConvert prediction to one known classEnd ifReturn result
逻辑回归: 1+ e-xw
SVM线性分类器: x * w, then binarize to (-1,1)
线性回归: x * w
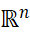 中的点集合P,输出是k点集合C(称为中心),其最小化以下全局函数
中的点集合P,输出是k点集合C(称为中心),其最小化以下全局函数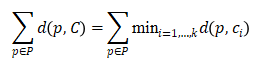
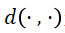 是为上述计算选择的距离函数。虽然最自然的距离函数是欧几里得距离(L_2) ,但实际上更多的函数是欧几里得距离的平方,由于其计算更简单,所以使用最广泛的是欧几里得距离的平方:
是为上述计算选择的距离函数。虽然最自然的距离函数是欧几里得距离(L_2) ,但实际上更多的函数是欧几里得距离的平方,由于其计算更简单,所以使用最广泛的是欧几里得距离的平方: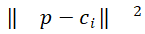 。另一种选择通常是L_1公制(曼哈顿距离),或
。另一种选择通常是L_1公制(曼哈顿距离),或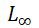 例如。
例如。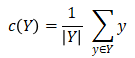
typedef struct Centroid {IncrementalStatistics statistics;ArrayType* coordinates = nullptr;uint32_t id = 0U;} Centroid;
点集中点的数量,
点集中的点到中心的平均距离,
点集中的点到中心距离的标准差,
点集中的点到中心距离的最大值和最小值。
struct KMeans{Plan plan;AlgorithmML algorithm;KMeansDescriptor description;KMeansHyperparameters parameters;};
struct KMeansDescription{char const* name = nullptr;SeedingFunction seeding = KMEANS_RANDOM_SEED;DistanceFunction distance = KMEANS_L2_SQUARED;uint32_t n_features = 0U;uint32_t batch_size = 0U;uint32_t verbose = 0U;}
struct KMeansHyperParameter{uint32_t num_centroids = 0U;uint32_t num_iterations = 0U;double tolerance = 0.000001;};
typedef struct KMeansStateDescription{Centroid* centroids[2] = {nullptr};ArrayType* bbox_min = nullptr;ArrayType* bbox_max = nullptr;double (*distance)(double const*, double const*, uint32_t const dimension) = nullptr;IncrementalStatistics solution_statistics[2];uint64_t num_good_points = 0UL;uint64_t num_dead_points = 0UL;uint32_t current_iteration = 0U;uint32_t current_centroid = 0U;uint32_t dimension = 0U;uint32_t num_centroids = 0U;bool verbose = false;} KMeansStateDescription
GradientDescent gd_pca = {{PCA,"pca",ALGORITHM_ML_UNSUPERVISED | ALGORITHM_ML_RESCANS_DATA,gd_metrics_loss,gd_get_hyperparameters_PCA,gd_make_hyperparameters_PCA,gd_update_hyperparameters,gd_create,gd_run,gd_end,gd_predict_prepare,gd_predict,PCA_explain},false,FLOAT8ARRAYOID, // default return type0., // default feature0.,0.,nullptr,gd_init_optimizer_PCA,nullptr,nullptr,nullptr,PCA_gradients,PCA_test,PCA_predict,nullptr,};
迭代次数
总体执行时间
设计处理的元组数量
删除的元组数量 (含有NULL)
权重: 浮点数数组
类别: 二进制算法的不重复值数组
PCA_predict:Extract weights and classesExtract tupleCompute prediction (through predict callback of the algorithm)If algorithm is classification then:Extract classesConvert prediction to one known classEnd ifReturn result
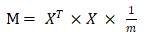
xgboost_regression_logistic
xgboost_binary_logistic
xgboost_regression_squarederror
xgboost_regression_gamma
迭代次数
总体执行时间
设计处理的元组数量
删除的元组数量 (含有NULL)
权重: 浮点数数组
类别: 二进制算法的不重复值数组
得分:
xgboost_binary_logistic: mse(平均方差)
xgboost_regression_logistic、xgboost_regression_squarederror、xgboost_regression_gamma: recall(召回率)、F1-score、precision(精确率)、accuracy(准确率)、loss(损失)
以上内容从机器学习算法的训练和推理方面对GaussDB的库内AI引擎进行了详细解读,下篇我们将从模型管理与数据集管理两方面,继续介绍GaussDB库内AI引擎,敬请期待~