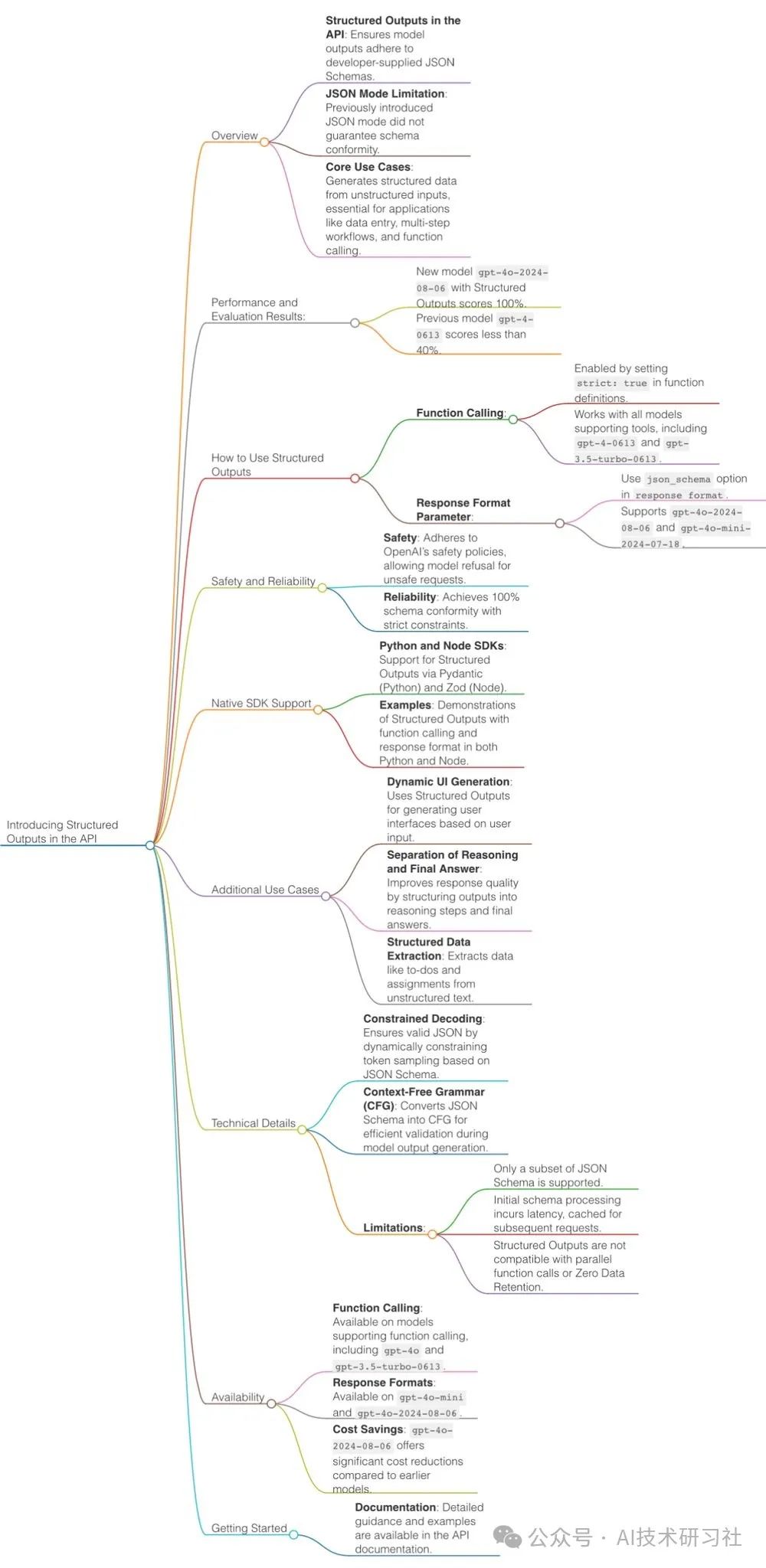
官宣:根据非常普遍的需求,OpenAI的API 中开始支持结构化输出。

在 API 中引入结构化输出 - 模型输出现在遵循开发人员提供的 JSON 模式。让大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)进行结构化输出是自然语言处理(NLP)领域中的一个重要目标。结构化输出指的是将自然语言转换成具有明确格式和结构的数据,如表格、数据库条目、JSON对象等。

快速进行尝试一个。这个真香,再也不用为没有固定返回格式发愁了。
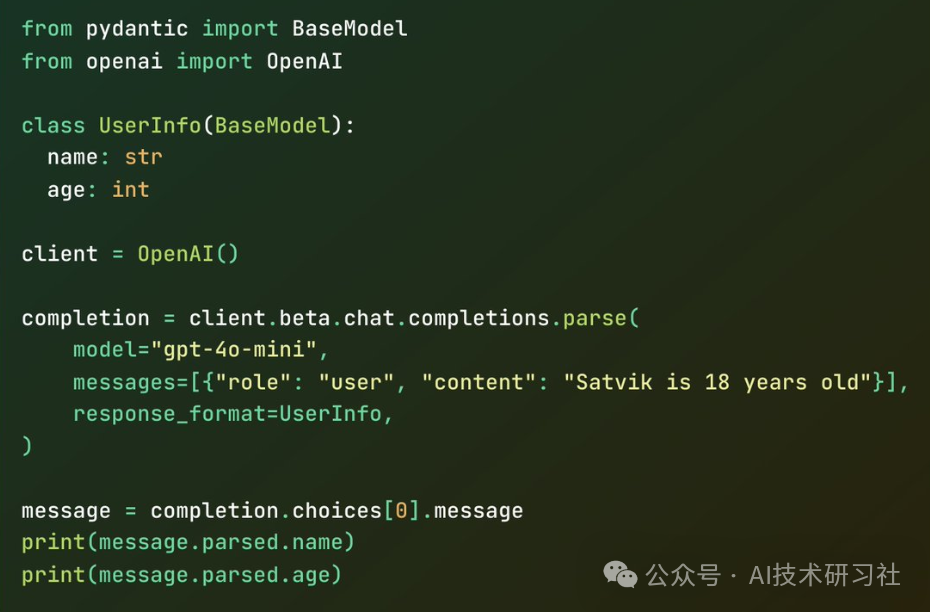
通过实现这一点,不仅可以提高模型输出的可预测性和可用性,还能增强其在各种应用场景中的实用性。结构化输出有助于减少误差,提高数据处理效率,并确保在与其他系统和应用程序集成时的一致性和兼容性。这一特性对于自动化工作流程、数据分析、自然语言处理任务以及智能助手等方面尤为重要。
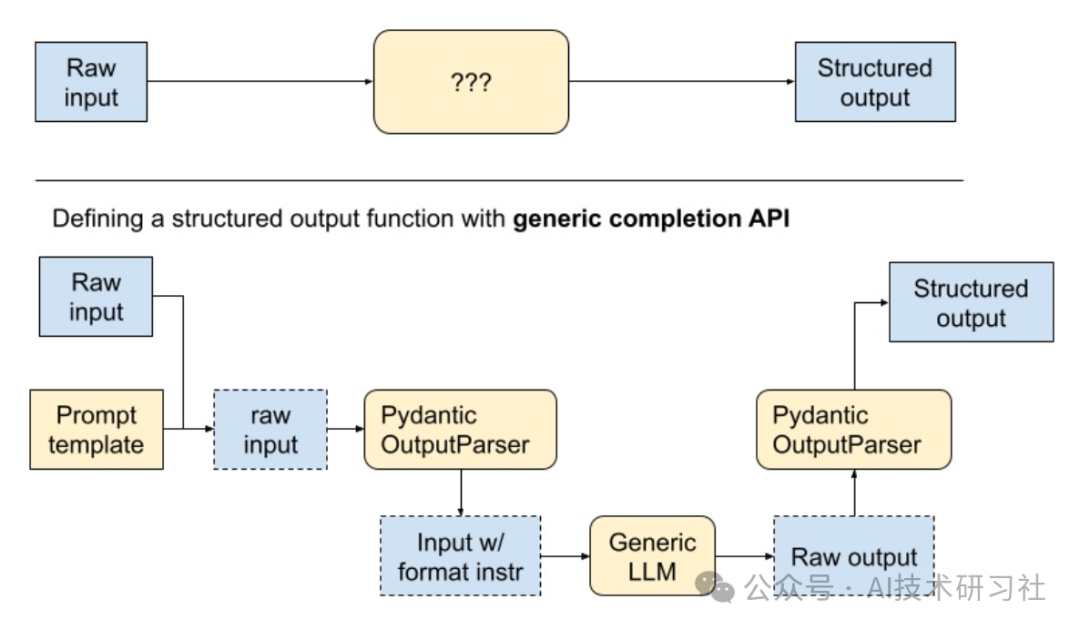 LLMs返回结构化的输出通常至关重要。这是因为LLMs的输出通常用于下游应用程序,其中需要特定的参数。为此,必须可靠地提供结构化输出。这不仅能确保数据的一致性和准确性,还能提高系统的整体效率和性能。通过结构化的输出,可以更容易地进行数据处理、分析和集成,从而更好地支持决策和业务流程的优化。
LLMs返回结构化的输出通常至关重要。这是因为LLMs的输出通常用于下游应用程序,其中需要特定的参数。为此,必须可靠地提供结构化输出。这不仅能确保数据的一致性和准确性,还能提高系统的整体效率和性能。通过结构化的输出,可以更容易地进行数据处理、分析和集成,从而更好地支持决策和业务流程的优化。
下面通过几个示例来看。
第一,用于思维链数学辅导的结构化输出。
from pydantic import BaseModelfrom openai import OpenAIclient = OpenAI()class Step(BaseModel):explanation: stroutput: strclass MathReasoning(BaseModel):steps: list[Step]final_answer: strcompletion = client.beta.chat.completions.parse(model="gpt-4o-2024-08-06",messages=[{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful math tutor. Guide the user through the solution step by step."},{"role": "user", "content": "how can I solve 8x + 7 = -23"}],response_format=MathReasoning,)math_reasoning = completion.choices[0].message.parsed
返回结果如下。
{"steps": [{"explanation": "Start with the equation 8x + 7 = -23.","output": "8x + 7 = -23"},{"explanation": "Subtract 7 from both sides to isolate the term with the variable.","output": "8x = -23 - 7"},{"explanation": "Simplify the right side of the equation.","output": "8x = -30"},{"explanation": "Divide both sides by 8 to solve for x.","output": "x = -30 8"},{"explanation": "Simplify the fraction.","output": "x = -15 4"}],"final_answer": "x = -15 4"}
第二,定义结构化字段以从非结构化输入数据(例如检索论文)中提取。
from pydantic import BaseModelfrom openai import OpenAIclient = OpenAI()class ResearchPaperExtraction(BaseModel):title: strauthors: list[str]abstract: strkeywords: list[str]completion = client.beta.chat.completions.parse(model="gpt-4o-2024-08-06",messages=[{"role": "system", "content": "You are an expert at structured data extraction. You will be given unstructured text from a research paper and should convert it into the given structure."},{"role": "user", "content": "..."}],response_format=ResearchPaperExtraction,)research_paper = completion.choices[0].message.parsed
返回结果如下。
{"title": "Application of Quantum Algorithms in Interstellar Navigation: A New Frontier","authors": ["Dr. Stella Voyager","Dr. Nova Star","Dr. Lyra Hunter"],"abstract": "This paper investigates the utilization of quantum algorithms to improve interstellar navigation systems. By leveraging quantum superposition and entanglement, our proposed navigation system can calculate optimal travel paths through space-time anomalies more efficiently than classical methods. Experimental simulations suggest a significant reduction in travel time and fuel consumption for interstellar missions.","keywords": ["Quantum algorithms","interstellar navigation","space-time anomalies","quantum superposition","quantum entanglement","space travel"]}
结构化输出是JSON模式的演变。虽然两者都确保生成有效的 JSON,但只有结构化输出确保架构合规性。Chat Completions API、Assistants API、Fine-tuning API 和 Batch API 都支持结构化输出和 JSON 模式。
建议尽可能始终使用结构化输出而不是 JSON 模式。但是,只有 gpt-4o-mini、gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18 和 gpt-4o-2024-08-06 模型快照及更高版本支持结构化输出。
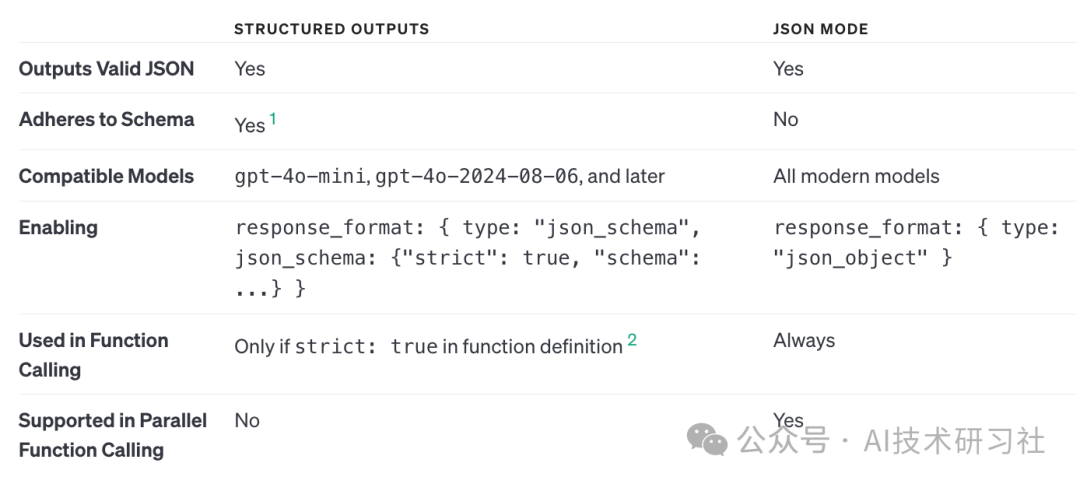
最关心的还是价格,貌似挤牙膏,不是很理想,哈哈。

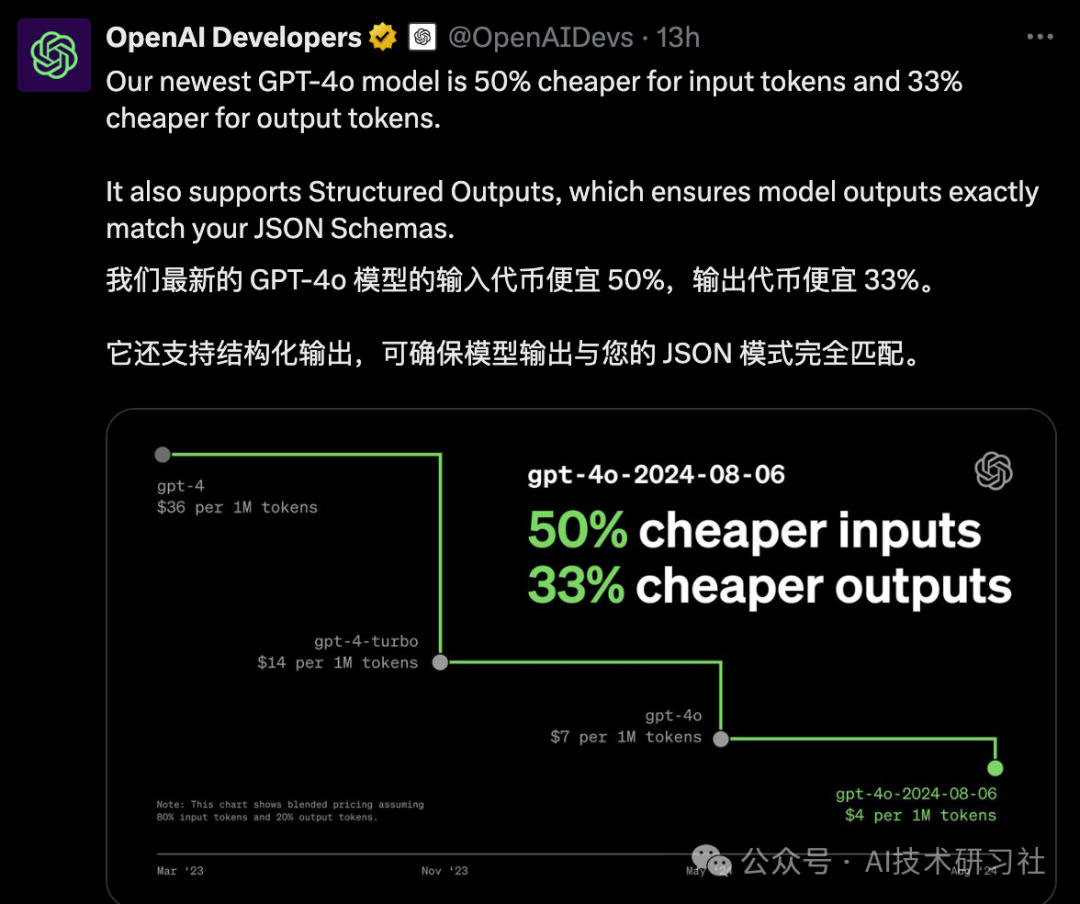
有热心网友整理的思维导图,赶紧收藏吧!
在此之前从中获取结构化输出的方法LLM,在Github上即可搜到。
LangChain和LlamaIndex 提供了大量结构化输出的方式,下面我们整理一下。
LangChain 的结构化输出方式。
JSON 输出:LangChain 支持通过特定格式和标签生成 JSON 格式的数据,方便后续处理和分析。
from typing import Listfrom langchain.prompts import PromptTemplatefrom langchain_community.chat_models import ChatOpenAIfrom langchain_core.output_parsers import JsonOutputParserfrom langchain_core.pydantic_v1 import BaseModel, Fieldmodel = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0)# 定义所需的数据结构。class Joke(BaseModel):setup: str = Field(description="问题以设置笑话")punchline: str = Field(description="回答以解决笑话")# 以提示模型填充数据结构的查询意图。joke_query = "Tell me a joke."# 设置解析器+将说明注入提示模板。parser = JsonOutputParser(pydantic_object=Joke)prompt = PromptTemplate(template="回答用户的查询。\n{format_instructions}\n{query}\n",input_variables=["query"],partial_variables={"format_instructions": parser.get_format_instructions()},)chain = prompt | model | parserchain.invoke({"query": joke_query})
表格数据:可以生成 CSV 或 Excel 格式的表格数据,适用于各种数据分析和报告需求。
from langchain.output_parsers import CommaSeparatedListOutputParserfrom langchain.prompts import PromptTemplatefrom langchain_community.chat_models import ChatOpenAIoutput_parser = CommaSeparatedListOutputParser()format_instructions = output_parser.get_format_instructions()prompt = PromptTemplate(template="List five {subject}.\n{format_instructions}",input_variables=["subject"],partial_variables={"format_instructions": format_instructions})model = OpenAI(temperature=0)_input = prompt.format(subject="ice cream flavors")output = model(_input)result = output_parser.parse(output)# 输出:# ['Vanilla', 'Chocolate', 'Strawberry', 'Mint Chocolate Chip', 'Cookies and Cream']
API 集成:通过与其他 API 集成,实现结构化数据的自动化传输和处理。
from langchain_community.chat_models import ChatOpenAIfrom langchain_community.utils.openai_functions import (convert_pydantic_to_openai_function,)from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplatefrom langchain_core.pydantic_v1 import BaseModel, Field, validatorclass Joke(BaseModel):setup: str = Field(description="问题以设置笑话")punchline: str = Field(description="回答以解决笑话")openai_functions = [convert_pydantic_to_openai_function(Joke)]model = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0)prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([("system", "You are a helpful assistant"), ("user", "{input}")])
Pydantic声明:使用Pydantic声明你的数据模型。Pydantic的BaseModel就像是Python的数据类,但具有实际的类型检查和强制转换。
from typing import Listfrom langchain.output_parsers import PydanticOutputParserfrom langchain.prompts import PromptTemplatefrom langchain_community.chat_models import ChatOpenAIfrom langchain_core.pydantic_v1 import BaseModel, Field, validatormodel = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0)# 定义你期望的数据结构。class Joke(BaseModel):setup: str = Field(description="设立笑话的问题")punchline: str = Field(description="解决笑话的答案")# 你可以轻松地用Pydantic添加自定义验证逻辑。@validator("setup")def question_ends_with_question_mark(cls, field):if field[-1] != "?":raise ValueError("问题格式不正确!")return field# 并且一个旨在提示语言模型填充数据结构的查询。joke_query = "给我讲个笑话。"# 设置解析器 + 将指令注入提示模板。parser = PydanticOutputParser(pydantic_object=Joke)prompt = PromptTemplate(template="回答用户查询。\n{format_instructions}\n{query}\n",input_variables=["query"],partial_variables={"format_instructions": parser.get_format_instructions()},)chain = prompt | model | parserchain.invoke({"query": joke_query})
参考资料:
https://openai.com/index/introducing-structured-outputs-in-the-api/
https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/structured-outputs/supported-schemas?context=ex2
3. https://langchain114.com/docs/modules/model_io/output_parsers/types/pydantic






