


作者简介:杨宏俊——蚂蚁数据部数据库基础设施智能体团队技术专家,DB-GPT项目核心开发者,专注于AI应用架构和实际应用落地。
本文整理自DB-GPT源码解读系列直播第三期,欢迎大家持续关注 EosphorosAI 公众号~
 背景
背景 设计思路和方案
设计思路和方案 1.关于LLM Agent的一些基础
1.关于LLM Agent的一些基础优点是响应迅速,但在复杂任务中表现可能不理想。 反应快但改变较慢,就像人类的习惯难以快速改变。
通过生成中间推理步骤来解决问题。依赖记忆调用,存储思考过程和对行为结果的反思,累积经验以优化后续行为。 反应时间比系统1慢,但改变所需时间相对较快。 优点是推理能力强,不过需要更多计算资源和时间。
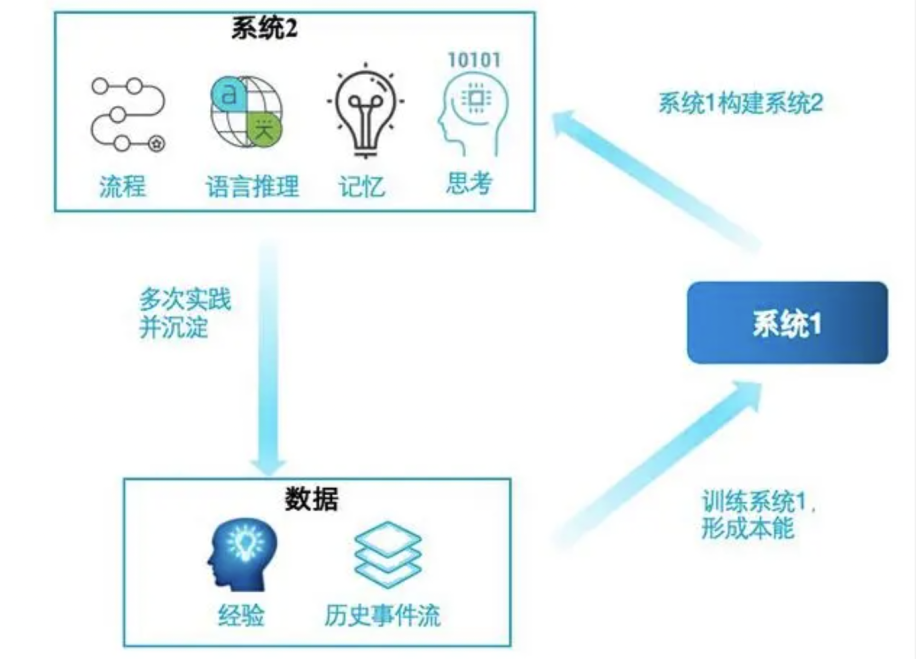
LLM Agent架构的最早提出
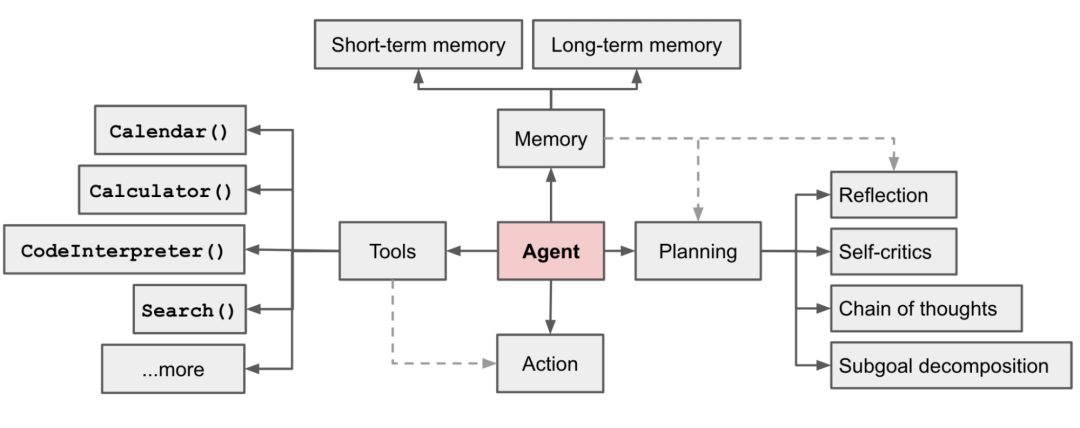
 2.DB-GPT实践落地的Agent方案设计
2.DB-GPT实践落地的Agent方案设计
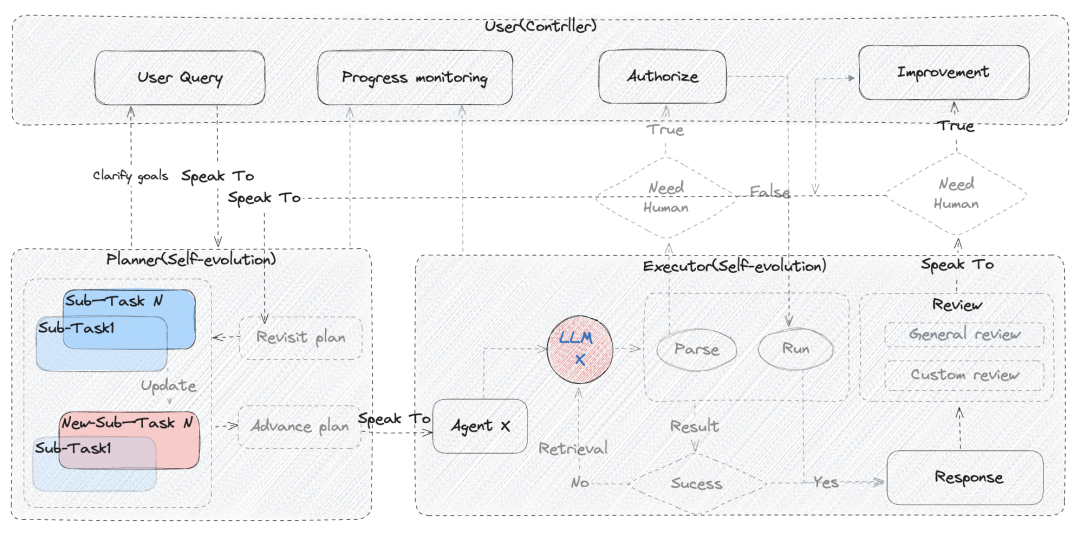
下图是第一版DB-GPT对Agent整体交互流程的思考和设计, 除了规划部分相对没有实现的这么复杂,其他部分基本已经按照最初的方案进行了落地。
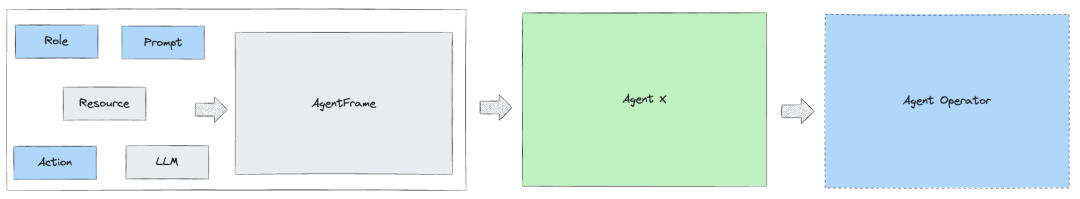
对于单个Agent,为了能简单开发拓展和更好的结合DB-GPT的平台组件资源进行了如下的层级抽象, Agent可以绑定DB-GPT平台各类资源数据、绑定模型服务、绑定Action执行器和通过定义角色和Prompt构造一个具体场景能力的Agent,再通过AgentOperator容器让Agent可以在AWEL FlOW里使用。
 源码架构解析
源码架构解析 1.Agent API
1.Agent API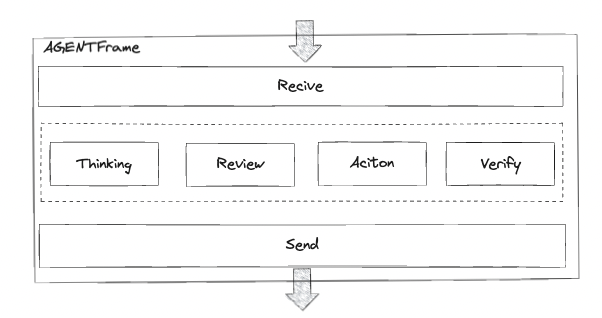
发送消息
@abstractmethodasync def send(self,message: AgentMessage,recipient: Agent,reviewer: Optional[Agent] = None,request_reply: Optional[bool] = True,is_recovery: Optional[bool] = False,silent: Optional[bool] = False,is_retry_chat: bool = False,last_speaker_name: Optional[str] = None,) -> None:"""Send a message to recipient agent.Args:message(AgentMessage): the message to be sent.recipient(Agent): the recipient agent.reviewer(Agent): the reviewer agent.request_reply(bool): whether to request a reply.is_recovery(bool): whether the message is a recovery message.Returns:None"""
接收消息
@abstractmethodasync def receive(self,message: AgentMessage,sender: Agent,reviewer: Optional[Agent] = None,request_reply: Optional[bool] = None,silent: Optional[bool] = False,is_recovery: Optional[bool] = False,is_retry_chat: bool = False,last_speaker_name: Optional[str] = None,) -> None:"""Receive a message from another agent.Args:message(AgentMessage): the received message.sender(Agent): the sender agent.reviewer(Agent): the reviewer agent.request_reply(bool): whether to request a reply.silent(bool): whether to be silent.is_recovery(bool): whether the message is a recovery message.Returns:None"""
回答生成
消息准备(基类方法) 推理 审查 行动 校验
@abstractmethodasync def generate_reply(self,received_message: AgentMessage,sender: Agent,reviewer: Optional[Agent] = None,rely_messages: Optional[List[AgentMessage]] = None,is_retry_chat: bool = False,last_speaker_name: Optional[str] = None,**kwargs,) -> AgentMessage:"""Generate a reply based on the received messages.Args:received_message(AgentMessage): the received message.sender: sender of an Agent instance.reviewer: reviewer of an Agent instance.rely_messages: a list of messages received.Returns:AgentMessage: the generated reply. If None, no reply is generated."""
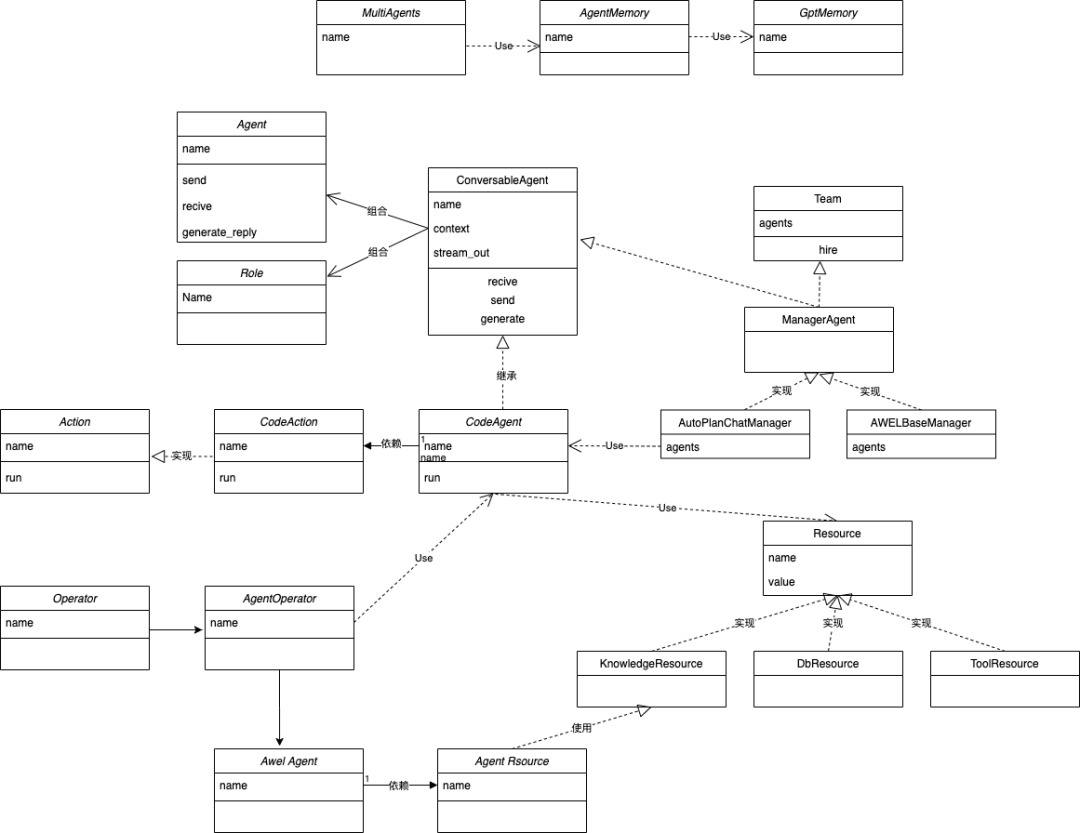
 2.Agent 核心类
2.Agent 核心类
 3.Agent 注册机制
3.Agent 注册机制
内置Agent默认注册 扩展Agent使用如下方法注册
 4.Agent 资源绑定机制
4.Agent 资源绑定机制
资源绑定
# 资源基础类class Resource(ABC, Generic[P]):"""Resource for the agent."""# 数据库资源对象class DBResource(Resource[P], Generic[P]):#知识资源对象(将召回对象作为资源绑定)class RetrieverResource(Resource[ResourceParameters]):#知识库空间资源对象(将DBGPT的知识库空间作为资源对象)class KnowledgeSpaceRetrieverResource(RetrieverResource):# 资源包(将多个资源变成一个资源包的方式绑定引用)class ResourcePack(Resource[PackResourceParameters]):# 内置工具资源class ToolPack(ResourcePack):# 插件工具资源包,可加载Autogpt插件class PluginToolPack(ToolPack):class AutoGPTPluginToolPack(ToolPack):# 内置工具定义和使用方法@tool(description="List the supported models in DB-GPT project.")def list_dbgpt_support_models(model_type: Annotated[str, Doc("The model type, LLM(Large Language Model) and EMBEDDING).")] = "LLM",) -> str:...@tool(description="Get current host CPU status.")def get_current_host_cpu_status() -> str:...@tool(description="Baidu search and return the results as a markdown string. Please set ""number of results not less than 8 for rich search results.",)def baidu_search(query: Annotated[str, Doc("The search query.")],num_results: Annotated[int, Doc("The number of search results to return.")] = 8,) -> str:...
数据库 知识库 Tool(早期Plugin的变种) 文件(待实现)
模型绑定、Prompt绑定
llm_client = OpenAILLMClient(model_alias="gpt-3.5-turbo")context: AgentContext = AgentContext(conv_id="test456")agent_memory = AgentMemory()tools = ToolPack([simple_calculator, count_directory_files])prompt_template: PromptTemplate = prompt_service.get_template(prompt_code=record.prompt_template)await ToolAssistantAgent().bind(context) #agent 运行上下文 会话id、应用名、推理参数等.bind(LLMConfig(llm_client=llm_client)) #当前agent使用的模型服务.bind(agent_memory) # 绑定当前agent的记忆对象.bind(prompt_template) # 绑定Agent的prompt 覆盖角色定义 暂时依赖Prompt模块,后续改造为面向API.bind(tools) # 绑定当前agent要使用的资源.build() #Agent准备检查和预加载等工作
 5.Agent 记忆、消息缓存机制
5.Agent 记忆、消息缓存机制
AgentMemory (个体记忆,单个角色,在不同问题对话中的消息记录, 帮助Agent进行错误纠正和推理提速进化)
# 默认短期记忆 默认使用 ShortTermMemory(buffer_size=5) 内存队列作为存储agent_memory = AgentMemory(gpts_memory=self.memory)# 短期记忆class ShortTermMemory(Memory, Generic[T])# 长期记忆class LongTermMemory(Memory, Generic[T])embedding_factory = EmbeddingFactory.get_instance(CFG.SYSTEM_APP)embedding_fn = embedding_factory.create(model_name=EMBEDDING_MODEL_CONFIG[CFG.EMBEDDING_MODEL])vstore_name = f"_chroma_agent_memory_{dbgpts_name}_{conv_id}"Just use chroma store nowvector_store_connector = VectorStoreConnector(vector_store_type=CFG.VECTOR_STORE_TYPE,vector_store_config=VectorStoreConfig(name=vstore_name, embedding_fn=embedding_fn),)memory = HybridMemory[AgentMemoryFragment].from_chroma(vstore_name=vstore_name,embeddings=embedding_fn,)# 感知记忆class SensoryMemory(Memory, Generic[T])# 混合记忆class HybridMemory(Memory, Generic[T])# 增强短期记忆class EnhancedShortTermMemory(ShortTermMemory[T])
GptsMemory (公共记忆, 多Agent之间对话消息输出通道, 实现Agent之间消息感知和对话记录对外传递) 需要按会话id进行初始化和关闭:
self.memory.init({conv_id})try:# 这里开始一个Agent的对话await user_proxy.initiate_chat(recipient=tool_engineer,reviewer=user_proxy,message="Calculate the product of 10 and 99",)finally:await self.memory.clear({conv_id}))## 外部通过集体记忆对象的通道获取Agent的对话消息,支持流式输出async def chat_messages(self, conv_id: str, user_code: str = None, system_app: str = None,):while True:queue = self.memory.queue(conv_id)if not queue:breakitem = await queue.get()if item == "[DONE]":queue.task_done()breakelse:yield itemawait asyncio.sleep(0.005)
 6.Agent 意图识别和应用链接机制
6.Agent 意图识别和应用链接机制
多应用链接启动:
# 参考这个Acitonclass StartAppAction(Action[LinkAppInput]):async def run(self,ai_message: str,resource: Optional[AgentResource] = None,rely_action_out: Optional[ActionOutput] = None,need_vis_render: bool = True,**kwargs,) -> ActionOutput:conv_id = kwargs.get("conv_id")user_input = kwargs.get("user_input")paren_agent = kwargs.get("paren_agent")init_message_rounds = kwargs.get("init_message_rounds")# TODO 这里放应用启动前的逻辑代码from dbgpt.serve.agent.agents.controller import multi_agentsawait multi_agents.agent_team_chat_new(new_user_input if new_user_input else user_input,conv_id,gpts_app,paren_agent.memory,False,link_sender=paren_agent,app_link_start=True,init_message_rounds=init_message_rounds,)return ActionOutput(is_exe_success=True, content="", view=None, have_retry=False)
Agent Flow的分支使用方法:
# 参考这个Actionclass LinkAppAction(Action[LinkAppInput]):async def run(self,ai_message: str,resource: Optional[AgentResource] = None,rely_action_out: Optional[ActionOutput] = None,need_vis_render: bool = True,**kwargs,) -> ActionOutput:# TODO 这里根据模型输出解析出下一步要走到的Agent角色名称role = "xxxx"# 当前Agent返回时指定下一个发言者信息return ActionOutput(is_exe_success=True,content=json.dumps(app_link_param, ensure_ascii=False),view=await self.render_protocal.display(content=app_link_param),next_speakers=[role],)
 7.Agent 消息输出展示机制
7.Agent 消息输出展示机制
Agent消息通过GptsMemory作为通道对外输出,消息展示格式在Action里构建,使用GPT-VIS组件进行可视化数据转换,Vis组件显示效果有前端页面实现效果,Action决定内容。
self._render_protocol = VisChart()view = await self.render_protocol.display(chart=json.loads(model_to_json(param)), data_df=data_df)
 8.Agent 身份定义和其他属性特性
8.Agent 身份定义和其他属性特性
每个Agent可以通过构建自己的profile对象来定义当前Agent的身份信息,这些信息也会默认变成prompt的一部分。
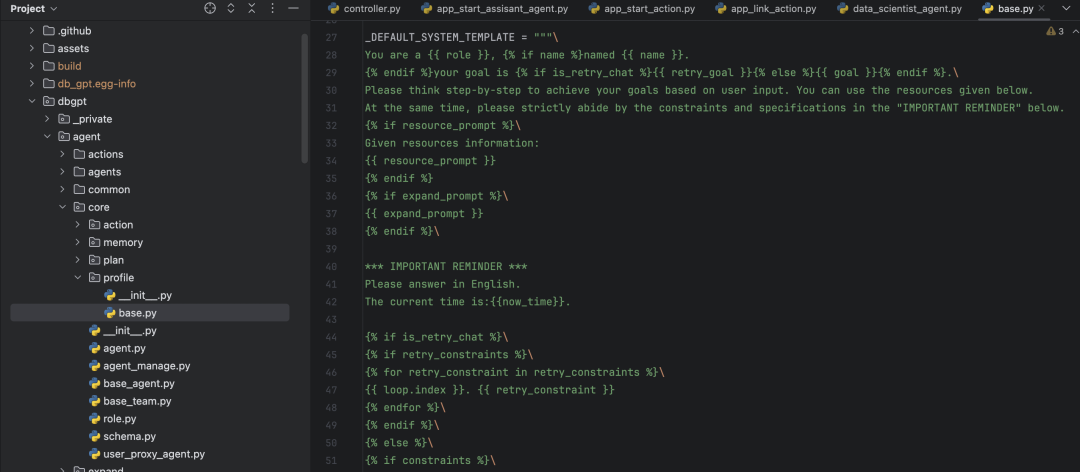
Agent可继承属性介绍
bind_prompt 绑定的外部Promptm模版内容,可以使用外部的prompt模版文本直接覆盖默认模版生成内容,支持参数替换 max_retry_count Agent对于自己答案执行解析错误可以自优化重试的次数 stream_out Agent消息是否流式输出,直接把模型的流式消息输出,Action结果会作为流式的最后一个chunk show_reference Agent是否展示依赖引用的的资源信息,开启的话消息里会记录资源内容
 9.Agent 推理模型选择策略
9.Agent 推理模型选择策略
# 基类 和接口class LLMStrategy:# 默认使用当前模型服的默认模型async def next_llm(self, excluded_models: Optional[List[str]] = None):## 优先级策略的模型选择策略实现class LLMStrategyPriority(LLMStrategy):# 按配置优先级进行选择和重试async def next_llm(self, excluded_models: Optional[List[str]] = None) -> str:"""Return next available llm model name."""try:if not excluded_models:excluded_models = []all_models = await self._llm_client.models()if not self._context:raise ValueError("No context provided for priority strategy!")priority: List[str] = json.loads(self._context)can_uses = self._excluded_models(all_models, excluded_models, priority)if can_uses and len(can_uses) > 0:return can_uses[0].modelelse:raise ValueError("No model service available!")except Exception as e:logger.error(f"{self.type} get next llm failed!{str(e)}")raise ValueError(f"Failed to allocate model service,{str(e)}!")
 Agent拓展开发
Agent拓展开发 1.角色
1.角色
class DataScientistAgent(ConversableAgent):"""Data Scientist Agent."""profile: ProfileConfig = ProfileConfig(name=DynConfig("Edgar",category="agent",key="dbgpt_agent_expand_dashboard_assistant_agent_profile_name",),role=DynConfig("DataScientist",category="agent",key="dbgpt_agent_expand_dashboard_assistant_agent_profile_role",),goal=DynConfig("Use correct {{dialect}} SQL to analyze and resolve user ""input targets based on the data structure information of the ""database given in the resource.",category="agent",key="dbgpt_agent_expand_dashboard_assistant_agent_profile_goal",),constraints=DynConfig(["Please ensure that the output is in the required format. ""Please ensure that each analysis only outputs one analysis ""result SQL, including as much analysis target content as possible.","If there is a recent message record, pay attention to refer to ""the answers and execution results inside when analyzing, ""and do not generate the same wrong answer.Please check carefully ""to make sure the correct SQL is generated. Please strictly adhere ""to the data structure definition given. The use of non-existing ""fields is prohibited. Be careful not to confuse fields from ""different tables, and you can perform multi-table related queries.","If the data and fields that need to be analyzed in the target are in ""different tables, it is recommended to use multi-table correlation ""queries first, and pay attention to the correlation between multiple ""table structures.","It is prohibited to construct data yourself as query conditions. ""Only the data values given by the famous songs in the input can ""be used as query conditions.","Please select an appropriate one from the supported display methods ""for data display. If no suitable display type is found, ""use 'response_table' as default value. Supported display types: \n""{{ display_type }}",],category="agent",key="dbgpt_agent_expand_dashboard_assistant_agent_profile_constraints",),desc=DynConfig("Use database resources to conduct data analysis, analyze SQL, and provide ""recommended rendering methods.",category="agent",key="dbgpt_agent_expand_dashboard_assistant_agent_profile_desc",),)
 2.推理
2.推理
async def thinking(self,messages: List[AgentMessage],sender: Optional[Agent] = None,prompt: Optional[str] = None,) -> Tuple[Optional[str], Optional[str]]:
 3.记忆
3.记忆
Agent记忆默认使用的短期记忆, 如果需要使用长期记忆和混合记忆, 需要去对话入口处修改,构建记忆对象,提供相应的向量库存储对象和embbeding的方法, 参考上文混合记忆的代码示例,修改地方如下 :
def get_or_build_agent_memory(self, conv_id: str, dbgpts_name: str) -> AgentMemory:from dbgpt.agent.core.memory.hybrid import HybridMemoryfrom dbgpt.configs.model_config import EMBEDDING_MODEL_CONFIGfrom dbgpt.rag.embedding.embedding_factory import EmbeddingFactorymemory_key = f"{dbgpts_name}_{conv_id}"if memory_key in self.agent_memory_map:return self.agent_memory_map[memory_key]# embedding_factory = EmbeddingFactory.get_instance(CFG.SYSTEM_APP)# embedding_fn = embedding_factory.create(# model_name=EMBEDDING_MODEL_CONFIG[CFG.EMBEDDING_MODEL]# )# vstore_name = f"_chroma_agent_memory_{dbgpts_name}_{conv_id}"# Just use chroma store now# vector_store_connector = VectorStoreConnector(# vector_store_type=CFG.VECTOR_STORE_TYPE,# vector_store_config=VectorStoreConfig(# name=vstore_name, embedding_fn=embedding_fn# ),# )# memory = HybridMemory[AgentMemoryFragment].from_chroma(# vstore_name=vstore_name,# embeddings=embedding_fn,# )agent_memory = AgentMemory(gpts_memory=self.memory)self.agent_memory_map[memory_key] = agent_memoryreturn agent_memory
公共记忆目前作为一个通道不需要额外关注和改造。
 4.行动
4.行动
Agent的核心代码逻辑基本都在Action中时需要编码最多的一部分,继承Action基础类,定义自己的模型输出、输出执行、执行展示三部分逻辑, 参考如下代码:
class SqlInput(BaseModel):"""SQL input model."""display_type: str = Field(...,description="The chart rendering method selected for SQL. If you don’t know ""what to output, just output 'response_table' uniformly.",)sql: str = Field(..., description="Executable sql generated for the current target/problem")thought: str = Field(..., description="Summary of thoughts to the user")class ChartAction(Action[SqlInput]):"""Chart action class."""def __init__(self, **kwargs):"""Chart action init."""super().__init__(**kwargs)self._render_protocol = VisChart()@propertydef out_model_type(self):"""Return the output model type."""return SqlInputasync def run(self,ai_message: str,resource: Optional[AgentResource] = None,rely_action_out: Optional[ActionOutput] = None,need_vis_render: bool = True,**kwargs,) -> ActionOutput:"""Perform the action."""try:param: SqlInput = self._input_convert(ai_message, SqlInput)except Exception as e:logger.exception(f"{str(e)}! \n {ai_message}")return ActionOutput(is_exe_success=False,content="Error:The answer is not output in the required format.",)try:if not self.resource_need:raise ValueError("The resource type is not found!")if not self.render_protocol:raise ValueError("The rendering protocol is not initialized!")db_resources: List[DBResource] = DBResource.from_resource(self.resource)if not db_resources:raise ValueError("The database resource is not found!")db = db_resources[0]data_df = await db.query_to_df(param.sql)view = await self.render_protocol.display(chart=json.loads(model_to_json(param)), data_df=data_df)return ActionOutput(is_exe_success=True,content=model_to_json(param),view=view,resource_type=self.resource_need.value,resource_value=db._db_name,)except Exception as e:logger.exception("Check your answers, the sql run failed!")return ActionOutput(is_exe_success=False,content=f"Error:Check your answers, the sql run failed!Reason:{str(e)}",)
Action对于Agent其他参数信息的需求。如果因为Action逻辑相对复杂 需要使用到类似历史消息,推理的prompt等标准接口定义外的内容可以通过实现如下方法,在Agent里给Action传入需要的参数:
class XXXAgent(ConversableAgent):......# 为Action准备的额外执行参数def prepare_act_param(self, received_message: Optional[AgentMessage], sender: Agent,rely_messages: Optional[List[AgentMessage]] = None,**kwargs) -> Dict[str, Any]:historical_dialogues = kwargs.get("historical_dialogues", None)return {"user_input": received_message.content,"conv_id": self.agent_context.conv_id,"paren_agent": self,"rely_messages": rely_messages,"historical_dialogues": historical_dialogues,}
 5.资源
5.资源
资源在应用中绑定,代码层面无需处理,如果特殊未实现资源参考上文资源绑定机制里的资源实现逻辑进行扩展 资源加载如果有特殊逻辑可通过重载如下方法来实现:
# 资源加载方法,此处会默认会将资源包通过资源类的方法转成资源输入给LLMasync def load_resource(self, question: str, is_retry_chat: bool = False, **kwargs):logger.info(f"DomainApi load_resource:{question}")
 6.用户交互和跨主题多轮对话
6.用户交互和跨主题多轮对话
当前多Agent模式下如果要进行用户多轮输入,类似模型提示用户补充输入有两个方案:
会话等待,主动像用户发起提问: (优点:模型依赖不强,可以随时在Flow任意点向用户发起提问;缺点:一旦进入会话等待,不终止话题会一直卡在当前步骤)
class XXXAction(Action[xxInput]):async def run(self,ai_message: str,resource: Optional[AgentResource] = None,rely_action_out: Optional[ActionOutput] = None,need_vis_render: bool = True,**kwargs,) -> ActionOutput:...return ActionOutput(is_exe_success=False, # 提示当前Agent进展失败content=json.dumps(intent.to_dict(), ensure_ascii=False), # 问题内容view=intent.ask_user if intent.ask_user else ai_message, # 问题展示效果(可以配合GptVis像用户发起类似动态表单的消息)have_retry=False, # 并主动向用户发起提问ask_user=True)
多Agent下的历史对话意图使用:
 多Agent协作
多Agent协作manager = AutoPlanChatManager()manager = (await manager.bind(context).bind(agent_memory).bind(llm_config).build())manager.hire(employees)user_proxy: UserProxyAgent = (await UserProxyAgent().bind(context).bind(agent_memory).build())await user_proxy.initiate_chat(recipient=manager,message=user_query,is_retry_chat=is_retry_chat,last_speaker_name=last_speaker_name,message_rounds=init_message_rounds,**ext_info,)
 AutoPlan协作模式的Agent
AutoPlan协作模式的Agent
class AutoPlanChatManager(ManagerAgent):"""A chat manager agent that can manage a team chat of multiple agents."""
自动规划模式暂时使用了一个内置的任务规划Agent实现任务拆分和分配
class PlannerAgent(ConversableAgent):"""Planner Agent.
 AWEL协作模式的Agent
AWEL协作模式的Agent
class AWELBaseManager(ManagerAgent, ABC):"""AWEL base manager."""
算子
## Agent相关算子### Agent Flow触发器,无实际逻辑,Flow的特性必须从触发器开始class AgentDummyTrigger(Trigger):### Agent算子容器,拥有一致的输入输出,可以实现Agent Flow的自由拼接class AWELAgentOperator(MixinLLMOperator, MapOperator[AgentGenerateContext, AgentGenerateContext]):## Agent Flow特性算子### 实现Agent Flow分支的算子class AgentBranchOperator(BranchOperator[AgentGenerateContext, AgentGenerateContext]):### 实现Agent Flow分支合并的算子class AgentBranchJoinOperator(BranchJoinOperator[AgentGenerateContext]):
资源
# 实际Agent在Flow里的绑定节点(把Agent作为Agent算子容器的资源)class AWELAgent(BaseModel):# Agent的绑定资源,将Agent的绑定资源作为Agent资源节点的资源节点### Agent资源class AWELAgentResource(AgentResource):"""AWEL Agent Resource."""### Agent知识库资源class AWELAgentKnowledgeResource(AgentResource):### Agent的Prompt资源class AgentPrompt(BaseModel):### Agent的模型配置资源class AWELAgentConfig(LLMConfig):
欢迎扫码关注EosphorosAI视频号,下一期直播我们聊聊大家都感兴趣GraghRAG~


文章转载自EosphorosAI,如果涉嫌侵权,请发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。






